Mutations in Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI2) genes affecting transcription of SPI1 genes and resistance to antimicrobial agents - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mutations in Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI2) genes affecting transcription of SPI1 genes and resistance to antimicrobial agents
J Deiwick et al. J Bacteriol. 1998 Sep.
Abstract
The Salmonella typhimurium genome contains two pathogenicity islands (SPI) with genes encoding type III secretion systems for virulence proteins. SPI1 is required for the penetration of the epithelial layer of the intestine. SPI2 is important for the subsequent proliferation of bacteria in the spleens of infected hosts. Although most mutations in SPI2 lead to a strong reduction of virulence, they have different effects in vitro, with some mutants having significantly increased sensitivity to gentamicin and the antibacterial peptide polymyxin B. Previously we showed that certain mutations in SPI2 affect the ability of S. typhimurium to secrete SPI1 effector proteins and to invade cultured eukaryotic cells. In this study, we show that these SPI2 mutations affect the expression of the SPI1 invasion genes. Analysis of reporter fusions to various SPI1 genes reveals highly reduced expression of sipC, prgK, and hilA, the transcriptional activator of SPI1 genes. These observations indicate that the expression of one type III secretion system can be influenced dramatically by mutations in genes encoding a second type III secretion system in the same cell.
Figures
FIG. 1
SPI2. The positions and orientations of insertions of mTn_5_ insertions (open arrows) and the aphT gene cassette (solid arrow) in mutant strains used in this study are shown. The transcriptional orientation of SPI2 genes encoding the type III secretion system apparatus (ssa) and the two-component regulatory system (ssr) is indicated by arrows. cs, centisomes.
FIG. 2
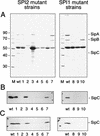
Protein secreted by S. typhimurium and detection of SipC. (A) Secreted protein was precipitated from 2 ml of culture supernatant, separated by SDS-PAGE, and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. Positions of the SPI1 effector proteins SipABC (right) and the molecular weight marker (in thousands on the left) are indicated. (B) As for panel A except that protein was transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes after electrophoretic separation. The presence of SipC was detected with a polyclonal antiserum raised against rSipC. (C) Detection of SipC in total cell fractions of S. typhimurium. Equal amounts of protein (about 20 μg) of cells from overnight cultures were separated on SDS–12% polyacrylamide gels and subsequently transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. SipC was detected after incubation with the rabbit antiserum against rSipC as described above. Lanes: M, marker; wt, wild-type S. typhimurium 1 to 7, SPI2 mutant strains P2D6, P11C3, P9B6, P11D10, P9B7, P8G12, and NP_ssaV_, respectively; 8 to 10, SPI1 mutant strains P4H2, P6E11, and P7B12, respectively.
FIG. 3
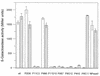
Effect of SPI2 mutations on expression of SPI1 genes. The expression of lacZ fusions to prgK (hatched bars) and sipC (open bars) was analyzed in various SPI1 and SPI2 backgrounds. Bacterial cultures were grown overnight under inducing conditions, and enzyme activity was determined as described in Materials and Methods. wt, wild type.
FIG. 4
Effect of SPI2 mutations on expression of hilA. The expression of a lacZ fusion to hilA was analyzed in various SPI1 and SPI2 backgrounds as indicated for Fig. 3. wt, wild type.
Similar articles
- The Small RNA PinT Contributes to PhoP-Mediated Regulation of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.
Kim K, Palmer AD, Vanderpool CK, Slauch JM. Kim K, et al. J Bacteriol. 2019 Sep 6;201(19):e00312-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00312-19. Print 2019 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31262841 Free PMC article. - Salmonella typhimurium leucine-rich repeat proteins are targeted to the SPI1 and SPI2 type III secretion systems.
Miao EA, Scherer CA, Tsolis RM, Kingsley RA, Adams LG, Bäumler AJ, Miller SI. Miao EA, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1999 Nov;34(4):850-64. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01651.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10564523 - The ATP-dependent lon protease of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium regulates invasion and expression of genes carried on Salmonella pathogenicity island 1.
Takaya A, Tomoyasu T, Tokumitsu A, Morioka M, Yamamoto T. Takaya A, et al. J Bacteriol. 2002 Jan;184(1):224-32. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.1.224-232.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11741864 Free PMC article. - Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.
Ellermeier JR, Slauch JM. Ellermeier JR, et al. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review. - Salmonella pathogenicity islands encoding type III secretion systems.
Hansen-Wester I, Hensel M. Hansen-Wester I, et al. Microbes Infect. 2001 Jun;3(7):549-59. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01411-3. Microbes Infect. 2001. PMID: 11418329 Review.
Cited by
- Characterization of Salmonella enterica derivatives harboring defined aroC and Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system (ssaV) mutations by immunization of healthy volunteers.
Hindle Z, Chatfield SN, Phillimore J, Bentley M, Johnson J, Cosgrove CA, Ghaem-Maghami M, Sexton A, Khan M, Brennan FR, Everest P, Wu T, Pickard D, Holden DW, Dougan G, Griffin GE, House D, Santangelo JD, Khan SA, Shea JE, Feldman RG, Lewis DJ. Hindle Z, et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Jul;70(7):3457-67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.7.3457-3467.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12065485 Free PMC article. - Salmonella typhimurium virulence genes are induced upon bacterial invasion into phagocytic and nonphagocytic cells.
Pfeifer CG, Marcus SL, Steele-Mortimer O, Knodler LA, Finlay BB. Pfeifer CG, et al. Infect Immun. 1999 Nov;67(11):5690-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.11.5690-5698.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10531217 Free PMC article. - Involvement of SPI-2-encoded SpiC in flagellum synthesis in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.
Uchiya K, Sugita A, Nikai T. Uchiya K, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2009 Aug 25;9:179. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-179. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19706157 Free PMC article. - Effect of the O-antigen length of lipopolysaccharide on the functions of Type III secretion systems in Salmonella enterica.
Hölzer SU, Schlumberger MC, Jäckel D, Hensel M. Hölzer SU, et al. Infect Immun. 2009 Dec;77(12):5458-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00871-09. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19797066 Free PMC article. - Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 mediates protection of intracellular Salmonella from reactive nitrogen intermediates.
Chakravortty D, Hansen-Wester I, Hensel M. Chakravortty D, et al. J Exp Med. 2002 May 6;195(9):1155-66. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011547. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 11994420 Free PMC article.
References
- Bajaj V, Hwang C, Lee C A. hilA is a novel ompR/toxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:715–727. - PubMed
- Bajaj V, Lucas R L, Hwang C, Lee C A. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol Microbiol. 1996;22:703–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous