Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene
K Becker et al. J Clin Microbiol. 1998 Sep.
Abstract
Two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays (PCR-EIAs) were developed for Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin gene screening as an alternative to the conventional biological assays, which depend on detectable amounts of toxins produced. One set of oligonucleotide primers and probes was designed to search for enterotoxin A to E genes (entA, entB, entC, entD, and entE), and the other one was designed to detect the staphylococcal exfoliative toxin genes (eta and etb) and the toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene (tst). Oligonucleotide primers were used as published previously, modified or newly developed to meet the requirements of both good size-distinguishable amplification bands of multiplex PCR and the temperature limit of the uracil DNA glycosylase system for carryover protection. Amplification products were visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis, and specificity was controlled with the aid of a DNA EIA system using oligonucleotide probes derived from the sequences of the S. aureus toxin genes. PCR procedures were performed by using template nucleic acids extracted from a panel of S. aureus reference strains and from a collection of 50 clinical strains. The PCR results were compared with those of immunological toxin production assays. This multiplex PCR-EIA system offers an alternative method for the rapid, sensitive, specific, and simultaneous detection of the clinically important exotoxin potency of isolated S. aureus strains for diagnostic purposes as well as research studies.
Figures
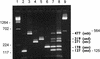
FIG. 1
Agarose gel electrophoresis patterns showing PCR-amplified products in multiplex PCR for the staphylococcal enterotoxin genes. Lanes 1, DNA molecular weight marker λ _Hin_dIII; 2, sea; 3, seb; 4, sec; 5, sed; 6, see; 7, multiplex PCR with all enterotoxin genes simultaneously (sea to see); 8, artificial arrangement of the amplification fragments of sea to see; 9, DNA molecular weight marker λ _Bst_E II. Sizes are marked in base pairs on the left and right.
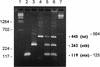
FIG. 2
Agarose gel electrophoresis patterns showing PCR-amplified products in multiplex PCR for the staphylococcal ET genes (eta and etb) and TSST-1 gene (tst). Lanes 1: DNA molecular weight marker λ _Hin_dIII; 2, eta; 3, etb; 4, tst; 5, multiplex PCR with both ET genes and the TSST-1 gene simultaneously; 8, artificial arrangement of the amplification fragments of eta, etb, and tst; 9, DNA molecular weight marker λ _Bst_E II. Sizes are marked in base pairs on the left and right.
Similar articles
- Multiplex PCR for detection of genes for Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1, and methicillin resistance.
Mehrotra M, Wang G, Johnson WM. Mehrotra M, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Mar;38(3):1032-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.3.1032-1035.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10698991 Free PMC article. - Detection of genes for enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus by the polymerase chain reaction.
Johnson WM, Tyler SD, Ewan EP, Ashton FE, Pollard DR, Rozee KR. Johnson WM, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):426-30. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.426-430.1991. J Clin Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 2037659 Free PMC article. - Survey of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene in non-Staphylococcus aureus species.
Becker K, Haverkämper G, von Eiff C, Roth R, Peters G. Becker K, et al. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2001 Jun;20(6):407-9. doi: 10.1007/pl00011281. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11476441 - Exfoliative toxins of Staphylococcus aureus.
Bukowski M, Wladyka B, Dubin G. Bukowski M, et al. Toxins (Basel). 2010 May;2(5):1148-65. doi: 10.3390/toxins2051148. Epub 2010 May 25. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069631 Free PMC article. Review. - Nonenteric toxins of Staphylococcus aureus.
Rogolsky M. Rogolsky M. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):320-60. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.320-360.1979. Microbiol Rev. 1979. PMID: 161608 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Correlations of Host and Bacterial Characteristics with Clinical Parameters and Survival in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia.
Wächter H, Yörük E, Becker K, Görlich D, Kahl BC. Wächter H, et al. J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 28;10(7):1371. doi: 10.3390/jcm10071371. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33800644 Free PMC article. - Characterization of Clinical MRSA Isolates from Northern Spain and Assessment of Their Susceptibility to Phage-Derived Antimicrobials.
Salas M, Wernecki M, Fernández L, Iglesias B, Gutiérrez D, Álvarez A, García L, Prieto E, García P, Rodríguez A. Salas M, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Jul 25;9(8):447. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9080447. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722499 Free PMC article. - Virulence genes and genotypic associations in nasal carriage, community-associated methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant USA400 Staphylococcus aureus isolates.
Shukla SK, Karow ME, Brady JM, Stemper ME, Kislow J, Moore N, Wroblewski K, Chyou PH, Warshauer DM, Reed KD, Lynfield R, Schwan WR. Shukla SK, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Oct;48(10):3582-92. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00657-10. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20668125 Free PMC article. - Toxin genes and other characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from milk of cows with mastitis.
Akineden O, Annemüller C, Hassan AA, Lämmler C, Wolter W, Zschöck M. Akineden O, et al. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001 Sep;8(5):959-64. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.8.5.959-964.2001. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11527811 Free PMC article. - Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains causing neonatal toxic shock syndrome-like exanthematous disease in neonatal and perinatal wards.
Kikuchi K, Takahashi N, Piao C, Totsuka K, Nishida H, Uchiyama T. Kikuchi K, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Jul;41(7):3001-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.7.3001-3006.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12843033 Free PMC article.
References
- Avena R M, Bergdoll M S. Purification and some physicochemical properties of enterotoxin C, Staphylococcus aureus strain 361. Biochemistry. 1967;6:1474–1480. - PubMed
- Bergdoll M S, Crass B A, Reiser R F, Robbins R N, Davis J P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981;i:1017–1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources