Hybrid Queries - Qdrant (original) (raw)
Hybrid and Multi-Stage Queries
Available as of v1.10.0
With the introduction of many named vectors per point, there are use-cases when the best search is obtained by combining multiple queries, or by performing the search in more than one stage.
Qdrant has a flexible and universal interface to make this possible, called Query API (API reference).
The main component for making the combinations of queries possible is the prefetch parameter, which enables making sub-requests.
Specifically, whenever a query has at least one prefetch, Qdrant will:
- Perform the prefetch query (or queries),
- Apply the main query over the results of its prefetch(es).
Additionally, prefetches can have prefetches themselves, so you can have nested prefetches.
Hybrid Search
One of the most common problems when you have different representations of the same data is to combine the queried points for each representation into a single result.
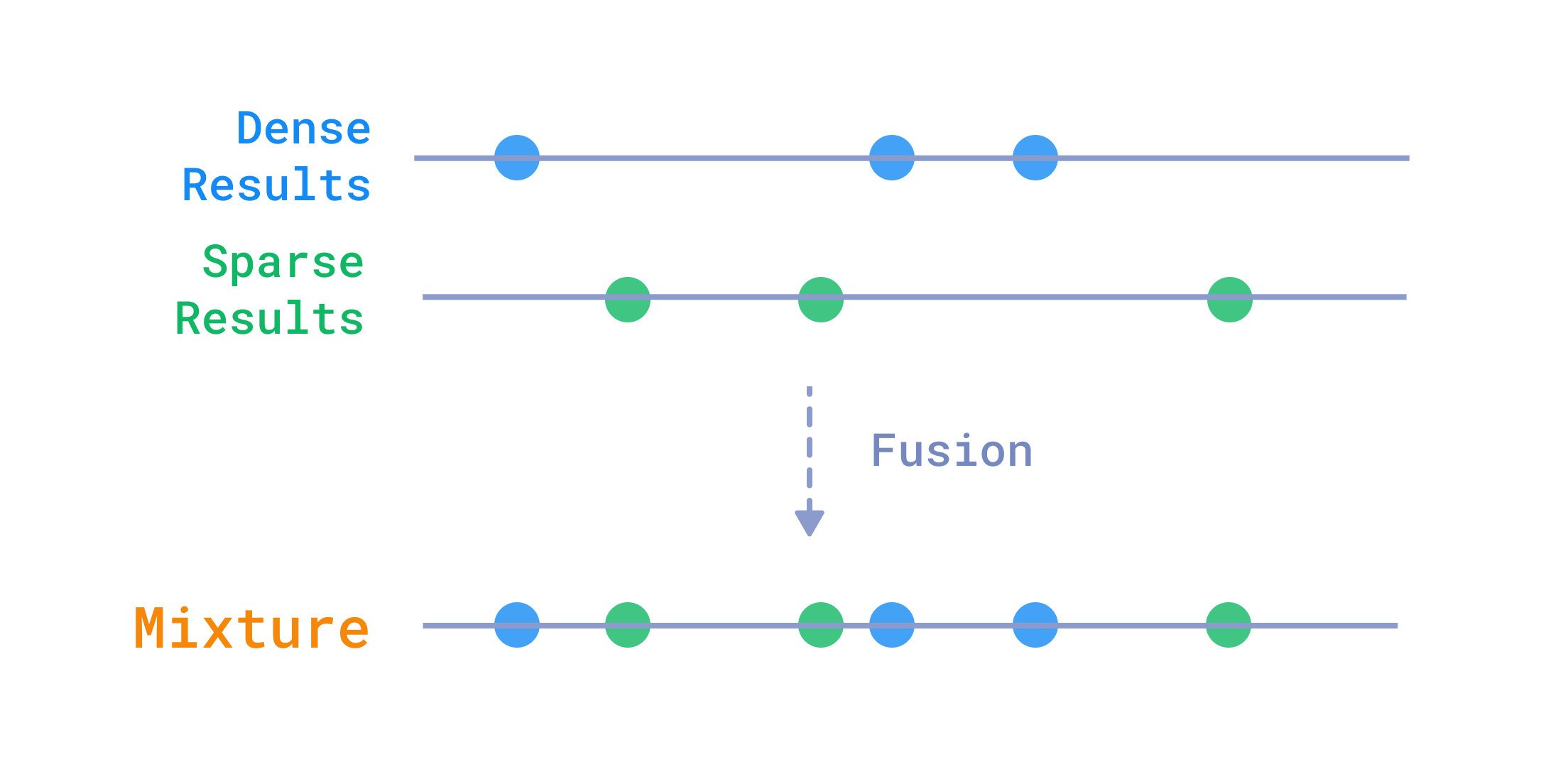
Fusing results from multiple queries
For example, in text search, it is often useful to combine dense and sparse vectors get the best of semantics, plus the best of matching specific words.
Qdrant currently has two ways of combining the results from different queries:
rrf-Reciprocal Rank Fusion
Considers the positions of results within each query, and boosts the ones that appear closer to the top in multiple of them.dbsf-Distribution-Based Score Fusion(available as of v1.11.0)
Normalizes the scores of the points in each query, using the mean +/- the 3rd standard deviation as limits, and then sums the scores of the same point across different queries.
Here is an example of Reciprocal Rank Fusion for a query containing two prefetches against different named vectors configured to respectively hold sparse and dense vectors.
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": [
{
"query": {
"indices": [1, 42], // <┐
"values": [0.22, 0.8] // <┴─sparse vector
},
"using": "sparse",
"limit": 20
},
{
"query": [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- dense vector
"using": "dense",
"limit": 20
}
],
"query": { "fusion": "rrf" }, // <--- reciprocal rank fusion
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=[
models.Prefetch(
query=models.SparseVector(indices=[1, 42], values=[0.22, 0.8]),
using="sparse",
limit=20,
),
models.Prefetch(
query=[0.01, 0.45, 0.67], # <-- dense vector
using="dense",
limit=20,
),
],
query=models.FusionQuery(fusion=models.Fusion.RRF),
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: [
{
query: {
values: [0.22, 0.8],
indices: [1, 42],
},
using: 'sparse',
limit: 20,
},
{
query: [0.01, 0.45, 0.67],
using: 'dense',
limit: 20,
},
],
query: {
fusion: 'rrf',
},
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{Fusion, PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest([(1, 0.22), (42, 0.8)].as_slice()))
.using("sparse")
.limit(20u64)
)
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67]))
.using("dense")
.limit(20u64)
)
.query(Query::new_fusion(Fusion::Rrf))
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.fusion;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Fusion;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client = new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(List.of(0.22f, 0.8f), List.of(1, 42)))
.setUsing("sparse")
.setLimit(20)
.build())
.addPrefetch(PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(List.of(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f)))
.setUsing("dense")
.setLimit(20)
.build())
.setQuery(fusion(Fusion.RRF))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List < PrefetchQuery > {
new() {
Query = new(float, uint)[] {
(0.22f, 1), (0.8f, 42),
},
Using = "sparse",
Limit = 20
},
new() {
Query = new float[] {
0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f
},
Using = "dense",
Limit = 20
}
},
query: Fusion.Rrf
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQuerySparse([]uint32{1, 42}, []float32{0.22, 0.8}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("sparse"),
},
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.45, 0.67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("dense"),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryFusion(qdrant.Fusion_RRF),
})
Multi-stage queries
In many cases, the usage of a larger vector representation gives more accurate search results, but it is also more expensive to compute.
Splitting the search into two stages is a known technique:
- First, use a smaller and cheaper representation to get a large list of candidates.
- Then, re-score the candidates using the larger and more accurate representation.
There are a few ways to build search architectures around this idea:
- The quantized vectors as a first stage, and the full-precision vectors as a second stage.
- Leverage Matryoshka Representation Learning (MRL) to generate candidate vectors with a shorter vector, and then refine them with a longer one.
- Use regular dense vectors to pre-fetch the candidates, and then re-score them with a multi-vector model like ColBERT.
To get the best of all worlds, Qdrant has a convenient interface to perform the queries in stages, such that the coarse results are fetched first, and then they are refined later with larger vectors.
Re-scoring examples
Fetch 1000 results using a shorter MRL byte vector, then re-score them using the full vector and get the top 10.
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
"using": "mrl_byte"
"limit": 1000
},
"query": [0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- full vector
"using": "full",
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[1, 23, 45, 67], # <------------- small byte vector
using="mrl_byte",
limit=1000,
),
query=[0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67], # <-- full vector
using="full",
limit=10,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: {
query: [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
using: 'mrl_byte',
limit: 1000,
},
query: [0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67], // <-- full vector,
using: 'full',
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![1.0, 23.0, 45.0, 67.0]))
.using("mlr_byte")
.limit(1000u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67]))
.using("full")
.limit(10u64)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(1, 23, 45, 67)) // <------------- small byte vector
.setLimit(1000)
.setUsing("mrl_byte")
.build())
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.299f, 0.45f, 0.67f)) // <-- full vector
.setUsing("full")
.setLimit(10)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List<PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Query = new float[] { 1,23, 45, 67 }, // <------------- small byte vector
Using = "mrl_byte",
Limit = 1000
}
},
query: new float[] { 0.01f, 0.299f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, // <-- full vector
usingVector: "full",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{1, 23, 45, 67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("mrl_byte"),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(1000)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.299, 0.45, 0.67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("full"),
})
Fetch 100 results using the default vector, then re-score them using a multi-vector to get the top 10.
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- dense vector
"limit": 100
},
"query": [ // <─┐
[0.1, 0.2, ...], // < │
[0.2, 0.1, ...], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9, ...] // < │
], // <─┘
"using": "colbert",
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[0.01, 0.45, 0.67, 0.53], # <-- dense vector
limit=100,
),
query=[
[0.1, 0.2, 0.32], # <─┐
[0.2, 0.1, 0.52], # < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9, 0.93], # < ┘
],
using="colbert",
limit=10,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: {
query: [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
limit: 100,
},
query: [
[0.1, 0.2], // <─┐
[0.2, 0.1], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9], // < ┘
],
using: 'colbert',
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67]))
.limit(100u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![
vec![0.1, 0.2],
vec![0.2, 0.1],
vec![0.8, 0.9],
]))
.using("colbert")
.limit(10u64)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f)) // <-- dense vector
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
nearest(
new float[][] {
{0.1f, 0.2f}, // <─┐
{0.2f, 0.1f}, // < ├─ multi-vector
{0.8f, 0.9f} // < ┘
}))
.setUsing("colbert")
.setLimit(10)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List <PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Query = new float[] { 0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, // <-- dense vector****
Limit = 100
}
},
query: new float[][] {
[0.1f, 0.2f], // <─┐
[0.2f, 0.1f], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8f, 0.9f] // < ┘
},
usingVector: "colbert",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.45, 0.67}),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(100)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryMulti([][]float32{
{0.1, 0.2},
{0.2, 0.1},
{0.8, 0.9},
}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("colbert"),
})
It is possible to combine all the above techniques in a single query:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"prefetch": {
"query": [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------ small byte vector
"using": "mrl_byte"
"limit": 1000
},
"query": [0.01, 0.45, 0.67, ...], // <-- full dense vector
"using": "full"
"limit": 100
},
"query": [ // <─┐
[0.1, 0.2, ...], // < │
[0.2, 0.1, ...], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9, ...] // < │
], // <─┘
"using": "colbert",
"limit": 10
}
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333")
client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[1, 23, 45, 67], # <------ small byte vector
using="mrl_byte",
limit=1000,
),
query=[0.01, 0.45, 0.67], # <-- full dense vector
using="full",
limit=100,
),
query=[
[0.17, 0.23, 0.52], # <─┐
[0.22, 0.11, 0.63], # < ├─ multi-vector
[0.86, 0.93, 0.12], # < ┘
],
using="colbert",
limit=10,
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
client.query("{collection_name}", {
prefetch: {
prefetch: {
query: [1, 23, 45, 67], // <------------- small byte vector
using: 'mrl_byte',
limit: 1000,
},
query: [0.01, 0.45, 0.67], // <-- full dense vector
using: 'full',
limit: 100,
},
query: [
[0.1, 0.2], // <─┐
[0.2, 0.1], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8, 0.9], // < ┘
],
using: 'colbert',
limit: 10,
});
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{PrefetchQueryBuilder, Query, QueryPointsBuilder};
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![1.0, 23.0, 45.0, 67.0]))
.using("mlr_byte")
.limit(1000u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67]))
.using("full")
.limit(100u64)
)
.query(Query::new_nearest(vec![
vec![0.1, 0.2],
vec![0.2, 0.1],
vec![0.8, 0.9],
]))
.using("colbert")
.limit(10u64)
).await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(1, 23, 45, 67)) // <------------- small byte vector
.setUsing("mrl_byte")
.setLimit(1000)
.build())
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f)) // <-- dense vector
.setUsing("full")
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
nearest(
new float[][] {
{0.1f, 0.2f}, // <─┐
{0.2f, 0.1f}, // < ├─ multi-vector
{0.8f, 0.9f} // < ┘
}))
.setUsing("colbert")
.setLimit(10)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch: new List <PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Prefetch = {
new List <PrefetchQuery> {
new() {
Query = new float[] { 1, 23, 45, 67 }, // <------------- small byte vector
Using = "mrl_byte",
Limit = 1000
},
}
},
Query = new float[] {0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f}, // <-- dense vector
Using = "full",
Limit = 100
}
},
query: new float[][] {
[0.1f, 0.2f], // <─┐
[0.2f, 0.1f], // < ├─ multi-vector
[0.8f, 0.9f] // < ┘
},
usingVector: "colbert",
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{1, 23, 45, 67}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("mrl_byte"),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(1000)),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryDense([]float32{0.01, 0.45, 0.67}),
Limit: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(100)),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("full"),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryMulti([][]float32{
{0.1, 0.2},
{0.2, 0.1},
{0.8, 0.9},
}),
Using: qdrant.PtrOf("colbert"),
})
Score boosting
Available as of v1.14.0
When introducing vector search to specific applications, sometimes business logic needs to be considered for ranking the final list of results.
A quick example is our own documentation search bar. It has vectors for every part of the documentation site. If one were to perform a search by “just” using the vectors, all kinds of elements would be equally considered good results. However, when searching for documentation, we can establish a hierarchy of importance:
title > content > snippets
One way to solve this is to weight the results based on the kind of element. For example, we can assign a higher weight to titles and content, and keep snippets unboosted.
Pseudocode would be something like:
score = score + (is_title * 0.5) + (is_content * 0.25)
Query API can rescore points with custom formulas. They can be based on:
- Dynamic payload values
- Conditions
- Scores of prefetches
To express the formula, the syntax uses objects to identify each element. Taking the documentation example, the request would look like this:
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": {
"query": [0.2, 0.8, ...], // <-- dense vector
"limit": 50
}
"query": {
"formula": {
"sum": [
"$score,
{
"mult": [
0.5,
{
"key": "tag",
"match": { "any": ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"] } }
]
},
{
"mult": [
0.25,
{
"key": "tag",
"match": { "any": ["p", "li"] }
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
from qdrant_client import models
tag_boosted = client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[0.2, 0.8, ...], # <-- dense vector
limit=50
),
query=models.FormulaQuery(
formula=models.SumExpression(sum=[
"$score",
models.MultExpression(mult=[0.5, models.FieldCondition(key="tag", match=models.MatchAny(any=["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"]))]),
models.MultExpression(mult=[0.25, models.FieldCondition(key="tag", match=models.MatchAny(any=["p", "li"]))])
]
))
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const tag_boosted = await client.query(collectionName, {
prefetch: {
query: [0.2, 0.8, 0.1, 0.9],
limit: 50
},
query: {
formula: {
sum: [
"$score",
{
mult: [ 0.5, { key: "tag", match: { any: ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"] }} ]
},
{
mult: [ 0.25, { key: "tag", match: { any: ["p", "li"] }} ]
}
]
}
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
Condition, Expression, FormulaBuilder, PrefetchQueryBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
let _tag_boosted = client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67])
.limit(100u64)
)
.query(FormulaBuilder::new(Expression::sum_with([
Expression::score(),
Expression::mult_with([
Expression::constant(0.5),
Expression::condition(Condition::matches("tag", ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"])),
]),
Expression::mult_with([
Expression::constant(0.25),
Expression::condition(Condition::matches("tag", ["p", "li"])),
]),
])))
.limit(10)
).await?;
import java.util.List;
import static io.qdrant.client.ConditionFactory.matchKeywords;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.condition;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.constant;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.mult;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.sum;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.variable;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.formula;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Formula;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.MultExpression;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SumExpression;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f))
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
formula(
Formula.newBuilder()
.setExpression(
sum(
SumExpression.newBuilder()
.addSum(variable("$score"))
.addSum(
mult(
MultExpression.newBuilder()
.addMult(constant(0.5f))
.addMult(
condition(
matchKeywords(
"tag",
List.of("h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"))))
.build()))
.addSum(mult(MultExpression.newBuilder()
.addMult(constant(0.25f))
.addMult(
condition(
matchKeywords(
"tag",
List.of("p", "li"))))
.build()))
.build()))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Conditions;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch:
[
new PrefetchQuery { Query = new float[] { 0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, Limit = 100 },
],
query: new Formula
{
Expression = new SumExpression
{
Sum =
{
"$score",
new MultExpression
{
Mult = { 0.5f, Match("tag", ["h1", "h2", "h3", "h4"]) },
},
new MultExpression { Mult = { 0.25f, Match("tag", ["p", "li"]) } },
},
},
},
limit: 10
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.01, 0.45, 0.67),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryFormula(&qdrant.Formula{
Expression: qdrant.NewExpressionSum(&qdrant.SumExpression{
Sum: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionVariable("$score"),
qdrant.NewExpressionMult(&qdrant.MultExpression{
Mult: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionConstant(0.5),
qdrant.NewExpressionCondition(qdrant.NewMatchKeywords("tag", "h1", "h2", "h3", "h4")),
},
}),
qdrant.NewExpressionMult(&qdrant.MultExpression{
Mult: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionConstant(0.25),
qdrant.NewExpressionCondition(qdrant.NewMatchKeywords("tag", "p", "li")),
},
}),
},
}),
}),
})
There are multiple expressions available, check the API docs for specific details.
- constant - A floating point number. e.g.
0.5. "$score"- Reference to the score of the point in the prefetch. This is the same as"$score[0]"."$score[0]","$score[1]","$score[2]", … - When using multiple prefetches, you can reference specific prefetch with the index within the array of prefetches.- payload key - Any plain string will refer to a payload key. This uses the jsonpath format used in every other place, e.g.
keyorkey.subkey. It will try to extract a number from the given key. - condition - A filtering condition. If the condition is met, it becomes
1.0, otherwise0.0. - mult - Multiply an array of expressions.
- sum - Sum an array of expressions.
- div - Divide an expression by another expression.
- abs - Absolute value of an expression.
- pow - Raise an expression to the power of another expression.
- sqrt - Square root of an expression.
- log10 - Base 10 logarithm of an expression.
- ln - Natural logarithm of an expression.
- exp - Exponential function of an expression (
e^x). - geo distance - Haversine distance between two geographic points. Values need to be
{ "lat": 0.0, "lon": 0.0 }objects. - decay - Apply a decay function to an expression, which clamps the output between 0 and 1. Available decay functions are linear, exponential, and gaussian. See more.
- datetime - Parse a datetime string (see formats here), and use it as a POSIX timestamp, in seconds.
- datetime key - Specify that a payload key contains a datetime string to be parsed into POSIX seconds.
It is possible to define a default for when the variable (either from payload or prefetch score) is not found. This is given in the form of a mapping from variable to value. If there is no variable, and no defined default, a default value of 0.0 is used.
Boost points closer to user
Another example. Combine the score with how close the result is to a user.
Considering each point has an associated geo location, we can calculate the distance between the point and the request’s location.
Assuming we have cosine scores in the prefetch, we can use a helper function to clamp the geographical distance between 0 and 1, by using a decay function. Once clamped, we can sum the score and the distance together. Pseudocode:
score = score + gauss_decay(distance)
In this case we use a gauss_decay function.
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query
{
"prefetch": { "query": [0.2, 0.8, ...], "limit": 50 },
"query": {
"formula": {
"sum": [
"$score",
{
"gauss_decay": {
"x": {
"geo_distance": {
"origin": { "lat": 52.504043, "lon": 13.393236 }
"to": "geo.location"
}
},
"scale": 5000 // 5km
}
}
]
},
"defaults": { "geo.location": {"lat": 48.137154, "lon": 11.576124} }
}
}
from qdrant_client import models
geo_boosted = client.query_points(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
prefetch=models.Prefetch(
query=[0.2, 0.8, ...], # <-- dense vector
limit=50
),
query=models.FormulaQuery(
formula=models.SumExpression(sum=[
"$score",
models.GaussDecayExpression(
gauss_decay=models.DecayParamsExpression(
x=models.GeoDistance(
geo_distance=models.GeoDistanceParams(
origin=models.GeoPoint(
lat=52.504043,
lon=13.393236
), # Berlin
to="geo.location"
)
),
scale=5000 # 5km
)
)
]),
defaults={"geo.location": models.GeoPoint(lat=48.137154, lon=11.576124)} # Munich
)
)
import { QdrantClient } from "@qdrant/js-client-rest";
const client = new QdrantClient({ host: "localhost", port: 6333 });
const distance_boosted = await client.query(collectionName, {
prefetch: {
query: [0.2, 0.8, ...],
limit: 50
},
query: {
formula: {
sum: [
"$score",
{
gauss_decay: {
x: {
geo_distance: {
origin: { lat: 52.504043, lon: 13.393236 }, // Berlin
to: "geo.location"
}
},
scale: 5000 // 5km
}
}
]
},
defaults: { "geo.location": { lat: 48.137154, lon: 11.576124 } } // Munich
}
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::{
GeoPoint, DecayParamsExpressionBuilder, Expression, FormulaBuilder, PrefetchQueryBuilder, QueryPointsBuilder,
};
use qdrant_client::Qdrant;
let client = Qdrant::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;
let _geo_boosted = client.query(
QueryPointsBuilder::new("{collection_name}")
.add_prefetch(
PrefetchQueryBuilder::default()
.query(vec![0.01, 0.45, 0.67])
.limit(100u64),
)
.query(
FormulaBuilder::new(Expression::sum_with([
Expression::score(),
Expression::exp_decay(
DecayParamsExpressionBuilder::new(Expression::geo_distance_with(
// Berlin
GeoPoint { lat: 52.504043, lon: 13.393236 },
"geo.location",
))
.scale(5_000.0),
),
]))
// Munich
.add_default("geo.location", GeoPoint { lat: 48.137154, lon: 11.576124 }),
)
.limit(10),
)
.await?;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.expDecay;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.geoDistance;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.sum;
import static io.qdrant.client.ExpressionFactory.variable;
import static io.qdrant.client.PointIdFactory.id;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.formula;
import static io.qdrant.client.QueryFactory.nearest;
import static io.qdrant.client.ValueFactory.value;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantClient;
import io.qdrant.client.QdrantGrpcClient;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.DecayParamsExpression;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.Formula;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.GeoDistance;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.GeoPoint;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.PrefetchQuery;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.QueryPoints;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SumExpression;
QdrantClient client =
new QdrantClient(QdrantGrpcClient.newBuilder("localhost", 6334, false).build());
client
.queryAsync(
QueryPoints.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.addPrefetch(
PrefetchQuery.newBuilder()
.setQuery(nearest(0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f))
.setLimit(100)
.build())
.setQuery(
formula(
Formula.newBuilder()
.setExpression(
sum(
SumExpression.newBuilder()
.addSum(variable("$score"))
.addSum(
expDecay(
DecayParamsExpression.newBuilder()
.setX(
geoDistance(
GeoDistance.newBuilder()
.setOrigin(
GeoPoint.newBuilder()
.setLat(52.504043)
.setLon(13.393236)
.build())
.setTo("geo.location")
.build()))
.setScale(5000)
.build()))
.build()))
.putDefaults(
"geo.location",
value(
Map.of(
"lat", value(48.137154),
"lon", value(11.576124))))
.build()))
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
using Qdrant.Client.Grpc;
using static Qdrant.Client.Grpc.Expression;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
prefetch:
[
new PrefetchQuery { Query = new float[] { 0.01f, 0.45f, 0.67f }, Limit = 100 },
],
query: new Formula
{
Expression = new SumExpression
{
Sum =
{
"$score",
FromExpDecay(
new()
{
X = new GeoDistance
{
Origin = new GeoPoint { Lat = 52.504043, Lon = 13.393236 },
To = "geo.location",
},
Scale = 5000,
}
),
},
},
Defaults =
{
["geo.location"] = new Dictionary<string, Value>
{
["lat"] = 48.137154,
["lon"] = 11.576124,
},
},
}
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.Query(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPoints{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Prefetch: []*qdrant.PrefetchQuery{
{
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.8),
},
},
Query: qdrant.NewQueryFormula(&qdrant.Formula{
Expression: qdrant.NewExpressionSum(&qdrant.SumExpression{
Sum: []*qdrant.Expression{
qdrant.NewExpressionVariable("$score"),
qdrant.NewExpressionExpDecay(&qdrant.DecayParamsExpression{
X: qdrant.NewExpressionGeoDistance(&qdrant.GeoDistance{
Origin: &qdrant.GeoPoint{
Lat: 52.504043,
Lon: 13.393236,
},
To: "geo.location",
}),
}),
},
}),
Defaults: qdrant.NewValueMap(map[string]any{
"geo.location": map[string]any{
"lat": 48.137154,
"lon": 11.576124,
},
}),
}),
})
For all decay functions, there are these parameters available
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | N/A | The value to decay |
| target | 0.0 | The value at which the decay will be at its peak. For distances it is usually set at 0.0, but can be set to any value. |
| scale | 1.0 | The value at which the decay function will be equal to midpoint. This is in terms of x units, for example, if x is in meters, scale of 5000 means 5km. Must be a non-zero positive number |
| midpoint | 0.5 | Output is midpoint when x equals scale. Must be in the range (0.0, 1.0), exclusive |
The formulas for each decay function are as follows:
Decay functions
lin_decay (green), range: [0, 1]
textlindecay(x)=maxleft(0,−fracleft(1−midpointright)scalecdotabsleft(x−targetright)+1right)\text{lin_decay}(x) = \max\left(0,\ -\frac{\left(1-m_{idpoint}\right)}{s_{cale}}\cdot {abs}\left(x-t_{arget}\right)+1\right)textlindecay(x)=maxleft(0,−fracleft(1−midpointright)scalecdotabsleft(x−targetright)+1right)
exp_decay (red), range: (0, 1]
textexpdecay(x)=expleft(fraclnleft(midpointright)scalecdotabsleft(x−targetright)right)\text{exp_decay}(x) = \exp\left(\frac{\ln\left(m_{idpoint}\right)}{s_{cale}}\cdot {abs}\left(x-t_{arget}\right)\right)textexpdecay(x)=expleft(fraclnleft(midpointright)scalecdotabsleft(x−targetright)right)
gauss_decay (purple), range: (0, 1]
textgaussdecay(x)=expleft(fraclnleft(midpointright)scale2cdotleft(x−targetright)2right)\text{gauss_decay}(x) = \exp\left(\frac{\ln\left(m_{idpoint}\right)}{s_{cale}^{2}}\cdot \left(x-t_{arget}\right)^{2}\right)textgaussdecay(x)=expleft(fraclnleft(midpointright)scale2cdotleft(x−targetright)2right)
Grouping
Available as of v1.11.0
It is possible to group results by a certain field. This is useful when you have multiple points for the same item, and you want to avoid redundancy of the same item in the results.
REST API (Schema):
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/query/groups
{
// Same as in the regular query API
"query": [1.1],
// Grouping parameters
"group_by": "document_id", // Path of the field to group by
"limit": 4, // Max amount of groups
"group_size": 2 // Max amount of points per group
}
client.query_points_groups(
collection_name="{collection_name}",
# Same as in the regular query_points() API
query=[1.1],
# Grouping parameters
group_by="document_id", # Path of the field to group by
limit=4, # Max amount of groups
group_size=2, # Max amount of points per group
)
client.queryGroups("{collection_name}", {
query: [1.1],
group_by: "document_id",
limit: 4,
group_size: 2,
});
use qdrant_client::qdrant::QueryPointGroupsBuilder;
client
.query_groups(
QueryPointGroupsBuilder::new("{collection_name}", "document_id")
.query(vec![0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7])
.group_size(2u64)
.with_payload(true)
.with_vectors(true)
.limit(4u64),
)
.await?;
import java.util.List;
import io.qdrant.client.grpc.Points.SearchPointGroups;
client.queryGroupsAsync(
QueryPointGroups.newBuilder()
.setCollectionName("{collection_name}")
.setQuery(nearest(0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f))
.setGroupBy("document_id")
.setLimit(4)
.setGroupSize(2)
.build())
.get();
using Qdrant.Client;
var client = new QdrantClient("localhost", 6334);
await client.QueryGroupsAsync(
collectionName: "{collection_name}",
query: new float[] { 0.2f, 0.1f, 0.9f, 0.7f },
groupBy: "document_id",
limit: 4,
groupSize: 2
);
import (
"context"
"github.com/qdrant/go-client/qdrant"
)
client, err := qdrant.NewClient(&qdrant.Config{
Host: "localhost",
Port: 6334,
})
client.QueryGroups(context.Background(), &qdrant.QueryPointGroups{
CollectionName: "{collection_name}",
Query: qdrant.NewQuery(0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7),
GroupBy: "document_id",
GroupSize: qdrant.PtrOf(uint64(2)),
})
For more information on the grouping capabilities refer to the reference documentation for search with grouping and lookup.
Was this page useful?
Thank you for your feedback! 🙏
We are sorry to hear that. 😔 You can edit this page on GitHub, or create a GitHub issue.
On this page: