Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 binds to the transcription-regulatory region of mouse hepatitis virus RNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 binds to the transcription-regulatory region of mouse hepatitis virus RNA
H P Li et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
A cellular protein, previously described as p35/38, binds to the complementary (-)-strand of the leader RNA and intergenic (IG) sequence of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) RNA. The extent of the binding of this protein to IG sites correlates with the efficiency of the subgenomic mRNA transcription from that IG site, suggesting that it is a requisite transcription factor. We have purified this protein and determined by partial peptide sequencing that it is heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A1, an abundant, primarily nuclear protein. hnRNP A1 shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm and plays a role in the regulation of alternative RNA splicing. The MHV(-)-strand leader and IG sequences conform to the consensus binding motifs of hnRNP A1. Recombinant hnRNP A1 bound to these two RNA regions in vitro in a sequence-specific manner. During MHV infection, hnRNP A1 relocalizes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where viral replication occurs. These data suggest that hnRNP A1 is a cellular factor that regulates the RNA-dependent RNA transcription of the virus.
Figures
Figure 1
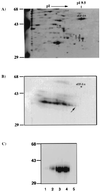
Two-dimensional PAGE analysis of the partially purified HeLa cytoplasmic extracts. (A) Silver-stained, 2-D nonequilibrium pH gradient electrophoresis gel of the partially purified p35/38 (spot nos. 1–4) that have been crosslinked to the 32P-labeled (−)-strand leader. Molecular weight markers in kDa are indicated, and eEF-1α is identified. (B) Autoradiogram of the same silver-stained 2-D gel. The arrow indicates the radiolabeled spot that matches spot no. 1 in the silver-stained gel. (C) UV-crosslinking of gel-purified spots 1–4 (lanes 1–4) and eEF-1α (lane 5) (0.5 μg each) with 32P-labeled (−)-strand leader RNA. The products were resolved by SDS/PAGE on a 10% polyacrylamide gel and autoradiographed.
Figure 2
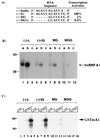
Immunoprecipitation of UV-crosslinked proteins. Cytoplasmic extracts from HeLa (lanes 1–4), DBT (lanes 5–8), and A59-infected DBT cells (lanes 9–12) were UV-crosslinked with 32P-labeled (−)-strand leader RNA. Different antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation, and the precipitated proteins were analyzed by SDS/PAGE, a, mAb for hnRNP A1, 4B10; b, polyclonal antibody for TFIIB; and c, polyclonal antibody for Sam68. The asterisk indicates the potential protein specific for MHV-infected cells.
Figure 3
UV-crosslinking of recombinant hnRNP A1 with various RNAs. Three different RNAs: MHV (−)-strand leader, (+)-strand leader, and adenovirus early pre-mRNA were UV-crosslinked with 60 μg of (a) HeLa nuclear extract, (b) E. coli expressed (human) hnRNP A1 lysates, and (c) GST-fused (murine) hnRNP A1 lysates.
Figure 4
The specificity of binding between the recombinant hnRNP A1 and IG sequences. The sequences of the (−)-strand leader and wild-type and mutant IG are shown. (A) The relative transcription efficiencies from the various IG sites were derived from Zhang and Lai (12). (B) 32P-labeled RNA probes were UV-crosslinked with 60 μg of (a) HeLa nuclear extract, (b) E. coli expressed (human) hnRNP A1 lysates, and (c) E. coli (vector) lysates. (C) Similar to (B), except that a GST or GST-hnRNP A1 (murine) fusion protein (GSTmA1) was used. Two different concentrations (2 and 10 μg) of each protein were used for UV crosslinking.
Figure 5
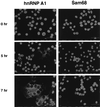
The relocalization of hnRNP A1 in MHV-infected cells. Immunofluorescent staining of MHV-infected cells (×200 magnification) at various time points postinfection. hnRNP A1 or Sam68 antibodies were used.
Similar articles
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein a1 binds to the 3'-untranslated region and mediates potential 5'-3'-end cross talks of mouse hepatitis virus RNA.
Huang P, Lai MM. Huang P, et al. J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(11):5009-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5009-5017.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11333880 Free PMC article. - Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein binds to the leader RNA of mouse hepatitis virus and serves as a regulator of viral transcription.
Li HP, Huang P, Park S, Lai MM. Li HP, et al. J Virol. 1999 Jan;73(1):772-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.772-777.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9847386 Free PMC article. - Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 in health and neurodegenerative disease: from structural insights to post-transcriptional regulatory roles.
Bekenstein U, Soreq H. Bekenstein U, et al. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:436-46. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23247072 Review. - Autoantibodies to the A/B proteins of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex: novel tools for the diagnosis of rheumatic diseases.
Steiner G, Skriner K, Smolen JS. Steiner G, et al. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1996 Dec;111(4):314-9. doi: 10.1159/000237386. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8957102 Review.
Cited by
- Genome-wide bioinformatic analyses predict key host and viral factors in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis.
Ferrarini MG, Lal A, Rebollo R, Gruber AJ, Guarracino A, Gonzalez IM, Floyd T, de Oliveira DS, Shanklin J, Beausoleil E, Pusa T, Pickett BE, Aguiar-Pulido V. Ferrarini MG, et al. Commun Biol. 2021 May 17;4(1):590. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02095-0. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34002013 Free PMC article. - RNA splicing at human immunodeficiency virus type 1 3' splice site A2 is regulated by binding of hnRNP A/B proteins to an exonic splicing silencer element.
Bilodeau PS, Domsic JK, Mayeda A, Krainer AR, Stoltzfus CM. Bilodeau PS, et al. J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8487-97. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8487-8497.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507194 Free PMC article. - Arterivirus discontinuous mRNA transcription is guided by base pairing between sense and antisense transcription-regulating sequences.
van Marle G, Dobbe JC, Gultyaev AP, Luytjes W, Spaan WJ, Snijder EJ. van Marle G, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Oct 12;96(21):12056-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.12056. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10518575 Free PMC article. - SYNCRIP, a member of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein family, is involved in mouse hepatitis virus RNA synthesis.
Choi KS, Mizutani A, Lai MM. Choi KS, et al. J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(23):13153-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.23.13153-13162.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15542667 Free PMC article. - Subgenomic negative-strand RNA function during mouse hepatitis virus infection.
Baric RS, Yount B. Baric RS, et al. J Virol. 2000 May;74(9):4039-46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.9.4039-4046.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10756015 Free PMC article.
References
- Lai M M C. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:303–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials