Prevalence of specific language impairment in kindergarten children - PubMed (original) (raw)
Prevalence of specific language impairment in kindergarten children
J B Tomblin et al. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1997 Dec.
Abstract
This epidemiologic study estimated the prevalence of specific language impairment (SLI) in monolingual English-speaking kindergarten children. From a stratified cluster sample in rural, urban, and suburban areas in the upper midwest, 7,218 children were screened. The language screening failure rate was 26.2%. Children who failed the screening and a similar number of controls were then administered a diagnostic battery (n = 2,084) that provided for a diagnosis of SLI using common diagnostic standards. Results provided an estimated overall prevalence rate of 7.4%. The prevalence estimate for boys was 8% and for girls 6%. Variation in prevalence was found among children of different racial/cultural backgrounds; however, these background variables were found to be correlated with parental education, which was also associated with SLI. The parents of 29% of the children identified as SLI reported they had previously been informed that their child had a speech or language problem. The prevalence estimates obtained fell within recent estimates for SLI, but demonstrated that this condition is more prevalent among females than has been previously reported. Also, the clinical identification of these children remains low among kindergarteners.
Figures
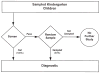
Figure 1
A diagram of flow of participants through the screening and diagnostic phases of the study design.
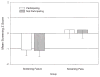
Figure 2
Means and standard deviations on the language screening test of children who participated and children who did not participate in the diagnostic phase.
Figure 3
Prevalence rates of SLI among children who passed and failed the language screening and the resulting estimated prevalence rate for the sample of children screened.
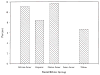
Figure 4
Prevalence of SLI across racial/ethnic groups.
Similar articles
- Prevalence of speech delay in 6-year-old children and comorbidity with language impairment.
Shriberg LD, Tomblin JB, McSweeny JL. Shriberg LD, et al. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1999 Dec;42(6):1461-81. doi: 10.1044/jslhr.4206.1461. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1999. PMID: 10599627 - Grammatical morphology is not a sensitive marker of language impairment in Icelandic in children aged 4-14 years.
Thordardottir E. Thordardottir E. J Commun Disord. 2016 Jul-Aug;62:82-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 8. J Commun Disord. 2016. PMID: 27314205 - Retelling stories: Grammatical and lexical measures for identifying monolingual spanish speaking children with specific language impairment (SLI).
Auza B A, Harmon MT, Murata C. Auza B A, et al. J Commun Disord. 2018 Jan-Feb;71:52-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 5. J Commun Disord. 2018. PMID: 29274509 - Population-based screening of children for specific speech and language impairment in Germany: a systematic review.
Kasper J, Kreis J, Scheibler F, Möller D, Skipka G, Lange S, von dem Knesebeck O. Kasper J, et al. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2011;63(5):247-63. doi: 10.1159/000321000. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2011. PMID: 21304231 Review. - Past Tense Production in Children With and Without Specific Language Impairment Across Germanic Languages: A Meta-Analysis.
Krok WC, Leonard LB. Krok WC, et al. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015 Aug;58(4):1326-40. doi: 10.1044/2015_JSLHR-L-14-0348. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015. PMID: 26049065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A model-based meta-analytic examination of specific reading comprehension deficit: how prevalent is it and does the simple view of reading account for it?
Wagner RK, Beal B, Zirps FA, Spencer M. Wagner RK, et al. Ann Dyslexia. 2021 Jul;71(2):260-281. doi: 10.1007/s11881-021-00232-2. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Ann Dyslexia. 2021. PMID: 34080138 Free PMC article. - Predictors of second language acquisition in Latino children with specific language impairment.
Gutiérrez-Clellen V, Simon-Cereijido G, Sweet M. Gutiérrez-Clellen V, et al. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2012 Feb;21(1):64-77. doi: 10.1044/1058-0360(2011/10-0090). Epub 2012 Jan 9. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22230174 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The Predictive Value of Language Scales: Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development Third Edition in Correlation With Korean Sequenced Language Scale for Infant.
Doh JH, Kim SA, Oh K, Kim Y, Park N, Park S, Heo NH. Doh JH, et al. Ann Rehabil Med. 2020 Oct;44(5):378-385. doi: 10.5535/arm.19198. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Ann Rehabil Med. 2020. PMID: 32986945 Free PMC article. - A balanced t(10;15) translocation in a male patient with developmental language disorder.
Ercan-Sencicek AG, Davis Wright NR, Sanders SJ, Oakman N, Valdes L, Bakkaloglu B, Doyle N, Yrigollen CM, Morgan TM, Grigorenko EL. Ercan-Sencicek AG, et al. Eur J Med Genet. 2012 Feb;55(2):128-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2011.12.005. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Eur J Med Genet. 2012. PMID: 22266071 Free PMC article. - Studies assessing domains pertaining to structural language in autism vary in reporting practices and approaches to assessment: A systematic review.
Girolamo T, Shen L, Monroe Gulick A, Rice ML, Eigsti IM. Girolamo T, et al. Autism. 2024 Jul;28(7):1602-1621. doi: 10.1177/13623613231216155. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Autism. 2024. PMID: 38145307 Free PMC article.
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
- Aram DM, Morris R, Hall NE. Clinical and research congruence in identifying children with specific language impairment. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research. 1993;36:580–591. - PubMed
- Bangs TE. Language and learning disorders of the pre-academic child. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts; 1968.
- Beitchman JH, Nair R, Clegg M, Patel PG. Prevalence of speech and language disorders in 5-year-old kindergarten children in the Ottawa-Carleton region. Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders. 1986;51:98–110. - PubMed
- Beitchman JH, Nair R, Clegg M, Ferguson B. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in children with speech and language disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry. 1986;25:528–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical