Data protection vs. security vs. privacy: Key differences (original) (raw)
Data protection, privacy and security might look alike but their differences can make or break a comprehensive compliance program to collect, manage, access, erase and secure data.

By
Published: 15 Apr 2024
Data is the lifeblood of every business. But as companies of all sizes grapple with the challenges of storing and using ever-more data, they also face greater pressures from government regulations as well as user expectations.
Today, even small businesses must address formidable challenges, including classifying, storing and safeguarding a diversified assortment of data types across increasingly granular data lifecycles. The three key aspects of safeguarding data include protection, security and privacy, each of which plays a distinctive role:
- Data protection. Making data available. Data preservation, immutability and retention or broader lifecycle considerations from data creation to destruction.
- Data security. Preserving the integrity of data. Revolves around ensuring authorized access and protecting data from theft, corruption, improper alternation or loss.
- Data privacy. Maintaining control of data. Addresses the proper use and management of sensitive personal data, in some cases extending a measure of control to data sources such as individuals.
Although these three functions are often considered interchangeable, there are important distinctions that business and IT leaders need to understand.
What is data protection?
Data protection embraces the technologies, practices, processes and workflows that impact the availability of data, so the data is there when it's needed. Proper data protection can include various technical assets or considerations:
- Storage hardware includes traditional magnetic or solid-state drive devices that retain data as well as broader collections of physical storage, such as storage servers and storage arrays.
- Availability mechanisms include traditional data backups, continuous data protection and high-availability techniques such as RAID, or redundant array of independent disks. All these mechanisms must include a corresponding mechanic to recover and validate data.
- Storage performance techniques include storage tiering, which is storing more important or frequently accessed data on higher-performing storage hardware. Higher-tier storage is often coupled with corresponding availability techniques. A higher storage tier with more important data, for example, might use more sophisticated availability techniques such as RAID; lower-tier storage might simply use traditional data backups.
Data protection must also include careful consideration of policies and procedures to ensure data is retained and handled in a suitable manner:
- Data inventory. This can determine the amounts and types of data present across the enterprise as well as ensure all detected data is included in data protection schemes and proper lifecycle management.
- Backup and recovery. There are tools and practices used to guard data against hardware failures, accidental loss or intentional malfeasance. They track and document the type of backup used, where those hardware assets are located, how often backups are performed and the process of data recovery.
- Data lifecycle management. This involves tools and processes that affect the way data is classified, stored in an appropriate performance tier, protected with corresponding availability mechanisms throughout its lifecycle and destroyed according to policy at the end of its lifecycle.
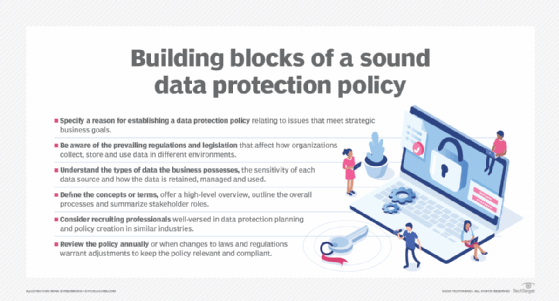
Effective data protection starts with an all-inclusive policy.
Data protection can also carry significant regulatory and governance implications for businesses. Accidentally losing data due to disk failure or inadvertent deletion, for example, can impact the organization's ability to function normally, potentially violating compliance requirements or other data protection laws. Many organizations employ a dedicated data protection officer who's specifically responsible for ensuring all data storage meets business requirements.
What is data security?
Data security is all about safeguarding the data against theft, corruption or unauthorized access throughout the entire data lifecycle from creation to destruction. Proper data security can include an array of technologies and processes:
- Physical security of the storage devices, servers, network devices and overall physical computing environment within the data center and across the entire enterprise.
- Access control systems such as identity and access management, which define who can access what data and how that data can be used once accessed.
- Logging and monitoring to track data access and changes over time as well as alerting administrators when unauthorized access or usage patterns are detected. Logging and monitoring also help with data security audits by ensuring security safeguards are in place and operating as expected.
- Encryption technologies, which can safeguard data both at rest and in flight, including encryption key and certificate management.
Data security also involves detailed policies and procedures related to the way data is secured and accessed as well as suitable approaches to managing security breach incidents. These documents may include business policies, such as how to determine what data employees can access and use, ongoing employee education sessions, and technical policies such as how encryption is implemented.
As with data protection, data security is a vital element of regulatory compliance and business governance for almost all organizations. Suitable data security policies may be a prerequisite for business partnerships or subcontracting and even business investments like venture capital.

Data protection, security and privacy work in complementary fashion.
What is data privacy?
Data privacy is primarily a matter of ethical data management and use. Conscientious data privacy can ensure users or other data sources understand a variety of matters related to the collection, use and management of sensitive data, including the following:
- Why data is collected.
- How data is being used or shared.
- How data is being managed and protected.
- Which rights are necessary to add, change or limit data and its use.
Fundamentally, data privacy is a means of bringing a level of transparency to the ways in which a business collects, stores and uses data. In addition, data privacy concepts support some amount of user control over the data that a business possesses. Various data privacy principles can help a user do the following:
- See the data that pertains to the user.
- See when and how that data was collected.
- Correct or update data that's wrong, outdated or no longer relevant.
- Redact or restrict some data elements from being stored or used.
- Request that some or all data pertaining to the user be deleted, which is known as the right to be forgotten.
Data privacy has become a significant legislative issue for many businesses. Regulatory pressure is applied by different government entities ranging from different states within the U.S. to national-level mandates to entire geopolitical regions. Noteworthy data privacy regulations include the following:
- California Online Privacy Protection Act of 2003.
- California Consumer Privacy Act, or CCPA.
- Utah Consumer Privacy Act.
- Australian Privacy Act 1988.
- Canada's Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act.
- European Union's General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR.
The sheer number of data privacy laws is compounded by the varied terms and obligations presented in each law. Any business that operates in a market governed by data protection regulations is obligated to observe those regulations or face serious fines and other legal penalties for violations. Consequently, a global company might be subject to different regulations, which has complicated business governance and regulatory compliance issues for many large enterprises.
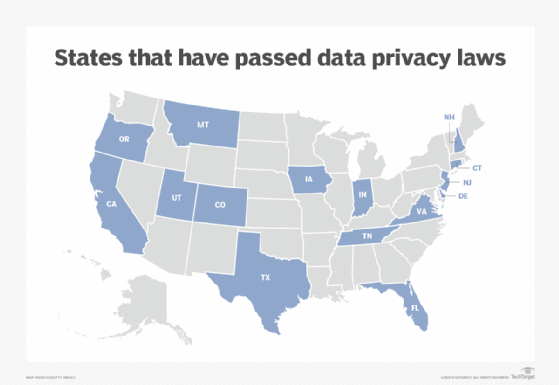
The number of states enacting data privacy laws has risen to 15 and counting.
Creating a data management team
Data protection, data security and data privacy are separate but closely aligned practices that every business must address. Meeting the goals of each concept can be overwhelming for a single company or technology leader. Fortunately, this suite of data management objectives can be handled with the collaboration of a carefully selected team including the following roles:
- Business leaders who are responsible for ensuring the organization meets its protection, security and privacy requirements.
- Legal counsel versed in data protection, security and privacy regulations who can advise business and technology leaders on the legal issues involved in each of the three practices.
- Data management officers with deep expertise on issues of protection, security and privacy who can collaborate with business leaders and legal counsel to craft and maintain well-designed policies and processes.
- Technology leaders who can select, implement and maintain the technologies best suited to meet the operational implications of data protection, security and privacy.
- Employees who are properly educated and trained in the various issues pertaining to their access to, use of and safeguarding of sensitive business data.
Data protection, security and privacy are still evolving issues that impact everyone -- individuals, businesses and state and national governments. It's vital for every company to treat data management as a dynamic and ever-changing challenge that must be reviewed, reevaluated and updated frequently to ensure the business remains in compliance with legislation and best practices.
Stephen J. Bigelow, senior technology editor at TechTarget, has more than 20 years of technical writing experience in the PC and technology industry.
 What is data privacy? By: Cameron Hashemi-Pour
What is data privacy? By: Cameron Hashemi-Pour  What is data protection and why is it important?
What is data protection and why is it important?  By: Ron Karjian
By: Ron Karjian  data minimization
data minimization  By: Sean Kerner
By: Sean Kerner  data sovereignty
data sovereignty  By: Paul Kirvan
By: Paul Kirvan