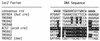Expression of the Bacillus subtilis acsA gene: position and sequence context affect cre-mediated carbon catabolite repression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Expression of the Bacillus subtilis acsA gene: position and sequence context affect cre-mediated carbon catabolite repression
J M Zalieckas et al. J Bacteriol. 1998 Dec.
Abstract
In Bacillus subtilis, carbon catabolite repression (CCR) of many genes is mediated at cis-acting carbon repression elements (cre) by the catabolite repressor protein CcpA. Mutations in transcription-repair coupling factor (mfd) partially relieve CCR at cre sites located downstream of transcriptional start sites by abolishing the Mfd-mediated displacement of RNA polymerase stalled at cre sites which act as transcriptional roadblocks. Although the acsA cre is centered 44.5 bp downstream of the acsA transcriptional start site, CCR of acsA expression is not affected by an mfd mutation. When the acsA cre is centered 161.5 bp downstream of the transcriptional start site for the unregulated tms promoter, CCR is partially relieved by the mfd mutation. Since CCR mediated at an acsA cre centered 44.5 bp downstream of the tms start site is not affected by the mfd mutation, the inability of Mfd to modulate CCR of acsA expression most likely results from the location of the acsA cre. Higher levels of CCR were found to occur at cre sites flanked by A+T-rich sequences than at cre sites bordered by G and C nucleotides. This suggests that nucleotides adjacent to the proposed 14-bp cre consensus sequence participate in the formation of the CcpA catabolite repression complex at cre sites. Examination of CCR of acsA expression revealed that this regulation required the Crh and seryl-phosphorylated form of the HPr proteins but not glucose kinase.
Figures
FIG. 1
cre DNA sequences. The HUT924 sequence corresponds to the hut cre and flanking DNA present in the HUT924 lacZ fusion (P_tms_ -hut cre-lacZ). The ACS7 sequence corresponds to the acsA cre with its flanking DNA present in ACS7 (acsA-lacZ) and is shown in reverse text. HUT940, HUT942, and HUT948 were derived from HUT924; the nucleotides shown in reverse text denote the positions within the hut cre that were changed to match the sequence of the acsA cre (ACS7). The TMS922 sequence corresponds to DNA located 44.5 bp downstream of the tms promoter (30). TMS951 and TMS952 were derived from TMS922; the nucleotides shown in reverse text denote nucleotides downstream of the tms promoter that were changed to match the sequence of the acsA cre.
Similar articles
- Phosphorylation of either crh or HPr mediates binding of CcpA to the bacillus subtilis xyn cre and catabolite repression of the xyn operon.
Galinier A, Deutscher J, Martin-Verstraete I. Galinier A, et al. J Mol Biol. 1999 Feb 19;286(2):307-14. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2492. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 9973552 - Transcription-repair coupling factor is involved in carbon catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis hut and gnt operons.
Zalieckas JM, Wray LV Jr, Ferson AE, Fisher SH. Zalieckas JM, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1998 Mar;27(5):1031-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00751.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9535092 - Antitermination by GlpP, catabolite repression via CcpA and inducer exclusion triggered by P-GlpK dephosphorylation control Bacillus subtilis glpFK expression.
Darbon E, Servant P, Poncet S, Deutscher J. Darbon E, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Feb;43(4):1039-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02800.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11929549 - Catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: a global regulatory mechanism for the gram-positive bacteria?
Hueck CJ, Hillen W. Hueck CJ, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Feb;15(3):395-401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02252.x. Mol Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7540244 Review. - CcpA-independent carbon catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis.
Dahl MK. Dahl MK. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 May;4(3):315-21. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11931564 Review.
Cited by
- CcpA-dependent regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamate dehydrogenase gene expression.
Belitsky BR, Kim HJ, Sonenshein AL. Belitsky BR, et al. J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(11):3392-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.11.3392-3398.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15150224 Free PMC article. - Roadblock repression of transcription by Bacillus subtilis CodY.
Belitsky BR, Sonenshein AL. Belitsky BR, et al. J Mol Biol. 2011 Aug 26;411(4):729-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.06.012. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21699902 Free PMC article. - CcpA mediates the catabolite repression of tst in Staphylococcus aureus.
Seidl K, Bischoff M, Berger-Bächi B. Seidl K, et al. Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5093-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00724-08. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18710862 Free PMC article. - Mfd Affects Global Transcription and the Physiology of Stressed Bacillus subtilis Cells.
Martin HA, Sundararajan A, Ermi TS, Heron R, Gonzales J, Lee K, Anguiano-Mendez D, Schilkey F, Pedraza-Reyes M, Robleto EA. Martin HA, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 28;12:625705. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.625705. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33603726 Free PMC article. - Staphylococcus aureus adapts to exploit collagen-derived proline during chronic infection.
Urso A, Monk IR, Cheng YT, Predella C, Wong Fok Lung T, Theiller EM, Boylan J, Perelman S, Baskota SU, Moustafa AM, Lohia G, Lewis IA, Howden BP, Stinear TP, Dorrello NV, Torres V, Prince AS. Urso A, et al. Nat Microbiol. 2024 Oct;9(10):2506-2521. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01769-9. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39134708 Free PMC article.
References
- Biaudet V, Samson F, Anagnostopoulos C, Ehrlich S D, Bessières P. Computerized genetic map of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. 1996;142:2669–2729. - PubMed
- Chambers S P, Prior S E, Barstow D A, Minton N P. The pMTL nic− cloning vectors. I. Improved pUC polylinker regions to facilitate the use of sonicated DNA for nucleotide sequencing. Gene. 1988;68:139–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources