Isolation of a multispecific organic anion and cardiac glycoside transporter from rat brain - PubMed (original) (raw)
Isolation of a multispecific organic anion and cardiac glycoside transporter from rat brain
B Noé et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
A novel multispecific organic anion transporting polypeptide (oatp2) has been isolated from rat brain. The cloned cDNA contains 3,640 bp. The coding region extends over 1,983 nucleotides, thus encoding a polypeptide of 661 amino acids. Oatp2 is homologous to other members of the oatp gene family of membrane transporters with 12 predicted transmembrane domains, five potential glycosylation, and six potential protein kinase C phosphorylation sites. In functional expression studies in Xenopus laevis oocytes, oatp2 mediated uptake of the bile acids taurocholate (Km approximately 35 microM) and cholate (Km approximately 46 microM), the estrogen conjugates 17beta-estradiol-glucuronide (Km approximately 3 microM) and estrone-3-sulfate (Km approximately 11 microM), and the cardiac gylcosides ouabain (Km approximately 470 microM) and digoxin (Km approximately 0.24 microM). Although most of the tested compounds are common substrates of several oatp-related transporters, high-affinity uptake of digoxin is a unique feature of the newly cloned oatp2. On the basis of Northern blot analysis under high-stringency conditions, oatp2 is highly expressed in brain, liver, and kidney but not in heart, spleen, lung, skeletal muscle, and testes. These results provide further support for the overall significance of oatps as a new family of multispecific organic anion transporters. They indicate that oatp2 may play an especially important role in the brain accumulation and toxicity of digoxin and in the hepatobiliary and renal excretion of cardiac glycosides from the body.
Figures
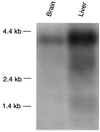
Figure 1
Northern blot analysis of rat brain and rat liver mRNA with the human-OATP-specific oligonucleotide HOT 584. mRNA (2 μg) was isolated, denatured, and electrophoresed in a 1% agarose/formaldehyde gel. After transfer to a nylon membrane (Hybond N, Amersham), prehybridization was performed for 2 h at 60°C. The radiolabeled oligonucleotide HOT 584 was added and hybridization was performed overnight in standard hybridization solution. The blot was washed for two 15-min periods in 6× SSC/0.1% SDS at 55°C. The blot was exposed to autoradiography film for 3 days.
Figure 2
Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences between oatp2, oatp1, OATP, and OAT-K1. Putative membrane-spanning domains are indicated by lines and numbered M1 to M12. ★, Putative N-linked glycosylation sites of oatp2; ▪, potential protein kinase C phosphorylation sites of oatp2. Overlapping putative Cys–Cys zinc-finger motifs conserved in all oatps are boxed.
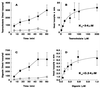
Figure 3
Oatp2-mediated taurocholate and digoxin transport in Xenopus laevis oocytes. (A) Time course of sodium-independent uptake of [3H]taurocholate (10 μM) in oatp2 cRNA (5 ng)-injected (•) and in water-injected (○) oocytes. (B) Saturation kinetics of initial (15 min) sodium-independent [3H]taurocholate uptake in oatp2 cRNA (5 ng)-injected oocytes. (C) Time course of sodium-independent uptake of [3H]digoxin (0.57 μM) in oatp2 cRNA (5 ng)-injected (•) and in water-injected (○) oocytes. (D) Saturation kinetics of initial (15 min) sodium-independent [3H]digoxin uptake in oatp2 cRNA (5 ng)-injected oocytes. In the kinetic uptake curves (B and D), nonspecific taurocholate and digoxin uptakes into water-injected oocytes were subtracted from total uptake values. Individual data points represent the mean ± SD of 10–15 oocyte uptake measurements. The curves were fitted by computerized nonlinear regression analysis (
systat
).
Figure 4
Northern blot analysis for oatp2 mRNA in various rat tissues. The multiple tissue Northern blot containing 2 μg from various rat tissues was purchased from CLONTECH. The blot was prehybridized for 2 h at 42°C in 50% formamide/5× SSPE (SSPE = 0.18 M NaCl/10 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4/1 mM EDTA)/5× Denhardt’s solution/0.2% SDS/denatured salmon sperm DNA (100 μg/ml). After overnight hybridization with a PCR-amplified 32P-labeled oatp2 cDNA probe (nucleotides 1–360), the blot was washed for two 5-min periods in 2× SSC/0.1% SDS at room temperature and for 30 min in 0.1× SSC/0.1% SDS at 65°C. Subsequently, the blot was exposed to autoradiography film for 1 day. A human β-actin probe served as a control. The different sizes of β-actin transcripts are due to the detection of various isoforms of β-actin mRNAs, as specified by the supplier of the multiple tissue Northern blot.
Similar articles
- Functional characterization of the mouse organic-anion-transporting polypeptide 2.
van Montfoort JE, Schmid TE, Adler ID, Meier PJ, Hagenbuch B. van Montfoort JE, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Aug 19;1564(1):183-8. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(02)00445-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12101011 - Molecular cloning and characterization of a new multispecific organic anion transporter from rat brain.
Kusuhara H, Sekine T, Utsunomiya-Tate N, Tsuda M, Kojima R, Cha SH, Sugiyama Y, Kanai Y, Endou H. Kusuhara H, et al. J Biol Chem. 1999 May 7;274(19):13675-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.13675. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10224140 - Pravastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, is transported by rat organic anion transporting polypeptide, oatp2.
Tokui T, Nakai D, Nakagomi R, Yawo H, Abe T, Sugiyama Y. Tokui T, et al. Pharm Res. 1999 Jun;16(6):904-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1018838405987. Pharm Res. 1999. PMID: 10397612 - Sinusoidal (basolateral) bile salt uptake systems of hepatocytes.
Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ. Hagenbuch B, et al. Semin Liver Dis. 1996 May;16(2):129-36. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007226. Semin Liver Dis. 1996. PMID: 8781018 Review.
Cited by
- Differential effect of acute hepatic failure on in vivo and in vitro P-glycoprotein functions in the intestine.
Yumoto R, Murakami T, Takano M. Yumoto R, et al. Pharm Res. 2003 May;20(5):765-71. doi: 10.1023/a:1023485519485. Pharm Res. 2003. PMID: 12751632 - Thyroid hormone transporters in the brain.
Suzuki T, Abe T. Suzuki T, et al. Cerebellum. 2008;7(1):75-83. doi: 10.1007/s12311-008-0029-9. Cerebellum. 2008. PMID: 18418673 Review. - Comparative bioinformatics, temporal and spatial expression analyses of Ixodes scapularis organic anion transporting polypeptides.
Radulović Z, Porter LM, Kim TK, Mulenga A. Radulović Z, et al. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014 Apr;5(3):287-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.12.002. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014. PMID: 24582512 Free PMC article. - Targeted drug delivery to treat pain and cerebral hypoxia.
Ronaldson PT, Davis TP. Ronaldson PT, et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2013 Jan 23;65(1):291-314. doi: 10.1124/pr.112.005991. Print 2013 Jan. Pharmacol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23343976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Kullak-Ublick G A, Hagenbuch B, Stieger B, Schteingart C D, Hofmann A F, Wolkoff A W, Meier P J. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:1274–1282. - PubMed
- Bergwerk A J, Shi X, Ford A C, Kanai N, Jacquemin E, Burk R D, Bai S, Novikoff P M, Stieger B, Meier P J, Schuster V L, Wolkoff A W. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:G231–G238. - PubMed
- Bossuyt X, Müller M, Hagenbuch B, Meier P J. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;276:891–896. - PubMed
- Eckhardt U, Horz J A, Petzinger E, Stüber W, Reers M, Dickneite G, Daniel H, Wagener M, Hagenbuch B, Stieger B, Meier P J. Hepatology. 1996;24:380–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases