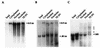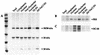The nucleolus is the site of Borna disease virus RNA transcription and replication - PubMed (original) (raw)
The nucleolus is the site of Borna disease virus RNA transcription and replication
J M Pyper et al. J Virol. 1998 Sep.
Abstract
Borna disease virus (BDV) is a neurotropic nonsegmented negative-strand RNA virus with limited homology to rhabdoviruses and paramyxoviruses. A distinguishing feature of BDV is that it replicates in the nucleus of infected cells. Strand-specific probes used for in situ hybridization of infected rat brain showed that there was differential localization of positive- and negative-strand RNAs within the nucleus of neurons. Within nuclei, sense-strand RNAs were preferentially localized within nucleolar regions while genomic-sense RNAs were found in both nucleolar and nonnucleolar regions. These results suggested a role for the nucleolus in BDV replication. Nucleoli isolated from persistently infected neuroblastoma cells contained both genomic and antigenomic BDV RNA species as well as an enrichment of the 39/38-kDa and gp18 BDV proteins. Since the nucleolus is the site of rRNA transcription, we examined BDV transcription in the presence of inhibitors of RNA polymerase I. Inhibition of RNA polymerase I did not affect levels of BDV transcription.
Figures
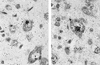
FIG. 1
In situ hybridization of BDV-infected rat brain 12 days postinfection. Sections were hybridized with single-stranded DNA probes that detect sense-strand RNA (a) and genomic RNA (b). (a) The nucleolus is densely labeled, while there are few grains in the remainder of the nucleus. (b) The nucleolus is spared, but grains are densely distributed at the periphery of the nucleolus and found more diffusely in the nucleoplasm of the neuron. The figure was prepared with Photoshop.
FIG. 2
Detection of RNA species in subcellular fractions of BDV-infected cells. RNA isolated from subcellular fractions was subjected to Northern blot analysis with probes specific for BDV genomic RNA (A), BDV sense RNA (B), and 18S rRNA (C). The locations of the full-length genomic and antigenomic RNAs are indicated in panels A and B. Panel B also shows the location of the abundant 0.85-kb mRNA. The location of the mature 18S rRNA species is indicated in panel C; asterisks show the precursor species detected in the nuclear and nucleolar fractions and in the TE wash of nucleoli. The figure was made from scanned fluorographs with Photoshop and Illustrator.
FIG. 3
Detection of protein species in subcellular fractions of BDV-infected cells. Equivalent levels of 35S-incorporated radioactivity were used for immunoprecipitations of subcellular fractions by using antisera specific for BDV proteins (A) and for markers of nucleolar proteins (B23) and nonnucleolar nuclear proteins (SC-35) (B and C). (A) Immunoprecipitation of BDV proteins. (B) Immunoprecipitation of B23. (C) Immunoprecipitation of SC-35. The figure was made from scanned fluorographs with Photoshop and Illustrator.
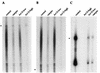
FIG. 4
RNase protection analysis of RNA species synthesized in the presence of RNA Pol inhibitors. 32P-labeled RNA was isolated from cells that were metabolically labeled during treatment with Pol inhibitors. The labeled RNA was hybridized with unlabeled antisense transcripts generated in vitro. Following digestion with RNase A, the protected fragments were resolved by gel electrophoresis. The specific full-length protected band is indicated by an asterisk in each panel. (A) BDV probe. (B) Actin probe. (C) 18S rRNA probe. For panel C, 1 μg of total labeled cellular RNA was used for hybridization. For panels A and B, 10 μg of total labeled cellular RNA was used for hybridization. The figure was made from scanned fluorographs with Photoshop and Illustrator. campto, camptothecin; Act D, actinomycin D.
Similar articles
- Borna disease virus replicates in astrocytes, Schwann cells and ependymal cells in persistently infected rats: location of viral genomic and messenger RNAs by in situ hybridization.
Carbone KM, Moench TR, Lipkin WI. Carbone KM, et al. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1991 May;50(3):205-14. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199105000-00003. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1991. PMID: 2022964 - Alpha/beta interferon promotes transcription and inhibits replication of borna disease virus in persistently infected cells.
Staeheli P, Sentandreu M, Pagenstecher A, Hausmann J. Staeheli P, et al. J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(17):8216-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.17.8216-8223.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11483767 Free PMC article. - Restricted expression of Borna disease virus glycoprotein in brains of experimentally infected Lewis rats.
Werner-Keiss N, Garten W, Richt JA, Porombka D, Algermissen D, Herzog S, Baumgärtner W, Herden C. Werner-Keiss N, et al. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2008 Dec;34(6):590-602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2008.00940.x. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18282160 - Molecular and cellular biology of Borna disease virus infection.
Tomonaga K, Kobayashi T, Ikuta K. Tomonaga K, et al. Microbes Infect. 2002 Apr;4(4):491-500. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(02)01564-2. Microbes Infect. 2002. PMID: 11932200 Review. - The atypical strategies used for gene expression of Borna disease virus, a nonsegmented, negative-strand RNA virus.
Schneemann A, Schneider PA, Lipkin WI. Schneemann A, et al. Uirusu. 1995 Dec;45(2):165-74. doi: 10.2222/jsv.45.165. Uirusu. 1995. PMID: 8820535 Review.
Cited by
- Isolation of Ontario aquatic bird bornavirus 1 and characterization of its replication in immortalized avian cell lines.
Pham PH, Leacy A, Deng L, Nagy É, Susta L. Pham PH, et al. Virol J. 2020 Jan 31;17(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-1286-6. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32005267 Free PMC article. - IFIT1: A dual sensor and effector molecule that detects non-2'-O methylated viral RNA and inhibits its translation.
Diamond MS. Diamond MS. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Oct;25(5):543-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 May 17. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 24909568 Free PMC article. Review. - Adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2) uncoating is a stepwise process and is linked to structural reorganization of the nucleolus.
Sutter SO, Lkharrazi A, Schraner EM, Michaelsen K, Meier AF, Marx J, Vogt B, Büning H, Fraefel C. Sutter SO, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jul 11;18(7):e1010187. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010187. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35816507 Free PMC article. - Nucleolar localization of non-structural protein 3b, a protein specifically encoded by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
Yuan X, Yao Z, Shan Y, Chen B, Yang Z, Wu J, Zhao Z, Chen J, Cong Y. Yuan X, et al. Virus Res. 2005 Dec;114(1-2):70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.06.001. Epub 2005 Jul 25. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 16046244 Free PMC article. - Ribozyme-mediated inhibition of HIV 1 suggests nucleolar trafficking of HIV-1 RNA.
Michienzi A, Cagnon L, Bahner I, Rossi JJ. Michienzi A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 1;97(16):8955-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.8955. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10922055 Free PMC article.
References
- Adachi Y, Copeland T D, Hatanaka M, Oroszlan S. Nucleolar targeting signal of rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I specifically binds to nucleolar shuttle protein B-23. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:13930–13934. - PubMed
- Biedler J L, Helson L, Spengler B A. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity, and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973;33:2643–2652. - PubMed
- Borer R A, Lehner C F, Eppenberger H M, Nigg E A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989;56:379–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources