The periplasmic, group III catalase of Vibrio fischeri is required for normal symbiotic competence and is induced both by oxidative stress and by approach to stationary phase - PubMed (original) (raw)
The periplasmic, group III catalase of Vibrio fischeri is required for normal symbiotic competence and is induced both by oxidative stress and by approach to stationary phase
K L Visick et al. J Bacteriol. 1998 Apr.
Abstract
The catalase gene, katA, of the sepiolid squid symbiont Vibrio fischeri has been cloned and sequenced. The predicted amino acid sequence of KatA has a high degree of similarity to the recently defined group III catalases, including those found in Haemophilus influenzae, Bacteroides fragilis, and Proteus mirabilis. Upstream of the predicted start codon of katA is a sequence that closely matches the consensus sequence for promoters regulated in Escherichia coli by the alternative sigma factor encoded by rpoS. Further, the level of expression of the cloned katA gene in an E. coli rpoS mutant is much lower than in wild-type E. coli. Catalase activity is induced three- to fourfold both as growing V. fischeri cells approach stationary phase and upon the addition of a small amount of hydrogen peroxide during logarithmic growth. The catalase activity was localized in the periplasm of wild-type V. fischeri cells, where its role could be to detoxify hydrogen peroxide coming from the external environment. No significant catalase activity could be detected in a katA null mutant strain, demonstrating that KatA is the predominately expressed catalase in V. fischeri and indicating that V. fischeri carries only a single catalase gene. The catalase mutant was defective in its ability to competitively colonize the light organs of juvenile squids in coinoculation experiments with the parent strain, suggesting that the catalase enzyme plays an important role in the symbiosis between V. fischeri and its squid host.
Figures
FIG. 1
(A) Partial maps of plasmids used in this study. Plasmids pLP2, pKV48, and pKV75 are derivatives of pBluescript KS (Stratagene), a portion of which, including the multiple cloning site, is denoted by the thin line. The V. fischeri catalase gene, katA, is indicated by the black box, and the erythromycin resistance gene, erm, is indicated by the gray box. Transcription of the lacZ gene is in the direction of the arrow. (B) Nucleotide sequence upstream of the V. fischeri katA gene from the _Eco_RI site to the putative ATG start codon. Nucleotides in the putative ribosome binding site upstream of the gene are underlined in bold, and a potential −10 promoter sequence is in boldface. Nucleotides that match the proposed OxyR consensus sequence (41, 42) are in boldface and underlined, while those that match the region upstream of the H. influenzae hktE gene, where an OxyR binding site has been proposed (6), are underlined. The proposed OxyR motifs are displayed above. The putative ATG start site is shown in shadowbox letters.
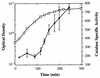
FIG. 2
Catalase specific activity during the growth of V. fischeri ES114. The average optical density of the cultures is indicated by open squares; catalase specific activity, reported in units/milligram of protein, is designated by black circles. The data are averages of activity assays performed on extracts of triplicate cultures. The error bars are equal to 1 standard deviation.
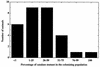
FIG. 3
Colonization of juveniles of the squid E. scolopes by the katA mutant and its parent. Juveniles of E. scolopes were exposed to a 1:1 mixture of the katA mutant and its wild-type parent. The percentage of the katA mutant strain in the population of V. fischeri cells colonizing the light organ was determined for each animal at 17 h postinoculation.
Similar articles
- LitR, a new transcriptional activator in Vibrio fischeri, regulates luminescence and symbiotic light organ colonization.
Fidopiastis PM, Miyamoto CM, Jobling MG, Meighen EA, Ruby EG. Fidopiastis PM, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;45(1):131-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02996.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12100554 - Vibrio fischeri outer membrane protein OmpU plays a role in normal symbiotic colonization.
Aeckersberg F, Lupp C, Feliciano B, Ruby EG. Aeckersberg F, et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Nov;183(22):6590-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.22.6590-6597.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11673429 Free PMC article. - Role for phosphoglucomutase in Vibrio fischeri-Euprymna scolopes symbiosis.
DeLoney CR, Bartley TM, Visick KL. DeLoney CR, et al. J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(18):5121-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.18.5121-5129.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12193629 Free PMC article. - Lessons from a cooperative, bacterial-animal association: the Vibrio fischeri-Euprymna scolopes light organ symbiosis.
Ruby EG. Ruby EG. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1996;50:591-624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.591. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8905092 Review. - An exclusive contract: specificity in the Vibrio fischeri-Euprymna scolopes partnership.
Visick KL, McFall-Ngai MJ. Visick KL, et al. J Bacteriol. 2000 Apr;182(7):1779-87. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.7.1779-1787.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10714980 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Characterization of htrB and msbB mutants of the light organ symbiont Vibrio fischeri.
Adin DM, Phillips NJ, Gibson BW, Apicella MA, Ruby EG, McFall-Ngai MJ, Hall DB, Stabb EV. Adin DM, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Feb;74(3):633-44. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02138-07. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18065606 Free PMC article. - Signal Recognition Particle RNA Contributes to Oxidative Stress Response in Deinococcus radiodurans by Modulating Catalase Localization.
Han R, Fang J, Jiang J, Gaidamakova EK, Tkavc R, Daly MJ, Contreras LM. Han R, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 18;11:613571. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.613571. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391243 Free PMC article. - Reactive oxygen species in the world ocean and their impacts on marine ecosystems.
Morris JJ, Rose AL, Lu Z. Morris JJ, et al. Redox Biol. 2022 Jun;52:102285. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102285. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 35364435 Free PMC article. Review. - GacA regulates symbiotic colonization traits of Vibrio fischeri and facilitates a beneficial association with an animal host.
Whistler CA, Ruby EG. Whistler CA, et al. J Bacteriol. 2003 Dec;185(24):7202-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.24.7202-7212.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 14645281 Free PMC article. - Competitive dominance among strains of luminous bacteria provides an unusual form of evidence for parallel evolution in Sepiolid squid-vibrio symbioses.
Nishiguchi MK, Ruby EG, McFall-Ngai MJ. Nishiguchi MK, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998 Sep;64(9):3209-13. doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.9.3209-3213.1998. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9726861 Free PMC article.
References
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
- Beers R F, Jr, Sizer I W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952;195:133–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources