Content and quality of 2000 controlled trials in schizophrenia over 50 years - PubMed (original) (raw)
Content and quality of 2000 controlled trials in schizophrenia over 50 years
B Thornley et al. BMJ. 1998.
Abstract
Objective: To provide a comprehensive survey of the content and quality of intervention studies relevant to the treatment of schizophrenia.
Design: Data were extracted from 2000 trials on the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's register.
Main outcome measures: Type and date of publication, country of origin, language, size of study, treatment setting, participant group, interventions, outcomes, and quality of study.
Results: Hospital based drug trials undertaken in the United States were dominant in the sample (54%). Generally, studies were short (54%<6 weeks), small (mean number of patients 65), and poorly reported (64% had a quality score of <=2 (maximum score 5)). Over 600 different interventions were studied in these trials, and 640 different rating scales were used to measure outcome.
Conclusions: Half a century of studies of limited quality, duration, and clinical utility leave much scope for well planned, conducted, and reported trials. The drug regulatory authorities should stipulate that the results of both explanatory and pragmatic trials are necessary before a compound is given a licence for everyday use.
Figures
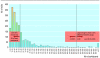
Figure
Size of trials (n=1941; 59 studies did not report study size)
Comment in
- Practical problems in recruiting patients with schizophrenia into randomised controlled trials.
Lester H, Wilson S. Lester H, et al. BMJ. 1999 Apr 17;318(7190):1075. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7190.1075. BMJ. 1999. PMID: 10205118 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Content and quality of 10,000 controlled trials in schizophrenia over 60 years.
Miyar J, Adams CE. Miyar J, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2013 Jan;39(1):226-9. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr140. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Schizophr Bull. 2013. PMID: 22290267 Free PMC article. - The future of Cochrane Neonatal.
Soll RF, Ovelman C, McGuire W. Soll RF, et al. Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834 - Modafinil for people with schizophrenia or related disorders.
Ortiz-Orendain J, Covarrubias-Castillo SA, Vazquez-Alvarez AO, Castiello-de Obeso S, Arias Quiñones GE, Seegers M, Colunga-Lozano LE. Ortiz-Orendain J, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 12;12(12):CD008661. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008661.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31828767 Free PMC article. - Control group bias in randomized atypical antipsychotic medication trials for schizophrenia.
Woods SW, Gueorguieva RV, Baker CB, Makuch RW. Woods SW, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005 Sep;62(9):961-70. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.9.961. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16143728 Review. - Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) for schizophrenia.
Schmidt L, Phelps E, Friedel J, Shokraneh F. Schmidt L, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Aug 10;8(8):CD012116. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012116.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31425623 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for the prevention of migraine in adults.
Banzi R, Cusi C, Randazzo C, Sterzi R, Tedesco D, Moja L. Banzi R, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 1;4(4):CD002919. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002919.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25829028 Free PMC article. Review. - Content and quality of 10,000 controlled trials in schizophrenia over 60 years.
Miyar J, Adams CE. Miyar J, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2013 Jan;39(1):226-9. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr140. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Schizophr Bull. 2013. PMID: 22290267 Free PMC article. - How can we regulate medicines better?
Garattini S, Bertele' V. Garattini S, et al. BMJ. 2007 Oct 20;335(7624):803-5. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39281.615706.94. BMJ. 2007. PMID: 17947785 Free PMC article. Review. - Fluphenazine (oral) versus placebo for schizophrenia.
Matar HE, Almerie MQ, Sampson S. Matar HE, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 17;7(7):CD006352. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006352.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23861067 Free PMC article. Updated. Review. - External validity of studies on aggressive behavior in patients with schizophrenia: systematic review.
Steinert T, Hamann K. Steinert T, et al. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2012;8:74-80. doi: 10.2174/1745017901208010074. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2012. PMID: 22934120 Free PMC article.
References
- Freeman H. The tranquilizing drugs. In: Bellek L, editor. Schizophrenia: a review of the syndrome. New York: Logos; 1958. pp. 473–500.
- Adams CE, Duggan L, Whalbeck K, White P. The Cochrane Schizophrenia Group. Schizophr Res (in press). - PubMed
- Fahey T, Hyde C, Milne R, Thorogood M. The type and quality of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in UK public health journals. J Public Health Med. 1995;17:469–474. - PubMed
- Lent V, Langenbach A. A retrospective quality analysis of 102 randomized trials in four leading urological journals from 1984-1989. Urol Res. 1996;24:119–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical