Mohamed Ramy - Profile on Academia.edu (original) (raw)
6-OHDA Lesions and Behavioral Effects
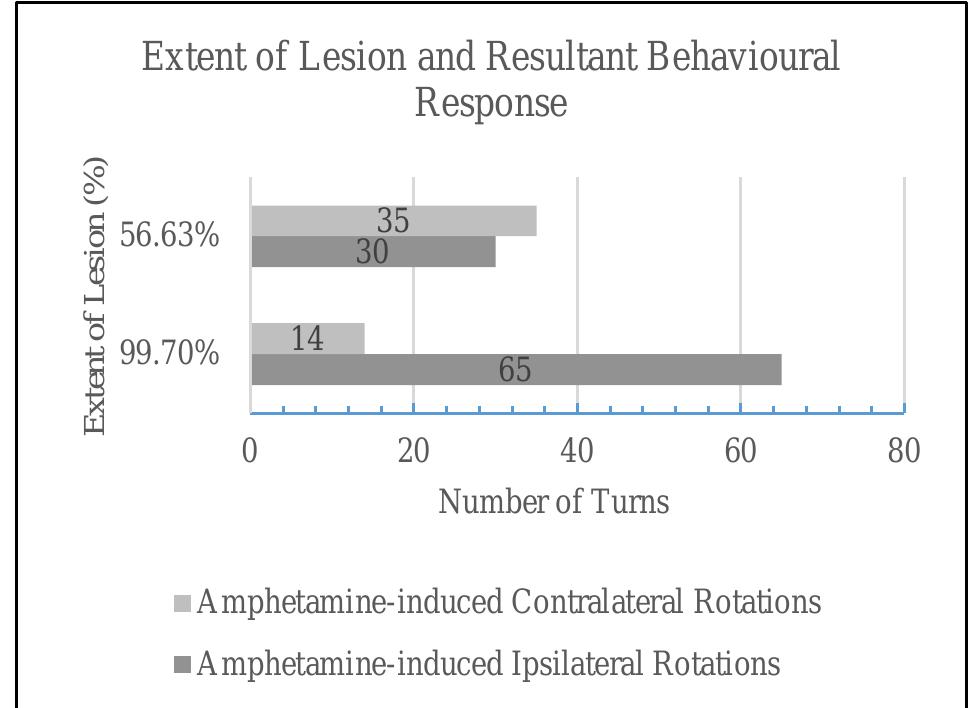
6-OHDA, a neurotoxin, selectively destroys dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons of the nigrostr... more 6-OHDA, a neurotoxin, selectively destroys dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons of the nigrostriatal pathway. Similarly, in this research study, we did an MFB injection of 6-OHDA. Predicted rotational behavior is noted .
DownloadEdit