Qucs-S: Qucs with SPICE (original) (raw)
| Download linksThe latest stable release is Qucs-S-25.1.2 Quick reference guide as PDF Video tutorial from Kasper Nielsen Source tarball: qucs-s-25.1.2.tar.gz Github repository Linux reporsitories for Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, OpenSUSE. Find packages for your distribution here AppImage for other Linux distributions FreeBSD using ports Windows portable package: Qucs-S-25.1.2-win64.zip Windows installer with Ngspice: Qucs-S-25.1.2-setup.exe MacOS using homebrew: https://github.com/ra3xdh/homebrew-qucs-s (Installation instructions...) Contribution guideQucs-S is open for everyone's contribution. See here for contribution guide.DonationsQucs-S accepts donations using Boosty: https://boosty.to/qucs_s | News February, 20, 2025 Qucs-S-25.1.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link October, 31, 2024 Qucs-S-24.4.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link July, 23, 2024 Qucs-S-24.3.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link March, 25, 2024 Qucs-S-24.2.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link February, 16, 2024 Qucs-S-24.1.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link October, 26, 2023 Qucs-S-2.1.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link August, 19, 2023 Qucs-S-2.0.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link June, 07, 2023 Qucs-S-1.1.0 is released! See Release notes and dowload link April, 23, 2023 Qucs-S-1.0.2 is released! February, 4, 2023 Qucs-S-1.0.1 is released! October, 30, 2022 Qucs-S-1.0.0 is released! July, 01, 2022 Qucs-S-0.0.24 is released! February, 20, 2022 Qucs-S-0.0.23 is released! Application ported to Qt5. January, 19, 2020 Qucs-S-0.0.22 is released! October, 31, 2018 Qucs-S-0.0.21 is released! June, 24, 2018 Added packages for Ubuntu 18.04 October, 31, 2017 Qucs-S-0.0.20 is released! October, 25, 2017 Added packages for CentOS and Fedora January, 26, 2017 Qucs-S 0.0.19 is released! The first stable release. July 25, 2015 Qucs-S RC1 released. | Simulation example with Qucs-S and Ngspice 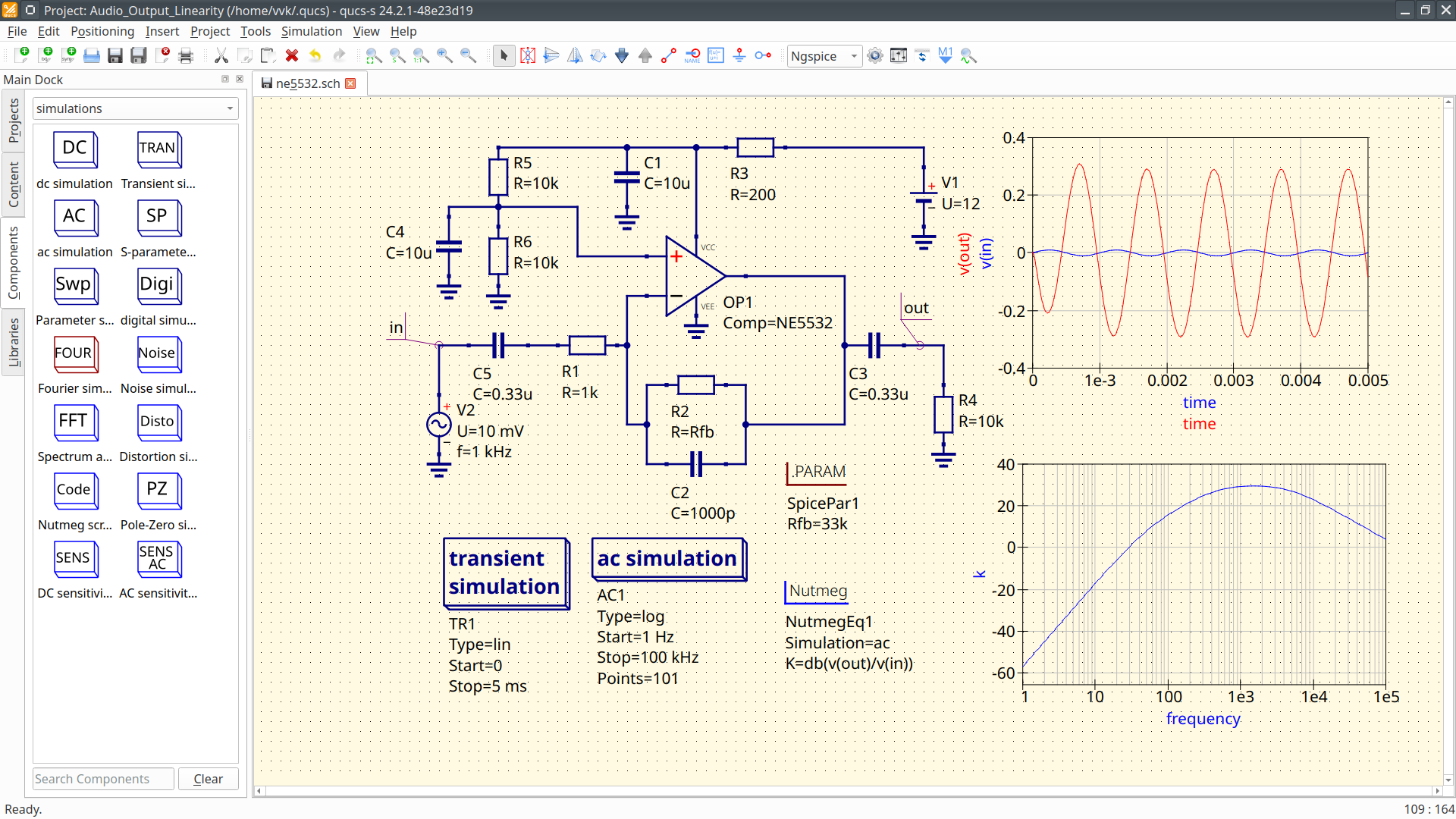 (More screenshots...) Support Forum: https://github.com/ra3xdh/qucs_s/discussions Bugtracker: https://github.com/ra3xdh/qucs_s/issues PublicationsQucs-S is also a research software. Check our publication list. (More screenshots...) Support Forum: https://github.com/ra3xdh/qucs_s/discussions Bugtracker: https://github.com/ra3xdh/qucs_s/issues PublicationsQucs-S is also a research software. Check our publication list. |
|---|
What is Qucs-S?
Qucs-S is a circuit simulation program based onQucscircuit simulator. The "S" letter indicates SPICE. The purpose of the Qucs-S project is to use free circuit simulation kernels (Ngspice, Qucsator, Xyce) with the unified GUI based on Qt6 toolkit. It merges the power of SPICE and the simplicity of the Qucs GUI. Qucs-S is not a simulator by itself, but it requires to use an external simulation backend with it. Qucs-S allows to use the following open-source simulation kernels:
- Ngspice is recommended to use. Ngspice is powerful mixed-level/mixed-signal circuit simulator. The most of industrial SPICE models are compatible with Ngspice. It has an excellent simulation performance and powerful postprocessor. Google Skywater 130nm PDK supports Ngspice.
- XYCE is a new SPICE-compatible circuit simulator written by Sandia from the scratch. It supports basic SPICE simulation types and has an advanced RF simulation features such as Harmonic balance simulation.
- QucsatorRF for RF and microwave circuits design. It provides advanced models for such devices microstrip lines and waveguides. QucsatorRF is not SPICE compatible. The general purpose circuits simulation is also possible but not recommended.
- SpiceOpus is developed by the Faculty of Electrical Engineering of the Ljubljana University. It based on the SPICE-3f5 code
Screenshots
Main features
- Basic and advanced simulation types: AC, DC, transient, S-parameter, FFT, distortion, pole-zero, parametric sweep.
- Advanced RF simulation with Qucsator RF backend;
- Quick switching of the simulation kernel without application restart;
- Tuner simulation mode
- Direct support of SPICE models from components datasheets;
- Basic SPICE components: RCL, BJT, MOSFET, JFET, MESFET, switches;
- Advanced SPICE components: Equation-defined sources and RCLs, transmission lines;
- Parametric circuits (.PARAM) and SPICE postrprocessor (Nutmeg)
- Basic SPICE simulations: DC, AC, TRAN;
- Advanced SPICE simulation: DISTO, NOISE, SENS (added in 0.0.20), Spectrum analysis;
- Harmonic balance analysis with XYCE and Qucsator RF backends;
- Nutmeg script simulation: direct access to the SPICE code and construct your own simulation;
- XYCE script simulation type;
- XYCE digital devices library;
Installation
Linux
Binary packages
The usage of binary packages is the preffered way to get Qucs-S.
- The DEB and RPM packages for Qucs-S are prepared with openSUSE build service. Check the package for your distribution here Then click on distribution icon and find the installation instructions. You may need to install ngspice manually.
- Arch and Manjaro users may install Qucs-S from AUR
- The packages for AltLinux are available from Sysyphus repository here
AppImage for all Linux distributions
You can run Qucs-S on all Linux platforms using AppImage without building it from source. This way is preferrable, if there is no prebuilt package for your distribution and/or you have not root access to the machine. Otherwise it is recommneded to install the binary package from the repository (see the section above).
Download AppImage and make it executable, then run it from the console or your file manager. Please note that AppImage doesn't include Ngspice and you need to install it using system package manager.
Building from source
If binary packages are not available for your distrubution, then you will need to build Qucs-S from source:
- Install all necessary dependencies: Qt, C++ compilers, etc.
- Install desired simulation backends: Ngspice, XYCE, SpiceOpus. You can use all these backends together or only one of them. QucsatorRF backend is shipped with Qucs-S.
- Download and unpack tarball
- Use CMake to configure.
- Invoke make and make install Refer to the README.md of the Qucs-S github repository for the recent build instructions.
FreeBSD
Qucs could be installed on FreeBSD using ports or binary package.
- Execute the following command to install port:
cd /usr/ports/cad/qucs-s/ && make install clean
- Use the following command to add the package:
pkg install qucs-s
Windows
Windows portable package could be downloaded as zipped distribution. Unpack and launch qucs-s.exefrom bin subdirectory. Only 64-bit windows packages are available:
You need to download and install Ngspice and/or XYCE manually from official websites: http://ngspice.org/ https://xyce.sandia.gov respectively.
You may also use Windows installer. Launch the installer executable and follow the installation wizard guide. Windows installer includes both Ngspice and QucsatorRF simulation kernels. You may download and update simulation backends manually and specify the simulator paths in application settings.
MacOS
Use homebrew to install Qucs-S. Run below command to install latest Qucs-S.
brew install --cask ra3xdh/qucs-s/qucs-s@nightly
Linux
Run qucs-s from the the command line or launch Qucs-S icon in your desktop environment menu after the installation. Ngspice is set as the default simulation backend at the first run. You can change it later in the application settings.
Windows
For portable package run the qucs-s.exe binary to launch application. You may create a desktop shortcut for it.
Developers
Project founders:
- Vadim Kuznetsov ra3xdh@gmail.com
- Mike Brinson mbrin72043@yahoo.co.uk
See the full contributors list at the Github repository page: https://github.com/ra3xdh/qucs_s/graphs/contributors
Contribution guide
Steps to contribute
Source code of the Qucs-S is hosted at the Github in the following repository: https://github.com/ra3xdh/qucs_s. You need to clone this repository if you wish to contribute.
git clone https://github.com/ra3xdh/qucs\_s
cd qucs_s
git checkout -b your_feature
Use CMake to compile Qucs-S. After you make changes, prepare a pull request to Qucs-S repository.
Branching model
Currently there are two main branches in Qucs-S repository:
- master reflects the state of the latest Qucs-S release.
- current is development branch. Use this branch to target patches.
- QucsatorRF repository hosts the RF simulation backend code. It has a separate release system.
Build instruction (development branches)
Refer to the README.md of the Qucs-S github repository for the recent build instructions.(to top...)
Documentation
- Presentation at the Spring MOS-AK 2016 at Lausanne
- Presentation at the Spring MOS-AK 2017 at Lausanne
- Presentation at the MIXDES2017 conference: Part 1 and Part 2
Publications
Qucs-S is not a simple circuit simulator, but also a research software. Please cite our articles, if you are using Qucs-S in your research.
- Brinson, M. E., and Kuznetsov, V. (2016) A new approach to compact semiconductor device modelling with Qucs Verilog-A analogue module synthesis. Int. J. Numer. Model., 29: 1070-1088. (BibTeX)
- D. Tomaszewski, G. Głuszko, M. Brinson, V. Kuznetsov and W. Grabinski, "FOSS as an efficient tool for extraction of MOSFET compact model parameters," 2016 MIXDES - 23rd International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, Lodz, 2016, pp. 68-73. (BibTeX)
- M. Brinson and V. Kuznetsov, "Qucs-0.0.19S: A new open-source circuit simulator and its application for hardware design," 2016 International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications (SIBCON), Moscow, 2016, pp. 1-5. (BibTeX)
- M. Brinson and V. Kuznetsov, "Improvements in Qucs-S equation-defined modelling of semiconductor devices and IC's," 2017 MIXDES - 24th International Conference "Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, Bydgoszcz, 2017, pp. 137-142. (BibTeX)
- M. Brinson and V. Kuznetsov, "Extended behavioural device modelling and circuit simulation with Qucs-S" International Journal of Electronics, 2017, pp.1 - 14 (BibTeX)