Cultured basophils but not cultured mast cells induce human IgE synthesis in B cells after immunologic stimulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cultured basophils but not cultured mast cells induce human IgE synthesis in B cells after immunologic stimulation
Y Yanagihara et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Jan.
Abstract
By generating human mast cells and basophils from umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells cultured in the presence of appropriate cytokines, we investigated whether these two cultured cells could provide the cytokine and cell contact signals that are required to induce IgE synthesis in B cells. To activate cultured mast cells and basophils, cross-linking of cell surface high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilonRI) was performed with specific antigen after sensitization with murine IgE. Upon Fc epsilonRI stimulation, basophils, but not mast cells, secreted significant amounts of immunoreactive IL-4 and IL-13 and expressed detectable CD40 ligand (CD40L) and a very low level of Fas ligand (FasL). These observations at the protein level were consistent with the data obtained at the gene transcriptional level, except for the faint expression of only IL-13 mRNA in mast cells. When added to normal human B cells, activated basophils induced IgE and IgG4 synthesis as well as soluble CD23 release. In contrast, neither IgE nor IgG4 synthesis could be induced by the interaction of B cells with activated mast cells, even in the presence of recombinant IL-4. The induction of IgE synthesis by activated basophils was completely abrogated by two neutralizing MoAbs against IL-4 and IL-13 and by a soluble form of CD40. This abrogation was accompanied by abolished mature C epsilon transcription in both cases. Addition of anti-FasL MoAb, however, did not significantly affect IgE induction mediated by activated basophils. These results demonstrate that unlike cultured mast cells, cultured basophils produce biologically active IL-4 and IL-13 and express functional CD40L after Fc epsilonRI stimulation, thereby contributing to IgE production by B cells, and suggest that relatively weak expression of FasL by cultured basophils is not involved in IgE regulation.
Figures
Fig. 1
Kinetics of IgE-dependent production of IL-4 (○) and IL-13 (•) by cultured human mast cells or basophils. Mast cells (a) or basophils (b) were sensitized with murine IgE, washed, and stimulated with antigen for the indicated times. The concentrations of secreted IL-4 and IL-13 were measured by specific ELISA kits. Each point represents the mean ± s.e.m. of three or four separate experiments. Neither IL-4 nor IL-13 was detectable in the supernatants from unstimulated mast cells and basophils (data not shown).
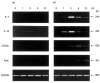
Fig. 2
Analysis of the kinetics of IgE-dependent expression for mRNA of IL-4, IL-13, CD40L, and FasL in cultured human mast cells or basophils. Mast cells (a) or basophils (b) were stimulated with or without antigen after sensitization with murine IgE. After extraction of total cellular RNA at the indicated time points, mRNA for IL-4, IL-13, CD40L, FasL and G3PDH was amplified by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), subjected to electrophoresis, and then visualized by ethidium bromide. Similar results were obtained in two other experiments.
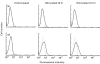
Fig. 3
Analysis of IgE-dependent expression of CD40L on cultured human mast cells or basophils. Mast cells (a) or basophils (b) were stimulated with or without antigen after sensitization with murine IgE. Cells were harvested at the indicated times and stained with FITC-conjugated control antibody (- - -) or anti-CD40L MoAb (—). The stained cells were analysed by flow cytometry. Typical results obtained in three independent experiments are shown.
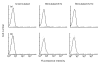
Fig. 4
Analysis of IgE-dependent expression of FasL on cultured human mast cells or basophils. Mast cells (a) or basophils (b) were stimulated with or without antigen after sensitization with murine IgE. Cells were harvested at the indicated times and stained with biotinylated control antibody (- - -) or anti-FasL MoAb (—) followed by PE-conjugated streptavidin. The stained cells were analysed by flow cytometry. Typical results obtained in three (a) or four (b) independent experiments are shown.
Fig. 5
Production of IgE, IgG4 and soluble CD23 by normal B cells mixed with cultured human mast cells or basophils. Mast cells or basophils were stimulated for 2h with antigen after sensitization with murine IgE, washed, added to highly purified B cells, and then cultured for 12 days. Stimulated mast cells were incubated with B cells in the absence or presence of recombinant IL-4. Stimulated basophils were incubated with B cells in the absence or presence of two neutralizing anti-IL-4 and anti-IL-13 MoAbs or a soluble form of CD40. Supernatants were collected and measured for concentrations of IgE, IgG4 and soluble CD23. The net synthesis of IgE and IgG4 was determined, as described in Materials and Methods. Results represent the mean ± s.e.m. of triplicate cultures. One of two comparable experiments is shown. IgE production by B cells was neither induced by unstimulated basophils, nor significantly affected in the cultures containing B cells plus stimulated basophils by the addition of control antibody or IgM (data not shown).
Fig. 6
Analysis of germ-line and mature Cε mRNA expression in normal B cells mixed with cultured human mast cells or basophils. The cell pellets obtained in Fig. 5 were used for the analysis of germ-line and mature Cε transcription. Highly purified B cells were incubated with medium alone (lane 1) or with stimulated mast cells in the absence (lane 2) or presence (lane 3) of recombinant IL-4. Stimulated basophils were incubated with B cells in the absence (lane 4) or presence of two neutralizing anti-IL-4 and anti-IL-3 MoAbs (lane 5) or a soluble form of CD40 (lane 6). After extraction of total cellular RNA, mRNA for germ-line Cε, mature Cε, and G3PDH was amplified by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), subjected to electrophoresis, and then visualized by ethidium bromide. One of two comparable experiments is shown. Neither germ-line nor mature transcripts were detected in the cultures containing B cells plus unstimulated basophils (data not shown).
Similar articles
- Induction of human IgE synthesis in B cells by a basophilic cell line, KU812.
Yanagihara Y, Kajiwara K, Basaki Y, Ikizawa K, Akiyama K, Saito H. Yanagihara Y, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997 May;108(2):295-301. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.d01-1001.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9158101 Free PMC article. - Nasal mast cells in perennial allergic rhinitics exhibit increased expression of the Fc epsilonRI, CD40L, IL-4, and IL-13, and can induce IgE synthesis in B cells.
Pawankar R, Okuda M, Yssel H, Okumura K, Ra C. Pawankar R, et al. J Clin Invest. 1997 Apr 1;99(7):1492-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI119311. J Clin Invest. 1997. PMID: 9119992 Free PMC article. - Induction of human IgE synthesis in B cells by mast cells and basophils.
Gauchat JF, Henchoz S, Mazzei G, Aubry JP, Brunner T, Blasey H, Life P, Talabot D, Flores-Romo L, Thompson J, et al. Gauchat JF, et al. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):340-3. doi: 10.1038/365340a0. Nature. 1993. PMID: 7690905 - Pairs of surface molecules involved in human IgE regulation: CD23-CD21 and CD40-CD40L.
Bonnefoy JY, Gauchat JF, Life P, Graber P, Mazzei G, Aubry JP. Bonnefoy JY, et al. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996 Aug;22:63s-66s. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8871046 Review. - Regulation of IgE synthesis by CD23/CD21 interaction.
Bonnefoy JY, Gauchat JF, Life P, Graber P, Aubry JP, Lecoanet-Henchoz S. Bonnefoy JY, et al. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995 May-Jun;107(1-3):40-2. doi: 10.1159/000236924. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7542093 Review.
Cited by
- Histamine-releasing factor/translationally controlled tumor protein (HRF/TCTP)-induced histamine release is enhanced with SHIP-1 knockdown in cultured human mast cell and basophil models.
Langdon JM, Schroeder JT, Vonakis BM, Bieneman AP, Chichester K, Macdonald SM. Langdon JM, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Oct;84(4):1151-8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0308172. Epub 2008 Jul 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18625911 Free PMC article. - Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite.
Min B, Prout M, Hu-Li J, Zhu J, Jankovic D, Morgan ES, Urban JF Jr, Dvorak AM, Finkelman FD, LeGros G, Paul WE. Min B, et al. J Exp Med. 2004 Aug 16;200(4):507-17. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040590. J Exp Med. 2004. PMID: 15314076 Free PMC article. - Basophils are increased and express increased levels of interleukin-4 in the parotid lesions of Kimura disease.
Nonaka M, Sakitani E, Ono E, Yamamura Y, Seo Y, Shibata N, Pawankar R, Yoshihara T. Nonaka M, et al. Asia Pac Allergy. 2017 Oct;7(4):221-226. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.4.221. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Asia Pac Allergy. 2017. PMID: 29094020 Free PMC article. - Basophil activation by mosquito extracts in patients with hypersensitivity to mosquito bites.
Sakakibara Y, Wada T, Muraoka M, Matsuda Y, Toma T, Yachie A. Sakakibara Y, et al. Cancer Sci. 2015 Aug;106(8):965-71. doi: 10.1111/cas.12696. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25990049 Free PMC article. - Basophil Activation-Dependent Autoantibody and Interleukin-17 Production Exacerbate Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Pan Q, Gong L, Xiao H, Feng Y, Li L, Deng Z, Ye L, Zheng J, Dickerson CA, Ye L, An N, Yang C, Liu HF. Pan Q, et al. Front Immunol. 2017 Mar 27;8:348. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00348. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28396669 Free PMC article.
References
- Gordon JR, Burd PR, Galli SJ. Mast cells as a source of multifunctional cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990;11:458–64. - PubMed
- Gauchat J-F, Henchoz S, Mazzei G, et al. Induction of human IgE synthesis by mast cells and basophils. Nature. 1993;365:340–3. - PubMed
- MacGlashan D, Jr, White JM, Huang S-K, et al. Secretion of IL-4 from human basophils. The relationship between IL-4 mRNA and protein in resting and stimulated basophils. J Immunol. 1994;152:3006–16. - PubMed
- Okayama Y, Petit-Frére C, Kassel O, et al. IgE-dependent expression of mRNA for IL-4 and IL-5 in human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1995;155:1796–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous