Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) interferes with extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) activation, but does not affect phosphorylation of T cell receptor zeta and ZAP70 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) interferes with extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) activation, but does not affect phosphorylation of T cell receptor zeta and ZAP70
C R Calvo et al. J Exp Med. 1997.
Abstract
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) is an important regulator of T cell homeostasis. Ligation of this receptor leads to prominent downregulation of T cell proliferation, mainly as a consequence of interference with IL-2 production. We here report that CTLA-4 engagement strikingly selectively shuts off activation of downstream T cell receptor (TCR)/CD28 signaling events, i.e., activation of the microtubule-associated protein kinase (MAPKs) ERK and JNK. In sharp contrast, proximal TCR signaling events such as ZAP70 and TCR-zeta chain phosphorylation are not affected by CTLA-4 engagement on activated T cells. Since activation of the ERK and JNK kinases is required for stimulation of interleukin (IL)-2 transcription, these data provide a molecular explanation for the block in IL-2 production imposed by CTLA-4.
Figures
Figure 1
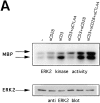
CTLA-4 inhibits ERK2 activity induced by anti-CD3 in preactivated T cells, but not in naive T cells. (A) 2-d preactivated T cells were coated on ice with the indicated combinations of anti-CD3, anti-CD28, and anti–CTLA-4. 1 min after addition of cross-linking anti– hamster antibody (10 μg/ml) in warm (37°C) medium the cells were lysed, ERK2 was immunoprecipitated, and in vitro kinase reactions were performed using MBP as substrate in the presence of γ-[32P]ATP. Indicated by arrows are the bands representing phosphorylated MBP (top). The same lysates were tested for equal protein abundance on immunoblot (bottom). (B) Naive purified T cells were rested for 5 h and coated with the different combinations of antibodies as indicated. Cells were lysed 1 or 5 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody and in vitro kinase reactions were performed as in A.
Figure 1
CTLA-4 inhibits ERK2 activity induced by anti-CD3 in preactivated T cells, but not in naive T cells. (A) 2-d preactivated T cells were coated on ice with the indicated combinations of anti-CD3, anti-CD28, and anti–CTLA-4. 1 min after addition of cross-linking anti– hamster antibody (10 μg/ml) in warm (37°C) medium the cells were lysed, ERK2 was immunoprecipitated, and in vitro kinase reactions were performed using MBP as substrate in the presence of γ-[32P]ATP. Indicated by arrows are the bands representing phosphorylated MBP (top). The same lysates were tested for equal protein abundance on immunoblot (bottom). (B) Naive purified T cells were rested for 5 h and coated with the different combinations of antibodies as indicated. Cells were lysed 1 or 5 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody and in vitro kinase reactions were performed as in A.
Figure 2
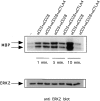
Combined triggering of CD3 and CD28 delays downregulation of ERK2 activity by CTLA-4. Preactivated T cells were coated with different combinations of antibodies as in Fig. 1 and lysed 1, 5, or 10 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody. ERK2 was immunoprecipitated and in vitro kinase reactions were performed (top). The same lysates were tested for ERK2 protein abundance (middle). ERK2 activities were quantified using a phosphorimager and represented as relative values compared to ERK2 activities from unstimulated cells (unstimulated = 1; bottom).
Figure 2
Combined triggering of CD3 and CD28 delays downregulation of ERK2 activity by CTLA-4. Preactivated T cells were coated with different combinations of antibodies as in Fig. 1 and lysed 1, 5, or 10 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody. ERK2 was immunoprecipitated and in vitro kinase reactions were performed (top). The same lysates were tested for ERK2 protein abundance (middle). ERK2 activities were quantified using a phosphorimager and represented as relative values compared to ERK2 activities from unstimulated cells (unstimulated = 1; bottom).
Figure 3
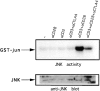
CTLA-4 reduces JNK activity induced by CD3 and CD28 triggering. Preactivated T cells were coated with different combinations of antibodies and lysed 10 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody. Lysates were tested for JNK activity by precipitation with GST–c-jun precoupled to glutathione beads followed by in vitro kinase reactions as described in Materials and Methods. Phosphorylated GST–c-jun is indicated by the arrow (top). The same lysates were tested for JNK protein abundance on immunoblot (middle). JNK activities were quantified using a phosphorimager and represented as relative values compared to JNK activity from unstimulated cells (unstimulated = 1; bottom). Data for the 10-min time point are shown because no JNK activity could be measured at earlier times.
Figure 3
CTLA-4 reduces JNK activity induced by CD3 and CD28 triggering. Preactivated T cells were coated with different combinations of antibodies and lysed 10 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody. Lysates were tested for JNK activity by precipitation with GST–c-jun precoupled to glutathione beads followed by in vitro kinase reactions as described in Materials and Methods. Phosphorylated GST–c-jun is indicated by the arrow (top). The same lysates were tested for JNK protein abundance on immunoblot (middle). JNK activities were quantified using a phosphorimager and represented as relative values compared to JNK activity from unstimulated cells (unstimulated = 1; bottom). Data for the 10-min time point are shown because no JNK activity could be measured at earlier times.
Figure 4
Anti-CD3–induced phosphorylation of TCR-ζ and ZAP70 is not affected by CTLA-4. (A) Preactivated T cells were coated with different combinations of antibodies and lysed 1, 5, or 10 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody. TCR-ζ was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10. Indicated with arrows are the p21 and p23 isoforms of tyrosine phosphorylated TCR-ζ. (B) Lysates prepared as in A from cells stimulated for 1 min were immunoprecipitated with anti-ZAP70 antibody and immunoblotted with antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10. Indicated with an arrow is phosphorylated ZAP70. Similar results were also obtained on lysates from 5 and 10 min–stimulated cells (not shown).
Figure 4
Anti-CD3–induced phosphorylation of TCR-ζ and ZAP70 is not affected by CTLA-4. (A) Preactivated T cells were coated with different combinations of antibodies and lysed 1, 5, or 10 min after addition of warm cross-linking antibody. TCR-ζ was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10. Indicated with arrows are the p21 and p23 isoforms of tyrosine phosphorylated TCR-ζ. (B) Lysates prepared as in A from cells stimulated for 1 min were immunoprecipitated with anti-ZAP70 antibody and immunoblotted with antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10. Indicated with an arrow is phosphorylated ZAP70. Similar results were also obtained on lysates from 5 and 10 min–stimulated cells (not shown).
Similar articles
- The inhibitory function of CTLA-4 does not require its tyrosine phosphorylation.
Baroja ML, Luxenberg D, Chau T, Ling V, Strathdee CA, Carreno BM, Madrenas J. Baroja ML, et al. J Immunol. 2000 Jan 1;164(1):49-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.1.49. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10604992 - Expression and functional significance of CTLA-4, a negative regulator of T cell activation.
Kosmaczewska A, Ciszak L, Boćko D, Frydecka I. Kosmaczewska A, et al. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2001;49(1):39-46. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2001. PMID: 11266089 Review.
Cited by
- EGF-Receptor against Amphiregulin (AREG) Influences Costimulatory Molecules on Monocytes and T Cells and Modulates T-Cell Responses.
Dreschers S, Platen C, Oppermann L, Doughty C, Ludwig A, Babendreyer A, Orlikowsky TW. Dreschers S, et al. J Immunol Res. 2023 Nov 24;2023:8883045. doi: 10.1155/2023/8883045. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 38046264 Free PMC article. - Unleashing the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: factors, strategies, and ongoing trials.
Yu J, Li M, Ren B, Cheng L, Wang X, Ma Z, Yong WP, Chen X, Wang L, Goh BC. Yu J, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1261575. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1261575. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37719852 Free PMC article. Review. - Tumor microenvironment signaling and therapeutics in cancer progression.
Goenka A, Khan F, Verma B, Sinha P, Dmello CC, Jogalekar MP, Gangadaran P, Ahn BC. Goenka A, et al. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023 May;43(5):525-561. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12416. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37005490 Free PMC article. Review. - Motility Dynamics of T Cells in Tumor-Draining Lymph Nodes: A Rational Indicator of Antitumor Response and Immune Checkpoint Blockade.
Kanda Y, Okazaki T, Katakai T. Kanda Y, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 15;13(18):4616. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184616. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572844 Free PMC article. Review. - Immune Checkpoints in Cancers: From Signaling to the Clinic.
Pisibon C, Ouertani A, Bertolotto C, Ballotti R, Cheli Y. Pisibon C, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 12;13(18):4573. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184573. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Abbas AK. Die and let live: eliminating dangerous lymphocytes. Cell. 1996;84:655–658. - PubMed
- Zheng L, Fisher G, Miller RE, Peschon J, Lynch DH, Lenardo MJ. Induction of apoptosis in mature T cells by tumour necrosis. Nature (Lond) 1995;377:348–352. - PubMed
- Tivol EA, Schweitzer AN, Sharpe AH. Costimulation and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:822–830. - PubMed
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:233–258. - PubMed
- Walunas TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, Linsley PS, Freeman GJ, Green JM, Thompson CB, Bluestone JA. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1:405–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous