(Closed) SENTINEL – Novel injectable biosensor for continuous remote monitoring of cancer patients at high-risk of relapse - UT Austin Portugal (original) (raw)
Summary
Worldwide, the estimated number of people alive within 5 years of a cancer diagnosis is 43.8 million. Despite prostate-specific antigen (PSA) being the first approved cancer biomarker for diagnosing and screening prostate cancer, the benefits of PSA based screening for prostate cancer do not outweigh its harms. The SENTINEL project will develop a minimally invasive and biocompatible implantable biosensor based on novel plasmonic particles and hydrogel-based formulations.
We know that cancer, when identified early, is likely to respond more effectively to treatment, resulting in a greater probability of survival, hence less morbidity, and lower cost of treatment. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) of cancer diseases can potentially generate personalized patient data, and support the detection of disease onset or its progression. So far, RPM has been predominantly applied for the monitorization of vital signs. The extension of RPM to the cancer field would constitute a significant jump forward in preventing and early diagnosing high-risk profile patients.
SENTINEL proposes to acquire transdermal Raman signals based on the implanted biosensor using a handheld device and to analyze acquired data using machine learning algorithms. The development of computational predictive diagnostic protocols will enable the breakthrough development of remote monitoring tools for cancer patients at higher risk of tumour relapse.
The technology aims to increase the positive predictive value of cancer screening while facilitating the remote and ubiquitous monitoring of patients at a large scale.
Expected Outcomes
- A novel generation of products and components, as well as related intellectual property;
- Novel injectable hydrogels, novel plasmonic nanoparticles and novel injectable formulations to be used in the monitoring of clinically relevant physiological biomarkers;
- An overarching system of cloud-based data processing and diagnostic analysis software system to support the adoption of biosensor technology in the relevant healthcare context.
| Start Date – End Date: | April 1, 2020 – April 1, 2023 |
|---|---|
| Scientific Area: | Nanotechnology and Advanced Computing |
| Keywords: | Cancer, biosensor, SERS, remote monitoring, artificial intelligence |
| Lead Beneficiary (PT): | Stemmatters – Biotecnologia e Medicina Regenerativa S.A. |
| Co-beneficiaries: | Laboratório Ibérico Internacional de Nanotecnologia (LIN) Universidade do Minho Centro Clínico Académico – Braga, Associação |
| PIs at UT Austin: | James Tunnell (Cockrell School of Engineering, Department of Biomedical Engineering, UT Austin) |
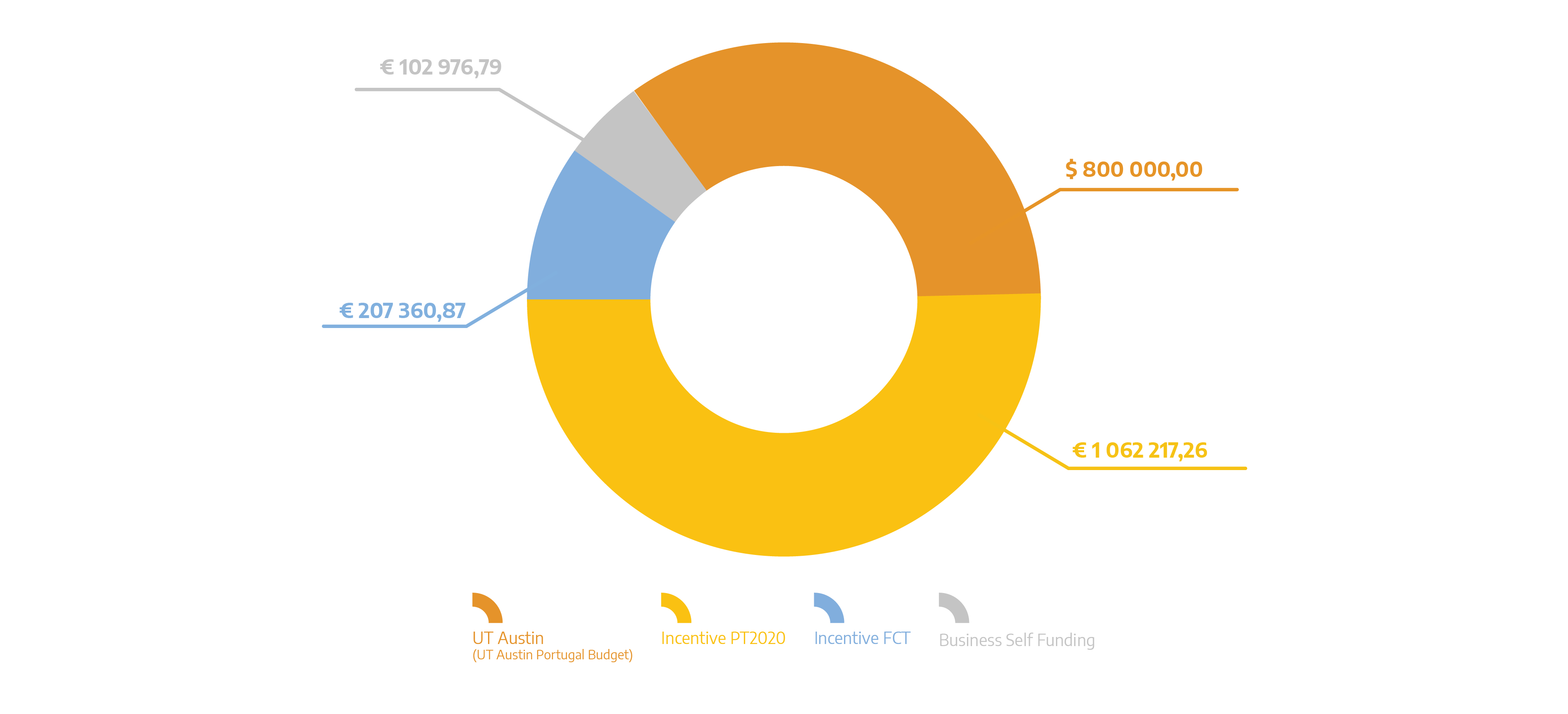
| Total Eligible Investment (PT): | 1 372 554,92 EUR |
| Total Eligible Investment (US): | 800 000,00 USD |
| Funding Sources Distribution: |
Papers and Communications
- Hashemi, M., King, J., Chen, M., Relvas, M., Aranda, M., Cela, S. A., Dieguez, L., & Tunnell, J. (2022). Machine Learning Model for Multiplexed Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Quantification in Skin. In Biophotonics Congress: Biomedical Optics 2022 (Translational, Microscopy, OCT, OTS, BRAIN). Clinical and Translational Biophotonics. Optica Publishing Group. https://doi.org/10.1364/translational.2022.tw3b.7
E-Posters
2020 Annual Conference
2021 Annual Conference
Co-funded by: