CpG oligodeoxynucleotides act as adjuvants that switch on T helper 1 (Th1) immunity - PubMed (original) (raw)
CpG oligodeoxynucleotides act as adjuvants that switch on T helper 1 (Th1) immunity
R S Chu et al. J Exp Med. 1997.
Abstract
Synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN) that contain unmethylated CpG motifs (CpG ODN) induce macrophages to secrete IL-12, which induces interferon (IFN)-gamma secretion by natural killer (NK) cells. Since these cytokines can induce T helper 1 (Th1) differentiation, we examined the effects of coadministered CpG ODN on the differentiation of Th responses to hen egg lysozyme (HEL). In both BALB/c (Th2-biased) and B10.D2 (Th1-biased) mice, immunization with HEL in incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA) resulted in Th2-dominated immune responses characterized by HEL-specific secretion of IL-5 but not IFN-gamma. In contrast, immunization with IFA-HEL plus CpG ODN switched the immune response to a Th1-dominated cytokine pattern, with high levels of HEL-specific IFN-gamma secretion and decreased HEL-specific IL-5 production. IFA-HEL plus CpG ODN also induced anti-HEL IgG2a (a Th1-associated isotype), which was not induced by IFA-HEL alone. Control non-CpG ODN did not induce IFN-gamma or IgG2a, excepting lesser increases in B10.D2 (Th1-biased) mice. Thus, CpG ODN provide a signal to switch on Th1-dominated responses to coadministered antigen and are potential adjuvants for human vaccines to elicit protective Th1 immunity.
Figures
Figure 1
Th1-associated antigen-specific IgG2a responses are induced by immunization of BALB/c mice with IFA-HEL-CpG ODN but not IFA-HEL-non–CpG ODN. (A–C). Mice were injected i.p. with CFA-HEL (a control for a Th1-dominated response), IFA-HEL (a control for a Th2-dominated response), or IFA-HEL with 100 μg of CpG ODN 1826 or non–CpG ODN 1745. Sera were collected from mice 15–18 d after injection and assayed by ELISA for: (A) anti-HEL IgG2a, an isotype associated with Th1-dominated responses; (B) anti-HEL IgG1; and (C) anti-HEL total Ig response. A–C represent data from a single experiment representative of three similar experiments. (D) BALB/c mice were immunized as above, except that 30 μg of CpG ODN 1585, non–CpG ODN 1972, CpG ODN 1760, or non–CpG ODN 1908 was used for each mouse. Anti-HEL IgG2a antibodies were detected by serum ELISA. Data shown in D are representative of three similar experiments.
Figure 2
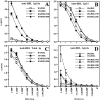
CpG ODN enhance HEL-specific IFN-γ production by BALB/c splenocytes. Mice were immunized as in Fig. 1 with 100 μg ODN/mouse in A and 30 μg ODN/mouse in panel B. After 3 wk, splenocytes were isolated and incubated with HEL (closed circles) or medium alone (open circles). ELISA spot assay was performed and spots were quantitated by a computerized image analysis program. Each point represents the mean number of spots per well for one mouse (assayed in duplicate); horizontal bars indicate the mean of points for each group of mice. Similar results were observed in five independent experiments with CpG- and non–CpG ODN in BALB/c mice.
Figure 3
ELISA spot assessment of IFN-γ production by splenocytes from immunized BALB/c mice. Pictures show representative images of ELISA spot wells from the experiment shown in Fig. 2_A_. The number of spots, as quantitated by an image analysis program, is indicated next to each well. Each well contained HEL (100 μg/ml) and 106 splenocytes isolated from mice immunized with IFA-HEL (A), IFA-HEL-non–CpG ODN 1745 (B) or IFA-HEL-CpG ODN 1826 (C).
Figure 4
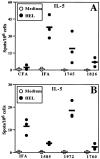
CpG ODN decrease HEL-specific IL-5 production by BALB/c splenocytes. Mice were immunized as in Fig. 2 (30 μg ODN/mouse), and splenocytes were harvested for in vitro restimulation with or without HEL. ELISA spot analysis was performed for IL-5. The data are representative of five similar experiments with CpG- and non–CpG ODN in BALB/c mice.
Figure 5
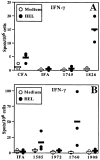
Induction of HEL-specific IFN-γ responses by CpG ODN in B10.D2 mice. B10.D2 mice were immunized as in Fig. 1, except that ODN were used at 30 μg per mouse. Three weeks after immunization, HEL-specific production of IFN-γ by splenocytes was measured by ELISA spot assay as in Fig. 2. The data shown are representative of three similar experiments.
Similar articles
- CpG DNA is a potent enhancer of specific immunity in mice immunized with recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen.
Davis HL, Weeratna R, Waldschmidt TJ, Tygrett L, Schorr J, Krieg AM. Davis HL, et al. J Immunol. 1998 Jan 15;160(2):870-6. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9551923 - CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotides, in combination with conventional adjuvants, enhance the magnitude and change the bias of the immune responses to a herpesvirus glycoprotein.
Ioannou XP, Gomis SM, Karvonen B, Hecker R, Babiuk LA, van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S. Ioannou XP, et al. Vaccine. 2002 Nov 22;21(1-2):127-37. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00378-x. Vaccine. 2002. PMID: 12443671 - Increased levels of interferon-gamma primed by culture filtrate proteins antigen and CpG-ODN immunization do not confer significant protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.
Fonseca DM, Silva CL, Paula MO, Soares EG, Marchal G, Horn C, Bonato VL. Fonseca DM, et al. Immunology. 2007 Aug;121(4):508-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02597.x. Epub 2007 Apr 13. Immunology. 2007. PMID: 17433075 Free PMC article. - Clinical evaluation of CpG oligonucleotides as adjuvants for vaccines targeting infectious diseases and cancer.
Scheiermann J, Klinman DM. Scheiermann J, et al. Vaccine. 2014 Nov 12;32(48):6377-89. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.06.065. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24975812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- CpG DNA facilitate the inactivated transmissible gastroenteritis virus in enhancing the local and systemic immune response of pigs via oral administration.
Lin J, Tu C, Mou C, Chen X, Yang Q. Lin J, et al. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016 Apr;172:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 27032496 Free PMC article. - Advax-CpG Adjuvant Provides Antigen Dose-Sparing and Enhanced Immunogenicity for Inactivated Poliomyelitis Virus Vaccines.
Honda-Okubo Y, Baldwin J, Petrovsky N. Honda-Okubo Y, et al. Pathogens. 2021 Apr 21;10(5):500. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10050500. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33919442 Free PMC article. - Evidence for Anti-Viral Effects of Complete Freund's Adjuvant in the Mouse Model of Enterovirus Infection.
Gangaplara A, Massilamany C, Lasrado N, Steffen D, Reddy J. Gangaplara A, et al. Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Jul 7;8(3):364. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030364. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32645845 Free PMC article. - Vaccine adjuvants for infectious disease in the clinic.
Goetz M, Thotathil N, Zhao Z, Mitragotri S. Goetz M, et al. Bioeng Transl Med. 2024 Mar 22;9(4):e10663. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10663. eCollection 2024 Jul. Bioeng Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39036089 Free PMC article. Review. - The Role of Liposomal CpG ODN on the Course of L. major Infection in BALB/C Mice.
Hejazi H, Tasbihi M, Jaafari M, Badiee A, Pestechian N, Javadi A, Khamesipour A. Hejazi H, et al. Iran J Parasitol. 2010 Mar;5(1):47-54. Iran J Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 22347235 Free PMC article.
References
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature (Lond) 1996;383:787–793. - PubMed
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. - PubMed
- Seder RA, Paul WE. Acquisition of lymphokine-producing phenotype by CD4+ T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:635–673. - PubMed
- Finkelman FD, Holmes J, Katona IM, Urban JF, Beckmann MP, Park LS, Schooley KA, Coffman RL, Mosmann TR, Paul WE. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:303–333. - PubMed
- Kelso A. Th1 and Th2 subsets: paradigms lost? . Immunol Today. 1995;16:374–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI035726/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA70149/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI034343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI35726/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI34343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous