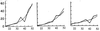The high spontaneous mutation rate: is it a health risk? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The high spontaneous mutation rate: is it a health risk?
J F Crow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
The human mutation rate for base substitutions is much higher in males than in females and increases with paternal age. This effect is mainly, if not entirely, due to the large number of cell divisions in the male germ line. The mutation-rate increase is considerably greater than expected if the mutation rate were simply proportional to the number of cell divisions. In contrast, those mutations that are small deletions or rearrangements do not show the paternal age effect. The observed increase with the age of the father in the incidence of children with different dominant mutations is variable, presumably the result of different mixtures of base substitutions and deletions. In Drosophila, the rate of mutations causing minor deleterious effects is estimated to be about one new mutation per zygote. Because of a larger number of genes and a much larger amount of DNA, the human rate is presumably higher. Recently, the Drosophila data have been reanalyzed and the mutation-rate estimate questioned, but I believe that the totality of evidence supports the original conclusion. The most reasonable way in which a species can cope with a high mutation rate is by quasi-truncation selection, whereby a number of mutant genes are eliminated by one "genetic death."
Figures
Figure 1
Relative frequency of affected children of normal parents (ordinate) as a function of paternal age (abscissa). (Left) Apert syndrome, n = 111. (Center) Achondroplasia, n = 152. (Right) Neurofibromatosis, n = 243. From ref. .
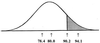
Figure 2
Truncation selection. All of the individuals to the right of the truncation point (those in the shaded area) are eliminated by pre-reproductive death or failure to reproduce. In this example, 10% are eliminated and 90% contribute to the next generation. From left to right, the numbers along the abscissa are the mean number of mutations per individual in the selected group, in the population before selection, at the truncation point, and in the group eliminated by selection.
Similar articles
- How much do we know about spontaneous human mutation rates?
Crow JF. Crow JF. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1993;21(2):122-9. doi: 10.1002/em.2850210205. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1993. PMID: 8444142 - Spontaneous mutation as a risk factor.
Crow JF. Crow JF. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1995;12(3):121-8. doi: 10.1159/000424865. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1995. PMID: 8534499 Review. - The origins, patterns and implications of human spontaneous mutation.
Crow JF. Crow JF. Nat Rev Genet. 2000 Oct;1(1):40-7. doi: 10.1038/35049558. Nat Rev Genet. 2000. PMID: 11262873 Review. - A strategy to identify de novo mutations in common disorders such as autism and schizophrenia.
Julie G, Hamdan FF, Rouleau GA. Julie G, et al. J Vis Exp. 2011 Jun 15;(52):2534. doi: 10.3791/2534. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21712793 Free PMC article. - The conflict theory of genomic imprinting: how much can be explained?
Iwasa Y. Iwasa Y. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1998;40:255-93. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60369-5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9673853 Review.
Cited by
- Properties and rates of germline mutations in humans.
Campbell CD, Eichler EE. Campbell CD, et al. Trends Genet. 2013 Oct;29(10):575-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 May 16. Trends Genet. 2013. PMID: 23684843 Free PMC article. Review. - Low frequency of parental mosaicism in de novo COL4A5 mutations in X-linked Alport syndrome.
Helle OMB, Pedersen TH, Ousager LB, Thomassen M, Hertz JM. Helle OMB, et al. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Oct;8(10):e1452. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1452. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32812400 Free PMC article. - Evolution of female preference for younger males.
Beck CW, Promislow DE. Beck CW, et al. PLoS One. 2007 Sep 26;2(9):e939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000939. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17895980 Free PMC article. - There is no universal molecular clock for invertebrates, but rate variation does not scale with body size.
Thomas JA, Welch JJ, Woolfit M, Bromham L. Thomas JA, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 9;103(19):7366-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510251103. Epub 2006 May 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16651532 Free PMC article. - EMS-induced polygenic mutation rates for nine quantitative characters in Drosophila melanogaster.
Keightley PD, Ohnishi O. Keightley PD, et al. Genetics. 1998 Feb;148(2):753-66. doi: 10.1093/genetics/148.2.753. Genetics. 1998. PMID: 9504922 Free PMC article.
References
- Weinberg W. Arch Rass Gesamte Biol. 1912;9:710–718.
- Haldane J B S. Ann Eugen. 1947;13:262–271. - PubMed
- Vogel F, Rathenberg R. Adv Hum Genet. 1975;5:223–318. - PubMed
- Crow J F, Denniston C. Adv Hum Genet. 1985;14:59–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases