Two-component signal transduction as a target for microbial anti-infective therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Two-component signal transduction as a target for microbial anti-infective therapy
J F Barrett et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998 Jul.
No abstract available
Figures
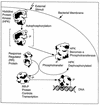
FIG. 1
Typical two-component signal transduction system.
FIG. 2
Simple example of some principles of networking in two-component signal transduction.
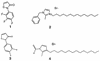
FIG. 3
Chemical structures of the antialginate two-component kinase inhibitors. More than 95% of algD promoter inhibition activity was observed for inhibitors 1 and 2 at 2 to 2.5 μg/ml. Compounds 1 and 3 also inhibit AlgR1, whereas compounds 2 and 4 do not, but compounds 2 and 4 do inhibit other kinases (66, 67).
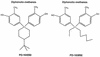
FIG. 4
Prototypical structures of diphenolic methanes with NRII inhibitory activity and weak activity against gram-positive bacteria (19).
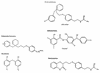
FIG. 5
Prototypical structures from the efforts of the R. W. Johnson Pharmaceutical Research Institute. These five series represent the reported inhibitors in a variety of in vitro, microbiological, and in vivo test systems (27, 47, 48, 52, 62, 79, 87, 88, 91).
Similar articles
- Bacterial signaling as an antimicrobial target.
Ellermann M, Sperandio V. Ellermann M, et al. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020 Oct;57:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32916624 Free PMC article. Review. - Two-component signal transduction as potential drug targets in pathogenic bacteria.
Gotoh Y, Eguchi Y, Watanabe T, Okamoto S, Doi A, Utsumi R. Gotoh Y, et al. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Apr;13(2):232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.008. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20138000 Review. - [Interactions between bacteria and antimicrobials during the postantibiotic effect phase].
Pastor A, Cantón E. Pastor A, et al. Rev Esp Quimioter. 1999 Dec;12(4):294-9. Rev Esp Quimioter. 1999. PMID: 10855007 Review. Spanish. No abstract available. - Who or what is the source of antibiotic resistance?
Bergogne-Bérézin E. Bergogne-Bérézin E. J Med Microbiol. 1997 Jun;46(6):461-4. J Med Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9379476 No abstract available. - New trends in antimicrobial development.
Setti EL, Micetich RG. Setti EL, et al. Curr Med Chem. 1998 Apr;5(2):101-13. Curr Med Chem. 1998. PMID: 9481036 Review.
Cited by
- Breaking Barriers: Exploiting Envelope Biogenesis and Stress Responses to Develop Novel Antimicrobial Strategies in Gram-Negative Bacteria.
Bisht R, Charlesworth PD, Sperandeo P, Polissi A. Bisht R, et al. Pathogens. 2024 Oct 11;13(10):889. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100889. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452760 Free PMC article. Review. - Thiazolidione derivatives targeting the histidine kinase YycG are effective against both planktonic and biofilm-associated Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Huang RZ, Zheng LK, Liu HY, Pan B, Hu J, Zhu T, Wang W, Jiang DB, Wu Y, Wu YC, Han SQ, Qu D. Huang RZ, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Mar;33(3):418-25. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.166. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22231397 Free PMC article. - Identification and characterization of potential therapeutic candidates in emerging human pathogen Mycobacterium abscessus: a novel hierarchical in silico approach.
Shanmugham B, Pan A. Shanmugham B, et al. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059126. Epub 2013 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527108 Free PMC article. - Adaptation to environmental stimuli within the host: two-component signal transduction systems of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Bretl DJ, Demetriadou C, Zahrt TC. Bretl DJ, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Dec;75(4):566-82. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05004-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22126994 Free PMC article. Review. - Teaching old drugs new tricks: Addressing resistance in Francisella.
Feldmann EA, Cavanagh J. Feldmann EA, et al. Virulence. 2015;6(5):414-6. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2015.1053689. Virulence. 2015. PMID: 26055396 Free PMC article.
References
- Allaoui A, Sansonetti P J, Parsot C. MxiD, an outer membrane protein necessary for the secretion of the Shigella flexneri Ipa invasins. Mol Microbiol. 1993;7:59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical