CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) sites are required for HIV-1 replication in primary macrophages but not CD4(+) T cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) sites are required for HIV-1 replication in primary macrophages but not CD4(+) T cells
A J Henderson et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
The importance of CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (C/EBPs) and binding sites for HIV-1 replication in primary macrophages, T cell lines and primary CD4(+) T cells was examined. When lines overexpressing the C/EBP dominant-negative protein LIP were infected with HIV-1, replication occurred in Jurkat T cells but not in U937 promonocytes, demonstrating a requirement for C/EBP activators by HIV-1 only in promonocytes. Primary macrophages did not support the replication of HIV-1 harboring mutant C/EBP binding sites in the long terminal repeat but Jurkat, H9 and primary CD4(+) T cells supported replication of wild-type and mutant HIV-1 equally well. Thus the requirement for C/EBP sites is also confined to monocyte/macrophages. The requirement for C/EBP proteins and sites identifies the first uniquely macrophage-specific regulatory mechanism for HIV-1 replication.
Figures
Figure 1
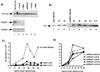
C/EBP activators are required to establish HIV-1 infection in monocytic cells but not in T cell lines. (A) Western blot analysis of whole cell extracts prepared from H9 T cells (lanes 1–3) and Jurkat T cells (lanes 4–6) cultured in the absence or presence of 10 ng/ml of concanavalin A (lanes 2 and 5) or phorbol myristate (lanes 3 and 6). (B) Immunoblots of U937 and Jurkat mock-transfected cells (lanes 1 and 4) and U937-LIP overexpressing cell lines (lanes 2 and 3), and Jurkat-LIP overexpressing cell lines (lanes 5–9). (C) U937-mock-transfected cells (○) or U937-LIP overexpressing cells (solid symbols) were infected with HIV-1 HXB2 and at various times supernatants from cell cultures were assayed for RT activity. These data are from a single experiment that is representative of three independent experiments. Each data point represents the mean of three independent infections. (D) Jurkat-mock-transfected cells (○) or Jurkat-LIP-overexpressing cells (solid symbols) were infected with HIV-1 HXB2, and at various times supernatants were assayed for RT activity. This is a single experiment that is representative of three independent experiments. Each data point represents the mean of three independent infections.
Figure 2
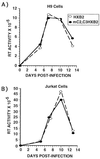
C/EBP sites are not required for HIV-1 replication in T cells. (A) H9 cells or (B) Jurkat cells were infected with wild-type HIV-1 HXB2 (○) or mC2,C3 HIV-1 HXB2 (•). At various times postinfection supernatants were collected and RT activity was measured. This is a single experiment that is representative of three individual experiments. Each data point represents the mean of four independent infections.
Figure 3
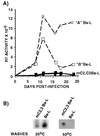
C/EBP sites are required for HIV-1 replication in human primary macrophages. (A) Mononuclear cells isolated from peripheral blood obtained from two healthy donors (donor A, circles; donor B, squares) were infected with either wild-type HIV-1 HXB2 containing a Ba-L envelope (open symbols) or mC2,C3 HIV-1 HXB2 with Ba-L envelope (solid symbols). Supernatants from infected cells were collected at various times and RT activity was measured. These data are a single experiment that is representative of three individual experiments. Each data point represents the mean of three independent infections. (B) Detection of mC2,C3 Ba-L provirus in primary macrophages by PCR. Genomic DNA was prepared from primary macrophages 4 weeks after infection with wild-type Ba-L or mutant Ba-L. Provirus sequences were amplified by PCR as described (31). Specific HIV-1 LTR sequences were detected by Southern blots using the mC3 oligonucleotide. All amplified LTR sequences were detected following washes at 25°C whereas PCR products with C/EBP mutations were specifically detected by more stringent washes at 55°C (31).
Figure 4
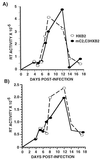
C/EBP sites are not required for HIV-1 replication in primary CD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells were positively selected and stimulated for 24 hr with 10 ng/ml of phytohemagglutinin prior to infection and maintained in medium with 50 units/ml IL-2. Cells were infected with equal amounts of wild-type HXB2 (open symbols) or HXB2 harboring C/EBP mutations (solid symbols). These data are representative of four individual experiments. Each data point represents the mean of four independent infections.
Similar articles
- Type I interferon induces inhibitory 16-kD CCAAT/ enhancer binding protein (C/EBP)beta, repressing the HIV-1 long terminal repeat in macrophages: pulmonary tuberculosis alters C/EBP expression, enhancing HIV-1 replication.
Honda Y, Rogers L, Nakata K, Zhao BY, Pine R, Nakai Y, Kurosu K, Rom WN, Weiden M. Honda Y, et al. J Exp Med. 1998 Oct 5;188(7):1255-65. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.7.1255. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9763605 Free PMC article. - C/EBP activators are required for HIV-1 replication and proviral induction in monocytic cell lines.
Henderson AJ, Connor RI, Calame KL. Henderson AJ, et al. Immunity. 1996 Jul;5(1):91-101. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80313-1. Immunity. 1996. PMID: 8758898 - [Molecular pathogenesis in tuberculosis complicated with AIDS].
Nakata K, Hoshino Y, Honda Y, Tanaka N, Hebisawa A, Weiden M. Nakata K, et al. Kekkaku. 2004 Nov;79(11):659-67. Kekkaku. 2004. PMID: 15729891 Review. Japanese. - Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression and pathogenesis by CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins in cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage.
Hogan TH, Krebs FC, Wigdahl B. Hogan TH, et al. J Neurovirol. 2002 Dec;8 Suppl 2:21-6. doi: 10.1080/13550280290167911. J Neurovirol. 2002. PMID: 12491147 Review.
Cited by
- Deployment of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein arsenal: combating the host to enhance viral transcription and providing targets for therapeutic development.
Dahiya S, Nonnemacher MR, Wigdahl B. Dahiya S, et al. J Gen Virol. 2012 Jun;93(Pt 6):1151-1172. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.041186-0. Epub 2012 Mar 14. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22422068 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA regulation of IFN-beta protein expression: rapid and sensitive modulation of the innate immune response.
Witwer KW, Sisk JM, Gama L, Clements JE. Witwer KW, et al. J Immunol. 2010 Mar 1;184(5):2369-76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902712. Epub 2010 Feb 3. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20130213 Free PMC article. - Development of co-selected single nucleotide polymorphisms in the viral promoter precedes the onset of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated neurocognitive impairment.
Li L, Aiamkitsumrit B, Pirrone V, Nonnemacher MR, Wojno A, Passic S, Flaig K, Kilareski E, Blakey B, Ku J, Parikh N, Shah R, Martin-Garcia J, Moldover B, Servance L, Downie D, Lewis S, Jacobson JM, Kolson D, Wigdahl B. Li L, et al. J Neurovirol. 2011 Feb;17(1):92-109. doi: 10.1007/s13365-010-0014-1. Epub 2011 Jan 12. J Neurovirol. 2011. PMID: 21225391 Free PMC article. - Genetic variation and HIV-associated neurologic disease.
Dahiya S, Irish BP, Nonnemacher MR, Wigdahl B. Dahiya S, et al. Adv Virus Res. 2013;87:183-240. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407698-3.00006-5. Adv Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23809924 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Feng Y, Broder C C, Kennedy P E, Berger E A. Science. 1996;272:872–877. - PubMed
- Choe H, Farzan M, Sun Y, Sullivan N, Rollins B, Ponath P D, Wu L, Mackay C R, LaRosa G, Newman W, Gerard N, Gerard C, Sodroski J. Cell. 1996;85:1135–1148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials