Disruption of hippocampal development in vivo by CR-50 mAb against reelin - PubMed (original) (raw)
Disruption of hippocampal development in vivo by CR-50 mAb against reelin
K Nakajima et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
We previously generated a monoclonal alloantibody, CR-50, by immunizing reeler mutant mice with homogenates of normal embryonic brains. This antibody recently was shown to recognize a Reelin protein, which is coded by the recently identified candidate gene for the reeler mutation. However, it is still unclear whether Reelin, especially the CR-50 epitope region, is indeed responsible for the reeler phenotype in vivo. Here we show that Reelin is localized on Cajal-Retzius neurons in the hippocampus and that intraventricular injection of CR-50 at the embryonic stage disrupts the organized development of the hippocampus in vivo, converting it to a reeler pattern. Labeling experiments with 5-bromodeoxyuridine demonstrated that the labeled cells in the stratum pyramidale of the CR-50-treated mice were distributed in a pattern similar to that of reeler. Thus, Cajal-Retzius neurons play a crucial function in hippocampus development, and the CR-50 epitope on Reelin plays a central role in this function.
Figures
Figure 1
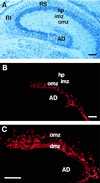
Immunolocalization of the CR-50 epitope in the developing hippocampus. (A) Toluidine blue staining of wild-type mouse hippocampus at E17. (B and C) Immunohistochemical staining of E17 hippocampus with CR-50, showing localization of its epitope in the outer marginal zone of the hippocampus proper and in the dentate marginal zone. AD, area dentata; dmz, dentate marginal zone; hp, hippocampal plate; imz, inner marginal zone; omz, outer marginal zone; RI, regio inferior; RS, regio superior. (Scale bars, 100 μm.)
Figure 2
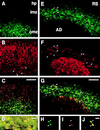
Characterization of the CR-50-positive cells. (A_–_C) Double-staining with CR-50 and anti-MAP2 on wild-type mouse hippocampus at E17. CR-50-positive cells (A) are also positive for anti-MAP2 (B) (arrowheads). A double-exposed photomicrograph of A and B is shown in C. (Scale bar in C, 50 μm.) (D) BrdUrd injected at E9.5 was detected with anti-BrdUrd antibody (red) at E17, showing that the CR-50-positive cells (green) arose at this stage (arrowheads). Some other CR-50-positive cells were labeled at E10 or E11 (not shown). (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (E_–_G) Double-staining with CR-50 (green) (E) and anti-calretinin (red) (F) on E17 mouse hippocampus revealed the existence of both calretinin-positive cells (arrowheads) and calretinin-negative cells (arrows) among the CR-50-positive population in the marginal zones. A double-exposed photomicrograph is shown in G. Early granule neurons in the area dentata are also calretinin-positive, but negative for CR-50. (Scale bar in G, 50 μm.) (H_–_J) Embryonic hippocampus was cultured at E17 and fixed the next day. The cells were double-stained with CR-50 (green) (H) and anti-calretinin (red) (I). A double-exposed photomicrograph is shown in J. There were both calretinin-positive cells (arrowheads) and calretinin-negative cells (arrows) among the CR-50-positive population. (Scale bar in J, 20 μm.)
Figure 3
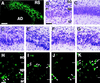
Disruption of the organized cell layering in the stratum pyramidale of the regio superior and conversion to the reeler pattern with CR-50. (A) Binding of CR-50 to its epitope in vivo visualized by FITC-conjugated secondary antibody alone. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (B) Cresyl violet staining of the regio superior of a P1 reeler mutant. Cell-poor rifts are shown with an arrowhead. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (C) Wild-type P1 mouse that was injected with control mouse IgG at E12 and E14. (D_–_G) Wild-type P1 mice that were injected with CR-50 at E12 and E14 (D) or at E13 and E15 (E_–_G). Note the presence of cell-poor rifts in the stratum pyramidale and that the cells are rather loosely packed. (H_–_K) Dividing cells were labeled with BrdUrd at E13 and immunostained with anti-BrdUrd at P1. (H) Noninjected reeler, (I) noninjected wild-type mouse, (J) CR-50-injected wild-type mouse, and (K) control mouse IgG-injected wild-type mouse. Intensely labeled cells are shown with arrowheads. (Scale bar in H, 20 μm.) so, stratum oriens; sp, stratum pyramidale; sr, stratum radiatum.
Similar articles
- A truncated Reelin protein is produced but not secreted in the 'Orleans' reeler mutation (Reln[rl-Orl]).
de Bergeyck V, Nakajima K, Lambert de Rouvroit C, Naerhuyzen B, Goffinet AM, Miyata T, Ogawa M, Mikoshiba K. de Bergeyck V, et al. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997 Oct 15;50(1-2):85-90. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(97)00166-6. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9406921 - Reelin is a secreted glycoprotein recognized by the CR-50 monoclonal antibody.
D'Arcangelo G, Nakajima K, Miyata T, Ogawa M, Mikoshiba K, Curran T. D'Arcangelo G, et al. J Neurosci. 1997 Jan 1;17(1):23-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-01-00023.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 8987733 Free PMC article. - Integrity of Cajal-Retzius cells in the reeler-mouse hippocampus.
Anstötz M, Karsak M, Rune GM. Anstötz M, et al. Hippocampus. 2019 Jun;29(6):550-565. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23049. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Hippocampus. 2019. PMID: 30394609 - [Developmental disorders and their responsible genes; the genes involved in neuronal positioning].
Mikoshiba K. Mikoshiba K. No To Hattatsu. 2000 May;32(3):208-19. No To Hattatsu. 2000. PMID: 10824569 Review. Japanese. - [Cytoarchitectonic abnormality in the facial nucleus of the reeler mouse].
Terashima T, Setsu T, Kikkawa S, Ikeda Y. Terashima T, et al. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1999 Aug;74(4):411-20. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10496086 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
- Reelin regulates the development and synaptogenesis of the layer-specific entorhino-hippocampal connections.
Borrell V, Del Río JA, Alcántara S, Derer M, Martínez A, D'Arcangelo G, Nakajima K, Mikoshiba K, Derer P, Curran T, Soriano E. Borrell V, et al. J Neurosci. 1999 Feb 15;19(4):1345-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-04-01345.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 9952412 Free PMC article. - Reelin is preferentially expressed in neurons synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid in cortex and hippocampus of adult rats.
Pesold C, Impagnatiello F, Pisu MG, Uzunov DP, Costa E, Guidotti A, Caruncho HJ. Pesold C, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 17;95(6):3221-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3221. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9501244 Free PMC article. - Reelin supplementation recovers synaptic plasticity and cognitive deficits in a mouse model for Angelman syndrome.
Hethorn WR, Ciarlone SL, Filonova I, Rogers JT, Aguirre D, Ramirez RA, Grieco JC, Peters MM, Gulick D, Anderson AE, L Banko J, Lussier AL, Weeber EJ. Hethorn WR, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2015 May;41(10):1372-80. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12893. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25864922 Free PMC article. - Reelin, very-low-density lipoprotein receptor, and apolipoprotein E receptor 2 control somatic NMDA receptor composition during hippocampal maturation in vitro.
Sinagra M, Verrier D, Frankova D, Korwek KM, Blahos J, Weeber EJ, Manzoni OJ, Chavis P. Sinagra M, et al. J Neurosci. 2005 Jun 29;25(26):6127-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1757-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15987942 Free PMC article. - Neuronal Heterotopias Affect the Activities of Distant Brain Areas and Lead to Behavioral Deficits.
Ishii K, Kubo K, Endo T, Yoshida K, Benner S, Ito Y, Aizawa H, Aramaki M, Yamanaka A, Tanaka K, Takata N, Tanaka KF, Mimura M, Tohyama C, Kakeyama M, Nakajima K. Ishii K, et al. J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 9;35(36):12432-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3648-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26354912 Free PMC article.
References
- Caviness V J. J Comp Neurol. 1973;151:113–120. - PubMed
- Stanfield B B, Cowan W M. J Comp Neurol. 1979;185:423–459. - PubMed
- Falconer D S. J Genet. 1951;50:192–201. - PubMed
- Meier H, Hoag W G. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1962;21:649.
- Caviness V S, Sidman R L. J Comp Neurol. 1973;147:235–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases