The spoIIE locus is involved in the Spo0A-dependent switch in the location of FtsZ rings in Bacillus subtilis - PubMed (original) (raw)
The spoIIE locus is involved in the Spo0A-dependent switch in the location of FtsZ rings in Bacillus subtilis
A Khvorova et al. J Bacteriol. 1998 Mar.
Abstract
A switch in the location of FtsZ ring structures from medial to polar is one of the earliest morphological indicators of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. This switch can be artificially caused during vegetative growth by induction of an active form, Sad67, of the transcription regulator, Spo0A (P. A. Levin and R. Losick, Genes Dev. 10:478-488, 1996). We have used immunofluorescence microscopy to show that the switch in FtsZ ring location during vegetative growth caused by Sad67 induction is blocked by a spoIIE deletion mutation. The spoIIE mutation also impaired polar FtsZ ring formation during sporulation. These results suggest that SpoIIE mediates the Spo0A-directed formation of polar FtsZ rings.
Figures
FIG. 1
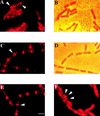
Immunolocalization of FtsZ. Scale bar, 1 μm. The photographs are of cells immunostained with affinity-purified antibodies against the B. subtilis FtsZ protein (A, C, E, and F) and viewed by phase-contrast microscopy with a yellow filter (B and D). A secondary antibody conjugated to the red fluorophore Cy3 was used to visualize FtsZ. Localization of FtsZ in the strains containing Pspac-sad-67 1 h after IPTG addition during vegetative growth in spoIIE+ (SL7260) (A and B [arrows indicate polar FtsZ bands]) and spoIIE::neo (SL7261) (C and D [arrow indicates a medial FtsZ band]) backgrounds. FtsZ localization in the strain containing Pspac-spoIIE without (E [arrow indicates a medial FtsZ band]) and 30 min after (F [arrows indicate medial and polar FtsZ bands within a single cell]) IPTG addition.
FIG. 2
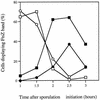
The position of FtsZ bands under sporulation conditions of a spo+ strain and a spoIIE mutant. Bacteria were grown in MSSM. The start of sporulation was defined as the end of exponential growth. The pattern of FtsZ localization was visualized with immunofluorescence microscopy. Results are expressed as percentages of all cells. Open symbols, cells with medial FtsZ bands; closed symbols, cells with polar bands (bipolar or unipolar); squares, spo+ strain (BR151); circles, the isogenic spoIIE::neo strain (SL7240).
FIG. 3
Schematic representation of the paths leading to polar FtsZ ring formation in B. subtilis. Spo0A-P is the active, phosphorylated form of Spo0A that is made at the start of sporulation. The Sad67 mutant form of Spo0A is active without phosphorylation and can substitute for Spo0A-P. The major path from active Spo0A is via SpoIIE. A minor SpoIIE-independent pathway can also function under sporulation conditions.
Similar articles
- Localization of the sporulation protein SpoIIE in Bacillus subtilis is dependent upon the cell division protein FtsZ.
Levin PA, Losick R, Stragier P, Arigoni F. Levin PA, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1997 Sep;25(5):839-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1997.mmi505.x. Mol Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9364910 - RefZ facilitates the switch from medial to polar division during spore formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Wagner-Herman JK, Bernard R, Dunne R, Bisson-Filho AW, Kumar K, Nguyen T, Mulcahy L, Koullias J, Gueiros-Filho FJ, Rudner DZ. Wagner-Herman JK, et al. J Bacteriol. 2012 Sep;194(17):4608-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00378-12. Epub 2012 Jun 22. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22730127 Free PMC article. - Bacterial sporulation: FtsZ rings do the twist.
Margolin W. Margolin W. Curr Biol. 2002 Jun 4;12(11):R391-2. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00882-5. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12062072 Review. - Signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis sporulation.
Strauch MA, Hoch JA. Strauch MA, et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):203-12. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90024-j. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993. PMID: 8504245 Review.
Cited by
- Direct interaction between the cell division protein FtsZ and the cell differentiation protein SpoIIE.
Lucet I, Feucht A, Yudkin MD, Errington J. Lucet I, et al. EMBO J. 2000 Apr 3;19(7):1467-75. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.7.1467. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10747015 Free PMC article. - Use of yeast two-hybrid system for detection of Bacillus subtilis FtsZ protein partners.
Prepiak P, Chromíková Z, Barák I. Prepiak P, et al. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2001;46(4):292-6. doi: 10.1007/BF02815616. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2001. PMID: 11830939 - Coupling of asymmetric division to polar placement of replication origin regions in Bacillus subtilis.
Graumann PL, Losick R. Graumann PL, et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Jul;183(13):4052-60. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.13.4052-4060.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11395470 Free PMC article. - Expression of soluble, active fragments of the morphogenetic protein SpoIIE from Bacillus subtilis using a library-based construct screen.
Rawlings AE, Levdikov VM, Blagova E, Colledge VL, Mas PJ, Tunaley J, Vavrova L, Wilson KS, Barak I, Hart DJ, Wilkinson AJ. Rawlings AE, et al. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2010 Nov;23(11):817-25. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzq057. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2010. PMID: 20817757 Free PMC article. - Cell Cycle Machinery in Bacillus subtilis.
Errington J, Wu LJ. Errington J, et al. Subcell Biochem. 2017;84:67-101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53047-5_3. Subcell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28500523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Arigoni F, Pogliano K, Webb C D, Stragier P, Losick R. Localization of protein implicated in establishment of cell type to sites of asymmetric division. Science. 1995;270:637–640. - PubMed
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons; 1990.
- Barák, I. Personal communication.
- Barák I, Behari J, Olmedo G, Guzmán P, Brown D P, Castro E, Walker D, Westpheling J, Youngman P. Structure and function of the Bacillus SpoIIE protein and its localization to sites of sporulation septum assembly. Mol Microbiol. 1996;19:1047–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources