Interleukin 6 is required for the development of collagen-induced arthritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Interleukin 6 is required for the development of collagen-induced arthritis
T Alonzi et al. J Exp Med. 1998.
Abstract
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is overproduced in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and, based on its multiple stimulatory effects on cells of the immune system and on vascular endothelia, osteoclasts, and synovial fibroblasts, is believed to participate in the development and clinical manifestations of this disease. In this study we have analysed the effect of ablating cytokine production in two mouse models of arthritis: collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DBA/1J mice and the inflammatory polyarthritis of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) transgenic mice. IL-6 was ablated by intercrossing an IL-6 null mutation into both arthritis-susceptible genetic backgrounds and disease development was monitored by measuring clinical, histological, and biochemical parameters. Two opposite responses were observed; while arthritis in TNF-alpha transgenic mice was not affected by inactivation of the IL-6 gene, DBA/1J, IL-6(-/-) mice were completely protected from CIA, accompanied by a reduced antibody response to type II collagen and the absence of inflammatory cells and tissue damage in knee joints. These results are discussed in the light of the present knowledge of cytokine networks in chronic inflammatory disorders and suggest that IL-6 receptor antagonists might be beneficial for the treatment of RA.
Figures
Figure 1
Serum levels of IL-6 in DBA/1J mice with CIA correlated with the arthritis index. Type II collagen immunized mice were bled 6 wk after CII immunization. IL-6 activity was measured by hybridoma growth assay and the arthritis index evaluated as described in Materials and Methods. Results were analyzed using the Spearman correlation coefficient. Rs = 0.694; P = 0.008.
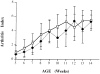
Figure 2
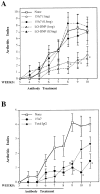
Effects of antibody treatment on arthritis index of CII-immunized DBA/1J mice. (A) Mice (n = 9 for each group) were treated once per week with 1 mg/mouse (white symbols) or 0.5 mg/mouse (black symbols) of either anti–IL-6Rα antibody 15A7 (circles), anti–dinitrophenyl hapten antibody LO-DNP (triangles), or left untreated (squares). *P <0.05 either 15A7 or LO-DNP versus none. (B) Mice were treated with 1 mg/ wk/mouse of either anti–IL6-Rα antibody 15A7 (circles; n = 9), rat total IgG antibodies (diamonds; n = 8), or left untreated (squares; n = 8). *P < 0.02 15A7 versus none; # P <0.04 total IgG versus none. Results were reported as mean ± SD. The weeks after the first immunization with CII and the duration of antibody treatment are indicated on the abscissa.
Figure 3
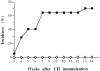
IL-6 is absolutely required for the development of CIA. DIL-6+/+ (squares; n = 17) and DIL-6−/− (diamonds; n = 16) mice were observed for arthritis lesions and the percentage of mice that developed CIA is reported. The figure represents two independent experiments. Weeks after the first immunization with CII are indicated.
Figure 4
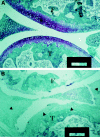
DIL-6−/− mice do not show any histological lesion of the joints. Representative examples of six knee joints for each genotype are shown: DIL-6−/− (A) and DIL-6+/+ (B). In A no signs of inflammatory lesions are detectable. In B severe signs of inflammatory process are depicted; the pannus completely infiltrated the articular cartilage (arrowheads); severe signs of cartilage and bone destruction and mononuclear cells infiltration are shown. Mice were killed 7 wk after first immunization with CII. Paraffin sections were stained with Villanueva staining. T, Tibia; F, femur. Bars: 50 μm.
Figure 5
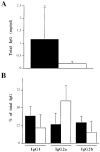
DIL-6−/− mice have abnormal humoral response to type II collagen. DIL-6+/+ (black bars; n = 9) and DIL-6−/− (white bars; n = 8) mice were bled 10 wk after the first immunization with CII, and levels of anti-CII antibodies were measured by ELISA. (A) Total IgG anti-CII antibodies were reported as mean ± SD (*P <0.02). (B) Isotype percentages of total IgG antibodies anti-CII were reported as mean ± SD. IgG isotypes are indicated.
Figure 6
The lack of IL-6 activity does not influence the onset and the development of arthritis in TNF-α transgenic mice. TIL-6−/− (squares; n = 16) and TIL-6+/+ (diamonds; n = 11) mice were scored for arthritic lesions as described in Materials and Methods. Arthritis index is expressed as mean values ± SD. The differences were not statistically significant.
Similar articles
- Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.
Joosten LA, Lubberts E, Helsen MM, Saxne T, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Heinegård D, van den Berg WB. Joosten LA, et al. Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article. - Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice by recombinant TSG-6, a tumor necrosis factor/interleukin-1-inducible protein.
Mindrescu C, Thorbecke GJ, Klein MJ, Vilcek J, Wisniewski HG. Mindrescu C, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Dec;43(12):2668-77. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200012)43:12<2668::AID-ANR6>3.0.CO;2-E. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. PMID: 11145024 - Phagocytic lining cells determine local expression of inflammation in type II collagen-induced arthritis.
van Lent PL, Holthuysen AE, van den Bersselaar LA, van Rooijen N, Joosten LA, van de Loo FA, van de Putte LB, van den Berg WB. van Lent PL, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Sep;39(9):1545-55. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390915. Arthritis Rheum. 1996. PMID: 8814067 - Point mutation of tyrosine 759 of the IL-6 family cytokine receptor, gp130, augments collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice.
Tsuji F, Yoshimi M, Katsuta O, Takai M, Ishihara K, Aono H. Tsuji F, et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009 Feb 19;10:23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-23. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009. PMID: 19228423 Free PMC article. - Anticytokine treatment of established type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. A comparative study using anti-TNF alpha, anti-IL-1 alpha/beta, and IL-1Ra.
Joosten LA, Helsen MM, van de Loo FA, van den Berg WB. Joosten LA, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 May;39(5):797-809. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390513. Arthritis Rheum. 1996. PMID: 8639177
Cited by
- Insights into Interactions between Interleukin-6 and Dendritic Polyglycerols.
Sanader Maršić Ž, Maysinger D, Bonačić-Kouteckỳ V. Sanader Maršić Ž, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 28;22(5):2415. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052415. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670858 Free PMC article. - Targeting interleukin-6: all the way to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Tanaka T, Kishimoto T. Tanaka T, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(9):1227-36. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.4666. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Int J Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23136551 Free PMC article. Review. - Ultra-Sensitive and Semi-Quantitative Vertical Flow Assay for the Rapid Detection of Interleukin-6 in Inflammatory Diseases.
Lei R, Arain H, Obaid M, Sabhnani N, Mohan C. Lei R, et al. Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 14;12(9):756. doi: 10.3390/bios12090756. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140141 Free PMC article. - Tocilizumab in pediatric rheumatology: the clinical experience.
Gurion R, Singer NG. Gurion R, et al. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013 Jul;15(7):338. doi: 10.1007/s11926-013-0338-y. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23715975 Review. - Bone marrow cells carrying the env-pX transgene play a role in the severity but not prolongation of arthritis in human T-cell leukaemia virus type-I transgenic rats: a possible role of articular tissues carrying the transgene in the prolongation of arthritis.
Abe A, Ishizu A, Ikeda H, Hayase H, Tsuji T, Miyatake Y, Tsuji M, Fugo K, Sugaya T, Higuchi M, Matsuno T, Yoshiki T. Abe A, et al. Int J Exp Pathol. 2004 Oct;85(4):191-200. doi: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2004.00384.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15312124 Free PMC article.
References
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 1996;85:307–310. - PubMed
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. - PubMed
- Houssiau FA, Devogelaer JP, Van Damme J, de Deuxchaines CN, Van Snick J. Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:784–788. - PubMed
- De Benedetti F, Massa M, Robbioni P, Ravelli A, Burgio GR, Martini A. Correlation of serum interleukin 6 levels with joint involvement and thrombocytosis in systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34:1158–1163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases