A family of stability determinants in pathogenic bacteria - PubMed (original) (raw)
A family of stability determinants in pathogenic bacteria
F Hayes. J Bacteriol. 1998 Dec.
Abstract
A novel segregational stability system was identified on plasmid R485, which originates from Morganella morganii. The system is composed of two overlapping genes, stbD and stbE, which potentially encode proteins of 83 and 93 amino acids, respectively. Homologs of the stbDE genes were identified on the enterotoxigenic plasmid P307 from Escherichia coli and on the chromosomes of Vibrio cholerae and Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius. The former two homologs also promote plasmid stability in E. coli. Furthermore, the stbDE genes share homology with components of the relBEF operon and with the dnaT gene of E. coli. The organization of the stbDE cassette is reminiscent of toxin-antitoxin stability cassettes.
Figures
FIG. 1
(A) Genetic organization of the stbDE genes and flanking regions from plasmid R485. Arrows indicate the length and orientation of open reading frames. Lines beneath the map indicate regions cloned in the stability probe vector, pALA136. The levels of retention conferred by these fragments after approximately 25 generations in the absence of selective pressure in a polA strain are shown. (B) Nucleotide sequence of the 1,154-bp _Sca_I-_Bgl_II fragment from plasmid R485. The inferred amino acid sequences of the four open reading frames are shown by the single-letter code.
FIG. 2
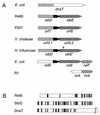
(A) Comparative organizations of the stbDE genes from plasmid R485 and homologous genes from plasmid P307 and from the chromosomes of V. cholerae, E. coli, and H. influenzae biogroup aegyptius. Homologous regions are denoted by similar shadings. The asterisk indicates the position of the −1 frameshift in the stbE gene of H. influenzae biogroup aegyptius. (B) Homology between the RelB, DnaT, and putative StbD proteins. The DnaT and StbD proteins are aligned from their N termini, whereas the RelB and StbD proteins are aligned from their C termini. No gaps were introduced into the alignments. Shaded lines represent amino acids which are identical between proteins.
FIG. 3
Homology in the StbD (A) and StbE (B) families of proteins. Residues which are identical in a majority of family members are shaded. Dashes indicate gaps introduced to optimize the alignments. Protein sequences were aligned with the PILEUP program (4) with subsequent manual modification. Note that for the StbE′ protein from H. influenzae biogroup aegyptius, a hypothetical +1 frameshift, indicated by an asterisk in the protein sequence, was introduced in the nucleotide sequence to maintain the integrity of the gene.
Similar articles
- The Escherichia coli relBE genes belong to a new toxin-antitoxin gene family.
Gotfredsen M, Gerdes K. Gotfredsen M, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1998 Aug;29(4):1065-76. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00993.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9767574 - Nucleotide sequence of the afimbrial-adhesin-encoding afa-3 gene cluster and its translocation via flanking IS1 insertion sequences.
Garcia MI, Labigne A, Le Bouguenec C. Garcia MI, et al. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(24):7601-13. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.24.7601-7613.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 8002584 Free PMC article. - Genomic subtraction for the identification of putative new virulence factors of an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain of O2 serogroup.
Schouler C, Koffmann F, Amory C, Leroy-Sétrin S, Moulin-Schouleur M. Schouler C, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2004 Sep;150(Pt 9):2973-2984. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27261-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 15347755 - Duplication of pilus gene complexes of Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius.
Read TD, Dowdell M, Satola SW, Farley MM. Read TD, et al. J Bacteriol. 1996 Nov;178(22):6564-70. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.22.6564-6570.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8932313 Free PMC article. - Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae El Tor lipase operon lipAB and a protease gene downstream of the hly region.
Ogierman MA, Fallarino A, Riess T, Williams SG, Attridge SR, Manning PA. Ogierman MA, et al. J Bacteriol. 1997 Nov;179(22):7072-80. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.22.7072-7080.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9371455 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Uncoupling of nucleotide hydrolysis and polymerization in the ParA protein superfamily disrupts DNA segregation dynamics.
Dobruk-Serkowska A, Caccamo M, Rodríguez-Castañeda F, Wu M, Bryce K, Ng I, Schumacher MA, Barillà D, Hayes F. Dobruk-Serkowska A, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 14;287(51):42545-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410324. Epub 2012 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23093445 Free PMC article. - Molecular characterization of a 21.4 kilobase antibiotic resistance plasmid from an α-hemolytic Escherichia coli O108:H- human clinical isolate.
Dawes FE, Bulach DM, Kuzevski A, Bettelheim KA, Venturini C, Djordjevic SP, Walker MJ. Dawes FE, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034718. Epub 2012 Apr 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22532831 Free PMC article. - Evaluating the Potential for Cross-Interactions of Antitoxins in Type II TA Systems.
Tu CH, Holt M, Ruan S, Bourne C. Tu CH, et al. Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jun 26;12(6):422. doi: 10.3390/toxins12060422. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32604745 Free PMC article. Review. - The toxin-antitoxin system of the streptococcal plasmid pSM19035.
Zielenkiewicz U, Ceglowski P. Zielenkiewicz U, et al. J Bacteriol. 2005 Sep;187(17):6094-105. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.17.6094-6105.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16109951 Free PMC article. - Pathometagenomics reveals susceptibility to intestinal infection by Morganella to be mediated by the blood group-related B4galnt2 gene in wild mice.
Vallier M, Suwandi A, Ehrhardt K, Belheouane M, Berry D, Čepić A, Galeev A, Johnsen JM, Grassl GA, Baines JF. Vallier M, et al. Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2164448. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2164448. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 36683151 Free PMC article.
References
- Genetics Computer Group. Program manual for the GCG package, version 8. Madison, Wis: Genetics Computer Group; 1994.
- Gerdes K, Bech F W, Jorgensen S T, Lobner-Olesen A, Rasmussen P B, Atlung T, Boe L, Karlstrom O, Molin S, von Meyenburg K. Mechanism of postsegregational killing by the hok gene product of the parB system of plasmid R1 and its homology with the relF gene product of the E. coli relB operon. EMBO J. 1986;5:2023–2029. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources