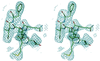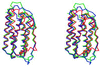The crystal structure of human interferon beta at 2.2-A resolution - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
The crystal structure of human interferon beta at 2.2-A resolution
M Karpusas et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Type I interferons (IFNs) are helical cytokines that have diverse biological activities despite the fact that they appear to interact with the same receptor system. To achieve a better understanding of the structural basis for the different activities of alpha and beta IFNs, we have determined the crystal structure of glycosylated human IFN-beta at 2.2-A resolution by molecular replacement. The molecule adopts a fold similar to that of the previously determined structures of murine IFN-beta and human IFN-alpha2b but displays several distinct structural features. Like human IFN-alpha2b, human IFN-beta contains a zinc-binding site at the interface of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit, raising the question of functional relevance for IFN-beta dimers. However, unlike the human IFN-alpha2b dimer, in which homologous surfaces form the interface, human IFN-beta dimerizes with contact surfaces from opposite sides of the molecule. The relevance of the structure to the effects of point mutations in IFN-beta at specific exposed residues is discussed. A potential role of ligand-ligand interactions in the conformational assembly of IFN receptor components is discussed.
Figures
Figure 1
Representative region of a simulated annealing omit map displayed in stereo for residues 61–67 of molecule A and contoured at 1σ. The figure was made with the program
quanta
.
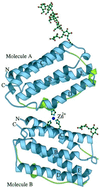
Figure 2
Schematic representation of the crystallographic dimer of huIFN-β. The modeled portion of the carbohydrates and part of the zinc-binding site are also shown. The sphere corresponds to the zinc ion. Helices and N and C termini are labeled. The AB loop is colored green. The figure was made with the program
molscript
(44).
Figure 3
Superposition of Cα traces of molecules A (in green), B (blue), and muIFN-β (red) in stereo. The figure was made with the program
molscript
(44).
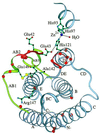
Figure 4
Ribbon diagram of huIFN-β Cα backbone with side chains of residues known to be important for activity. The yellow spheres represent the sulfur atoms of the disulfide bridge. The ribbon is colored red at positions of the alanine-scanning mutagenesis cited in ref. . Orange spheres correspond to Cα atoms of residues homologous to those of IFN-α that are important for activity. Part of the zinc-binding site is also shown. The figure was made with the program
molscript
(44).
Similar articles
- Zinc mediated dimer of human interferon-alpha 2b revealed by X-ray crystallography.
Radhakrishnan R, Walter LJ, Hruza A, Reichert P, Trotta PP, Nagabhushan TL, Walter MR. Radhakrishnan R, et al. Structure. 1996 Dec 15;4(12):1453-63. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00152-9. Structure. 1996. PMID: 8994971 - The structure of human interferon-beta: implications for activity.
Karpusas M, Whitty A, Runkel L, Hochman P. Karpusas M, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998 Nov;54(11):1203-16. doi: 10.1007/s000180050248. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998. PMID: 9849615 Free PMC article. Review. - Crystal structure of ovine interferon-tau at 2.1 A resolution.
Radhakrishnan R, Walter LJ, Subramaniam PS, Johnson HM, Walter MR. Radhakrishnan R, et al. J Mol Biol. 1999 Feb 12;286(1):151-62. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2480. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 9931256 - Differences in activity between alpha and beta type I interferons explored by mutational analysis.
Runkel L, Pfeffer L, Lewerenz M, Monneron D, Yang CH, Murti A, Pellegrini S, Goelz S, Uzé G, Mogensen K. Runkel L, et al. J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 3;273(14):8003-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.14.8003. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9525899 - Structural, functional and evolutionary implications of the three-dimensional crystal structure of murine interferon-beta.
Mitsui Y, Senda T, Shimazu T, Matsuda S, Utsumi J. Mitsui Y, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 1993;58(1):93-132. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90068-o. Pharmacol Ther. 1993. PMID: 8415875 Review.
Cited by
- Structural basis of the broadly neutralizing anti-interferon-α antibody rontalizumab.
Maurer B, Bosanac I, Shia S, Kwong M, Corpuz R, Vandlen R, Schmidt K, Eigenbrot C. Maurer B, et al. Protein Sci. 2015 Sep;24(9):1440-50. doi: 10.1002/pro.2729. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 26099203 Free PMC article. - Structural and dynamic determinants of type I interferon receptor assembly and their functional interpretation.
Piehler J, Thomas C, Garcia KC, Schreiber G. Piehler J, et al. Immunol Rev. 2012 Nov;250(1):317-34. doi: 10.1111/imr.12001. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23046138 Free PMC article. Review. - Crystal structure of human interferon-λ1 in complex with its high-affinity receptor interferon-λR1.
Miknis ZJ, Magracheva E, Li W, Zdanov A, Kotenko SV, Wlodawer A. Miknis ZJ, et al. J Mol Biol. 2010 Dec 10;404(4):650-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.09.068. Epub 2010 Oct 8. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20934432 Free PMC article. - Conformation and dynamics of biopharmaceuticals: transition of mass spectrometry-based tools from academe to industry.
Kaltashov IA, Bobst CE, Abzalimov RR, Berkowitz SA, Houde D. Kaltashov IA, et al. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2010 Mar;21(3):323-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2009.10.013. Epub 2009 Oct 29. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2010. PMID: 19963397 Free PMC article. - Molecular characterization and expression of type-I interferon gene in Labeo rohita.
Parhi J, Mukherjee SC, Saxena G, Sahoo L, Makesh M. Parhi J, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2014 May;41(5):2979-87. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3155-0. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24449367
References
- DeMaeyer E, Galasso G, Schellekens H. The Biology of the Interferon System. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North–Holland Biomedical; 1981.
- Weissmann C, Weber H. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:251–300. - PubMed
- Sprang S R, Bazan J F. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1993;3:815–827.
- Senda T, Saitoh S, Mitsui Y. J Mol Biol. 1995;253:187–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases