Targeted mutagenesis by duplication insertion in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans: radiation sensitivities of catalase (katA) and superoxide dismutase (sodA) mutants - PubMed (original) (raw)
Targeted mutagenesis by duplication insertion in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans: radiation sensitivities of catalase (katA) and superoxide dismutase (sodA) mutants
L M Markillie et al. J Bacteriol. 1999 Jan.
Abstract
Deinococcus radiodurans R1 is extremely resistant to both oxidative stress and ionizing radiation. A simple and general targeted mutagenesis method was developed to generate catalase (katA) and superoxide dismutase (sodA) mutants. Both mutants were shown to be more sensitive to ionizing radiation than the wild type.
Figures
FIG. 1
(A) PFGE analysis of wild type and transformants. DNA agarose plugs were digested with _Not_I restriction enzyme, and digested fragments were resolved with a contour-clamped homogeneous electric field mapper. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide. Lane 1, yeast markers; lane 2, R1 (wild type); lane 3, KKW7001 (complete katA); lane 4, KKW7002 (katA with its promoter region deleted); lane 5, KKW7003 (partial internal coding region of katA). The 485-kb _Not_I fragment (which disappears) is indicated by the white arrowhead. The two new _Not_I fragments are indicated by black arrowheads. The molecular sizes in kilobases are shown on the left. (B) Southern blot from gel shown in panel A and hybridized with fluorecein-labelled probe generated from pKKW1 plasmid DNA. The hybridization signal was detected with a FluorImager SI as described previously (24).
FIG. 2
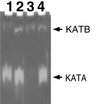
Analysis of catalase activity. Lane 1, R1 (wild type); lane 2, KKW7001 (complete katA); lane 3, KKW7003 (internal coding region of katA); lane 4, KKW7002 (katA with promoter region deleted). The two catalase bands shown are labelled KATA (catalase A) and KATB (catalase B).
FIG. 3
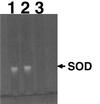
Analysis of superoxide dismutase activity. Lane 1, R1 (wild type); lane 2, KKW7003 (katA mutant); lane 3, KKW7004 (sodA mutant). SOD, superoxide dismutase.
FIG. 4
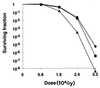
Cell survival after gamma ray exposure. Gamma radiation was from a 60Co source (GammaBeam 650). Circles, strain R1 (wild type); squares, strain KKW7003 (katA mutant); triangles, strain KKW7004 (sodA mutant). The exposure rate was 368 Gy per min.
Similar articles
- [Catalase and superoxide dismutase activity in isogenous bacterial strains with different degrees of radioresistance].
Vasil'eva EI, Goncharenko EN, Gudz' TI, Samoĭlenko II. Vasil'eva EI, et al. Nauchnye Doki Vyss Shkoly Biol Nauki. 1984;(9):30-3. Nauchnye Doki Vyss Shkoly Biol Nauki. 1984. PMID: 6388648 Russian. - A model for repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in the extreme radiophile Deinococcus radiodurans.
Minton KW, Daly MJ. Minton KW, et al. Bioessays. 1995 May;17(5):457-64. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170514. Bioessays. 1995. PMID: 7786292 Review. - [Superoxide dismutase--radiobiologic significance and possibilities (review)].
Gusev VA, Brusov OS, Panchenko LF. Gusev VA, et al. Vopr Med Khim. 1980 May-Jun;26(3):291-301. Vopr Med Khim. 1980. PMID: 7006203 Review. Russian.
Cited by
- A major role for nonenzymatic antioxidant processes in the radioresistance of Halobacterium salinarum.
Robinson CK, Webb K, Kaur A, Jaruga P, Dizdaroglu M, Baliga NS, Place A, Diruggiero J. Robinson CK, et al. J Bacteriol. 2011 Apr;193(7):1653-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.01310-10. Epub 2011 Jan 28. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21278285 Free PMC article. - Signal Recognition Particle RNA Contributes to Oxidative Stress Response in Deinococcus radiodurans by Modulating Catalase Localization.
Han R, Fang J, Jiang J, Gaidamakova EK, Tkavc R, Daly MJ, Contreras LM. Han R, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 18;11:613571. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.613571. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391243 Free PMC article. - Analysis of lineage-specific protein family variability in prokaryotes combined with evolutionary reconstructions.
Karamycheva S, Wolf YI, Persi E, Koonin EV, Makarova KS. Karamycheva S, et al. Biol Direct. 2022 Aug 30;17(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13062-022-00337-7. Biol Direct. 2022. PMID: 36042479 Free PMC article. - Across the tree of life, radiation resistance is governed by antioxidant Mn2+, gauged by paramagnetic resonance.
Sharma A, Gaidamakova EK, Grichenko O, Matrosova VY, Hoeke V, Klimenkova P, Conze IH, Volpe RP, Tkavc R, Gostinčar C, Gunde-Cimerman N, DiRuggiero J, Shuryak I, Ozarowski A, Hoffman BM, Daly MJ. Sharma A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 31;114(44):E9253-E9260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1713608114. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29042516 Free PMC article. - Global transcriptional and proteomic analysis of the Sig1 heat shock regulon of Deinococcus radiodurans.
Schmid AK, Howell HA, Battista JR, Peterson SN, Lidstrom ME. Schmid AK, et al. J Bacteriol. 2005 May;187(10):3339-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.10.3339-3351.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15866918 Free PMC article.
References
- Bauer A W, Kirby W M, Sherris J C, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Patrol. 1966;45:493–496. - PubMed
- Beauchamp C, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971;44:276–287. - PubMed
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
- Carbonneau M A, Melin A M, Perromat A, Clerc M. The action of free radicals on Deinococcus radiodurans carotenoids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989;275:244–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases