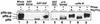Functional inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein requires sequential modification by at least two distinct cyclin-cdk complexes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Functional inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein requires sequential modification by at least two distinct cyclin-cdk complexes
A S Lundberg et al. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Feb.
Abstract
The retinoblastoma protein (pRb) acts to constrain the G1-S transition in mammalian cells. Phosphorylation of pRb in G1 inactivates its growth-inhibitory function, allowing for cell cycle progression. Although several cyclins and associated cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) have been implicated in pRb phosphorylation, the precise mechanism by which pRb is phosphorylated in vivo remains unclear. By inhibiting selectively either cdk4/6 or cdk2, we show that endogenous D-type cyclins, acting with cdk4/6, are able to phosphorylate pRb only partially, a process that is likely to be completed by cyclin E-cdk2 complexes. Furthermore, cyclin E-cdk2 is unable to phosphorylate pRb in the absence of prior phosphorylation by cyclin D-cdk4/6 complexes. Complete phosphorylation of pRb, inactivation of E2F binding, and activation of E2F transcription occur only after sequential action of at least two distinct G1 cyclin kinase complexes.
Figures
FIG. 1
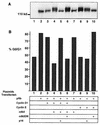
Specificity of function of p16_INK4A_ and cdk2DN. (B) Cell cycle analysis of SaOS-2 cells cotransfected with the indicated plasmids and a CD20 expression plasmid. DNA content was analyzed by propidium iodide staining and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of CD20-positive cells. % G0/G1, percent of CD20-positive cells with 2N DNA content. (A) Anti-pRb immunoblot of lysates prepared from the same transfected SaOS-2 cells analyzed in panel B.
FIG. 2
Cyclin D-associated kinase only partially phosphorylates pRb. U2-OS cells were cotransfected with empty vector (lanes 1 and 4), cdk2DN expression plasmid (lane 2), or p16_INK4A_ expression plasmid (lane 3) as described in the legend to Fig. 1, and pure populations of transfected cells were isolated by magnetic bead selection and flow cytometry. (A) Anti-pRb immunoblot of lysates prepared from purified transfected U2-OS cells. (B) Immunoprecipitations from lysates of purified transfected U2-OS cells with anti-cdk6 antibody (upper panel, lanes 1 to 3) or anti-cdk6 antibody preincubated with peptide (lane 4), or with anti-cyclin E antibody (lower panel, lanes 1 to 3) or isotype-matched irrelevant control (lane 4), were tested for kinase activity against either GST-pRb-COOH (Rb) or histone H1 (H1) substrate.
FIG. 3
Phosphopeptide analysis of pRb. [32P]orthophosphate-labeled pRb was immunoprecipitated from purified cells transfected with CD20 and cdk2DN expression plasmid (left) or CD20 alone (right) and subjected to tryptic phosphopeptide analysis. Arrows indicate phosphopeptides underrepresented in pRb from cdk2DN-transfected cells compared to pRb from asynchronously growing cells.
FIG. 4
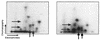
Nuclear affinity of partially phosphorylated pRb. U2-OS cells grown on coverslips were transfected with the indicated plasmids and CD20 expression plasmid, subjected to indirect immunofluorescence with anti-CD20 antibody, and then mock treated or subjected to low-salt extraction prior to indirect immunofluorescence with anti-pRb antibody. The mean and standard error of the mean from three independent experiments are shown. For each experimental sample, 50 CD20-positive cells were analyzed.
FIG. 5
Repression of E2F by partially phosphorylated pRb. (A) Repression of E2F transcriptional activity by p16_INK4A_ and cdk2DN. Cells transfected with the indicated plasmid and either a wild-type (3× E2F; ▪) or a mutant (3× mut; □) E2 promoter-luciferase reporter construct were analyzed for luciferase activity. The mean and standard error of the mean from three independent experiments are shown. (B) Identification of E2F-associated pRb by immunoblot analysis of pRb from lysates prepared from asynchronously growing (lanes 1 and 3) or cdk2DN-transfected but not sorted (lanes 2 and 4) U2-OS cells before (lanes 1 and 2) or after precipitation with Sepharose 4B–GST-DP1-E2F1 (lanes 3 and 4) or Sepharose 4B-GST alone (lanes 6 and 7) or prepared from cdk2DN-transfected sorted U2-OS cells (lane 5).
FIG. 6
Phosphatase treatment of E2F-associated pRb. Shown are immunoblots of untreated and phosphatase-treated pRb with an antibody specific for the carboxy terminus of pRb (αpRb). (Left) Immunoblot of pRb from lysates prepared from asynchronously growing U2-OS cells (lane 1) or after precipitation with Sepharose 4B–GST-DP1-E2F1 before (lane 4) or after (lane 3) treatment with phosphatase (PPase). (Right) Immunoblot of pRb after precipitation with Sepharose 4B–GST-DP1-E2F1 and subsequent phosphatase treatment (lane 5), pRb isolated from p16-transfected, sorted cells (lane 6), and pRb immunoprecipitated from lysates of asynchronously growing U2-OS cells before (lane 9) or after treatment with phosphatase in the absence (lane 8) or presence (lane 7) of sodium orthovanadate (Na3VO4).
References
- Buchkovich K, Duffy L A, Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989;58:1097–1105. - PubMed
- Chellappan S P, Hiebert S, Mudryj M, Horowitz J M, Nevins J R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991;65:1053–1061. - PubMed
- Chen P L, Scully P, Shew J Y, Wang J Y, Lee W H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989;58:1193–1198. - PubMed
- Chen W D, Otterson G A, Lipkowitz S, Khleif S N, Coxon A B, Kaye F J. Apoptosis is associated with cleavage of a 5 kDa fragment from RB which mimics dephosphorylation and modulates E2F binding. Oncogene. 1997;14:1243–1248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases