Our next generation release that is faster, more Pythonic and Dynamic as ever – PyTorch (original) (raw)
We are excited to announce the release of PyTorch® 2.0 which we highlighted during the PyTorch Conference on 12/2/22! PyTorch 2.0 offers the same eager-mode development and user experience, while fundamentally changing and supercharging how PyTorch operates at compiler level under the hood with faster performance and support for Dynamic Shapes and Distributed.
This next-generation release includes a Stable version of Accelerated Transformers (formerly called Better Transformers); Beta includes torch.compile as the main API for PyTorch 2.0, the scaled_dot_product_attention function as part of torch.nn.functional, the MPS backend, functorch APIs in the torch.func module; and other Beta/Prototype improvements across various inferences, performance and training optimization features on GPUs and CPUs. For a comprehensive introduction and technical overview of torch.compile, please visit the 2.0 Get Started page.
Along with 2.0, we are also releasing a series of beta updates to the PyTorch domain libraries, including those that are in-tree, and separate libraries including TorchAudio, TorchVision, and TorchText. An update for TorchX is also being released as it moves to community supported mode. More details can be found in this library blog.
This release is composed of over 4,541 commits and 428 contributors since 1.13.1. We want to sincerely thank our dedicated community for your contributions. As always, we encourage you to try these out and report any issues as we improve 2.0 and the overall 2-series this year.
Summary:
- torch.compile is the main API for PyTorch 2.0, which wraps your model and returns a compiled model. It is a fully additive (and optional) feature and hence 2.0 is 100% backward compatible by definition.
- As an underpinning technology of torch.compile, TorchInductor with Nvidia and AMD GPUs will rely on OpenAI Triton deep learning compiler to generate performant code and hide low level hardware details. OpenAI Triton-generated kernels achieve performance that’s on par with hand-written kernels and specialized cuda libraries such as cublas.
- Accelerated Transformers introduce high-performance support for training and inference using a custom kernel architecture for scaled dot product attention (SPDA). The API is integrated with torch.compile() and model developers may also use the scaled dot product attention kernels directly by calling the new scaled_dot_product_attention() operator.
- Metal Performance Shaders (MPS) backend provides GPU accelerated PyTorch training on Mac platforms with added support for Top 60 most used ops, bringing coverage to over 300 operators.
- Amazon AWS optimizes the PyTorch CPU inference on AWS Graviton3 based C7g instances. PyTorch 2.0 improves inference performance on Graviton compared to the previous releases, including improvements for Resnet50 and Bert.
- New prototype features and technologies across TensorParallel, DTensor, 2D parallel, TorchDynamo, AOTAutograd, PrimTorch and TorchInductor.
*To see a full list of public 2.0, 1.13 and 1.12 feature submissions click here.
Stable Features
[Stable] Accelerated PyTorch 2 Transformers
The PyTorch 2.0 release includes a new high-performance implementation of the PyTorch Transformer API. In releasing Accelerated PT2 Transformers, our goal is to make training and deployment of state-of-the-art Transformer models affordable across the industry. This release introduces high-performance support for training and inference using a custom kernel architecture for scaled dot product attention (SPDA), extending the inference “fastpath” architecture, previously known as “Better Transformer.”
Similar to the “fastpath” architecture, custom kernels are fully integrated into the PyTorch Transformer API – thus, using the native Transformer and MultiHeadAttention API will enable users to:
- transparently see significant speed improvements;
- support many more use cases including models using Cross-Attention, Transformer Decoders, and for training models; and
- continue to use fastpath inference for fixed and variable sequence length Transformer Encoder and Self Attention use cases.
To take full advantage of different hardware models and Transformer use cases, multiple SDPA custom kernels are supported (see below), with custom kernel selection logic that will pick the highest-performance kernel for a given model and hardware type. In addition to the existing Transformer API, model developers may also use the scaled dot product attention kernels directly by calling the new scaled_dot_product_attention() operator. Accelerated PyTorch 2 Transformers are integrated with torch.compile() . To use your model while benefiting from the additional acceleration of PT2-compilation (for inference or training), pre-process the model with model = torch.compile(model).
We have achieved major speedups for training transformer models and in particular large language models with Accelerated PyTorch 2 Transformers using a combination of custom kernels and torch.compile().
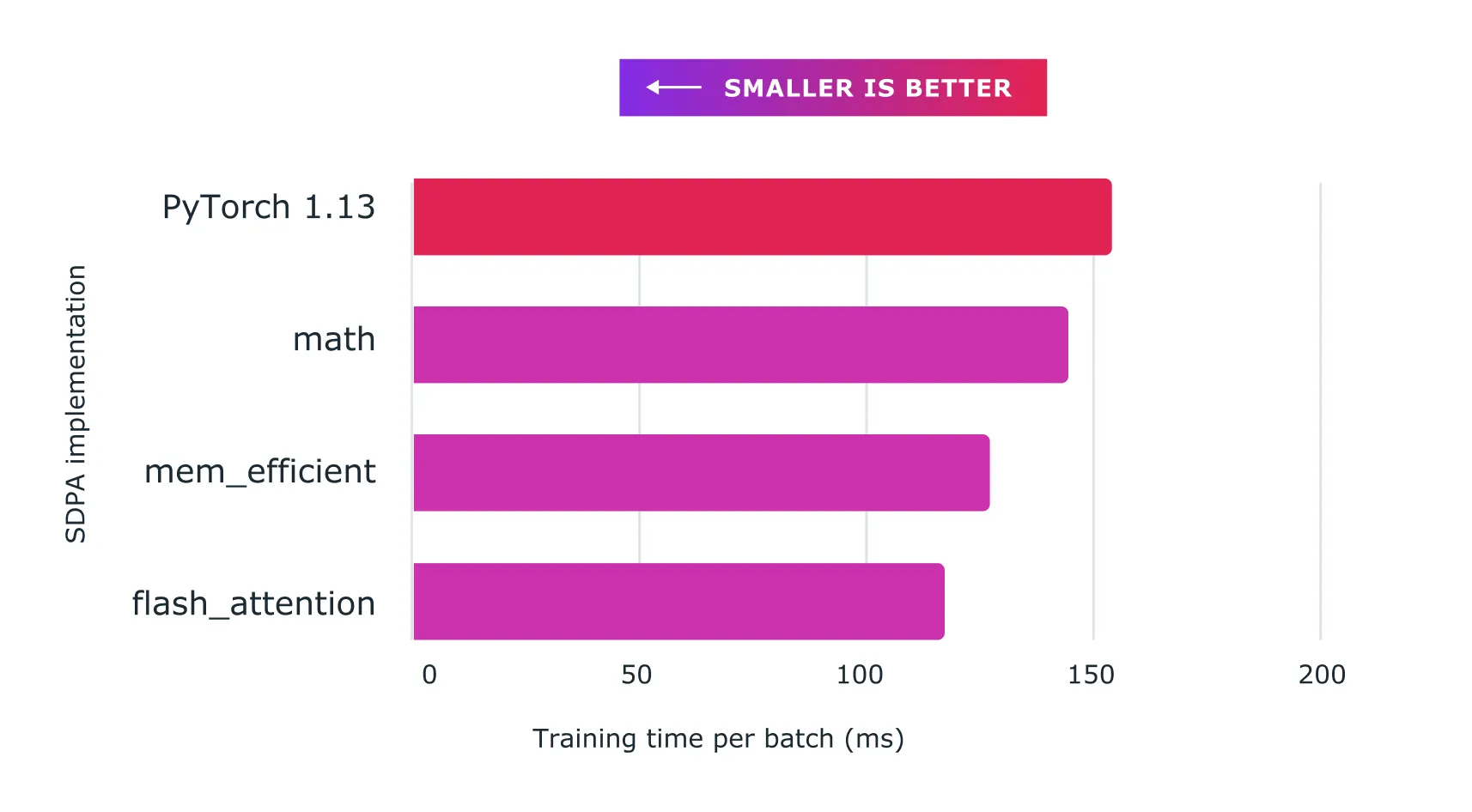 Figure: Using scaled dot product attention with custom kernels and torch.compile delivers significant speedups for training large language models, such as for nanoGPT shown here.
Figure: Using scaled dot product attention with custom kernels and torch.compile delivers significant speedups for training large language models, such as for nanoGPT shown here.
Beta Features
[Beta] torch.compile
torch.compile is the main API for PyTorch 2.0, which wraps your model and returns a compiled model. It is a fully additive (and optional) feature and hence 2.0 is 100% backward compatible by definition.
Underpinning torch.compile are new technologies – TorchDynamo, AOTAutograd, PrimTorch and TorchInductor:
- TorchDynamo captures PyTorch programs safely using Python Frame Evaluation Hooks and is a significant innovation that was a result of 5 years of our R&D into safe graph capture.
- AOTAutograd overloads PyTorch’s autograd engine as a tracing autodiff for generating ahead-of-time backward traces.
- PrimTorch canonicalizes ~2000+ PyTorch operators down to a closed set of ~250 primitive operators that developers can target to build a complete PyTorch backend. This substantially lowers the barrier of writing a PyTorch feature or backend.
- TorchInductor is a deep learning compiler that generates fast code for multiple accelerators and backends. For NVIDIA and AMD GPUs, it uses OpenAI Triton as a key building block. For intel CPUs, we generate C++ code using multithreading, vectorized instructions and offloading appropriate operations to mkldnn when possible.
With all the new technologies, torch.compile is able to work 93% of time across 165 open-source models and runs 20% faster on average at float32 precision and 36% faster on average at AMP precision.
For more information, please refer to https://pytorch.org/get-started/pytorch-2.0/ and for TorchInductor CPU with Intel here.
[Beta] PyTorch MPS Backend
MPS backend provides GPU-accelerated PyTorch training on Mac platforms. This release brings improved correctness, stability, and operator coverage.
MPS backend now includes support for the Top 60 most used ops, along with the most frequently requested operations by the community, bringing coverage to over 300 operators. The major focus of the release was to enable full OpInfo-based forward and gradient mode testing to address silent correctness issues. These changes have resulted in wider adoption of MPS backend by 3rd party networks such as Stable Diffusion, YoloV5, WhisperAI, along with increased coverage for Torchbench networks and Basic tutorials. We encourage developers to update to the latest macOS release to see the best performance and stability on the MPS backend.
Links
- MPS Backend
- Developer information
- Accelerated PyTorch training on Mac
- Metal, Metal Performance Shaders & Metal Performance Shaders Graph
[Beta] Scaled dot product attention 2.0
We are thrilled to announce the release of PyTorch 2.0, which introduces a powerful scaled dot product attention function as part of torch.nn.functional. This function includes multiple implementations that can be seamlessly applied depending on the input and hardware in use.
In previous versions of PyTorch, you had to rely on third-party implementations and install separate packages to take advantage of memory-optimized algorithms like FlashAttention. With PyTorch 2.0, all these implementations are readily available by default.
These implementations include FlashAttention from HazyResearch, Memory-Efficient Attention from the xFormers project, and a native C++ implementation that is ideal for non-CUDA devices or when high-precision is required.
PyTorch 2.0 will automatically select the optimal implementation for your use case, but you can also toggle them individually for finer-grained control. Additionally, the scaled dot product attention function can be used to build common transformer architecture components.
Learn more with the documentation and this tutorial.
[Beta] functorch -> torch.func
Inspired by Google JAX, functorch is a library that offers composable vmap (vectorization) and autodiff transforms. It enables advanced autodiff use cases that would otherwise be tricky to express in PyTorch. Examples include:
- model ensembling
- efficiently computing jacobians and hessians
- computing per-sample-gradients (or other per-sample quantities)
We’re excited to announce that, as the final step of upstreaming and integrating functorch into PyTorch, the functorch APIs are now available in the torch.func module. Our function transform APIs are identical to before, but we have changed how the interaction with NN modules work. Please see the docs and the migration guide for more details.
Furthermore, we have added support for torch.autograd.Function: one is now able to apply function transformations (e.g. vmap, grad, jvp) over torch.autograd.Function.
[Beta] Dispatchable Collectives
Dispatchable collectives is an improvement to the existing init_process_group() API which changes backend to an optional argument. For users, the main advantage of this feature is that it will allow them to write code that can run on both GPU and CPU machines without having to change the backend specification. The dispatchability feature will also make it easier for users to support both GPU and CPU collectives, as they will no longer need to specify the backend manually (e.g. “NCCL” or “GLOO”). Existing backend specifications by users will be honored and will not require change.
Usage example:
import torch.distributed.dist
…
# old
dist.init_process_group(backend=”nccl”, ...)
dist.all_reduce(...) # with CUDA tensors works
dist.all_reduce(...) # with CPU tensors does not work
# new
dist.init_process_group(...) # backend is optional
dist.all_reduce(...) # with CUDA tensors works
dist.all_reduce(...) # with CPU tensors works
Learn more here.
[Beta] torch.set_default_device and torch.device as context manager
torch.set_default_device allows users to change the default device that factory functions in PyTorch allocate on. For example, if you torch.set_default_device(‘cuda’), a call to torch.empty(2) will allocate on CUDA (rather than on CPU). You can also use torch.device as a context manager to change the default device on a local basis. This resolves a long standing feature request from PyTorch’s initial release for a way to do this.
Learn more here.
[Beta] “X86” as the new default quantization backend for x86 CPU
The new X86 quantization backend, which utilizes FBGEMM and oneDNN kernel libraries, replaces FBGEMM as the default quantization backend for x86 CPU platforms and offers improved int8 inference performance compared to the original FBGEMM backend, leveraging the strengths of both libraries, with 1.3X – 2X inference performance speedup measured on 40+ deep learning models. The new backend is functionally compatible with the original FBGEMM backend.
Table: Geomean Speedup of X86 Quantization Backend vs. FBGEMM Backend
| 1 core/instance | 2 cores/instance | 4 cores/instance | 1 socket (32 cores)/instance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8358 CPU @ 2.60GHz | 1.76X | 1.80X | 2.04X | 1.34X |
By default, users on x86 platforms will utilize the x86 quantization backend and their PyTorch programs will remain unchanged when using the default backend. Alternatively, users have the option to specify “X86” as the quantization backend explicitly. Example code is shown below:
import torch
from torch.ao.quantization import get_default_qconfig_mappingfrom torch.quantization.quantize_fx
import prepare_fx, convert_fx
# get default configuration
qconfig_mapping = get_default_qconfig_mapping()
# or explicitly specify the backend
# qengine = 'x86'
# torch.backends.quantized.engine = qengine
# qconfig_mapping = get_default_qconfig_mapping(qengine)
# construct fp32 model
model_fp32 = ...
# prepare
prepared_model = prepare_fx(model_fp32, qconfig_mapping, example_inputs=x)
# calibrate
...
# convert
quantized_model = convert_fx(prepared_model)
Find more information: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/83888 and https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/articles/technical/accelerate-pytorch-int8-inf-with-new-x86-backend.html.
[Beta] GNN inference and training optimization on CPU
PyTorch 2.0 includes several critical optimizations to improve GNN inference and training performance on CPU. Before 2.0, GNN models of PyG suffers from low efficiency on CPU due to lack of performance tuning for several critical kernels (scatter/gather, etc) and the lack of GNN-related sparse matrix multiplication ops. To be specific, optimizations include:
- scatter_reduce: performance hotspot in Message Passing when the edge index is stored in Coordinate format (COO).
- gather: backward of scatter_reduce, specially tuned for the GNN compute when the index is an expanded tensor.
- torch.sparse.mm with reduce flag: performance hotspot in Message Passing when the edge index is stored in Compressed Sparse Row (CSR). Supported reduce flag of: sum, mean, amax, amin.
On PyG benchmarks/examples, OGB benchmarks, a 1.12x – 4.07x performance speedup is measured (1.13.1 compared with 2.0) for single node inference and training.
| Model-Dataset | Option | Speedup Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| GCN-Reddit (inference) | 512-2-64-dense | 1.22x |
| 1024-3-128-dense | 1.25x | |
| 512-2-64-sparse | 1.31x | |
| 1024-3-128-sparse | 1.68x | |
| 512-2-64-dense | 1.22x | |
| GraphSage-ogbn-products (inference) | 1024-3-128-dense | 1.15x |
| 512-2-64-sparse | 1.20x | |
| 1024-3-128-sparse | 1.33x | |
| full-batch-sparse | 4.07x | |
| GCN-PROTEINS (training) | 3-32 | 1.67x |
| GCN-REDDIT-BINARY (training) | 3-32 | 1.67x |
| GCN-Reddit (training) | 512-2-64-dense | 1.20x |
| 1024-3-128-dense | 1.12x |
Learn more: PyG CPU Performance Optimization.
[Beta] Accelerating inference on CPU with PyTorch by leveraging oneDNN Graph
oneDNN Graph API extends oneDNN with a flexible graph API to maximize the optimization opportunity for generating efficient code on AI hardware.
- It automatically identifies the graph partitions to be accelerated via fusion.
- The fusion patterns focus on fusing compute-intensive operations such as convolution, matmul and their neighbor operations for both inference and training use cases.
- Although work is ongoing to integrate oneDNN Graph with TorchDynamo as well, its integration with the PyTorch JIT Fuser attained beta status in PyTorch 2.0 for Float32 & BFloat16 inference (on machines that support AVX512_BF16 ISA).
From a developer’s/researcher’s perspective, the usage is quite simple & intuitive, with the only change in code being an API invocation:
- Leverage oneDNN Graph, with JIT-tracing, a model is profiled with an example input.
- The context manager with torch.jit.fuser(“fuser3”): can also be used instead of invoking torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True).
- For accelerating BFloat16 inference, we rely on eager-mode AMP (Automatic Mixed Precision) support in PyTorch & disable JIT mode’s AMP, as both of them are currently divergent:
# Assuming we have a model of the name 'model'
example_input = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
# enable oneDNN Graph
torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True)
# Disable AMP for JIT
torch._C._jit_set_autocast_mode(False)
with torch.no_grad(), torch.cpu.amp.autocast():
model = torch.jit.trace(model, (example_input))
model = torch.jit.freeze(model)
# 2 warm-ups (2 for tracing/scripting with an example, 3 without an example)
model(example_input)
model(example_input)
# speedup would be observed in subsequent runs.
model(example_input)
Learn more here.
Prototype Features
Distributed API
[Prototype] DTensor
PyTorch DistributedTensor (DTensor) is a prototyping effort with distributed tensor primitives to allow easier distributed computation authoring in the SPMD (Single Program Multiple Devices) paradigm. The primitives are simple but powerful when used to express tensor distributions with both sharded and replicated parallelism strategies. PyTorch DTensor empowered PyTorch Tensor Parallelism along with other advanced parallelism explorations. In addition, it also offers a uniform way to save/load state_dict for distributed checkpointing purposes, even when there’re complex tensor distribution strategies such as combining tensor parallelism with parameter sharding in FSDP. More details can be found in this RFC and the DTensor examples notebook.
[Prototype] TensorParallel
We now support DTensor based Tensor Parallel which users can distribute their model parameters across different GPU devices. We also support Pairwise Parallel which shards two concatenated linear layers in a col-wise and row-wise style separately so that only one collective(all-reduce/reduce-scatter) is needed in the end.
[Prototype] 2D Parallel
We implemented the integration of the aforementioned TP with FullyShardedDataParallel(FSDP) as 2D parallel to further scale large model training. More details can be found in this slide.
[Prototype] torch.compile(dynamic=True)
Experimental support for PT2 compilation with dynamic shapes is available in this release. Inference compilation with inductor for simple models is supported, but there are a lot of limitations:
- Training available in a future release (This is partially fixed in nightlies!)
- Minifier available in a future release.
- It is easy to end up in a situation where the dimension you wanted to be dynamic gets specialized anyway. Some of these issues are fixed in nightlies, others are not.
- We do not appropriately propagate Inductor guards to the top-level, this is tracked at #96296.
- Data-dependent operations like nonzero still require a graph break.
- Dynamic does not work with non-standard modes like reduce-overhead or max-autotune.
- There are many bugs in Inductor compilation. To track known bugs, check the dynamic shapes label on the PyTorch issue tracker.
For the latest and greatest news about dynamic shapes support on master, check out our status reports.
Highlights/Performance Improvements
Deprecation of Cuda 11.6 and Python 3.7 support for PyTorch 2.0
If you are still using or depending on CUDA 11.6 or Python 3.7 builds, we strongly recommend moving to at least CUDA 11.7 and Python 3.8, as it would be the minimum versions required for PyTorch 2.0. For more detail, please refer to the Release Compatibility Matrix for PyTorch releases.
Python 3.11 support on Anaconda Platform
Due to lack of Python 3.11 support for packages that PyTorch depends on, including NumPy, SciPy, SymPy, Pillow and others on the Anaconda platform. We will not be releasing Conda binaries compiled with Python 3.11 for PyTorch Release 2.0. The Pip packages with Python 3.11 support will be released, hence if you intend to use PyTorch 2.0 with Python 3.11 please use our Pip packages. Please note: Conda packages with Python 3.11 support will be made available on our nightly channel. Also we are planning on releasing Conda Python 3.11 binaries as part of future release once Anaconda provides these key dependencies. More information and instructions on how to download the Pip packages can be found here.
Optimized PyTorch Inference with AWS Graviton processors
The optimizations focused on three key areas: GEMM kernels, bfloat16 support, primitive caching and the memory allocator. For aarch64 platforms, PyTorch supports Arm Compute Library (ACL) GEMM kernels via Mkldnn(OneDNN) backend. The ACL library provides Neon/SVE GEMM kernels for fp32 and bfloat16 formats. The bfloat16 support on c7g allows efficient deployment of bfloat16 trained, AMP (Automatic Mixed Precision) trained, or even the standard fp32 trained models. The standard fp32 models leverage bfloat16 kernels via OneDNN fast math mode, without any model quantization. Next we implemented primitive caching for conv, matmul and inner product operators. More information on the updated PyTorch user guide with the upcoming 2.0 release improvements and TorchBench benchmark details can be found here.