CXCR-4 is expressed by primary macrophages and supports CCR5-independent infection by dual-tropic but not T-tropic isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 - PubMed (original) (raw)
CXCR-4 is expressed by primary macrophages and supports CCR5-independent infection by dual-tropic but not T-tropic isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Y Yi et al. J Virol. 1998 Jan.
Abstract
Primary macrophages are infected by macrophage (M)-tropic but not T-cell line (T)-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) strains, and CCR5 and CXCR-4 are the principal cofactors utilized for CD4-mediated entry by M-tropic and T-tropic isolates, respectively. Macrophages from individuals homozygous for an inactivating mutation of CCR5 are resistant to prototype M-tropic strains that depend on CCR5 but are permissive for a dual-tropic isolate, 89.6, that can use both CCR5 and CXCR-4, as well as CCR2b, CCR3, and CCR8. Here we show that 89.6 entry into CCR5-deficient macrophages is blocked by an anti-CXCR-4 antibody and by the CXCR-4-specific chemokine SDF but not by the ligands to CCR2b or CCR3. Reverse transcription-PCR demonstrated expression of CXCR-4 but not CCR3 or CCR8 in macrophages, while CCR2b was variable. Macrophage surface expression of CXCR-4 was confirmed by immunofluorescence staining and flow cytometry. Thus, CXCR-4 is expressed by primary macrophages and functions as a cofactor for entry by dual-tropic but not T-tropic HIV-1 isolates, and macrophage resistance to T-tropic strains does not result from a lack of the T-tropic entry cofactor CXCR-4. Since CXCR-4 on macrophages can be used by some but not other isolates, these results indicate that HIV-1 strains differ in how they utilize chemokine receptors as cofactors for entry and that the ability of a chemokine receptor to mediate HIV-1 entry differs, depending on the cell type in which it is expressed.
Figures
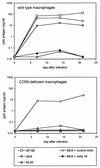
FIG. 1
HIV-1 replication in normal and CCR5-deficient macrophages. Monocytes were isolated from individuals homozygous for the wild-type CCR5 allele or ccr5Δ32, plated at 2 × 105 per well in 48-well plastic tissue culture plates, and allowed to differentiate into macrophages in vitro. After 7 days in culture they were infected overnight with 20 ng of p24 antigen of M-tropic (SF162 or ADA), T-tropic (NL43), or dual-tropic (89.6) strains. Cultures were then washed, and the supernatant was sampled periodically for p24 antigen. Cells infected with 89.6 were incubated for 1 h prior to and during infection with the anti-CD4 MAb no. 19 or the control MAb B33.1 (each at 10 μg/ml), which was then maintained in the medium throughout the experiment.
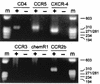
FIG. 2
RT-PCR detection of chemokine receptor expression in macrophages. RNA was extracted from 7-day-old macrophage cultures and subjected to reverse transcription and PCR amplification for CCR5, CXCR-4, CCR3, CCR8 (chemR1), and CCR2b, as well as CD4. Products were separated on agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide. Macrophages from a CCR5 wild-type-homozygous donor are shown, and the same pattern was seen with cells from _ccr5Δ32_-homozygous donors. Amplification was done following reverse transcription with (+) or without (−) reverse transcription enzyme present. m, molecular size standards.
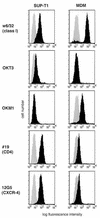
FIG. 3
Macrophage surface expression of CXCR-4 by flow cytometry. Seven-day-old cultures of monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) were detached and stained with MAbs for major histocompatibility complex class I as a positive control (w6/32), a T-cell marker (OKT3), a macrophage marker (OKM1), CD4 (#19), and CXCR-4 (12G5). Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry with a minimum of 104 cells. Specific MAb profiles are indicated by the black histogram, and the negative control antibody is shown as the shaded histogram in each graph. Macrophages from a CCR5 wild-type-homozygous donor are shown and are representative of cells from six different donors. The same patterns were seen with cells from _ccr5Δ32_-homozygous donors. The SUP-T1 cell line was stained in parallel.
FIG. 4
Inhibition of HIV-1 entry into normal and CCR5-deficient macrophages. Macrophages were isolated from individuals homozygous for the wild-type CCR5 allele (w/w) or the ccr5Δ32 allele (Δ/Δ). After 7 days in culture they were infected with 20 ng of p24 antigen of the dual-tropic isolate 89.6, the T-tropic strain NL43, or the M-tropic strain SF162. The indicated wells were incubated for 1 h prior to and throughout the infection with the anti-CD4 MAb no. 19 (#19), the anti-CXCR-4 MAb 12G5, or the control antibody B33.1 or with SDF, MCP-1 and MCP-3, or eotaxin. Three days after infection the cells were lysed and subjected to PCR amplification with primers that detect conserved regions of the HIV-1 LTR, followed by Southern blotting. Infections were done in duplicate and amplified in independent PCR reactions, both of which are shown. Amplification with β-globin primers showed a positive signal in all wells (data not shown). HIV plasmid DNA was used as a positive control (+) for amplification. Data are representative of replicate experiments with cells from three _ccr5Δ32_-homozygous donors.
Similar articles
- Cofactors for human immunodeficiency virus entry into primary macrophages.
Collman RG, Yi Y. Collman RG, et al. J Infect Dis. 1999 May;179 Suppl 3:S422-6. doi: 10.1086/314797. J Infect Dis. 1999. PMID: 10099111 - Role of CCR5 in infection of primary macrophages and lymphocytes by macrophage-tropic strains of human immunodeficiency virus: resistance to patient-derived and prototype isolates resulting from the delta ccr5 mutation.
Rana S, Besson G, Cook DG, Rucker J, Smyth RJ, Yi Y, Turner JD, Guo HH, Du JG, Peiper SC, Lavi E, Samson M, Libert F, Liesnard C, Vassart G, Doms RW, Parmentier M, Collman RG. Rana S, et al. J Virol. 1997 Apr;71(4):3219-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.4.3219-3227.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9060685 Free PMC article. - Role of CXCR4 in cell-cell fusion and infection of monocyte-derived macrophages by primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) strains: two distinct mechanisms of HIV-1 dual tropism.
Yi Y, Isaacs SN, Williams DA, Frank I, Schols D, De Clercq E, Kolson DL, Collman RG. Yi Y, et al. J Virol. 1999 Sep;73(9):7117-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.9.7117-7125.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10438797 Free PMC article. - Maraviroc Therapy and CCR5 Genotype.
Dean L. Dean L. 2015 Mar 18 [updated 2017 Apr 10]. In: Pratt VM, Scott SA, Pirmohamed M, Esquivel B, Kattman BL, Malheiro AJ, editors. Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012–. 2015 Mar 18 [updated 2017 Apr 10]. In: Pratt VM, Scott SA, Pirmohamed M, Esquivel B, Kattman BL, Malheiro AJ, editors. Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012–. PMID: 28520358 Free Books & Documents. Review. - HIV-1 target cells in the CNS.
Joseph SB, Arrildt KT, Sturdevant CB, Swanstrom R. Joseph SB, et al. J Neurovirol. 2015 Jun;21(3):276-89. doi: 10.1007/s13365-014-0287-x. Epub 2014 Sep 19. J Neurovirol. 2015. PMID: 25236812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and its homolog D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT) are significant promotors of UVB- but not chemically induced non-melanoma skin cancer.
Huth S, Huth L, Heise R, Marquardt Y, Lopopolo L, Piecychna M, Boor P, Fingerle-Rowson G, Kapurniotu A, Yazdi AS, Bucala R, Bernhagen J, Baron JM. Huth S, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 18;13(1):11611. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38748-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37464010 Free PMC article. - HIV replication and latency in monocytes and macrophages.
Veenhuis RT, Abreu CM, Shirk EN, Gama L, Clements JE. Veenhuis RT, et al. Semin Immunol. 2021 Jan;51:101472. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2021.101472. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Semin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33648815 Free PMC article. Review. - Human Immunodeficiency Virus Immune Cell Receptors, Coreceptors, and Cofactors: Implications for Prevention and Treatment.
Woodham AW, Skeate JG, Sanna AM, Taylor JR, Da Silva DM, Cannon PM, Kast WM. Woodham AW, et al. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2016 Jul;30(7):291-306. doi: 10.1089/apc.2016.0100. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2016. PMID: 27410493 Free PMC article. Review. - The macrophage: a therapeutic target in HIV-1 infection.
Kumar A, Herbein G. Kumar A, et al. Mol Cell Ther. 2014 Apr 2;2:10. doi: 10.1186/2052-8426-2-10. eCollection 2014. Mol Cell Ther. 2014. PMID: 26056579 Free PMC article. Review. - HIV-1 envelope-receptor interactions required for macrophage infection and implications for current HIV-1 cure strategies.
Gorry PR, Francella N, Lewin SR, Collman RG. Gorry PR, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2014 Jan;95(1):71-81. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0713368. Epub 2013 Oct 24. J Leukoc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24158961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Biti R, Ffrench R, Young J, Bennetts B, Stewart G. HIV-1 infection in an individual homozygous for the CCR5 deletion allele. Nat Med. 1997;3:252–253. - PubMed
- Bleul C C, Farzan M, Choe H, Parolin C, Clark-Lewis I, Sodroski J, Springer T A. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996;382:829–833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI-35502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL-58004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS027405/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-27405/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials