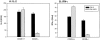B7-1 engagement of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 inhibits T cell activation in the absence of CD28 - PubMed (original) (raw)
B7-1 engagement of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 inhibits T cell activation in the absence of CD28
F Fallarino et al. J Exp Med. 1998.
Abstract
Ligation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA4) appears to inhibit T cell responses. Four mechanisms have been proposed to explain the inhibitory activity of CTLA4: competition for B7-1 and B7-2 binding by CD28; sequestration of signaling molecules away from CD28 via endocytosis; delivery of a signal that antagonizes a CD28 signal; and delivery of a signal that antagonizes a T cell receptor (TCR) signal. As three of these potential mechanisms involve functional antagonism of CD28, an experimental model was designed to determine whether CTLA4 could inhibit T cell function in the absence of CD28. TCR transgenic/recombinase activating gene 2-deficient/CD28-wild-type or CD28-deficient mice were generated and immunized with an antigen-expressing tumor. Primed T cells from both types of mice produced cytokines and proliferated in response to stimulator cells lacking B7 expression. However, whereas the response of CD28+/+ T cells was augmented by costimulation with B7-1, the response of the CD28-/- T cells was strongly inhibited. This inhibition was reversed by monoclonal antibody against B7-1 or CTLA4. Thus, CTLA4 can potently inhibit T cell activation in the absence of CD28, indicating that antagonism of a TCR-mediated signal is sufficient to explain the inhibitory effect of CTLA4.
Figures
Figure 1
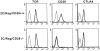
Flow cytometric analysis of T cells from mutant mice. 2C/Rag/CD28+/+ and CD28−/− mice were immunized by in vivo rejection of P1.HTR tumor cells. Splenic T cells were purified and restimulated for 2 d with mitomycin C–treated P815 cells to assess expression of TCR, CD28, and CTLA4. Flow cytometric analysis was performed after surface staining using the clonotypic TCR antibody 1B2 or the anti-CD28 mAb 37.51, or after intracellular staining with the anti-CTLA4 mAb 4F10. Similar results were obtained in three separate experiments.
Figure 2
Time course of proliferation of CD28+/+ or CD28−/− TCR Tg T cells in response to B7-1+ or B7-1− stimulator cells. CD8+ T cells purified by negative selection from primed CD28+/+or CD28−/− 2C/Rag2−/− mice were stimulated with mitomycin C–treated P815 or P815.B71 cells. Replicate cultures were pulsed daily with [3H]thymidine and harvested, and incorporated radioactivity was assessed. Similar results were obtained in at least two experiments.
Figure 3
Cytokine production by CD28+/+ or CD28−/− TCR Tg T cells in response to B7-1+ or B7-1− stimulator cells. CD8+ T cells purified as in Fig. 2 were stimulated with mitomycin C–treated P815 or P815.B71 cells. Supernatants were collected, and IL-2 and IFN-γ content were assessed. Similar results were obtained in at least three experiments.
Figure 4
Inhibition of cytokine production of CD28−/− T cells by B7-1 transfectants is prevented by anti–B7-1 or by anti-CTLA4 mAb. T cell stimulations were performed as in Fig. 3 without additions, or in the presence of anti–B7-1 mAb, anti-CTLA4 mAb, or the combination. IL-2 production was determined at 24 h. Similar results were obtained for IFN-γ production (data not shown), and in at least two separate experiments.
Similar articles
- Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA4) blockade accelerates the acute rejection of cardiac allografts in CD28-deficient mice: CTLA4 can function independently of CD28.
Lin H, Rathmell JC, Gray GS, Thompson CB, Leiden JM, Alegre ML. Lin H, et al. J Exp Med. 1998 Jul 6;188(1):199-204. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.1.199. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9653096 Free PMC article. - B7-CTLA4 interaction promotes cognate destruction of tumor cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vivo.
Bai XF, Liu J, May KF Jr, Guo Y, Zheng P, Liu Y. Bai XF, et al. Blood. 2002 Apr 15;99(8):2880-9. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.8.2880. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11929778 - B7-CD28 interaction is a late acting co-stimulatory signal for human T cell responses.
Zhang YQ, Joost van Neerven RJ, Van Gool SW, Coorevits L, de Boer M, Ceuppens JL. Zhang YQ, et al. Int Immunol. 1997 Aug;9(8):1095-102. doi: 10.1093/intimm/9.8.1095. Int Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9263006 - CD28/B7 costimulation: a review.
Greenfield EA, Nguyen KA, Kuchroo VK. Greenfield EA, et al. Crit Rev Immunol. 1998;18(5):389-418. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v18.i5.10. Crit Rev Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9784967 Review. - Costimulatory regulation of T cell function.
Chambers CA, Allison JP. Chambers CA, et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999 Apr;11(2):203-10. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80027-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10209159 Review.
Cited by
- Targeting the B7 family of co-stimulatory molecules: successes and challenges.
Podojil JR, Miller SD. Podojil JR, et al. BioDrugs. 2013 Feb;27(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s40259-012-0001-6. BioDrugs. 2013. PMID: 23329394 Free PMC article. Review. - Interaction of CTLA-4 (CD152) with CD80 or CD86 inhibits human T-cell activation.
Vandenborre K, Van Gool SW, Kasran A, Ceuppens JL, Boogaerts MA, Vandenberghe P. Vandenborre K, et al. Immunology. 1999 Nov;98(3):413-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00888.x. Immunology. 1999. PMID: 10583602 Free PMC article. - Antigen-specific blocking of CD4-specific immunological synapse formation using BPI and current therapies for autoimmune diseases.
Manikwar P, Kiptoo P, Badawi AH, Büyüktimkin B, Siahaan TJ. Manikwar P, et al. Med Res Rev. 2012 Jul;32(4):727-64. doi: 10.1002/med.20243. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Med Res Rev. 2012. PMID: 21433035 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic Heterogeneity, Therapeutic Hurdle Confronting Sorafenib and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Atwa SM, Odenthal M, El Tayebi HM. Atwa SM, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 27;13(17):4343. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174343. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503153 Free PMC article. Review. - T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: current knowledge and clinical significance.
Ye B, Liu X, Li X, Kong H, Tian L, Chen Y. Ye B, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2015 Mar 19;6(3):e1694. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.42. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25789969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:233–258. - PubMed
- Boise LH, Minn AJ, Noel PJ, June CH, Accavitti MA, Lindsten T, Thompson CB. CD28 stimulation can enhance T cell survival by inducing expression of Bcl-xL . Immunity. 1995;3:87–98. - PubMed
- Harding FA, McArthur JG, Gross JA, Raulet DH, Allison JP. CD28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature. 1992;356:607–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials