Preassembly of interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptor subunits on resting Kit 225 K6 T cells and their modulation by IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15: a fluorescence resonance energy transfer study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Preassembly of interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptor subunits on resting Kit 225 K6 T cells and their modulation by IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15: a fluorescence resonance energy transfer study
S Damjanovich et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Assembly and mutual proximities of alpha, beta, and gamma(c) subunits of the interleukin 2 receptors (IL-2R) in plasma membranes of Kit 225 K6 T lymphoma cells were investigated by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) using fluorescein isothiocyanate- and Cy3-conjugated monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that were directed against the IL-2R alpha, IL-2R beta, and gamma(c) subunits of IL-2R. The cell-surface distribution of subunits was analyzed at the nanometer scale (2-10 nm) by FRET on a cell-by-cell basis. The cells were probed in resting phase and after coculture with saturating concentrations of IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15. FRET data from donor- and acceptor-labeled IL-2R beta-alpha, gamma-alpha, and gamma-beta pairs demonstrated close proximity of all subunits to each other in the plasma membrane of resting T cells. These mutual proximities do not appear to represent mAb-induced microaggregation, because FRET measurements with Fab fragments of the mAbs gave similar results. The relative proximities were meaningfully modulated by binding of IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15. Based on FRET analysis the topology of the three subunits at the surface of resting cells can be best described by a "triangular model" in the absence of added interleukins. IL-2 strengthens the bridges between the subunits, making the triangle more compact. IL-7 and IL-15 act in the opposite direction by opening the triangle possibly because they associate their private specific alpha receptors with the beta and/or gamma(c) subunits of the IL-2R complex. These data suggest that IL-2R subunits are already colocalized in resting T cells and do not require cytokine-induced redistribution. This colocalization is significantly modulated by binding of relevant interleukins in a cytokine-specific manner.
Figures
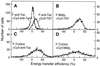
Figure 1
Representative flow cytometric histograms of energy transfer efficiencies measured between FITC (F)- and Cy3-conjugated mAbs bound to IL-2R α, β, and γ subunits on Kit 225 K6 T cells. Averages and error estimates (E ± Δ_E_) of mean values of flow cytometric energy transfer histograms for the indicated donor–acceptor pairs were calculated from data of three to five independent measurements: (A) 1.5 ± 0.1% for F-anti-Tac + Cy3-anti-Tac, 18.2 ± 3.5% for F-anti-Tac + Cy3–7G7; (B) 25.4 ± 5.9% for F-Mikβ3 + Cy3–7G7; (C) 20.6 ± 5.1% for F-TUGh4 + Cy3-anti-Tac; and (D) 12.4 ± 5.0% for F-TUGh4 + Cy3-Mikβ1. Displacement from a mean value of 0 indicates energy transfer and nonrandom proximity of the epitopes.
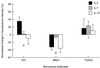
Figure 2
Effect of IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 on the accessibility of epitopes to FITC-conjugated mAbs 7G7/B6 (against IL-2Rα), Mikβ3 (against IL-2Rβ), and TUGh4 (against IL-2Rγ) added as single agents on Kit 225 K6 wild-type T cells. Interleukins were added to cell cultures 6 hr before harvesting at the following concentrations: IL-2 (solid bars), 20 units/ml; IL-7 (shaded bars) and IL-15 (open bars), both 1 ng/ml (20 pM). The mean values of fluorescence histograms collected on cells treated with the interleukins were expressed as percent change from control values. Bars represent mean ± SEM of four to six independent measurements.
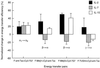
Figure 3
Effect of IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 on energy transfer efficiencies measured between FITC (F)- and Cy3-conjugated mAbs specific to the IL-2R α, β, and γ subunits on Kit 225 K6 T cells. The cells were treated with interleukins as described in the legend to Fig. 2 by IL-2 (solid bars), IL-7 (shaded bars), and IL-15 (open bars). The mean values of the fluorescence energy transfer histograms collected from cytokine-treated cells were expressed as percent change from the control values. Bars represent mean ± SEM of four to six independent measurements. Greek letters with arrows indicate the subunits labeled with the mAbs and the direction of energy transfer. The subscripts 1 and 2 on the letter α designate the two epitopes recognized by mAbs anti-Tac and 7G7, respectively, on the same IL-2Rα subunit.
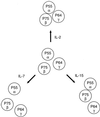
Figure 4
Schematic representation of lateral organization of the subunits of the IL-2 receptor complex on resting Kit 225 K6 T cells and the complex’s modulation by addition of IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15. FRET data suggested that IL-2R α, β, and γ subunits are preassembled, forming heterotrimers on the surface of resting cells (Middle). The proximity between the β and γ subunits was not altered significantly with any of the interleukins. Whereas IL-2 promoted a stronger contact of the α subunit with the β and γ chains (Top), IL-7 loosened it (Bottom Left). IL-15 induced a closer proximity of β and α subunits, whereas the contact between the γ and α subunits became weaker, thereby leading to a somewhat linearized configuration of the IL-2R complex (Bottom Right).
Similar articles
- Differential regulation of lymphokine production by distinct subunits of the T cell interleukin 2 receptor.
Burdach S, Zessack N, Dilloo D, Shatsky M, Thompson D, Levitt L. Burdach S, et al. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2114-21. doi: 10.1172/JCI115242. J Clin Invest. 1991. PMID: 1828253 Free PMC article. - Interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain expression on resting and activated lymphoid cells.
Nakarai T, Robertson MJ, Streuli M, Wu Z, Ciardelli TL, Smith KA, Ritz J. Nakarai T, et al. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):241-51. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.241. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 8006584 Free PMC article. - IL-15, a novel T cell growth factor that shares activities and receptor components with IL-2.
Giri JG, Anderson DM, Kumaki S, Park LS, Grabstein KH, Cosman D. Giri JG, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 1995 May;57(5):763-6. doi: 10.1002/jlb.57.5.763. J Leukoc Biol. 1995. PMID: 7759955 Review. - Characterization of interleukin-15 (IL-15) and the IL-15 receptor complex.
Kennedy MK, Park LS. Kennedy MK, et al. J Clin Immunol. 1996 May;16(3):134-43. doi: 10.1007/BF01540911. J Clin Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8734356 Review.
Cited by
- Visualization of Protein Interactions in Living Cells.
Zal T. Zal T. Self Nonself. 2011 Apr;2(2):98-107. doi: 10.4161/self.2.2.17932. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Self Nonself. 2011. PMID: 22299061 Free PMC article. - The first alpha helix of interleukin (IL)-2 folds as a homotetramer, acts as an agonist of the IL-2 receptor beta chain, and induces lymphokine-activated killer cells.
Eckenberg R, Rose T, Moreau JL, Weil R, Gesbert F, Dubois S, Tello D, Bossus M, Gras H, Tartar A, Bertoglio J, Chouaïb S, Goldberg M, Jacques Y, Alzari PM, Thèze J. Eckenberg R, et al. J Exp Med. 2000 Feb 7;191(3):529-40. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.3.529. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10662798 Free PMC article. - Dynamic, yet structured: The cell membrane three decades after the Singer-Nicolson model.
Vereb G, Szöllosi J, Matkó J, Nagy P, Farkas T, Vigh L, Mátyus L, Waldmann TA, Damjanovich S. Vereb G, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 8;100(14):8053-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1332550100. Epub 2003 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12832616 Free PMC article. Review. - Understanding FRET as a research tool for cellular studies.
Shrestha D, Jenei A, Nagy P, Vereb G, Szöllősi J. Shrestha D, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 25;16(4):6718-56. doi: 10.3390/ijms16046718. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25815593 Free PMC article. Review. - Distinct spatial relationship of the interleukin-9 receptor with interleukin-2 receptor and major histocompatibility complex glycoproteins in human T lymphoma cells.
Nizsalóczki E, Csomós I, Nagy P, Fazekas Z, Goldman CK, Waldmann TA, Damjanovich S, Vámosi G, Mátyus L, Bodnár A. Nizsalóczki E, et al. Chemphyschem. 2014 Dec 15;15(18):3969-78. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201402501. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Chemphyschem. 2014. PMID: 25297818 Free PMC article.
References
- Waldmann T A. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:875–911. - PubMed
- Taniguchi T, Minami Y. Cell. 1993;73:5–8. - PubMed
- Leonard W J, Depper J M, Uchiyama T, Smith K A, Waldmann T A, Greene W C. Nature (London) 1982;300:267–269. - PubMed
- Sharon M, Klausner R D, Cullen B R, Chizzonite R, Leonard W J. Science. 1986;234:859–863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials