Getting Started — python-pptx 1.0.0 documentation (original) (raw)
A quick way to get started is by trying out some of the examples below to get a feel for how to use python-pptx.
The API documentation can help you with the fine details of calling signatures and behaviors.
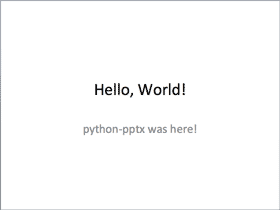
Hello World! example¶
from pptx import Presentation
prs = Presentation() title_slide_layout = prs.slide_layouts[0] slide = prs.slides.add_slide(title_slide_layout) title = slide.shapes.title subtitle = slide.placeholders[1]
title.text = "Hello, World!" subtitle.text = "python-pptx was here!"
prs.save('test.pptx')
Bullet slide example¶

from pptx import Presentation
prs = Presentation() bullet_slide_layout = prs.slide_layouts[1]
slide = prs.slides.add_slide(bullet_slide_layout) shapes = slide.shapes
title_shape = shapes.title body_shape = shapes.placeholders[1]
title_shape.text = 'Adding a Bullet Slide'
tf = body_shape.text_frame tf.text = 'Find the bullet slide layout'
p = tf.add_paragraph() p.text = 'Use _TextFrame.text for first bullet' p.level = 1
p = tf.add_paragraph() p.text = 'Use _TextFrame.add_paragraph() for subsequent bullets' p.level = 2
prs.save('test.pptx')
Not all shapes can contain text, but those that do always have at least one paragraph, even if that paragraph is empty and no text is visible within the shape. _BaseShape.has_text_frame can be used to determine whether a shape can contain text. (All shapes subclass _BaseShape.) When_BaseShape.has_text_frame is True,_BaseShape.text_frame.paragraphs[0] returns the first paragraph. The text of the first paragraph can be set using text_frame.paragraphs[0].text. As a shortcut, the writable properties _BaseShape.text and_TextFrame.text are provided to accomplish the same thing. Note that these last two calls delete all the shape’s paragraphs except the first one before setting the text it contains.
add_textbox() example¶

from pptx import Presentation from pptx.util import Inches, Pt
prs = Presentation() blank_slide_layout = prs.slide_layouts[6] slide = prs.slides.add_slide(blank_slide_layout)
left = top = width = height = Inches(1) txBox = slide.shapes.add_textbox(left, top, width, height) tf = txBox.text_frame
tf.text = "This is text inside a textbox"
p = tf.add_paragraph() p.text = "This is a second paragraph that's bold" p.font.bold = True
p = tf.add_paragraph() p.text = "This is a third paragraph that's big" p.font.size = Pt(40)
prs.save('test.pptx')
add_picture() example¶

from pptx import Presentation from pptx.util import Inches
img_path = 'monty-truth.png'
prs = Presentation() blank_slide_layout = prs.slide_layouts[6] slide = prs.slides.add_slide(blank_slide_layout)
left = top = Inches(1) pic = slide.shapes.add_picture(img_path, left, top)
left = Inches(5) height = Inches(5.5) pic = slide.shapes.add_picture(img_path, left, top, height=height)
prs.save('test.pptx')
add_shape() example¶
from pptx import Presentation from pptx.enum.shapes import MSO_SHAPE from pptx.util import Inches
prs = Presentation() title_only_slide_layout = prs.slide_layouts[5] slide = prs.slides.add_slide(title_only_slide_layout) shapes = slide.shapes
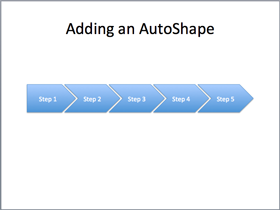
shapes.title.text = 'Adding an AutoShape'
left = Inches(0.93) # 0.93" centers this overall set of shapes top = Inches(3.0) width = Inches(1.75) height = Inches(1.0)
shape = shapes.add_shape(MSO_SHAPE.PENTAGON, left, top, width, height) shape.text = 'Step 1'
left = left + width - Inches(0.4) width = Inches(2.0) # chevrons need more width for visual balance
for n in range(2, 6): shape = shapes.add_shape(MSO_SHAPE.CHEVRON, left, top, width, height) shape.text = 'Step %d' % n left = left + width - Inches(0.4)
prs.save('test.pptx')
Constants representing each of the available auto shapes (like MSO_SHAPE.ROUNDED_RECT, MSO_SHAPE.CHEVRON, etc.) are listed on theautoshape-types page.
add_table() example¶
from pptx import Presentation from pptx.util import Inches
prs = Presentation() title_only_slide_layout = prs.slide_layouts[5] slide = prs.slides.add_slide(title_only_slide_layout) shapes = slide.shapes
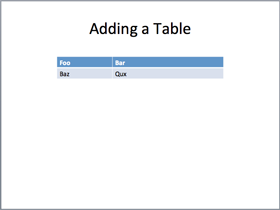
shapes.title.text = 'Adding a Table'
rows = cols = 2 left = top = Inches(2.0) width = Inches(6.0) height = Inches(0.8)
table = shapes.add_table(rows, cols, left, top, width, height).table
set column widths
table.columns[0].width = Inches(2.0) table.columns[1].width = Inches(4.0)
write column headings
table.cell(0, 0).text = 'Foo' table.cell(0, 1).text = 'Bar'
write body cells
table.cell(1, 0).text = 'Baz' table.cell(1, 1).text = 'Qux'
prs.save('test.pptx')