Aberfoyle International Security (original) (raw)
Post navigation
AIS Special Report
June 13, 2025
Andrew McGregor
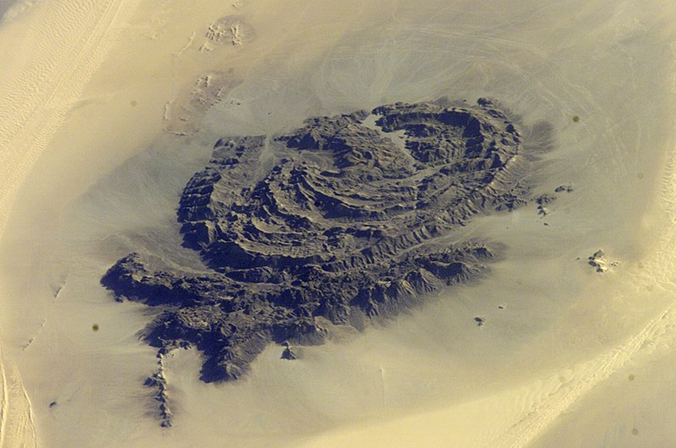
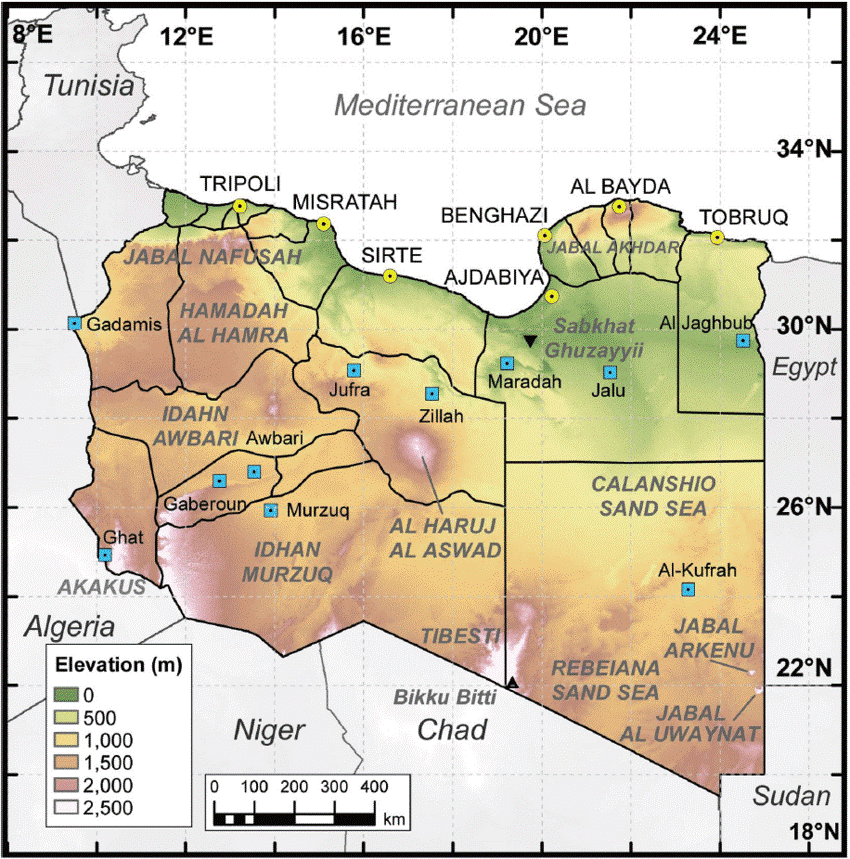
The year was 1923, and Egyptian explorer Hassanein Bey was on a camel-borne search for two “lost oases” in the unknown depths of the Libyan Desert. Even the South Pole had been visited less than 12 years earlier, but this corner of the south-eastern Libyan Desert remained blank on most charts despite rumors of two mountains where water could be found in an otherwise barren, burning wasteland. Hassanein Bey and his small party of desert dwellers were 111 days out from his starting point in the Libyan port of Sollum when an amazing sight appeared:
We were having a hard time of it crossing the high steep sand-dunes when suddenly mountains rose before us like medieval castles half hidden in the mist. A few minutes later the sun was on them, turning the cold gray into warm rose and pink… I had found what I came to seek. These were the mountains of Arkenu. [1]
Though Jabal Arkenu defined remote isolation at the time, Hassanein believed that “Arkenu may conceivably prove to have strategic value at some future time.” The explorer was right; only days ago the desert round Arkenu was the scene of a battle with great implications for the future of Sudan.
The Spiral Sisters
The area around Jabal Arkenu and its larger sister mountain Jabal ‘Uwaynat (25 km south-east of Jabal Arkenu) now mark the intersection of the borders of Libya, Egypt and Sudan, with the north-eastern corner of Chad not far to the south. As such, the region is now known as the Triangle area (al-Muthalath). The region around Jabal ‘Uwaynat, once a path for the Ancient Egyptians into the African interior according to recently discovered inscriptions, has now become a pathway for smugglers, mercenaries, rebels, human traffickers and gold miners. [2] In an otherwise waterless region, the massive spiral mountains collect local rainfall in natural basins within the rocks, a fact long known to the indigenous Tubu desert dwellers who brought their camels there to graze and water.
The recent discovery of gold in the region has attracted artisanal gold miners who operate in the region with little regard to borders. Egypt and Libya are seeking to replace these miners with modern mining operations, while Sudan is satisfied to collect fees through the Sudanese Minerals Resources Company without providing any services (Radio Dabanga, November 8, 2024).
The Attack on the Triangle
One hundred and two years after Hassanein Bey rediscovered the lost mountain oases, war has arrived in al-Muthalath. Possession of the desert crossing that passes through the Triangle region has suddenly become a strategic imperative for Sudanese government forces (the Sudan Armed Forces – SAF) and their adversaries in Sudan’s civil war, the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) led by Muhammad Hamdan Daglo “Hemetti.” The latter group, once a government paramilitary before breaking with the SAF, has acquired the support of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and an Islamist militia belonging to the so-called Libyan National Army of “Field Marshal” Khalifa Haftar.
This militia, known as Subul al-Salam (“Ways of Peace”), crossed 3 km into Sudan near Jabal Arkenu on June 6 in support of RSF units (Sudan Tribune, June 11). The joint Libyan-RSF movement displaced the main Sudanese units controlling the border, the Central Reserve Forces (a police paramilitary) and the Darfur Joint Force (Atalyar, March 21; Sudan Tribune, March 22). The SAF presence consisted of only a small number of intelligence and security agents (Mada Masr, June 14). The Darfur Joint Force (a.k.a. Sudanese Joint Force, or Juba Peace Agreement Joint Forces) consists of rebel forces that were signatories to the 2020 Juba Peace Agreement and have since sided with the Port Sudan-based Sudan government. The main elements hail from Darfur’s powerful Zaghawa minority – the Sudan Liberation Movement – Minni Minawi (SLM-MM) and Jibril Ibrahim’s Justice and Equality Movement (JEM). Some SLA fighters may be using Emirati-supplied weapons obtained when they were fighting as mercenaries on behalf of Khalifa Haftar before the signing of the Juba peace agreement (France24.com, April 20).
Fighting began on June 8. The RSF announced its takeover of the Triangle border region on June 11, claiming heavy SAF losses (AFP, June 11). After a “defensive withdrawal” of government forces, the closest Sudanese army presence may now be 400 km from the Triangle region (Sudan Tribune, June 11). According to the RSF, the region contains “rich natural resources, including oil, gas and minerals (Rapidsupportforce.com, June 12).
The SAF said its forces in the Triangle region were subject to a “surprise attack” by the RSF’s “terrorist militia” and Libya’s Subul al-Salam battalion (Libya Observer, June 11). Sudan’s military further declared the role of the Libyan militia was “a reprehensible and unprecedented gesture and a flagrant violation of international law… the direct intervention of Khalifa Haftar’s forces alongside the Rapid Support Forces in the war is a blatant aggression against Sudan, its land, and its people, and an extension of the international and regional conspiracy against our country…” (Darfur 24, June 10).
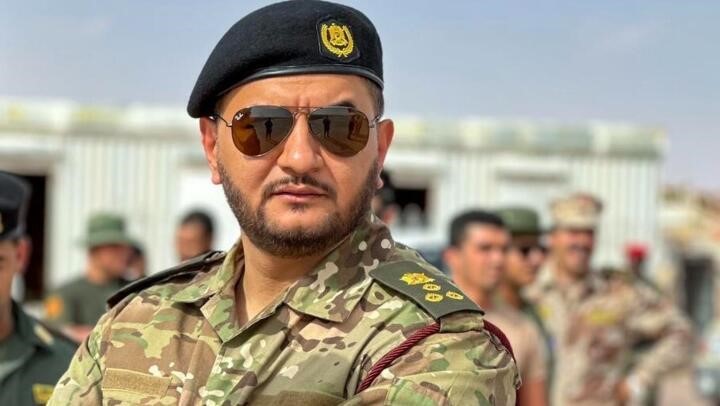
 ‘Abd al-Rahman Hasham al-Kilani
‘Abd al-Rahman Hasham al-Kilani
For his part, Subul al-Salam commander ‘Abd al-Rahman Hasham al-Kilani brushed over the encounter, claiming it was the result of a “misunderstanding” with the Darfur Joint Force, which believed the Libyan militia had crossed the border (Mada Masr, June 14). Haftar’s military command described allegations of participation by his forces as false and “a blatant attempt to export Sudan’s internal crisis” (Radio Dabanga, June 12).
 Colombian mercenaries after their convoy was attacked in North Sudan, November 20, 2024 (La Silla Vacía)
Colombian mercenaries after their convoy was attacked in North Sudan, November 20, 2024 (La Silla Vacía)
Late last year, a battalion of at least 350 Colombian mercenaries began moving in stages from Abu Dhabi to Benghazi, through the desert to the Kufra district and then south across the border into northern Darfur using a crossing just south of the Triangle region. The mercenaries, combat-experienced veterans of the Colombian army, were recruited by Dubai-based Colonel Álvaro Quijano on the understanding they would be deployed as static defense for oil installations in the Middle East. Instead their passports were seized by Libyan soldiers in Benghazi who explained they were being sent south to fight alongside the RSF in Sudan. Quijano, a Colombian, is an associate of a private security firm, the UAE-based Global Security Service Group. One convoy was ambushed by the Darfur Joint Force after crossing the border into Sudan, leading to the loss of three men. Once in Darfur, some of the Colombians have been sent into street-to-street fighting in the besieged North Darfur capital, al-Fashir, while others have been sent to train RSF fighters in Nyala, capital of South Darfur (La Silla Vacia [Bogota], November 26, 2024; March 2, 2025; March 3, 2025).
The Salafists of Kufra
The oasis of Kufra in south-eastern Libya, home of the Subul al-Salam brigade, was for centuries a major stage for trans-Saharan caravans and the shipment of slaves until its conquest by Italy in the 1930s. Kufra was dominated for centuries by indigenous Black semi-nomadic Tubu tribesmen until they were displaced by Zuwaya Arabs in 1840. Since the 2011 Libyan Revolution, Kufra has become an important stage for the transportation of sub-Saharan African migrants moving through the Triangle region to the Mediterranean coast, with numerous clashes occurring between the rival Zuwaya and Tubu communities (Libya Observer, March 5, 2018).
The brigade was formed by ‘Abd al-Rahman Hashim al-Kilani, a Madkhali Salafist, after Zuwaya clashes with the Tubu and their Darfuri allies in 2015. Salafism is a revivalist interpretation of Islam that believes Islam’s authentic form was found in the time of the Prophet Muhammad and his first three successors (the Salaf). With the encouragement and funding of Saudi Arabia, Salafism has grown rapidly in recent decades, often displacing traditional and more flexible forms of Islam around the world. It has become associated in its most extreme form with political and religious violence (Salafi-Jihadism). Madkhalism is a form of Salafism developed by Saudi shaykh Rabi’ bin Hadi al-Madkhali that emphasizes a “quietist” approach to religion, avoiding overt political involvement while emphasizing obedience to authoritarian leaders. Madkhalism has found fertile ground in Libya, where its followers have formed powerful militias in Kufra, Tripoli and other regions. [3]
Salafists oppose Sufi approaches to Islam, rejecting their rites and rituals as bid’ah (religious innovation, i.e. practices that did not exist in the times of the Salaf). Libya has a strong Sufi tradition, with the powerful Sanusi order leading the resistance to Italian colonialism. Though Kufra was the traditional headquarters of the Sanusi Sufi order, the anti-Sufi Madkhalists destroyed the funerary shrine of Sanusi leader Sayyid Muhammad al-Mahdi al-Sanusi (1844-1902) and stole his remains in 2018 (Terrorism Monitor, April 6, 2018). Since then, the Madkhalist Salafis have held the upper hand in southeastern Libya.
After its formation, Subul al-Salam quickly aligned with the forces of General Khalifa al-Haftar (a leading military commander under Mu’ammar Qaddafi until his defeat by Chadian forces in the 1987 “Toyota War” and later an alleged anti-Qaddafi CIA asset after his exile to the United States), who supplied the Zuwaya fighters with 40 armored Toyota trucks (Libya Herald, October 20, 2016).
Libya is currently divided politically between two factions – the Tobruk-based Libyan House of Representatives (HoR) dominated by al-Haftar’s Libyan National Army (LNA – an alignment of various militias and other armed groups under al-Haftar’s command rather than a true “national army”) versus the internationally recognized Government of National Unity (GNU) based in Tripoli. The latter controls western Libya (Tripolitania), while al-Haftar’s LNA controls the east (Cyrenaïca) and the south-west (Fezzan).
Tribal ties remain important in Libya; it is worth noting al-Haftar’s mother was from the Zuwaya, who have established a trading network from Kufra in the south to the Mediterranean coast in the north. Al-Haftar relies for weapons and other support from Russia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), which is also believed to supply weapons to the RSF. Prior to the Libyan offensive, satellite imagery revealed an increase in UAE cargo aircraft arriving at the Kufra airport, including three IL-76TD cargo planes present between May 21 and May 31 (X, June 10). After the Libyan/RSF takeover of the Triangle region, the Sudanese Foreign Ministry denounced the “dangerous escalation of the Abu Dhabi regime-sponsored external aggression against Sudan,” describing it as a “flagrant violation of international law” (Al-Monitor, June 11; Fes News, June 11). The ministry further condemned the “blatant aggression… supported by the United Arab Emirates and its militias in the region” (Radio Dabanga, June 12). Al-Haftar also has Egyptian backing and has been supported in the field by Russian military contractors, most notably in his failed 2019 campaign to take Tripoli and unite Libya under his rule.
The Subul al-Salam brigade has clashed with Sudanese fighters before, killing 13 members of the Darfuri Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) in 2016. The members of JEM, a mainly Zaghawa rebel group, were operating as mercenaries near the oasis of Jaghbub at the time alongside a group of indigenous Black Tubu fighters.
Saddam al-Hafter – The Heir Apparent
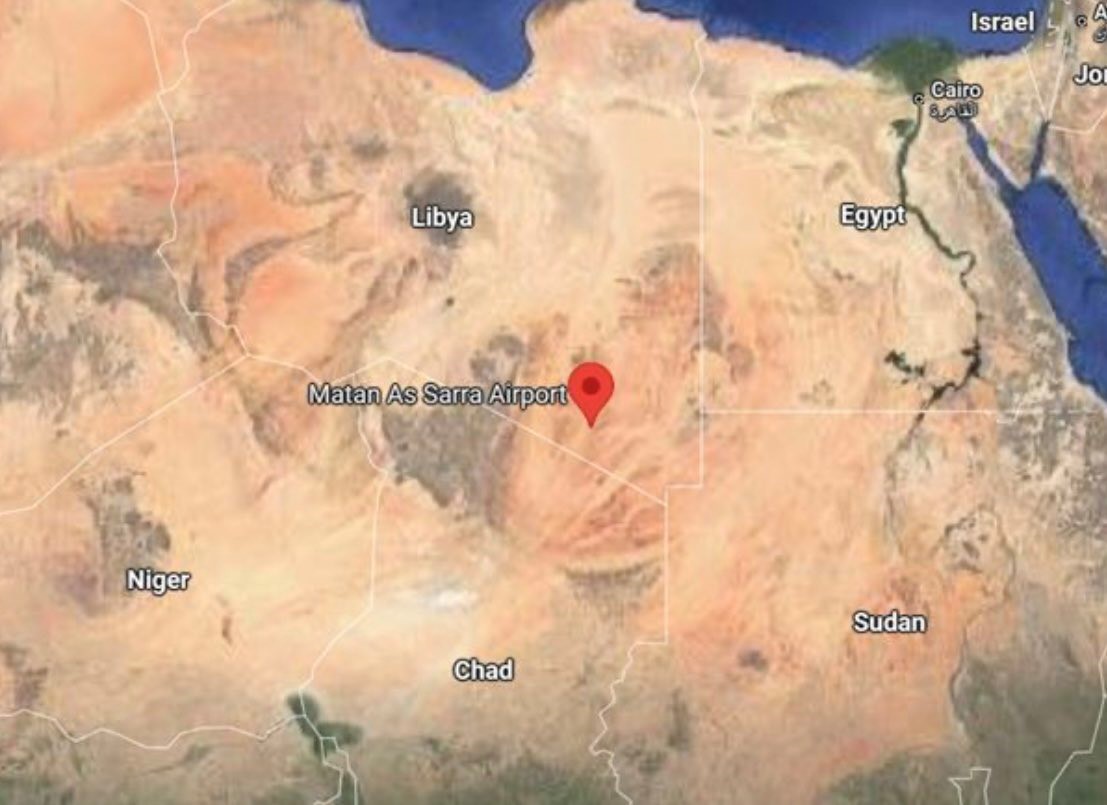
Subul al-Salam comes under the direction of Khalifa Haftar’s son, Saddam, who is being groomed to succeed his 81-year-old father. At the same time the Russian-backed Khalifa is being supplied with heavy weapons, armored vehicles and Pantsir air defense systems by the Kremlin, Saddam has been holding quiet meetings in Washington with top state department and intelligence officials in the Trump administration (Militarnyi.com, May 26; MEE, June 12). Saddam is overseeing the Russian rehabilitation of a disused Qaddafi-era airbase (Matan al-Sarra) in southeastern Libya for use by Russia’s Africa Corps (EDM, April 17). Al-Haftar has already been accused of using Matan al-Sarra as a distribution point for arms headed to the RSF. (Sudan Tribune, June 11). When completed, Matan al-Sarra will join six other bases used by Russian forces in Haftar-controlled regions of Libya – al-Khadim, al-Jufra, Brak al-Shati, al-Wigh, Tamanhint, and al-Qardabiya
RSF Strategic Objectives
The RSF is looking to take the war into the Northern Province (home of the Arab-Nubian elites that have governed Sudan since independence), and notes that control of the Triangle region “is a significant step that will impact multiple combat front lines, particularly in the northern desert” (Rapidsupportforce.com, June 12). The RSF is dominated by Sudan’s western Arabs (residents of Kordofan and Darfur) who have been rivals of the more politically and economically successful northern Arabs since the days of the Mahdiyya (1881-1899).
As a step towards consolidating control of northern Sudan and supply lines from southern Libya, the RSF took al-Malha (a Meidobi town 210 km northeast of al-Fashir) in March, killing 40 people and burning down the market after looting it. Al-Malha connects northeast to the strategic Nile town of al-Dabba in Northern State via the Wadi al-Milk and east to the town of Hamrat al-Shaykh in North Kordofan, which the RSF hopes to incorporate into a new state together with Darfur, one independent of the Transitional Sovereignty Council (TSC) government and the SAF in the temporary Sudanese capital in Port Sudan.
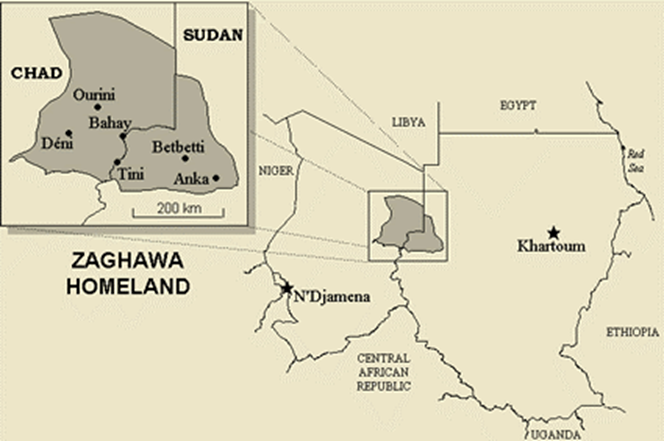 The RSF is increasingly concerned that it may lose its most important supply line for UAE arms and military materiel, which runs from an Emirati-built airbase in Um Jaras (or Amjarass, Ennedi province) east into West Darfur. SAF commander and TSC chairman General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan has demanded that Chad dismantle the Um Jaras base and close Chad’s border with Darfur to RSF-destined logistical convoys. Chad’s ruler, Mahamat Idris Déby Itno, like many of Chad’s ruling elite, is a member of the Zaghawa ethnic group, which straddles the Chad-Sudan border. However, the Darfur Zaghawa oppose the Arab-dominated RSF and sent a delegation of elders in February to meet with President Déby to urge an end to Chadian accommodation of the RSF (Mada Masr, March 7). Should Chad’s leadership decide to back away from the RSF, the establishment of a secure alternative supply route for UAE arms and supplies through Libya to northern Sudan will become imperative.
The RSF is increasingly concerned that it may lose its most important supply line for UAE arms and military materiel, which runs from an Emirati-built airbase in Um Jaras (or Amjarass, Ennedi province) east into West Darfur. SAF commander and TSC chairman General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan has demanded that Chad dismantle the Um Jaras base and close Chad’s border with Darfur to RSF-destined logistical convoys. Chad’s ruler, Mahamat Idris Déby Itno, like many of Chad’s ruling elite, is a member of the Zaghawa ethnic group, which straddles the Chad-Sudan border. However, the Darfur Zaghawa oppose the Arab-dominated RSF and sent a delegation of elders in February to meet with President Déby to urge an end to Chadian accommodation of the RSF (Mada Masr, March 7). Should Chad’s leadership decide to back away from the RSF, the establishment of a secure alternative supply route for UAE arms and supplies through Libya to northern Sudan will become imperative.
Notes
- AM Hassanein Bey: The Lost Oases, New York and London, 1925, pp. 210-217.
- Andrew McGregor, “Egyptian exploration of the African interior – Caravans to Yam,” Ancient History Magazine 15, April/May 2017, pp. 38-45. For Jabal ‘Uwaynat, see: “Jabal ‘Uwaynat: Mysterious Desert Mountain Becomes a Three-Border Security Flashpoint,” AIS Special Report, June 13, 2017, https://www.aberfoylesecurity.com/?p=3930
- Andrew McGregor, “Radical Loyalty and the Libyan Crisis: A Profile of Salafist Shaykh Rabi’ bin Hadi al-Madkhali,” Jamestown Foundation, January 2017, https://www.aberfoylesecurity.com/?p=5244
Andrew McGregor
AIS Special Report
June 2, 2025
During an April meeting with Italian prime minister Giorgia Meloni, President Donald Trump made a reference to the Congo, quickly adding “I don’t know what that is…” (Africa News, April 21). Trump’s senior advisor for Africa, Massad Boulos (whose son is married to Trump’s daughter, Tiffany), quickly reassured Africans that, despite his unfamiliarity with Africa’s second-largest country and its 110 million people, Trump “highly values Africa and African people… Africa is very important to Trump” (BBC, April 23).
Three weeks earlier, Boulos had provided the news that the United States was engaged in talks related to a security-for-critical minerals agreement with Congolese president Felix Tshisekedi (similar to that proposed to Ukraine), adding that “I am pleased to announce that the president and I have agreed on a path forward for its development.” According to Tshisekedi, American might would help keep armed factions like the Congo’s powerful rebel M23 movement “at bay” (AP, April 3). The M23 is widely believed to receive substantial military support from neighboring Rwanda.
It is difficult to say how this military security might be provided. The Congolese government envisions US forces replacing the massive but ineffective UN contingent in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), but any deployment of American troops under the current administration seems unlikely. General Michael Langley, commander of U.S. Africa Command (AFRICOM), told a gathering of African military leaders on May 29: “You can no longer depend on the military strength or the financial support of the United States” (Garowe Online, May 31). Washington is considering folding AFRICOM into US European Command, another step in abandoning the resource-rich continent to Russia (Reuters, May 27).
Further complicating matters is the endemic corruption and expectation of bribes that runs unchecked through Congolese society and all its business and government institutions. China has managed to navigate this system with some success in the Congo’s mineral sector through government investment and subsidies to become the DRC’s main mineral partner. Beijing is also expanding its military cooperation with African nations as America’s military steps back (Business Insider Africa, May 31).
The US administration is currently sponsoring peace negotiations between M23 and the government in Kinshasa. With both sides in the conflict having submitted draft peace agreements, US mining firms are reported to have expressed interest in operating in the Congo (The Africa Report, May 28).
The Battle for Tantalum
Tantalum is an especially rare critical mineral, yet its unique properties make it vital in the electronics industry and the manufacture of computer chips and medical implants. Everything from fighter jets to nuclear reactors to smart phones rely on tantalum, with new uses and demand growing daily (Institut für seltene erden und metalle AG [Lucerne], August 2024). The DRC is the world’s largest producer of tantalum, most of it coming from the northeastern provinces of Nord and Sud Kivu, war plagued regions rich in copper, tin, tungsten, gold, cobalt, lithium and the coltan from which tantalum is extracted (Mining.com, April 17).
In 2023, the DRC claimed Rwanda, a country with few mineral deposits of its own, was exporting over $1 billion a year in tantalum, tin, tungsten and gold: “It’s all coming from DRC – that’s obvious” (Financial Times, March 21, 2023). Nonetheless, Rwanda claims to be “among the top producers of Tantalum, producing about 9 per cent of the world’s Tantalum used in electronics manufacturing” (The Great Lakes Eye, November 7, 2023). Between them (regardless of actual origin), the DRC and Rwanda account for 58% of world production of tantalum, the price of which has risen 25% since January due to the insecurity in Kivu (Discovery Alert, May 7). The United States obtains all its tantalum from foreign sources, its own reserves of coltan being of poor quality.
The Warlord of Kivu: Sultani Makenga
“In brief, my life is war, my education is war, and my language is war” (New African, February 15, 2013). In this way, Congolese “General” Sultani Makenga defines his life and purpose as part of an endless cycle of conflict and brutality centered on the Congolese province of Nord Kivu. As the military leader of M23, Makenga currently dominates the eastern Congo and its production of critical minerals.
Like many of his contemporaries, Makenga is the product of the 1994 Rwandan genocide of Tutsis by their Hutu neighbors that eventually spilled over into the neighboring Nord and Sud Kivu provinces of the eastern DRC. Sharing borders with Uganda and Rwanda, the Kivu region is rich in minerals and other resources, but residents cope with poverty and violence as the region has become a relentless battleground for local Tutsis, exiled Hutu g énocidaires, Islamist extremists, bandit groups, a deeply corrupt Congolese army and regulars of the Ugandan and Rwandan militaries.
Under Makenga’s direction, Nord Kivu’s M23 movement has been accused of committing numerous atrocities and human rights violations, including massacres of civilians, mass rapes and the recruitment of child soldiers (US Treasury Department, November 13, 2012). Makenga is unapologetic for his role in the violence that plagues the Kivu region:
I am a soldier, and the language that I know is that of the gun. My home has been in the bush, fighting injustice and corrupt regimes in this region. Therefore, when a politician wants to play politics with me, my response won’t be the political podium but the barrel of the gun because that’s my way of fighting for my rights (New African, February 15, 2013).
Makenga’s Early Life
Makenga enjoys a reputation as one of the finest strategists and tacticians in east-central Africa (ChimpReports, February 6, 2017). Always well-guarded, Makenga avoids making speeches or public appearances, and walks with a cane after being wounded in Katanga during a rebellion there in the late 1990s (Le Monde, April 7, 2023).
This Tutsi warlord was born in the Nord Kivu town of Masisi in 1973 with the full name of Nziramakenga Ruzandiza Emmanuel Sultan, but grew up in the nearby town of Rutshuru. Makenga is a member of the Mugogwe sub-group of the Tutsi (New African, February 15, 2013). Like Makenga, many members of the M23 group are Congolese Tutsis closely related to the Tutsi population in neighboring Rwanda. Many of the Congo’s Tutsis descend from Rwandan migrant workers encouraged by Belgian colonialists to settle in Nord Kivu in the 1930s; as a result, accusations of being “foreigners” frequently surface during regional episodes of ethnic tension. Part of the M23’s effort to establish local control in these communities includes the destruction of records delineating the lineage of traditional authority in Nord Kivu (The Conversation, October 24, 2024).
The Rwandan Civil War
After dropping out of school, Makenga moved to Uganda, where he underwent six months of military training. He then joined the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) in 1990 at age 17 with the intention of fighting the anti-Tutsi regime of President Juvénal Habyarimana in Rwanda before the president’s assassination in 1994 (New African, February 15, 2013). The RPF was a movement of Tutsi exiles determined to end Hutu domination of Rwanda and restore “traditional” Tutsi rule.
Despite the minimal education common to herding boys like Makenga and a difficulty in speaking French or English (though he is fluent in Swahili and Kinyarwanda), the young Makenga rose to the rank of sergeant by the end of the conflict, one of the highest ranks available to Congolese Tutsis in the RPF (Le Monde, April 7, 2023; Riftvalley.net, 2018). He became known for his tactical skills, especially in setting ambushes (Riftvalley.net, 2018).
Roughly one million Hutus fled Rwanda after the RPF victory left them fearing retribution for the murder of 800,000 Tutsis and politically moderate Hutus. After their arrival in Nord Kivu, the Hutu destabilized the whole region by forming extremist militias (Interhamwe) that mounted cross-border raids and attacked local Congolese Tutsis. Little help could be obtained from the corrupt and incompetent army of dictator Mobutu Sese Seko, the Forces Armées Zaïroises (FAZ – the Congo was renamed Zaïre from 1981 to 1997). Their failure to provide security would eventually lead to a national rebellion supported by Rwanda and Uganda that would depose Mobutu.
When the Tutsi-Hutu struggle in Rwanda ended in 1996, Makenga decided to return home to the DRC and “fight for my country.” It was then that he met Laurent-Désiré Kabila and together, in Makenga’s words, “launched the liberation struggle for the Congo” (New African, February 15, 2013).
Makenga and the First Congo War – 1996-1997
Kabila’s chief strategist, the Rwandan James Kabarebe, led the rebel Alliance des Forces Démocratiques pour la Libération du Congo-Zaïre (AFDL), a coalition that captured Kinshasa, overthrew Mobutu and seized power on May 17, 1997. Burundi and Angola joined Uganda and Rwanda in supporting the broad-based military operation. Zaïre was renamed the “Democratic Republic of the Congo” (DRC) and Laurent-Désiré Kabila installed as the DRC’s new president.
Makenga broke with Kabila in 1997, accusing him of continuing the marginalization of the Congolese Tutsis. A refusal to obey AFDL orders left Makenga to serve a term on the Rwandan prison island of Iwawa in Lake Kivu (Le Monde, April 7, 2023).
The Congolese Tutsis who played a prominent part in the overthrow of Mobutu were later branded as “foreigners” by now-President Kabila, who insisted they “return” to Rwanda (New African, February 15, 2013). His declaration repeated Mobutu’s own November 1996 order for Congolese Tutsis to leave the country. As Makenga reflected: “You help someone to become president through the gun, but when he tastes power, you become his first victim” (New African, February 15, 2013).
Makenga and the Second Congo War – 1998-2003
Now opposed to the rule of Kabila, who had expelled his Rwandan supporters and persecuted the Congolese Tutsis, Makenga joined Uganda’s elite Nguruma Battalion. The unit took part in an audacious operation planned by Rwanda’s James Kabarebe, former chief-of-staff of Kabila’s armed forces before his dismissal in July 1998. The Kitona Airlift of August 1998 began with the capture of the airport at Goma (provincial capital of Nord Kivu) and the hijacking of four civilian passenger planes, which over two days ferried some 3,000 Rwandan and Ugandan troops 1200 miles to the DRC’s far west, where they seized the Atlantic port of Matadi and the Inga Dam, cutting off power to the capital of Kinshasa. The bold plan only failed due to the intervention of Zimbabwean, Namibian and Angolan troops. Both the operation and its repression were marked by widespread rape, murder and looting on all sides. Back in Nord Kivu, Rwandan forces attacked camps believed to host the Hutu militia known as the Forces démocratiques de libération du Rwanda (FDLR).
After nearly three years of war, Joseph Kabila succeeded his father Laurent as president after the latter’s assassination by one of his cousins on January 16, 2001. Joseph Kabila would remain president until 2019, when he was succeeded by current president Félix Tshisekedi after a series of bloody mass protests against his rule.
 Joseph Kabila (The Africa Report)
Joseph Kabila (The Africa Report)
Makenga became a major in the Rwandan-backed Tutsi rebel movement Rassemblement congolais pour la démocratie (RCD) in 1998. Many members were veterans of the AFDL. The movement succeeded in taking Goma in August 1998, but by 1999-2000, the group had splintered, diminishing its importance before a regional agreement brought an end to the Second Congo War in 2003.
Makenga and the New War of the CNDP
Backed by Uganda and Rwanda, the anti-Kabila General Laurent “The Chairman” Nkunda formed the Nord Kivu-based Congrès national pour la défense du people (CNDP) in December 2006. Kabila had fallen out of favor with his former backers, including Makenga, who joined many AFDL/RCD veterans in the new movement.
An October 2008 CNDP offensive brought the group to the outskirts of Goma after the Congolese garrison had looted the city and fled. Instead of occupying the city, Nkunda declared a unilateral ceasefire, creating dissension among CNDP fighters (al-Jazeera, October 30, 2008; UNSC November 2008 Monthly Forecast, October 30, 2008).
CNDP fighters under Makenga’s command were accused of participating in the November 4-5 2008 massacre of 67 civilians in the Nord-Kivu town of Kiwanja despite the nearby presence of UN peacekeepers who failed to intervene (Independent Online [Johannesburg], June 19, 2012).
After a violent split in the movement, Nkunda was arrested by Rwandan authorities in January 2009. General Bosco “The Terminator” Ntaganda (a Rwandan Tutsi) took over one faction of the movement, which quickly began cooperating with the Congo’s new national army, the Forces Armées de la République Démocratique du Congo (FARDC), against Hutu rebel movements (For Ntaganda, see Militant Leadership Monitor, August 31, 2012). FARDC is known for its indiscipline, poor morale and habitual shortages of food, ammunition and salaries.
Both CNDP factions were given refuge by Rwanda and Uganda, which ignored DRC extradition requests for Makenga and others (Africa Confidential, July 7, 2022). The CNDP agreed to a peace accord brokered in Nairobi on March 23, 2009 that saw many of its fighters integrated into the FARDC. Makenga was made a colonel in FARDC and served in Sud Kivu (Riftvalley.net, 2018; Le Monde, April 7, 2023).
The M23
On April 4, 2012, Ntaganda and 300 loyalists deserted the DRC but took losses in a clash with FARDC in the Rutshuru district (ChimpReports, February 6, 2017). Makenga, then second-in-command of DRC operations against the Hutu FDLR, followed Ntaganda by deserting in May. With his experience, he was made a general in the new M23 movement and took military command of the rebel force. Joseph Kabila suspended joint operations with Rwanda when the number of desertions to M23 became critical.
The new formation’s name, M23, derived from its demand for the full implementation of the March 23, 2009 accord between the DRC and the CNDP, which the DRC government was backing away from. Fuelling the new insurgency was the government’s failure to stabilize the eastern Congo and its inability to provide services to local people.
In November 2012, Makenga attracted international attention when UN defenders fled Goma and his forces briefly captured the city, the capital of Nord Kivu. It was apparently a step too far for his backers; visits from Rwandan Army chief Lieutenant General Charles Kayonga and top Ugandan officers encouraged Makenga to withdraw (ChimpReports, February 6, 2017).
Makenga claims to have taken advantage of FARDC’s corruption to equip his force: “When the Kinshasa government buys new weapons, I also get a share of it through my own contacts within the Congolese national army” (New African, February 15, 2013).
Makenga was sanctioned by the US in November 2012 for “contributing to the conflict in the DRC” (US Treasury Department, November 13, 2012). Specifically, Makenga was cited for committing or being responsible for murder, rape of children as young as eight, kidnapping and forcible recruitment of children in Makenga’s Rutshuru home territory (UNSC, October 29, 20_;_ BBC Africa, November 7, 2013; New African, February 15, 2013). According to Navi Pillay, then U.N. High Commissioner for Human Rights: “The leaders of the M23 figure among the worst perpetrators of human rights violations in the Democratic Republic of Congo, or in the world for that matter” (UN News, June 19, 2012).
M23 Defeat and Split – 2013
Factionalism disrupted M23 operations, preventing the group from exploiting its successes in Nord Kivu. Makenga was deeply involved in the splits, first coming to blows with a faction led by Bishop Jean-Marie Runiga Lugerero. In February 2013, Bishop Runiga, other M23 leaders and several hundred fighters were given refuge in Rwanda after intense fighting with the Makenga faction (East African, July 13, 2013).
Makenga’s forces also clashed with those of Bosco Ntaganda in March 2013 after Makenga learned Ntaganda was planning to have him killed. Ntaganda’s attack on Makenga’s base was repulsed with heavy casualties, forcing Ntaganda and 200 men to also take refuge in Rwanda. Ntaganda turned himself in to the US Embassy in Kigali and was extradited to face an ICC proceeding in the Hague (Al-Jazeera, November 5, 2013; ChimpReports, February 6, 2017).
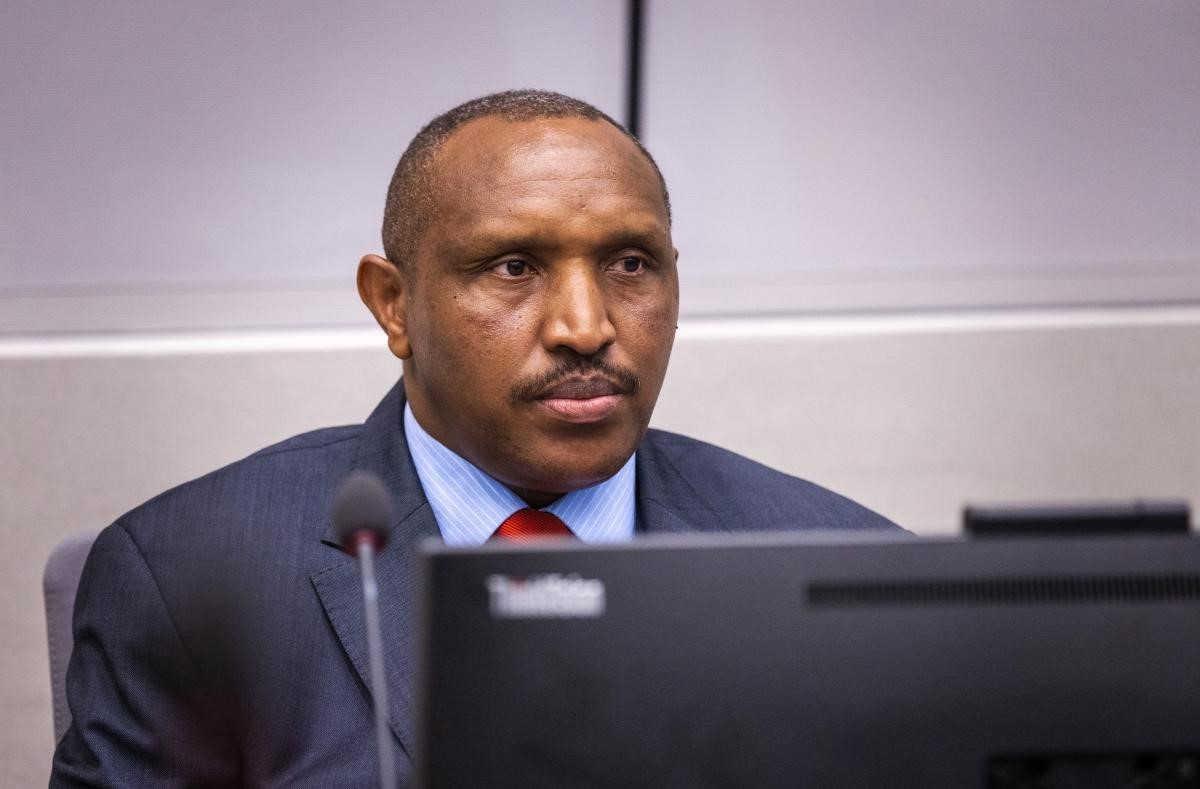 The Terminator on Trial: Bosco Ntaganda at the ICC
The Terminator on Trial: Bosco Ntaganda at the ICC
In November 2013 it was Makenga’s turn to flee Nord Kivu after defeat at the hands of FARDC and the UN’s Force Intervention Brigade. Rather than Rwanda, Makenga and other members of M23 crossed into Uganda, where they surrendered to authorities. The collapse of M23 through infighting and external military pressure led to the Kampala-brokered Declarations of Nairobi ceasefire agreement signed on December 12, 2013 by the DRC Government and the M23 movement.
Reviving the M23
In November 2016 Makenga left a demobilization camp in Uganda, crossed into Nord Kivu and began recruiting from Tutsi refugee camps in an effort to revive the M23 (ChimpReports [Kampala], November 13, 2016). He was joined there by former CNDP fighters who left their cantonment in Uganda.
Beginning with a small group of 400 men, Makenga eventually relaunched the M23 rebellion in November 2021. A new offensive took large parts of Nord Kivu before a ceasefire in November 2022. Makenga, however, accused the DRC authorities of insincerity: “If they desire peace, we will achieve it together. If they choose war, we will fight. That is our stance” (Igihe [Kigali], July 7, 2023).
Retaking Nord Kivu – 2024-2025
A July 2024 report by the UNSC Group of Experts presented evidence that the UPDF and Ugandan military intelligence were actively supporting Makenga and other M23 leaders. It also claimed there were 3,000 to 4,000 Rwandans fighting alongside M23, putting Rwanda in “de facto control” of M23 operations (UNSC, June 4). Uganda rejected the claims, while Kigali insisted that the DRC was financing and fighting alongside the FDLR; Rwanda was thus only acting in self-defense (AFP, July 10, 2024; al-Jazeera, July 9, 2024).
 DRC Wazalendo Militia near Rutshuru, 2022 (Moses Sawasawa/AP)
DRC Wazalendo Militia near Rutshuru, 2022 (Moses Sawasawa/AP)
Besides FARDC and the FDLR, Makenga’s M23 are also confronted by the Wazalendo (Kiswahili – “patriots), local militias traditionally known as Mayi-Mayi and nominally aligned with the DRC government. Among these are Guidon Shimiray Mwissa’s Nduma defense du Congo – Renové (NDC-R), Janvier Karairi’s Alliance des patriotes pour un Congo libre et souverain (APCLS) and the mostly Hutu Collectif des Mouvements pour le Changement-Forces de Défense du Peuple’ (CMC-FDP). All these loosely-organized, drug-fuelled Mayi-Mayi groups are feared by local communities and are known for brutality, extortion and mass rape. [1]
Makenga was sentenced to death in absentia, by a Congolese military court on August 8, 2024. The M23’s military leader was one of 26 armed-group leaders condemned after a trial, including Corneille Nangaa, political leader of the rebel Congo River Alliance (which includes M23), and M23 political chief Bertrand Bisimwa (al-Jazeera, August 9). The death penalty in the DRC had been under a moratorium since 2003, but was restored in March 2024.
As the M23 closed in on Goma in 2024, a FARDC spokesman claimed the M23 had blocked legitimate trade routes through Goma to focus on smuggling tanatalum supplies into Rwanda, a claim denied by Rwandan authorities (Bloomberg News, March 15, 2024).
Makenga launched a final offensive on Goma on January 23, in which his forces, allegedly supported by Rwandan troops, quickly broke through defenders that included FARDC troops, FDLR fighters, Wazalendo gunmen, peacekeepers from the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and Romanian mercenaries (for the latter, see MLM, June 27, 2024). By January 30, the conquest of Goma was complete; at the same time other M23 units were seizing a number of sites in Sud Kivu producing tantalum, tin and gold.
 Goma lies in the shadow of the active volcano Mount Nyiragongo
Goma lies in the shadow of the active volcano Mount Nyiragongo
Goma Again
Some 2900 people were slaughtered in the M23 conquest of Goma, which was accompanied by the escape of hundreds of prisoners from Goma’s Munzenze prison; over 100 female prisoners were immediately raped and then left to burn alive when the escapees set fire to the facility (BBC, February 5). Bizarrely, photos of the murdered women being carried out in body bags surfaced during Donald Trump’s May 21 Oval Office meeting with South African president Cyril Ramaphosa, when they were produced by Trump as visual proof of a “white genocide” in South Africa (Reuters, May 22; IBTimes, May 28). M23 forces then entered Bukavu, capital of Sud Kivu, on February 16, taking full control of the city two days later (Al-Jazeera, February 16).
 Residents greet a vehicle with M23 fighters on it in Bukavu, 2025 (Amani Alimasi/AFP)
Residents greet a vehicle with M23 fighters on it in Bukavu, 2025 (Amani Alimasi/AFP)
The Hutu Mayi Mayi CMC-FDP attacked Goma on April 11 in an attempt to drive out the M23, but were repulsed. M23 spokesmen claimed South African peacekeepers supported the assault (Congovirtuel, April 13; RFI, April 13). Violent crime has plagued the city since the January conquest with M23 fighters struggling to maintain order.
Ex-president Joseph Kabila, accused since February by President Tshisekedi of being behind the M23 offensive, and apparently back in favor with Makenga and Corneille Nangaa, returned to Goma on May 25 from a self-imposed exile in South Africa and Rwanda that began in 2023. Nangaa announced Kabila was welcome “in the only part of the country where arbitrariness, political persecution, death sentences, tribalism, discrimination, hate speech… do not exist” (New Times [Kigali], May 26).
The DRC government believes Kabila is now positioning himself to assume leadership of the rebel forces (Reuters, May 28). Kabila’s return is certain to complicate the US-sponsored negotiations between the competing factions in the DRC and the mineral deal desired by the Trump administration (Kivu Morning Post, May 27; Reuters, May 28). Just as Joseph Kabila’s father, Laurent-Désiré Kabila, had once labelled Congolese Tutsis as “foreigners,” the leader of President Tshisekedi’s Union for Democracy and Social Progress (UDPS) declared on May 25 that Joseph Kabila was “not Congolese… Let him leave the Congolese to deal with their own problems. He, a Rwandan subject whose rule was imposed on us, must leave the Congolese alone” (France 24, May 29).
Conclusion
While American military intervention to secure critical mineral supplies in the Congo appears unlikely at present, Trump supporter and mercenary chief Erik Prince has been engaged in working out an agreement with Congo’s finance ministry that would see private military contractors assigned to tax collection duties in the mineral sector and anti-smuggling operations (Reuters, April 17, 2025). There are reports that a recruiter allegedly working for Prince has been approaching former French Legionnaires regarding military contract work in the Congo (Africa Intelligence, May 12).
Rwandan media has accused Belgium of deploying two companies of commandos to fight against M23 alongside FARDC, FDLR and Wazalendo (Great Lakes Eye, March 24; Great Lakes Eye, May 7). Eight Belgian soldiers, including a “Sergeant Jimmy Luis Flander,” are said to have been killed while operating in Nord Kivu (Great Lakes Eye, April 3). This may be part of an effort to divert attention from international accusations that Kigali is supporting M23; Belgian Foreign minister Maxime Prévot described the assertions as “grotesque fake news” and disinformation designed to “undermine Belgium’s image, to increase tensions and to legitimise a certain interventionism” (Belga News Agency, March 26).
 Sultani Makenga (Chrispin Mvano)
Sultani Makenga (Chrispin Mvano)
Sultani Makenga’s career as a warlord, endlessly shifting from one faction to another in a process of continual self-enrichment, is emblematic of the interminable nature of the conflict in the Congo. The ceaseless struggle to control its abundant and strategically important wealth invites a steady stream of foreign interests willing to partner with corrupt businessmen, power hungry politicians and uniformed war criminals. Where the search for oil and gas reserves fueled international conflicts in the recent past, new elements are now sought after to achieve global dominance in a technological age. The struggle to possess these mineral properties, antagonized by post-colonial ethnic conflicts, has brought only death and displacement to millions of residents of Nord Kivu, with no end in sight. Men like Sultani Makenga, indulged and supported by parties (Western, African and Eastern) that wish to keep their hands clean of the blood of impoverished Africans, are ultimately the agents, not causes, of the resource-driven disease that ravages the Congo.
Note
- Mercenary leader Major Mike Hoare, who led his 5 Commando in the Kivu region in the 1960s, attributed the foundation of the Mayi Mayi movement to Chinese-trained revolutionary Pierre Mulele (1929-1968), who encouraged his Simba followers to chant “Mayi Mayi” (water water) or “Mayi Mulele” as they entered battle. The chant was intended to combine with magical water dispensed to the fighters to render them immune to bullets: “This, together with liberal doses of marijuana, rendered the recipient insensible to pain and totally incapable of intelligent action” (Hoare, Congo Mercenary, London, 1967). The practice was, in fact, an adaptation of earlier rituals used in Central Africa to overcome the superior firepower of colonial forces.
Eurasia Daily Monitor Vol. 22, Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC.
Andrew McGregor
May 28, 2025
Executive Summary:
- Russia’s plans to create a naval base on the Sudanese coast of the Red Sea have been upset by drone attacks launched on Port Sudan in early May. Sudan’s Rapid Support Forces claimed responsibility for the attack.
- The destruction of Port Sudan’s infrastructure demonstrates that Sudan’s domestic instability would threaten a Russian base, potentially jeopardizing a broader arms-for-access agreement that included Sudan’s acquisition of Russian warplanes.
- Sudan accused the United Arab Emirates (UAE) of supplying the People’s Republic of China (PRC)-made drones used in the attack. The UAE and the PRC may be acting to curb Russia’s naval ambitions.
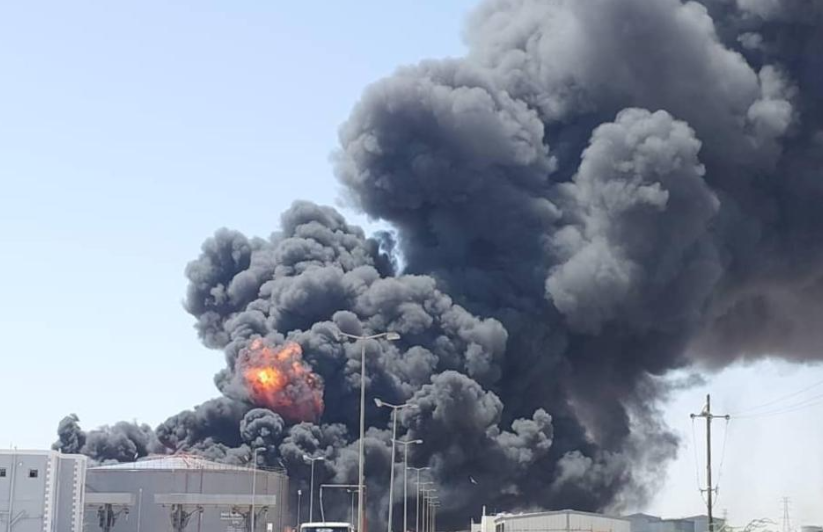 Fuel depot in Port Sudan burns after drone attack, May 5, 2025 (Xinhua).
Fuel depot in Port Sudan burns after drone attack, May 5, 2025 (Xinhua).
Russia’s hope of establishing a naval base along Sudan’s Red Sea coast took a serious blow when drones shattered infrastructure at its proposed site from May 4 to 8 (Sudan Tribune, May 7, 9). The week-long drone attack, believed to have been carried out by Sudan’s rebel paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF), exposed the vulnerability of the port’s proposed site to damage related to domestic instability. The alleged involvement of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) as the supplier of the RSF’s People’s Republic of China (PRC)-made drones complicates the international implications of the devastating attack.
 General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan, May 6, 2025 (Sudan Tribune)
General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan, May 6, 2025 (Sudan Tribune)
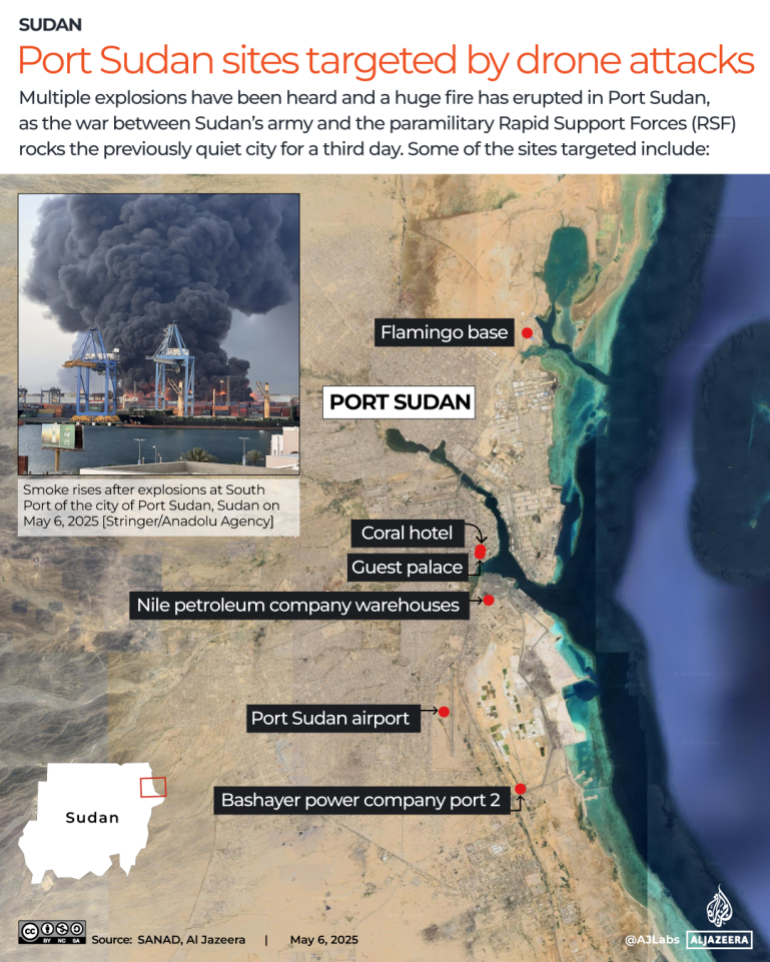
Following the destruction of the Khartoum/Omdurman capital region and its industrial base early in Sudan’s civil war in 2023, Port Sudan has acted as the political and military headquarters of the Sudanese state. Port Sudan operates under the unelected Transitional Sovereignty Council (TSC) and its dominant partner, the Sudan Armed Forces (SAF), commanded by General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan. Both the RSF and the UAE reject what they refer to as “the Port Sudan Authority” as the legitimate government of Sudan (Mada Masr, May 9). The city hosts Sudan’s most important port, its last functioning civil airport, a naval base, and a military airport. Crude oil from Sudan and South Sudan is exported from Port Sudan, and refined petroleum products for domestic use are stored there. It is the only delivery point for desperately needed aid and relief supplies in the war-ravaged nation.
Smoke billowed from the Sudanese Navy’s base at Flamingo Bay, 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) north of Port Sudan’s commercial port, after being struck by drones for five successive days in early May (Sudan Tribune, May 7, 9). Satellite imagery published by Russian site Insider.ru revealed what appeared to be large-scale destruction at the base (Insider.ru, May 13). Flamingo Bay is the proposed site for the new Russian naval base (AIS, March 24, 2022; see EDM, July 8, 2024, March 6, April 30; New Arab, May 8).
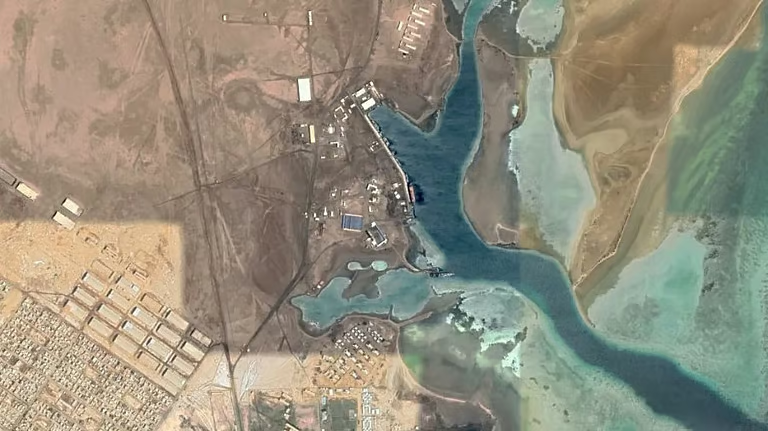 Flamingo Bay naval facility, north of Port Sudan (GoogleEarth)
Flamingo Bay naval facility, north of Port Sudan (GoogleEarth)
The destruction of oil depots at Port Sudan has created immediate fuel shortages and rising prices in government-held territory. The port is suffering from shortages of food and clean water, blackouts, and looting by desperate citizens (Radio Dabanga, May 8). Thousands have fled the city as civil authorities warn of an environmental and health disaster (Sudan Tribune, May 6; Mada Masr, May 9). Drones also struck radar installations, warehouses, and munitions stores at Osman Digna Air Base in Port Sudan, causing a series of explosions (Sudan TV, May 5). The strikes halted civilian air traffic, including humanitarian aid flights, by causing heavy damage at the adjacent Port Sudan International Airport (Sudan Tribune, May 7; Radio Dabanga, May 8). Other targets included General al-Burhan’s residence and the Marina Hotel, which often houses foreign diplomats (Mada Masr, May 9). Swarms of drones struck the historic Red Sea port of Suakin, some 50 kilometers (31 miles) south of Port Sudan, and the eastern city of Kassala on May 4 to 6 (Xinhua, May 6). Qatar, the UAE’s regional rival, is redeveloping Suakin in a $4 billion project.
 Osman Digna military airport in flames, May 4, 2025
Osman Digna military airport in flames, May 4, 2025
As the attacks continued, Moscow expressed “deep concern over the ongoing bloody armed confrontation” in Sudan (TASS, May 5). Despite three years of Russian attacks on civilian targets and infrastructure in Ukraine, the Kremlin statement added that “Russia believes that carrying out attacks on civilian infrastructure is unacceptable” (TASS, May 5). The Russian embassy in Sudan reported operations at its temporary embassy in Port Sudan were unaffected by the bombing, saying that “the situation is tense, naturally, but not critical” (RIA Novosti, May 6).
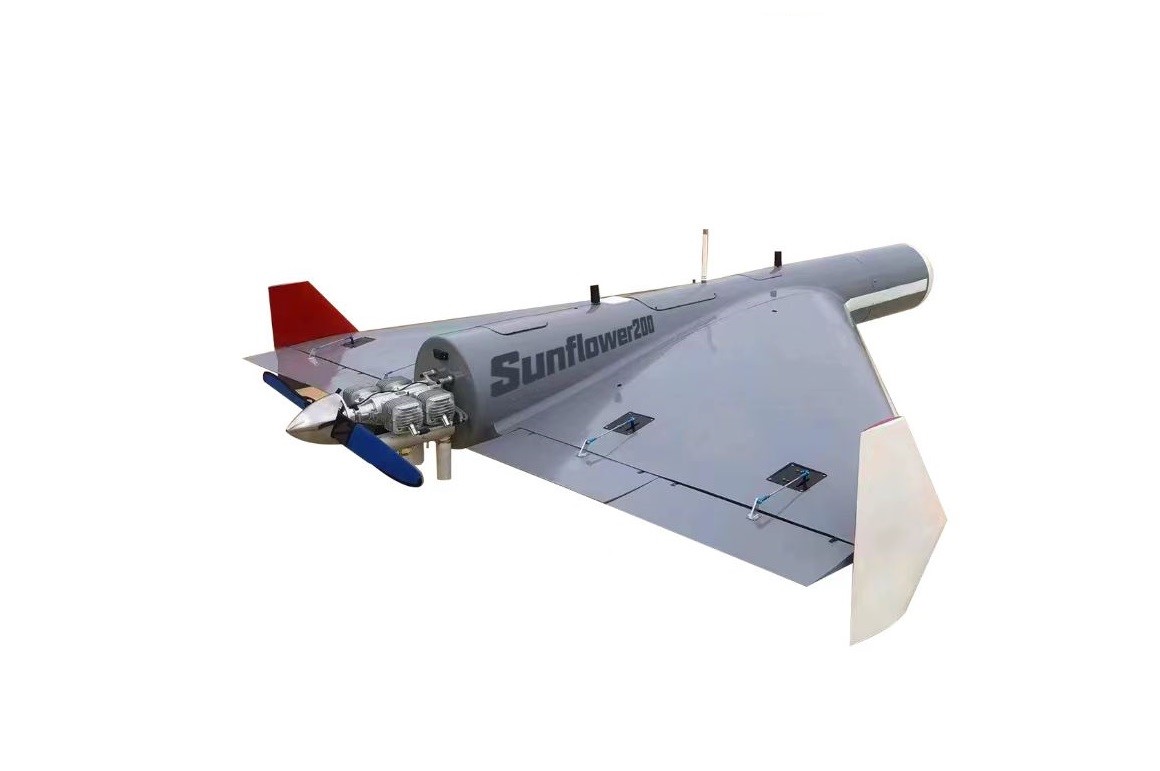
Other than drones, the RSF does not have aerial assets or personnel operating closer to Port Sudan than Omdurman, 670 kilometers (416 miles) away. The attack’s precise targeting suggests that the RSF obtained or was given accurate coordinates by means normally unavailable to the technologically weak paramilitary. The operational range of the PRC-made Sunflower-200 one-way attack drones, which military analysts believe the RSF used, is 1,500 to 2,000 kilometers (932 to 1,242 miles), with a 30- to 40-kilogram payload (Defense Express, May 6; Cobtec International, accessed May 21). The UAE obtained the Sunflower-200 in January 2024 (Janes, January 25, 2024).
The commander of the Red Sea military region and the Sudanese Navy, Lieutenant General Mahjub Bushra, claimed that drones were launched from UAE military facilities at Berbera in Somaliland and Bosaso in Puntland (Sudan TV, May 5). Puntland’s Minister of Information, Mahmoud Aydid Dirir, described the accusation that the UAE operated missiles from Bosaso as part of “a broader effort to undermine Puntland’s reputation and its ongoing fight against terrorism” (Mogadishu24, May 8).
SAF intelligence presented another scenario, suggesting the drones may have entered RSF-controlled regions of Sudan via the Libyan desert, past remote Jabal ‘Uwaynat (where Libya, Sudan, and Egypt meet) and into Darfur to be distributed to strategic launch points further east (AIS, June 13, 2017; France24.com, April 19; Mada Masr, May 9). Another possible route for the RSF to obtain the drones would be through the Amdjarass airstrip in Chad, close to RSF-held territory in Sudan. UAE transport aircraft make regular trips to Amdjarass. Many of the flights are believed to be delivering arms, though the UAE claims they deliver only humanitarian supplies (Reuters, December 12, 2024; Africa Defense Forum, January 7).
Sudan cut off diplomatic relations with Abu Dhabi on May 6 because of their alleged involvement in the attacks, denouncing it for “state terrorism” while threatening retaliation (Middle East Eye; Sudan Tribune, May 8; Mada Masr, May 9). RSF sources confirmed the paramilitary’s responsibility for the strikes on Port Sudan, Kassala, and oil depots in Kosti (White Nile Province) as part of a plan to take the war to Port Sudan and the relatively untouched north of Sudan (Mada Masr, May 9).
 An indefinite delay in the construction of a Russian naval facility at Port Sudan due to the attacks will likely jeopardize the Sudanese state’s planned acquisition of Russian warplanes, such as the Su-30 and Su-35, in exchange for the use of the port. The potential loss of Russian interest in Sudan could work in the PRC’s interest. Even though PRC-made drones caused the damage to Port Sudan, the Sudanese state (TSC/SAF) has only blamed the intermediary supplier, the UAE. If Russia backs off from the port deal and its reciprocal arms supplies, Beijing may be able to step in to make arrangements with the Sudanese state (TSC/SAF).
An indefinite delay in the construction of a Russian naval facility at Port Sudan due to the attacks will likely jeopardize the Sudanese state’s planned acquisition of Russian warplanes, such as the Su-30 and Su-35, in exchange for the use of the port. The potential loss of Russian interest in Sudan could work in the PRC’s interest. Even though PRC-made drones caused the damage to Port Sudan, the Sudanese state (TSC/SAF) has only blamed the intermediary supplier, the UAE. If Russia backs off from the port deal and its reciprocal arms supplies, Beijing may be able to step in to make arrangements with the Sudanese state (TSC/SAF).
The PRC is obliged, as a signatory to the United Nations’ Arms Trade Treaty, to prevent the UAE from selling PRC arms to a banned entity such as the RSF. It seems improbable that the PRC is unaware of how the UAE disposes of its hi-tech military imports. This raises the question of whether the UAE is mediating the transfer of PRC drones through established supply networks to the RSF to deter the expansion of Russian influence and facilities in Africa. The PRC has its own ambitions in Africa, as well as a naval base in Djibouti at the southern entrance to the Red Sea.
It is uncertain whether Russia has supplied Sudan with advanced air defense systems. Sudanese Major General Mutasim ‘Abd al-Qadir indicated that Russia has discretely supplied defense systems, while Sudanese intelligence sources indicate that Sudan turned down a Russian offer to deploy a S-400 air defense system at Port Sudan due to fears of negative U.S. and European reactions (Mada Masr, May 9; Insider.ru, May 13). Advanced air defense systems would be essential for the existence of a Russian base at Port Sudan, but would also raise issues regarding the touchy issue of Sudanese sovereignty.
The UAE has taken advantage of Russian naval base troubles. After the post-Assad government of Syria canceled 2019’s 49-year agreement with Russia’s Stroynasgas to manage the port of Tartus, the UAE’s DP World signed a memorandum of agreement to take over management of the port on May 16 with a projected $800 million investment (TASS, January 21; SANA, May 16). The Russian facility at Port Sudan was intended in part to replace the loss of Tartus. As the feasibility of establishing a Russian base in the Red Sea begins to diminish under the weight of domestic insecurity and foreign intervention, Moscow may intensify discussions to create an alternative naval base at the Libyan port of Tobruk.
Andrew McGregor
Eurasia Daily Monitor, Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC
April 17, 2025
Executive Summary:
- Russia’s rehabilitation of an abandoned airbase in the Libyan desert offers an opportunity to create a reliable line of supply to Russian forces operating in West Africa.
- A Russian military presence close to the borders of Egypt, Sudan, and Chad could make Moscow a player in regional politics and security activities.
- Moscow continues to feel its way through a complex system of regional rivalries and alliances that leaves it open to counter-moves by interested parties in the West.
One of former Libyan leader Mu’ammar Qaddafi’s greatest foreign policy failures was undoubtedly his 1980s attempt to use his Soviet-armed military to spread Libyan rule and influence in the African Sahel region. Now, Russia is focused on a similar effort in the Sahel, using the same remote airbase in south-eastern Libya that Qaddafi used to launch his offensive into neighboring Chad. The airbase at Matan al-Sarra is the latest addition to a network of Libyan bases hosting Russian military operations and arms shipments. These include al-Khadim, al-Jufra, Brak al-Shati, al-Wigh, Tamanhint, and al-Qardabiya (Middle East Eye, July 10, 2023; Libya Observer, January 15).
Matan al-Sarra is close to the historically strategic Kufra region, a series of small oases (see Terrorism Monitor, February 23, 2012, April 6, 2018; May 5, 2011). Today, Kufra is an important staging point for illegal African migrants making for the Mediterranean coast and ultimately Europe (Libyan News Agency, April 7).
Kufra and the rest of south-eastern Libya is now controlled by self-appointed “Field Marshal” Khalifa Haftar, commander of the so-called “Libyan National Army” (LNA, a.k.a. Libyan Arab Armed Forces). LNA is a composite force of militias, mercenaries, tribal groups, and more formal military formations supporting one of the two rival governments in Libya, the Tobruk-based Libyan House of Representatives (MENA Research Center, August 19, 2024; AIS Special Report, November 14, 2017).
Haftar’s 2020 Russian-backed attempt to seize Tripoli and bring Libya under his sole control with the aid of Wagner Group mercenaries was a failure, owing in part to the Government of National Accord’s (GNA) effective use of Turkish drones (see EDM, June 11, 2020, March 12, 2024). Rather than drop his alliance with Russia, Haftar instead decided to intensify relations with Moscow in the hope of obtaining more advanced weapons and other military materiel. Permitting Russian use of the airbase in south-eastern Cyrenaïca is part of this process.
 Mobile Chadian Troops in the Toyota War, 1988
Mobile Chadian Troops in the Toyota War, 1988
Before receiving support from Moscow for his military campaigns in Libya, Haftar had a history of cooperating with the United States. In 1987, after losing a military campaign as the then-commander of Libyan forces in Chad, Haftar was captured and disowned by Qaddafi (Libya Tribune, October 29, 2022; al-Arabiya, May 24, 2014). Valuable specimens of Soviet aircraft and radar abandoned by the Libyans were recovered from the battlefield by a US Special Operations group, temporarily damaging Libyan relations with Moscow (ARSOF, March 2022). By 1990, Haftar had agreed to move to the United States with 300 other Libyan prisoners, where he became a U.S. citizen and alleged asset for the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) in its efforts to overthrow Qaddafi, who continued to be backed by the Soviet Union until its collapse in 1991 (Libya Tribune, October 31, 2022; France24.com, May 19, 2014; al-Arabiya, May 24, 2014). Haftar returned to Libya in 2011, where he established a power base in Cyrenaïca against the internationally recognized Tripoli-based GNA, which controls most of northwestern Libya (Tripolitania) with the military assistance of Türkiye.
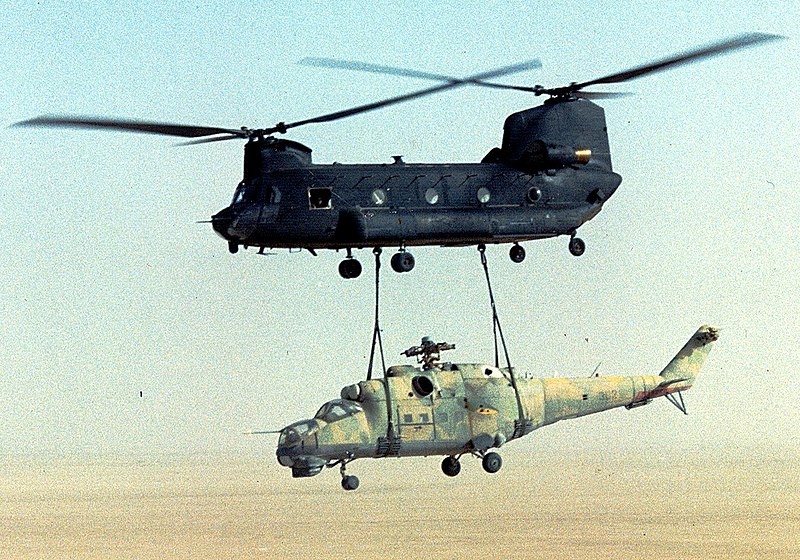 US Chinook Slings an Abandoned Russian-Made Libyan Mi-24 Hind from the Chadian Desert, June 11, 1988
US Chinook Slings an Abandoned Russian-Made Libyan Mi-24 Hind from the Chadian Desert, June 11, 1988
The new six square kilometer (2.3 square mile) base at Matan al-Sarra will provide a refueling stop for Russian aircraft heading into areas of West Africa where the Russian Africa Corps is active. It is located close to the Egyptian and Sudanese borders. Most importantly, the base lies just north of Libya’s border with Chad, the latest target for Russian influence since the recent withdrawal of French and U.S. military forces stationed there. Chad’s discontent with the West follows sustained Russian influence operations and the perceived inability of its Western allies to provide effective military aid in the struggle against regional Islamist insurgencies (see EDM, June 25, 2024). Kremlin objectives in Africa are furthered by an influence and propaganda campaign that uses regional influencers and social media to encourage belief in Russia as a viable and sympathetic alternative to the West for economic and security partnerships (Le Monde, August 6, 2023; RUSI Europe, October 25, 2023; MLM, December 4, 2019).
 Troops of the LNA’s Tariq bin Zayid Battalion
Troops of the LNA’s Tariq bin Zayid Battalion
Russia began transferring Syrian troops and contractors to Matan al-Sarra last December, where they were engaged alongside Russian personnel in repair and reconstruction efforts at the long-neglected base (The New Arab, January 28). Once a means of projecting Libyan power south into Chad and Sudan, the base lost its raison d’être in 2011 and was abandoned when Qaddafi’s death ended Libyan designs on the African interior. The region around the base, the supply line from Tobruk, and the route to Sudan have been secured by the LNA’s Tariq bin Ziyad Battalion, under the command of one of Khalifa Haftar’s sons, Saddam Haftar (Libya Observer, January 15). With daily temperature highs of over 90 degrees Fahrenheit (32 degrees Celsius) for six months of the year and almost zero annual precipitation, service at the isolated base will likely be considered a hardship posting for Russian personnel.
Russian operatives have been in contact with local tribal communities in the region to form useful alliances (Libya Observer, January 15). The area around Matan al-Sarra is dominated by the Tubu, the so-called “Black nomads of the Sahara” (as described by French soldier and ethnologist Jean Chapelle in his 1958 work Nomades noirs du Sahara) who were displaced from Kufra in the 1840s by their Arab rivals, the Zuwaya. Russian personnel will likely attempt to curry the favor of both groups as aligning with one against the other would create unwanted turmoil and insecurity.
A Russian presence at Matan al-Sarra would provide Moscow with the ability to ship arms to Sudanese or Chadian territory quietly. Even though Moscow has shifted most of its support in the Sudan conflict from the rebel Rapid Support Forces (RSF) to the rival Sudanese Armed Forces/Transitional Sovereignty Council (SAF/TSC), its forces in Libya do not appear to be interfering with Khalifa Haftar’s supply of arms and vehicles to the RSF (Middle East Eye, January 25, 2024; Agenzia Nova [Rome], January 17). Moscow likely wishes to avoid alienating the RSF and lose an opportunity to establish influence in a possible RSF-ruled state in Darfur, the home of most RSF fighters (Sudan Tribune, March 4).
Moscow’s overtures to the Chadian military regime are complicated by Moscow’s attempt to play both sides of the Sudanese conflict (see EDM, July 8, 2024). In late March, the SAF command declared that Chadian airports at N’Djamena and Amdjarras are now “legitimate targets for the Sudanese Armed Forces” following allegations that Chad is using them to forward arms from the United Arab Emirates to RSF forces inside Sudan (Middle East Eye, January 25, 2024; AFP, March 24).
Russian contractors have been heavily involved in gold-mining operations across the border in Sudanese Darfur to help pay for its war against Ukraine and may seek to expand into the Tubu-controlled Kalanga region (450 kilometers (280 miles) south-west of Kufra) in the foothills of the Tibesti Mountains along the border with Chad (Agenzia Nova [Rome], January 23). Chadian forces carried out airstrikes in the region last summer against Chadian rebels gathering there after working as mercenaries in Libya (Libya Security Monitor, August 22, 2024). The strikes came at the same time as Major General Hassan Matuq al-Zama led the LNA’s 128th Reinforced Brigade in operations to secure the border with Niger and Chad and to displace armed groups in Kalanga involved in smuggling and gold mining (Libya Review, August 19, 2024; Atalyar [Madrid], August 21, 2024).
 Russian Deputy Defense Minister Yunus-Bek Yevkurov and Field Marshal Khalifa Haftar (Libya Observer)
Russian Deputy Defense Minister Yunus-Bek Yevkurov and Field Marshal Khalifa Haftar (Libya Observer)
The United States Africa Command (AFRICOM) has been working in the last year to develop relations with Khalifa Haftar and encourage military unification in Libya to discourage Libyan partnerships with Russia. In late February, AFRICOM conducted training exercises in Libya involving U.S. B-52H Stratofortress bombers and Libyan military forces representing both rival Libyan governments designed to promote Libyan military unification while simultaneously slowing the growth of Russian influence (Libya Observer, March 4; Agenzia Nova, March 7). The exercise came amid regular contacts between Haftar and Russian deputy defense minister Yunus-Bek Yevkurov (responsible for Russian African Corps operations) and a growing number of Russians stationed at the LNA-controlled Brak al-Shati airbase in central Libya (Defense News, March 14).
Russian operations in Africa continue to be characterized by a certain diplomatic inconsistency that may be due in part to inexperience in the region and unfamiliarity with the motives and methods of their would-be partners. Besides trying to keep a foot in both camps in the Sudan conflict, Moscow continues to attempt to develop relations with the Tripoli-based GNA, which only encourages Khalifa Haftar to leave himself open to U.S. overtures. A failure to make firm and visible commitments makes Kremlin strategic policy in the region a work in progress, susceptible to local manipulation as well as countermoves by Russia’s global rivals.
Andrew McGregor
Terrorism Monitor 23(1), Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC
March 25, 2025
Executive Summary:
- Islamic State (IS) militants conducted a well-planned strike in Oman on a Shi’ite mosque on July 15, 2024. While early reports focused on the attack’s potential goal of inciting sectarian violence, it is more likely to have been meant as a warning to Muscat to cease diplomatic activities involving regional governments, Shi’ite groups, and/or the West.
- Oman’s peace with regard to jihadism is deep-rooted in local Ibadi Muslim traditions. Muscat’s tolerance has enabled it to serve as a diplomatic hub, facilitating negotiations between the United States and Iran as well as Saudi Arabia and the Houthi rebels in Yemen.
Islamic State (IS) militants struck a Shi’ite mosque in Oman on July 15, 2024, scything down dozens of worshipers while hundreds of others stampeded in a desperate effort to evade an unexpected hail of bullets (see Terrorism Monitor, August 21, 2024). The attack on Muscat’s ‘Ali bin Abi Talib mosque puzzled many observers of the Middle East, as sectarian violence is nearly unknown in Oman, where most citizens, rather than being Sunni or Shi’ite, follow the relatively little-known and non-aggressive Ibadi school of Islam.
 The Shi’ite mosque, on the fringe of Muscat, the Omani capital, has a mainly Pakistani congregation. Oman is a nation of four million people, of whom 40 percent are expatriate workers, mostly from South Asia. Though 400,000 of these are Pakistanis, Pakistan’s ambassador to Oman declared the attack was not “a Pakistan-targeted operation” (Times of Oman, July 17, 2024).
The Shi’ite mosque, on the fringe of Muscat, the Omani capital, has a mainly Pakistani congregation. Oman is a nation of four million people, of whom 40 percent are expatriate workers, mostly from South Asia. Though 400,000 of these are Pakistanis, Pakistan’s ambassador to Oman declared the attack was not “a Pakistan-targeted operation” (Times of Oman, July 17, 2024).
When the shooting began in the evening, nearly 500 people were assembled in the courtyard. Most worshipers were able to rush inside the mosque before a policeman gave his life closing the doors. Five other people were killed, including four Pakistanis and one Indian national. At least three of the dead died trying to shield children from the gunfire with their bodies (The National [Abu Dhabi], July 23, 2024). Some 30 were wounded, including emergency services personnel (Muscat Daily, July 16, 2024).
 ‘**Ali bin Abi Talib Mosque in Muscat** (Agenzia Nova)
‘**Ali bin Abi Talib Mosque in Muscat** (Agenzia Nova)
Many survivors credited the action of the Royal Oman Police in preventing a massacre: “If not for the counter-firing by security officials stationed around the mosque, the tragedy would have been unimaginable” (Times of Oman, July 16, 2024). Most of the mosque attendees had been rescued by 2:15 AM, but a firefight between the attackers and security services continued well into the morning.
IS timed the attack to occur on Ashura, the Shi’ite day of mourning for Husayn bin ‘Ali. He was the grandson of Muhammad who refused to recognize the Umayyad succession to the Caliphate in the seventh century and was consequently killed at the Battle of Karbala. Hatred of the Shi’a was likely only a means of inciting the attackers as a geopolitical strategy was unlikely to inspire the kind of fanaticism necessary to slaughter innocents. The timing of the attack thus inflicted religious insult while provoking a maximum emotional impact on the targeted worshipers.
Islamic State’s Attackers in Oman
On July 18, 2024, IS released a three-minute video through its Amaq news agency of the three self-styled “soldiers of the Islamic State” who carried out the attack. The three native Omani brothers were, according to the Royal Oman Police, “influenced by others and had misguided ideas” (Times of Oman, July 18, 2024; Al-Watan [Muscat], July 18, 2024). The brothers are likely to have had ties to the Islamic State in Yemen Province (ISYP), whose homeland in Yemen borders Oman.
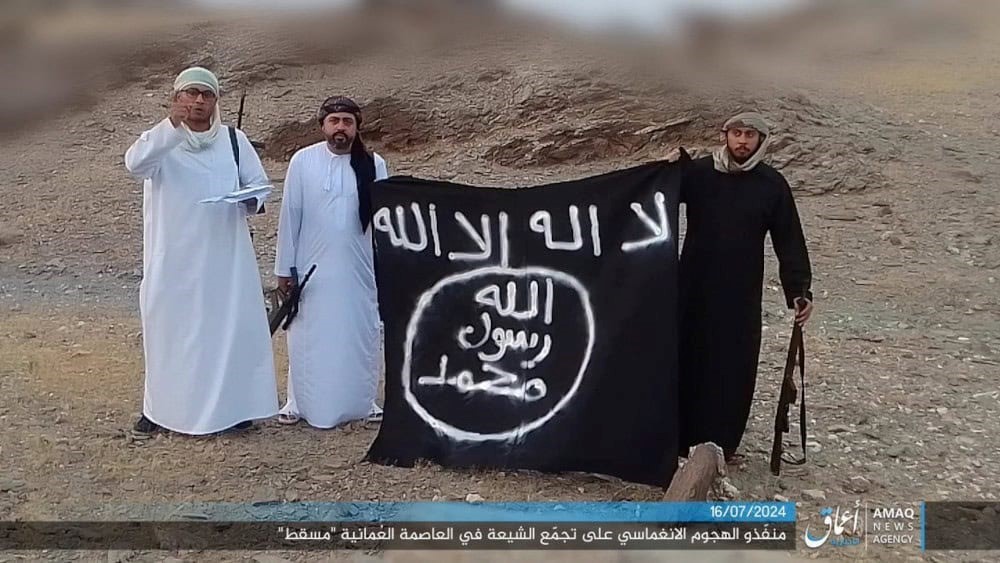 The Islamic State Attackers (Amaq)
The Islamic State Attackers (Amaq)
The video was filmed outdoors in front of an apparently homemade, spray-painted IS black flag. After calling on young Arab Muslims to combat “apostates” and “tyrants,” the speaker declared their attack would avenge both Sunni jihadists held in various Shi’a prisons and the reputation of Aisha, who is “the mother of believers” and the Prophet Muhammad’s third wife. [1]
The Omani perpetrators, who were likely Salafist Sunnis, made reference to Ibadism as a sectarian form of Islam in their video. Sunni militants condemn the Shi’a as rawafidh (“rejectionists,” i.e., of the first three caliphs, the successors of Muhammad). Most of the Sunni Muslims of southern Oman belong to the moderate Shafi’i madhab (school of Islamic jurisprudence), considered to be relatively infertile ground for religious extremism. Aside from their evident loathing for Oman’s long-accepted Shi’ite community, the attackers have thus also demonstrated an intolerance uncommon to Oman’s dominant Sunni faith.
Given the bloodshed in Gaza, the gunmen further explained that jihad did not need to only target Jews on behalf of “Palestine,” but must also strike at “polytheists” (a derogatory Salafist term for Shi’ites). The video concluded with the militants pledging allegiance to Abu Hafs al-Hashimi al-Qurashi, the fifth caliph (since August 2023) of IS’s so-called Islamic caliphate.
 Islamic State “Caliph” Abu Hafs al-Hashimi al-Quraishi
Islamic State “Caliph” Abu Hafs al-Hashimi al-Quraishi
The attack showed a significant degree of planning, with the assailants taking positions behind floodlights on the roof of a neighboring building. This provided a full view of their targets while preventing a precise location of their shifting positions. Chanting “You non-believers, this is your end,” they engaged Omani police and soldiers for ten hours before their deaths (The National [Abu Dhabi], July 17, 2024).
Background to Tolerance
The empire-building Portuguese arrived in Oman in 1507, unleashing seamen recruited from the prisons of Lisbon on Muscat and other ports. Using extreme brutality to make up for inferior numbers, the Portuguese burned the mosques and mutilated or killed those Arabs who resisted. [2] However, under nearly 150 years of Portuguese rule, Oman became a regional trading center, attracting migration from India, Iran, and other points. In this way, Oman emerged as a multi-faith, multi-ethnic, and multi-cultural bastion once the despised Portuguese were run out by the Ibadi Imams with Dutch and British naval assistance.
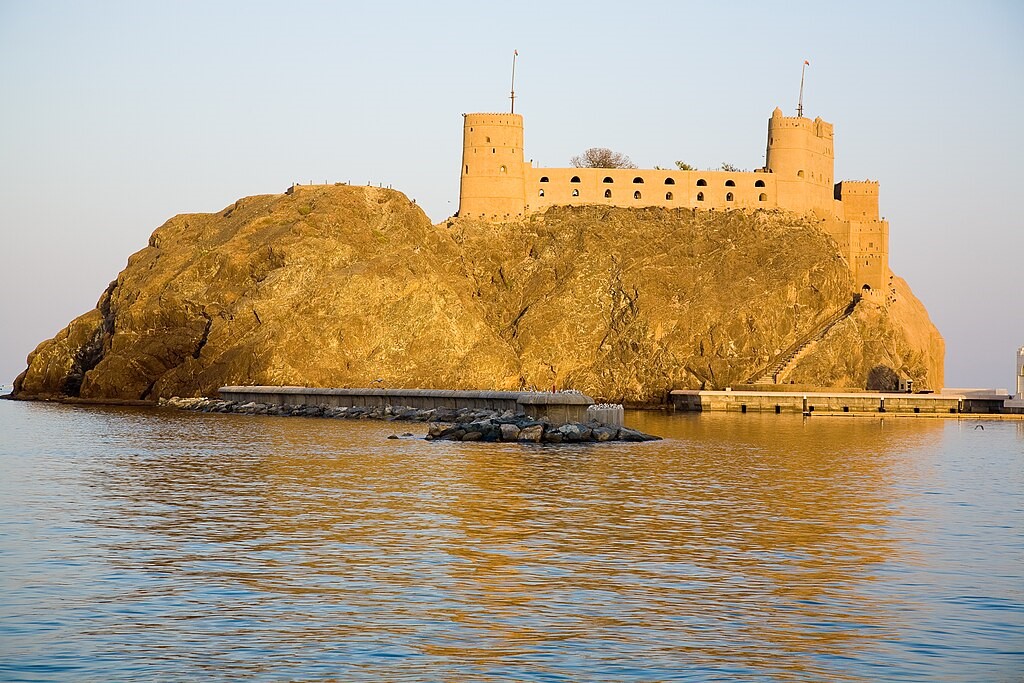 “Al-Jalali,” Portuguese Fort, Muscat (Andries Oudshoorn)
“Al-Jalali,” Portuguese Fort, Muscat (Andries Oudshoorn)
Oman’s commanding position on the Strait of Hormuz, the Gulf of Oman, and the Arabian Sea, with the latter’s connections to the Indian Ocean, has provided historical ties through seafaring traders and merchants to many parts of Asia, east Africa, and the Middle East. The result is that, despite its isolationist reputation, Oman is home to a variety of languages, ethnicities, and faiths, including Islam and Hinduism. Oman’s majority Muslim population is roughly split between Ibadis and Sunnis, with the Shi’a forming a smaller community representing some 5 percent of the population.
This exposure to other cultures and intellectual trends, combined with the moderate nature of Ibadi Islam, created in Oman a tolerant and diverse society that has largely escaped the religious and ethnic fissures that have so troubled its neighbors in recent decades.
Who Are the Ibadis?
The Ibadis are believed to be an offshoot of the early Islamic Kharijite movement, which fought a long war against Muslim rulers they accused of violating Islamic law. A focus on asceticism and egalitarianism brought many followers to the Kharijite ranks from the nomadic Bedouin and the mawali, who are non-Arab converts to Islam (including many Berbers). In 692, ‘Abd Allah bin Ibad created a more moderate but socially conservative breakaway version of the inflexible Khawarij movement that was prepared to live in harmony with other Muslims. This movement came to be known as Ibadism after its founder.
Oman’s Ibadi Muslims generally do not pursue the spread of their madhab. For example, during the long period of direct Omani rule over Zanzibar (1698–1861), little if any effort was made to convert East Africans to Ibadi Islam. [3] Ibadis do not seek the establishment of a global caliphate nor the territorial expansion of Islam.
Outside of Oman, Ibadis are found in smaller numbers in the Tunisian island of Djerba, in the Berber community of Libya’s Nafusa Mountains, and in the Berber Mzab Valley region of Algeria, where the Ibadis played a major role in facilitating the trans-Saharan African slave trade. The Omanis also had a long presence in Zanzibar and East Africa as merchants and slave traders, creating over the years a new class of Afro–Omanis whose most prominent member was the slaver and explorer Tippu Tib (1837–1905).
The Omani Reaction
Expressing his shock that Omanis carried out the attack in IS’s name, Oman’s Grand Mufti, Sheikh Ahmad bin Hamad al-Khalili, insisted that: “The norm in this good country is that Omani education rejects, by nature, any aggression against a citizen or expatriate due to an intellectual or sectarian disagreement” (IQNA [Tehran], July 19, 2024).
In contrast, one leading Omani commentator suggested responsibility for the attack lay with the United States, claiming that IS was created and directed in Washington, D.C. (Oman Daily, July 21). [4] Suspicion of American and Israeli direction of IS is common in the Middle East, especially due to IS’s focus on attacking fellow Muslims and its reluctance or inability to target Israel or Israeli interests. In Oman, a familiar but bitter joke made the rounds after the mosque massacre: Q. “When will Islamic State attack the Israelis?” A. “As soon as they convert to Islam.”
Another Omani commentator warned of the complacency created by popular belief in an “imagined Omani… tolerant, peaceful, innocent, a silent citizen…” a vision that ignores Omani society’s “many molds related to religious and political beliefs, ideas, and visions” (Oman Daily, July 22, 2024). Others, meanwhile, questioned why individuals “who have received qualitative education, hold high-level academic degrees from prestigious universities and hold lucrative jobs slip into such dangerous pitfalls” (Oman Daily, July 21, 2024). Only a handful of Omanis are known to have participated in jihadist movements since the 1990s.
The Jihadist Response
An editorial published in IS’s official magazine al-Naba condemned Oman for its good relations with Iran and called for the states of the Arabian Peninsula to expel all Shi’a to end their “cancerous infiltration.” The editorial further accused Oman’s “apostate” government of “throwing open the doors” of Oman to the Shi’a, despite their centuries-long presence there. [5] Al-Naba further accused Oman’s government of creating, through toleration, an equivalency between Sunnis and Ibadis as well as Shi’a and pagans.
Jordanian Salafist Abu Muhammad al-Maqdisi, a leading jihadist theorist, unfavorably contrasted the IS’s attack on a “remote and marginal” Shi’a mosque in Oman with the successful and strategic efforts of Shi’a groups like Hezbollah and the Yemen-based Houthis against the “Jews and Crusaders.” He mentioned the July 19, 2024, Houthi drone attack on Tel Aviv, in particular. According to al-Maqdisi, “only a mentally ill person” would prioritize attacks on Shi’a non-combatants over strikes on Jews and Christians. [6]
Conclusion
To understand the attack on the ‘Ali bin Abi Talib mosque in Muscat, it is necessary to recognize what caused this IS cell to be activated at this time. Though it is entirely possible for cells, like lone wolf terrorists, to self-activate, it seems unlikely in this case. The Middle East (and even Oman) abounds with more valuable targets than an obscure mosque frequented by Pakistani expats. The slaughter of a handful of worshippers by a dedicated team of jihadists willing to give their lives will not drive the Shi’a from Oman, nor is it likely to encourage other Omanis to take up the cause of IS. Hatred of the Shi’a was likely only a means of inciting the attackers, as geopolitical strategy was unlikely to inspire the kind of fanaticism necessary to slaughter innocents.
Though Oman has been described as a mediator in Middle East conflicts, its role is better described as facilitation, offering a discrete venue for antagonists to pass messages or engage in direct talks without Omani involvement. Conducted out of sight of the media, these back-channel negotiations often yield positive results.
Despite pressure from its Sunni neighbors in the Arabian Peninsula, Oman has maintained good relations with Shi’ite Iran and acted as a facilitator in Iranian contacts with Saudi Arabia and the United States. On May 19, 2024, the Iranian mission to the UN confirmed that Oman was hosting ongoing indirect talks between the United States and Iran (Iran International, May 19, 2024). Oman has similarly facilitated talks between the Iran-backed Houthi movement and its Saudi antagonists (Al Jazeera, July 24). On July 19, 2024, IS condemned all these communications, claiming the “infidel” powers were encouraged by Oman to unite in a war against it. [7]
If IS wished to warn off Oman from further facilitation of negotiations benefitting Shi’ite Iran and the Zaydi Shi’ite Houthi movement, the apparently pointless targeting of a Shi’a mosque in Muscat begins to make sense. Rather than being an attempt to sow sectarian discord, the attack on the ‘Ali bin Abi Talib mosque can more reasonably be interpreted as a warning to Oman to cease diplomatic activities involving Iran and its so-called proxies.
Notes:
[1] This extraordinarily long quarrel dates back to the lifetime of Aisha bint Abu Bakr (614–678), the Prophet Muhammad’s third wife. The daughter of Abu Bakr, first of the Rashidun (rightly guided) caliphs (the first four successors of Muhammad), she gained the eternal ire of the Shi’a for opposing the succession of ‘Ali, the last of the Rashidun and the first Imam of the Shi’a. In Shi’a discourse, she is condemned for her political involvement as a female and her alleged dislike of the Ahl al-Bayt (family of the Prophet).
[2] Roger Crowley, Conquerors: How Portugal Forged the First Global Empire, London, 2015, pp. 196–198.
[3] Ahmed al-Ismaili: “Ethnic, Linguistic, and Religious Pluralism in Oman: The Link with Political Stability, Al Muntaqa 1(3), December 2018, pp. 58–73. After Oman ended direct rule in 1856, Zanzibar continued to be ruled by local Omani Arabs as the Sultanate of Zanzibar until it was made a British protectorate in 1890. Sovereign Arab rule was restored when the British terminated the protectorate in 1963, but massacres of Arabs and Indians during the leftist 1964 Zanzibar Revolution brought a final end to Omani rule.
[4] On August 11, 2016, then-presidential candidate Donald Trump insisted: “ISIS is honoring President Obama. He is the founder of ISIS. He’s the founder of ISIS, OK? He’s the founder. He founded ISIS. And I would say, the co-founder would be crooked Hillary Clinton” (CBS, August 11, 2016). The following day the candidate was given numerous opportunities by a friendly interviewer to walk back a literal interpretation of his statement, but chose instead to double down: “No, I meant [President Obama] is the founder of ISIS. I do… No, it’s no mistake” (hughhewitt.com, August 12, 2016).
[5] Al-Naba no. 452, July 19, 2024
[6] Telegram, via BBCM, July 20, 2024
[7] Al-Naba no. 452, July 19, 2024
Eurasia Daily Monitor Vol. 22, Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC
Andrew McGregor
March 6, 2025
Executive Summary:
- Moscow is pursuing the construction of a naval port on Sudan’s Red Sea coast, reflected in the finalization of an agreement between Russia and Sudan in February.
- The deal appears to be part of the Kremlin’s efforts to create new strategic assets in Africa following the loss of air and naval bases in Syria.
- The elected government of Sudan’s inability to ratify the agreement reflects the salience of domestic and international opposition to a changed security situation on this vital maritime trade route.
Russia and the leading faction in Sudan’s ongoing civil war have reportedly finalized an agreement to establish a Russian naval base on the Red Sea coast. Since the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, there may be no more strategically important body of water in the world than the Red Sea. Access to the sea, which carries 10 to 12 percent of global trade on its waters, is gained only through the Egyptian-controlled canal to the north and the narrow Bab al-Mandab strait to the south (The Observatory of Economic Complexity, accessed March 4). So far, no state outside of the region has established a naval base between the canal and Bab al-Mandab since the departure of the British from Sudan’s primary Red Sea port, Port Sudan, in 1956. That appeared to change on February 12 with the announcement that an agreement had been reached to construct a Russian naval base in Port Sudan.
 The announcement was made by Dr. ‘Ali Yusuf Sharif, appointed in November 2024 as nominal foreign minister by Lieutenant General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan, whose faction controls most of Sudan. During a televised press conference in Moscow with his Russian counterpart, Sergey Lavrov, Sharif said “This is an easy question, there are no obstacles, we are in complete agreement” (Izvestiya, February 12; Al Arabiya; Atalayar, February 13). After the meeting, Lavrov expressed his appreciation for the “balanced and constructive position” taken by Sudan on the situation in Ukraine (TASS, February 12). There has been no confirmation from Moscow of the official signing of this deal.
The announcement was made by Dr. ‘Ali Yusuf Sharif, appointed in November 2024 as nominal foreign minister by Lieutenant General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan, whose faction controls most of Sudan. During a televised press conference in Moscow with his Russian counterpart, Sergey Lavrov, Sharif said “This is an easy question, there are no obstacles, we are in complete agreement” (Izvestiya, February 12; Al Arabiya; Atalayar, February 13). After the meeting, Lavrov expressed his appreciation for the “balanced and constructive position” taken by Sudan on the situation in Ukraine (TASS, February 12). There has been no confirmation from Moscow of the official signing of this deal.
 ‘Ali Yusuf Sharif and Sergei Lavrov
‘Ali Yusuf Sharif and Sergei Lavrov
Since 2017, Moscow and Khartoum, represented by the since-deposed Sudanese president, ‘Omar al-Bashir, have discussed the creation of a Russian naval base in Sudan (See EDM, December 6, 2017). A preliminary agreement, forming the basis for the current pact, was developed in 2020 but never implemented. This original agreement includes a 25-year lease with a possible ten-year extension (Uz Daily, November 15, 2020).
Moscow holds a vested interest in establishing a naval base in this region, especially as the future of its naval base in Tartus, Syria remains uncertain (Military Review, December 11, 2024; Izvestiya, January 22). The primary function of Russia’s new “logistical base,” as it is described by Moscow, is to repair and replenish up to four Russian naval craft at a time, including nuclear-powered vessels. The base will house up to 300 personnel, with an option to increase this number with Sudan’s permission (TASS, February 12; Sudan Tribune, February 12). Russia will be responsible for air defense and internal security, while Sudan will provide external security in tandem with temporary Russian defensive positions outside the base. Russia will be at liberty to import and export weapons, munitions, and military material to and from the base (Vreme, February 13).
 Sukhoi Su—25 Aircraft (Military Africa)
Sukhoi Su—25 Aircraft (Military Africa)
The completion of the deal may open the possibility for Sudan to purchase Russian-built SU-30 and SU-35 fighter jets, which it has sought since 2017 (Sudan Tribune, July 16, 2024). The sale has been complicated by an inability to finalize the port offer, U.S. sanctions on Russian manufacturers, and Sudan’s difficulty in making payments. Oil-rich Algeria, by comparison, has just completed a deal to obtain 14 fifth-generation Russian SU-57 stealth fighters (Janes.com, February 14).
Cooperation with Russia is also attractive to Sudan given Khartoum’s need to secure oil exports on its coast. Port Sudan serves as the export point for Sudan’s troubled oil industry, now operating at only slightly more than 40 percent of pre-war production. Sudan’s Ministry of Energy and Petroleum (MOP) is currently discussing a new partnership with Russia related to exploration, financing, and technical assistance (Sudan Tribune, January 25). In November 2024, MOP Minister Dr. Muhyaddin Na’im Muhammad Sa’id met with his Russian counterpart in Moscow to discuss prospects for joint projects and attractive areas for Russian companies to invest in oil and gas exploration (Sudan News Agency, November 16, 2024). The People’s Republic of China (PRC) was formerly Sudan’s main energy partner. According to one Sudanese economic expert, “the [civil] war has changed this equation” in favor of gaining expertise, especially related to oil extraction, from Russia (Sudan Tribune, January 25).
 Sudan Began to Run Out of Fuel, Medicines and Wheat When Beja Protests Closed Port Sudan in 2021 (AFP)
Sudan Began to Run Out of Fuel, Medicines and Wheat When Beja Protests Closed Port Sudan in 2021 (AFP)
For Russia, there is a risk in initiating the construction of an expensive naval facility during a period of continued instability in Sudan. There is also the question of overland supply from Khartoum to Port Sudan, which essentially follows a single highway that has been blocked in the past by Beja protestors (New Arab, October 27, 2021; see EDM, November 14, 2023). To mitigate such risks, Sudan appears to be trying to follow the “Djibouti approach” to hosting foreign military bases. Djibouti currently hosts separate French, Chinese, U.S., Italian, and Japanese military facilities while U.K. forces are hosted at the U.S. facility (see EDM, July 8, 2024). According to Sharif, the new Russian base in Sudan, like those in Djibouti, will not pose a threat to the sovereignty of its neighbors nor Sudan itself (Anadolu Ajansi, February 13).
There are, however, major and ongoing differences between the military and civil components of the de facto government in Port Sudan that could sideline Russian ambitions in the Red Sea. Sharif’s claim that there were “no obstacles” to implementing the agreement is not necessarily correct. There is broad opposition to the unelected leaders of the Transitional Sovereignty Council (TSC) and Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) making a deal with major implications for Sudanese sovereignty (see Terrorism Monitor, April 28, 2023). As the deal cannot presently be ratified by any elected body in Sudan, there is a strong possibility that a future government (elected or otherwise) might reject the deal entirely as having no legal legitimacy. The January 20 cancellation of Russia’s 2017 49-year lease on the port of Tartus by the new Syrian regime provides an exemplary lesson on such a danger (Maritime Executive, January 21).
Another approach the Sudanese leadership may use to mitigate security risks, and in turn, may increase Russia’s attraction to creating a naval base in the country, is via deliberate changes in government representation. The de facto leader of Sudan is Lieutenant General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan, chair of the unelected Transitional Sovereignty Council and commander-in-chief of the Sudanese Armed Forces. Al-Burhan’s government is now located in Port Sudan rather than war-torn Khartoum. Al-Burhan differs from previous leaders, as he has attempted to garner support from eastern Sudan, a traditionally impoverished area with little influence or representation in the central government. Most of the rebellions, coups, and civil conflicts that have plagued Sudan since independence and effectively prevented its successful development have been sparked by the inequality, domination, and monopolization of power. Since eastern Sudan has been dominated since independence by the Arab Nubian elites of northern and central Sudan, al-Burhan’s emphasis on involving eastern Sudan in his government represents a measure to prevent future coups or conflict. One of the figures who will likely be involved in establishing a Russian naval base in Sudan is ‘Umar Banfir, the new trade minister. Banfir is the former director of Sudan’s Sea Ports Authority and is expected to represent eastern interests to the government (Jordan Times, November 4, 2024).
Sanctions imposed by the United States on the SAF and al-Burhan personally in the last days of the Biden Administration appear correlated with al-Burhan’s renewed interest in securing the naval base deal with Russia (US Treasury Department, October 24, 2024; US Department of State, January 16; US Treasury Department, January 25).
Meanwhile, there is little evidence to suggest that the new Trump administration will impose additional sanctions or attempt to restrict Sudan’s pursuit of a new deal with Russia given the previous removal of sanctions under the first Trump administration (Congressional Research Service, July 5, 2017). Nearby Egypt and Saudi Arabia remain firmly opposed to the deal (Sudan Tribune, July 16, 2024).
Domestic political opposition, foreign objections, tribal unrest, and local fears that a Russian base might attract attacks from rivals, which in turn could damage or shut down Sudan’s most important port, remain considerable threats to the construction of a Russian naval facility in Port Sudan. These considerations also threaten Russian attempts to reinvigorate Sudan’s oil production, which has been declining for years due to a lack of investment and civil conflict. While the Russian naval base deal in Sudan holds strategic potential for Moscow, its success hinges on overcoming these political, domestic, and regional challenges.
Andrew McGregor
Terrorism Monitor 22(11), Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC
December 11, 2024
Executive Summary:
- Iran is supplying the Sudan Armed Forces (SAF) of General Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan with drones and other weaponry in its struggle against the rebel Rapid Support Forces (RSF) led by General Hamdan Daglo “Hemetti.” This has given rise to concerns that Tehran desires to establish a naval facility in Sudan.
- In combination with the Iran-friendly Houthi movement in Yemen, such a base would offer a point from which Iran could further threaten Red Sea shipping as well as the main maritime entry point for Muslims making the pilgrimage to Mecca and Medina.
- Iran–Sudan relations have fluctuated over the last several decades, especially since the overthrow of President Omar al-Bashir. In particular, tensions stemming from Sudan’s Sunni-majority population and Iran’s promotion of Shi’ism tend to place a limit on Tehran–Khartoum ties.
- Despite official denials, Iran is suspected of either attempting to establish a naval facility on Sudan’s Red Sea coast or gain access to preexisting ports there given the strategic advantages offered by doing so. Doing so may represent a bridge too far for U.S.–Sudan relations, which Khartoum has spent years working to improve.
A supporter of the Palestinian cause since the Islamic Revolution of 1979, Iran has adopted an aggressive stance in response to Israel’s offensive on Gaza. As part of a strategy to assert itself regionally, Tehran has taken advantage of its proximity to the Red Sea, one of the world’s most important trade conduits, to apply pressure on Israel and its Western backers. With the Iran-friendly Houthi movement in Yemen installed near the narrow Bab al-Mandab Strait at the southern end of the Red Sea, Iran is taking a new interest in Sudan and its 465-mile Red Sea coastline. To this end, Tehran is supplying the Sudan Armed Forces (SAF) of General Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan with potentially game-changing weaponry in its struggle against the rebel Rapid Support Forces (RSF) led by General Hamdan Daglo “Hemetti.” This raises two questions: What does Tehran want in return? And is it likely to get it?
Sudan’s Relations with Iran
In the 1990s, Iran enjoyed a close relationship with the Islamist military regime of President Omar al-Bashir. He welcomed Iranian technical and diplomatic support in his effort to create a more Islamic state and defeat South Sudanese separatists. Many of the Islamists who were ejected from power after al-Bashir’s overthrow in 2019 now support General al-Burhan’s SAF.
Relations with Iran were cut in January 2016 when Khartoum sided with Saudi Arabia after a mob attacked the Saudi embassy in Tehran in reaction to the execution of top Saudi Shi’ite cleric Sheikh Nimr Baqir al-Nimr and 46 others on January 2, 2016 (Press TV [Tehran], February 5). Al-Bashir’s government then turned to Iran’s Arab rivals in the Gulf states for support. During this time, Sudanese troops (mostly RSF) fought alongside Saudi forces against the Iranian-backed Houthi movement in Yemen.
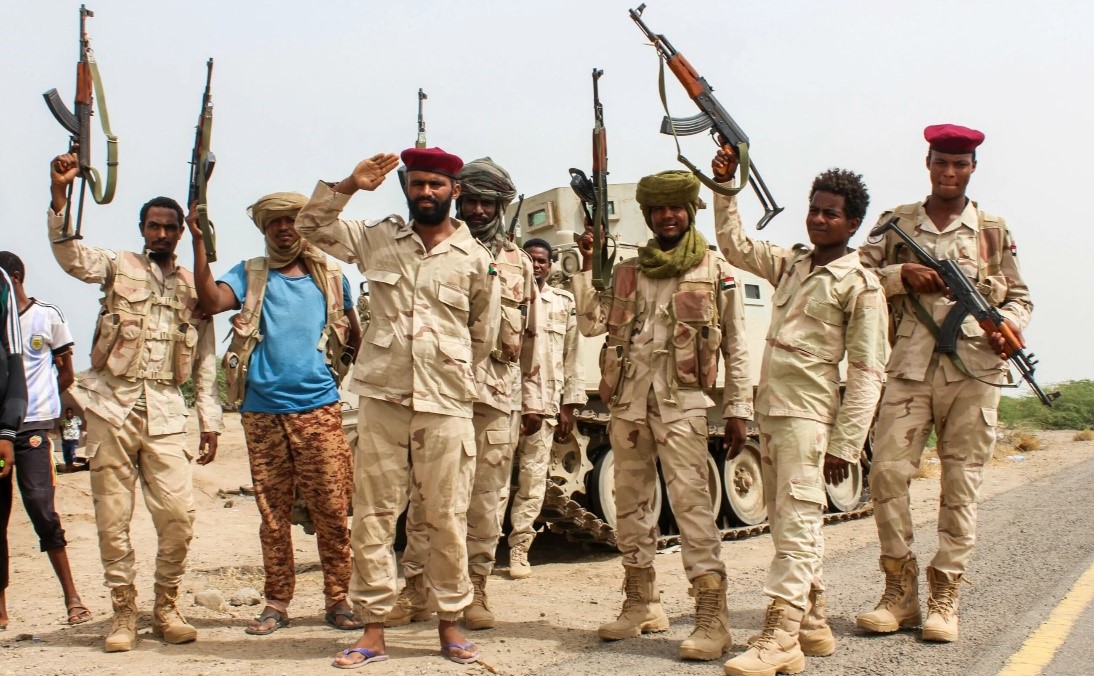 Sudanese Troops in Yemen (AFP)
Sudanese Troops in Yemen (AFP)
The centuries-old Sunni–Shi’ite religious divide complicates relations between Sunni Sudan and Shi’ite Iran. After al-Bashir downgraded relations with Iran in 2014, he made it clear the move was made in reaction to alleged attempts by Iranian diplomats to spread Shi’ism in Sudan: “We do not know Shi’ite Islam. We are Sunnis. We have enough problems and conflicts and we do not accept introducing a new element of conflict in Sudanese society” (Sudan Tribune, January 31, 2016).
A March 2023 Saudi–Iranian rapprochement brokered by Beijing allowed Khartoum to make its own move to renew relations with Tehran. The shift was welcomed at the time by Hemetti, who had risen from a minor member of the notorious Janjaweed militia to commander of the RSF paramilitary (X/@Generaldagllo, March 10, 2023). When the renewal of diplomatic relations was made official in October 2023, one of Tehran’s most immediate concerns was Sudan’s growing relationship with Israel through the U.S.-backed Abraham Accords (Sudan Tribune, October 9, 2023).
The Israel Issue in Sudan–Iran Relations
‘Ali al-Sadiq ‘Ali, Sudan’s acting minister of foreign affairs, met Iran’s late president, Ebrahim Raisi, in Tehran on February 5 to discuss their countries’ improved relationship. During the meeting, Raisi emphasized that the “criminal Zionist regime” could never be a friend to Islamic countries. Without mentioning Sudan by name, he condemned those Islamic nations that chose to pursue normalization of relations with Israel (Mehr News [Tehran], February 5).
 Sudanese Foreign Minister ‘Ali al-Sadiq ‘Ali (Osman Bakır – Anadolu Agency)
Sudanese Foreign Minister ‘Ali al-Sadiq ‘Ali (Osman Bakır – Anadolu Agency)
Following a law implemented in 1958, Sudanese leaders were forbidden from normalizing relations with Israel. The upheavals that followed the overthrow of President al-Bashir in 2019 provided an opening for the United States to bring Sudan into the Abraham Accords in exchange for a long-desired removal of American sanctions on Sudan. A member of Sudan’s ruling Sovereign Council, Admiral Ibrahim Jaber, rejected suggestions that relations with Iran spelled an end to the Accord, claiming that renewed relations with Iran would not affect diplomatic normalization with Israel: “We will pursue normalization when it benefits us and refrain from it otherwise” (Sudan Tribune, March 24).
On February 2, 2023, Sudan and Israel finalized a deal to normalize relations. Israel hoped the deal would facilitate the deportation of Sudanese asylum seekers, but the outbreak of hostilities in Sudan in mid-April 2023 put further developments in this area on hold (Haaretz, February 3, 2020). If Sudan grows closer to Iran, its commitment to the Abraham Accords—which were half-hearted at best, even before the Gaza offensive—is likely to wither on the vine.
Iran and al-Burhan
Iran’s support for al-Burhan and the SAF is assisted by the Sudanese army’s solidly Islamist officer corps (the result of repeated purges) and the backing of Islamist militias and leaders from the al-Bashir regime connected to the SAF. Despite the Sunni–Shi’a divide, Sudan’s Islamists have a long record of cooperation with Tehran. These ties in the past included Iranian military training for Sudan’s Popular Defense Forces. [1]
In return for arms, Iran will likely demand that Sudan cut its already damaged ties with Israel and abandon the Abraham Accords entirely. Israel has a long history of encouraging and arming conflicts within Sudan as a response to the opposition of successive regimes in Khartoum. In this tradition, acting foreign minister ‘Ali al-Sadiq ‘Ali blamed Israel for encouraging the RSF during a January visit to Tehran (Press TV [Tehran], January 20). Sudanese officials have also suggested that Washington step in to halt the United Arab Emirates’ (UAE) military support for the RSF before criticizing the SAF’s ties to Iran (Sudan Tribune, February 3).
Though relations between the UAE and Iran have shown signs of improvement over the last year, the issue of Sudan remains a point of contention, with the UAE being accused of providing weapons and financial support to the RSF. [2]
Iranian Drones and the Resurgence of the SAF
 Wad al-Bashir Bridge, Omdurman (Sudan Tribune)
Wad al-Bashir Bridge, Omdurman (Sudan Tribune)
In March, coordinated tactics using drones, artillery, and infantry enabled the SAF to retake the old city area of Omdurman, the national radio and television headquarters, and the Wad al-Bashir Bridge, which is a vital supply link for the RSF. The success of this offensive is believed to be partly due to the arrival of modern Iranian drones (Al Jazeera, March 12; Radio Dabanga, March 17). The drones, which are also used to direct artillery strikes, operate out of the Wadi Sayidna base north of Omdurman. The RSF claims that the SAF receives air deliveries of Iranian drones twice a week out of Port Sudan (Reuters, April 10).
Iran began supplying unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to Sudan in 2008. This allowed the SAF to build a small arsenal of Ababil-3 drones, which have capabilities useful in the type of urban warfare common to the ongoing Sudanese conflict. Sudan also produces its own copy of the Ababil-3, known as the Zagil-3. Iranian Mohajer-class drones are also used by the SAF, with the latest in the series, the Mohajer-6, providing game-changing capabilities, including an arms payload of up to 150 kg (Military Africa, April 20, 2023).
 Sudanese Zagil-3 Drone – variant of the Iranian Ababil-3 (Skyscrapercity.com)
Sudanese Zagil-3 Drone – variant of the Iranian Ababil-3 (Skyscrapercity.com)
First produced in 2018, the Mohajer-6 has a relatively low ceiling of 3.4 miles, which makes it vulnerable to anti-aircraft defenses. The drone has seen extensive use by Russia in its latest war against Ukraine. In mid-January, the RSF claimed to have shot down a Mohajer-6 drone in Khartoum State using a man-portable air-defense system (MANPAD) (Military Africa, January 15). The RSF released photos of another downed Mohajer-6 in Omdurman on January 28 (X/@RSFSudan, January 28; Asharq al-Awsat, January 29; Radio Dabanga, January 29). Despite these public losses, the new Iranian drones have played an important role in restoring the SAF’s military credibility.
A Red Sea Port for Iran
Citing Ahmad Hassan Muhammad, “a senior Sudanese intelligence official” and alleged advisor to General al-Burhan, the Wall Street Journal reported on March 3 that Iran had unsuccessfully pressed Sudan for permission to establish an Iranian naval port on the Red Sea in exchange for advanced weapons, drones, and a seagoing helicopter carrier (Wall Street Journal, March 3). Former Sudanese foreign minister ‘Ali al-Sadiq ‘Ali responded quickly and described the report as “incorrect,” saying “Iran has never asked Sudan to build an Iranian base. I recently visited Iran, and this was not discussed” (Sputnik [Moscow], March 4).
Other sources in Sudanese military intelligence suggested such an offer was likely never made, and its disclosure may have been a means for al-Burhan to express dissatisfaction with the lack of support the SAF has received from the international community (Asharq al-Awsat, March 4). An Iranian foreign ministry spokesman described the report as “baseless and politically motivated” (Radio Dabanga, March 5). SAF spokesman Brigadier General Nabil ‘Abd Allah refuted the claim as “absolutely untrue” and denied there was any advisor to al-Burhan bearing the name Ahmad Hassan Muhammad (Sudan Tribune, March 4).
Despite the strong denials, it would be odd if Iran had not brought up the possibility of using a port on Sudan’s Red Sea coast behind closed doors, even if Iran had not asked to build a military base. An Iranian military base or port access on the western coast of the Red Sea—combined with Iran-friendly Houthis on the eastern side of the Red Sea—would make it easier for Tehran to have an armed presence along one of the world’s most important maritime routes. Iran has also recently operated three ships in and around the Red Sea. The first, operating in the Red Sea, is the IRIS Alborz, an Alvand-class British-built frigate launched in 1969 that has since been modernized. It is accompanied by the IRIS Beshehr, a Bandar Abbas-class replenishment vessel. The third is the MV Behshad, a cargo vessel believed to operate as a spy ship for Iran in the Gulf of Aden since 2021. The Behshad was alleged to have supplied information to Houthi missile groups from the Gulf of Aden but appears to have returned to Iran in April, simultaneous with a severe drop in Houthi missile attacks (Radio Dabanga, March 5; Alma Research and Education Center [Israel], April 24).
An Iranian presence would be discouraged by Egypt, which backs the SAF and has four naval ports of its own on the Red Sea. Russia, which has long sought a naval base on Sudan’s coast, would no doubt be displeased to see its Iranian ally take precedence. Relations between Saudi Arabia and Iran remain tense, and the Saudis would not be happy to see an Iranian naval base opposite its port of Jeddah, the main maritime entry point for Muslims making the pilgrimage to Mecca and Medina. Sudan has its own concerns. As with a Russian naval base in Port Sudan, an Iranian base could attract unwanted military attention from other powers. Sudan cannot afford to have its only modern sea-based port and main inlet for trade damaged or destroyed through military action. The United States, believed to have carried out a crippling cyber-attack on the Behshad in February, would be almost certain to reimpose sanctions on Sudan should it provide a naval port to Iran.
Conclusion
Though its need for military support against the RSF is serious, Sudan’s government is likely to take a measured approach toward improving its relations with Iran. The SAF has no more public support than the RSF and is seen by many Sudanese as too deeply involved with the Islamists who wielded power in Sudan during the three decades of Omar al-Bashir’s unpopular regime. Sudan’s Islamists, proud Sunnis who are tightly tied to the transitional government, are poor candidates to become puppets of Shi’ite Iran. Sudan’s army (commanded by Sunni Islamists) is also unlikely to commit itself militarily to the pursuit of Iranian objectives. There is, of course, the possibility of an RSF victory in the ongoing struggle, but for now, the RSF has no presence in eastern Sudan and no ties to Iran.
Sudan has no interest in seeing damaging U.S. sanctions restored after spending years trying to convince Washington it is not a state sponsor of terrorism. Once the current conflict ends, Sudan will need help, not hindrance, in its reconstruction, and will need to look further than Iran for assistance. All these factors speak against the establishment of an Iranian naval facility in Sudan or a formal alliance. If, however, Iranian assistance brings about an SAF triumph, Tehran is certain to come calling for payment in some form.
Notes:
[1] Jago Salmon: A Paramilitary Revolution: The Popular Defence Forces, Small Arms Survey, Geneva, 2007, pp.17-18.
[2] Final report of the Panel of Experts on the Sudan, S/2024/65, January 15, 2024, pp. 14–15, 51–52.
Andrew McGregor
Eurasia Daily Monitor 21(169)
Washington DC, November 19, 2024
Executive summary:
- Ukraine is alleged to be providing military equipment and training to the Tuareg separatist coalition CSP-DPA in its armed struggle against Russian-backed Malian government forces.
- This support is framed as a strategic move by Ukraine to counter Russian influence in Africa, particularly targeting Russian forces and mercenaries in Mali.
- This commitment reflects Kyiv’s growing interest in subversive tactics to distract and weaken Moscow as Ukraine engages in a worldwide manhunt for Russian forces.
** **A mid-October investigative article that appeared in the French daily Le Monde alleged Ukraine is supplying military drones to Tuareg rebels operating in northern Mali. This support was described as “discreet but decisive” (Le Monde, October 13). The recipient of these drones is said to be the Tuareg separatist coalition known as CSP-DPA (Cadre Stratégique pour la Défense du Peuple de l’Azawad). Ukraine’s foreign ministry rejected the article’s accusations on October 14 as “false narratives of… the aggressor state Russia,” after allegedly asking the French government to prevent its publication (Le Pays [Ouagadougou], October 20; Kyiv Independent, October 15). The report also claimed, citing a source close to Ukrainian intelligence, that some Tuareg have been trained in Ukraine while a number of Ukrainian specialists have trained rebels in the Sahel. Never known for presenting a unified stand, Mali’s Tuareg remain divided between separatist, Islamist-Jihadist and pro-government militias.
**A mid-October investigative article that appeared in the French daily Le Monde alleged Ukraine is supplying military drones to Tuareg rebels operating in northern Mali. This support was described as “discreet but decisive” (Le Monde, October 13). The recipient of these drones is said to be the Tuareg separatist coalition known as CSP-DPA (Cadre Stratégique pour la Défense du Peuple de l’Azawad). Ukraine’s foreign ministry rejected the article’s accusations on October 14 as “false narratives of… the aggressor state Russia,” after allegedly asking the French government to prevent its publication (Le Pays [Ouagadougou], October 20; Kyiv Independent, October 15). The report also claimed, citing a source close to Ukrainian intelligence, that some Tuareg have been trained in Ukraine while a number of Ukrainian specialists have trained rebels in the Sahel. Never known for presenting a unified stand, Mali’s Tuareg remain divided between separatist, Islamist-Jihadist and pro-government militias.
Calling out Ukraine for its alleged support of “international terrorist organizations,” Russian foreign ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova declared that Ukrainian support for Malian separatists was “interference in the internal affairs of African countries” (Le Pays [Ouagadougou], October 20).
According to Le Monde, light quadcopter drones were used in September and October to drop explosives on Russian camps at Goundam (twice) and Léré, creating casualties before returning to base (Le Monde, October 13). Mali’s army, with likely assistance from their Russian advisors, is also deploying drone warfare. On the night of October 5-6, Malian drones struck what was described by the army as a column of vehicles bearing “terrorists” in CSP-DPA territory. Local sources reported the strike hit a convoy of civilian vehicles carrying Nigérien gold miners (Kyiv Post, October 9).
 FAMa Chinese-made Norinco MRAP VP11 Destroyed by Tuareg Militants (Militarnyi)
FAMa Chinese-made Norinco MRAP VP11 Destroyed by Tuareg Militants (Militarnyi)
In a September interview, CSP-DPA spokesman Mohamed Elmaouloud Ramadane emphasized the efforts of his group to establish relations with external partners, citing in particular a common cause between the peoples of “Azawad” (the name used by separatists for northern Mali) and Ukraine against Russian mercenaries: “Ukraine sees enemies where the Wagners are and we, in Azawad, are [also] facing this organization that is the cause of misfortune and destruction in many countries, in Libya, Syria, the Central African Republic, Sudan and of course in Ukraine” (Contre-Poison, September 9).
Describing cooperation with Ukraine as being “in its first phase,” the CSP-DPA spokesman requested arms and military training from Ukraine, placing the struggle of the Azawad separatists in the context of a greater war against Russian imperialism, describing this as “a global fight because Russia is a threat to the entire world… the entire international community must get behind us and help us put an end to this Malian and Russian occupation of our territory” (Contre-Poison, September 9).
Though Russian troops in Africa continue to be called “Wagner” in common parlance, Prigozhin’s mercenary forces in Africa were reorganized as the “Africa Corps” after his death, coming under the direct command of the Russian Defense Ministry. Accusing the Russians of participation in extrajudicial executions of civilians, population displacement, theft of all-important livestock and the destruction of infrastructure, the rebel spokesman warned that the changing status of Russian troops in Mali would have “legal consequences”: “It should be noted that since Wagner’s mercenaries have been dependent on the Russian Ministry of Defense, Moscow is directly and legally responsible for their actions, unlike when Prigozhin was alive” (Contre-Poison, September 9).
 Colonel Hamad-Rhissa Ag Hamad-Assalah (Contre-Poison)
Colonel Hamad-Rhissa Ag Hamad-Assalah (Contre-Poison)
Colonel Hamad-Rhissa Ag Hamad-Assalah, who led CSP-DPA fighters in the successful attack on Malian regulars and Russian mercenaries at Tinzawatène, has been more reticent on the issue of Ukrainian military assistance, stating: “We are not aware of any assistance from Ukraine in terms of intelligence and drone support.” The colonel has, however, called for help from France, which, at the time of independence in 1960, imposed Azawad’s narrow link to southern Mali and its much larger population, culturally and linguistically very different from the pastoral and semi-nomadic communities of Tuareg, Arabs, Fulani (a.k.a. Peul) and Songhay (a.k.a. Ayneha) in the arid north:
“If there is one African country whose sovereignty must be recognized by France, it is Azawad. It is France that brought us together with Mali in the past and today, it is France that must separate us from Mali” (Contre-Poison, August 16).
Some Malians see a reciprocal connection between French support for Ukraine and Ukrainian intervention in the former French colonies, or, alternatively, an effort by NATO to punitively destabilize West Africa after a recent decline in Western influence (Burkina24.com, October 19). These and other views are actively promoted by Russian influence experts active in the Sahel.
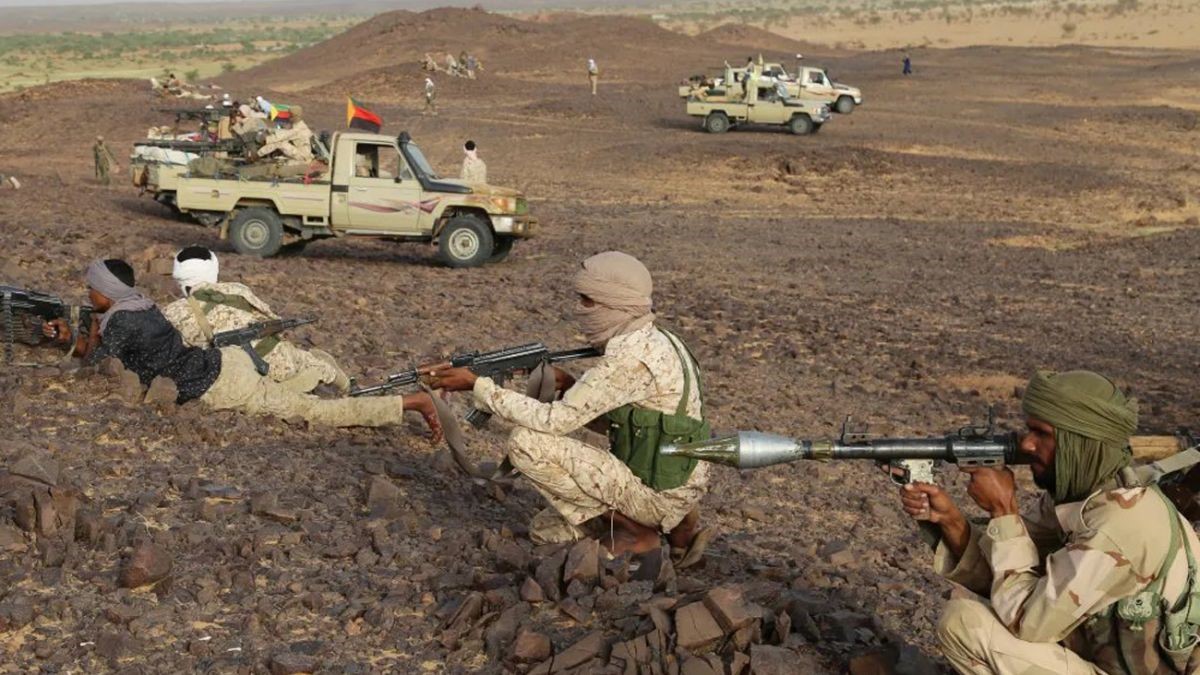 Tuareg Fighters on an Exercise (Apostrophe.UA)
Tuareg Fighters on an Exercise (Apostrophe.UA)
A peacetime Russia could find the troops and weapons needed to support a greater effort in Mali’s desert warfare, but it is not peacetime and North Korean drones and troops are being fed into the front lines to help a manpower-starved Russian military combat Ukraine’s Kursk incursion. As promised, the Ukrainians have internationalized the war on Russia’s official or unofficial militaries wherever they are deployed, including Syria, Sudan and Mali (Kyiv Post, October 9). Ironically, it is the Malian junta’s invitation to the Russians that has brought the Tuareg separatists the aerial power in the form of drones that they need to defeat government forces and their allies on the battlefield.
However, diplomatic support for “Azawad” from a Western nation would ultimately be more valuable than military assistance from Ukraine. To this point, the separatists are saying all the right things, offering strategic advantages in return for European support, potentially acting as “border guards” along the Sahel, capable of controlling the flow of migrants to Europe and stemming drug trafficking through the region (Contre-Poison, September 9). There is a strong possibility that Ukraine’s over-taxed military intelligence force may be forced to divert resources from distant Mali to interfere with the more immediate threat created by the flow of North Korean troops to the Ukraine front.
Andrew McGregor
Eurasia Daily Monitor 21(146)
Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC, October 9, 2024
Executive Summary:
- Over the past months, Russia’s “Africa Corps,” partly made up of former Wagnerites, has faced numerous blows from jihadist groups in Africa’s Sahel states.
- These defeats have begun to raise questions about the future of Russian military forces in the region following the eviction of French and US forces, replaced by Russian mercenaries whose massacres fuel rebel anger and desire for revenge.
- Having seized power unlawfully on the pretext of needing to evict the Western military presence, Sahelian coup leaders’ credibility rests on Russian-backed military success against the jihadists and separatists who challenge them.
Al-Qaeda has come hunting for Russian troops in the Sahel, scoring another blow against Moscow’s “Africa Corps” in the Malian capital of Bamako on September 17. The attack on Russian and Malian military facilities came a month after a devastating joint strike by al-Qaeda and Tuareg separatists on a Russian/Malian column at Tinzwatène, near the Algerian border. Recent defeats of Russian-backed government forces in Niger, the sudden departure of recently-arrived Russian paramilitaries for urgent deployment on the Kursk Front and the instability of military regimes in three Sahel states belonging to the pro-Russian Alliance des États du Sahel group (AES -Mali, Niger and Burkina Faso) are beginning to raise questions about the future of Russian forces in the region.
 Attacker Sets Fire to an Aircraft (Jeune Afrique)
Attacker Sets Fire to an Aircraft (Jeune Afrique)
The attack was carried out by militants of Jama’at Nusrat al-Islam wa’l-Muslimin (JNIM), led by a veteran Malian Tuareg jihadist, Iyad ag Ghali. JNIM was formed in 2017 as a coalition of smaller jihadist groups drawn from the Tuareg, Arab and Fulani communities. They pledged allegiance to al-Qaeda almost immediately, and were accepted into the movement. This by no means indicates a general support for al-Qaeda amongst these minority ethnic groups, who are targeted daily in Malian and Russian counterinsurgency operations.
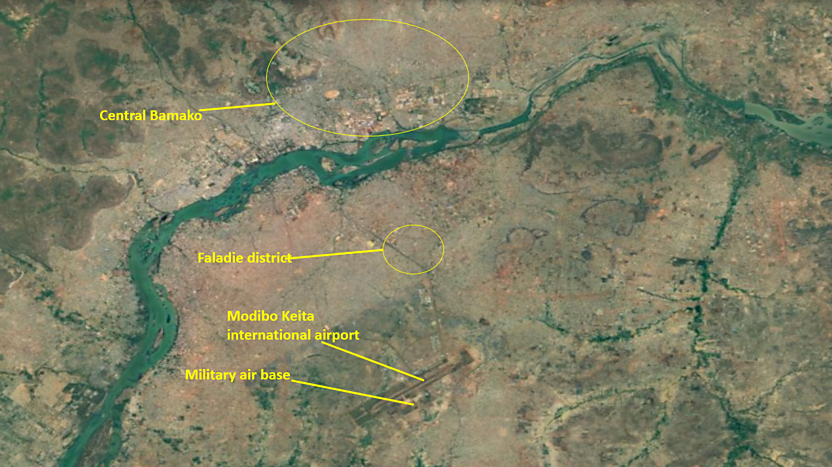 Location of Bamako Attacks (BBCM)
Location of Bamako Attacks (BBCM)
A small number of members of the mostly Fulani Katiba Macina (katiba = battalion) struck two military installations south of the Niger River in the morning of September 17. The leader of the attack on the first target, Senou Air Base 101, a launch point for drone operations against militants in northern Mali, was ‘Abd al-Salam al-Fulani (Chirpwire, September 17, 2024, via BBCM).
The second attack on a gendarmerie school in nearby Faladié was led by Salman “Abu Hudhaifa” al-Bambari, a member of the Muslim Bambara ethnic group. As the dominant ethnic group in the Malian military and government, the Bambara have more often been the target of the jihadists than their allies**.** The school also serves as a dormitory for Russian troops, who came under attack. Fulani preacher Amadou Koufa, leader of the Katiba Macina, said the operation was in response to massacres of civilians committed by government troops and their Russian allies (al-Zallaqa, September 20, via BBCM).
On the day of the attacks, JNIM issued an inflated claim of heavy losses of “hundreds of Wagner” personnel (Chirpwire, September 17, via BBCM). A more accurate figure is 77 dead and 200 wounded, Malians and Russians combined. Although the GRU (Russian military intelligence) has assumed command of the former Wagner fighters in Africa, former Wagner personnel (who still form about half of the force) are still allowed to wear Wagner insignia, leading many Sahelians to still refer to Russians as “Wagner” (Reuters, September 11). A short video released the day of the Bamako attack purports to show Russian mercenaries who had just killed several militants near the airport (X, September 17). Russian embassy officials deplored the loss of Malian troops, but said nothing about Russian losses (X, September 20).
 Young Fulani Men Were Rounded Up in Bamako After the Attack as Suspects: None Wear the Camo-pattern Uniforms Worn by the Attackers (ORTM)
Young Fulani Men Were Rounded Up in Bamako After the Attack as Suspects: None Wear the Camo-pattern Uniforms Worn by the Attackers (ORTM)
A week after the attack on Bamako, Tuareg separatists of the same group that worked with JNIM in the deadly Tinzwatène ambush (the Cadre stratégique pour la défense du peuple de l’Azawad – CSP-DPA), destroyed a Russian command post in Mali’s northern Timbuktu region with a bomb-carrying drone (X APMA, September 25; X Wamaps, September 26).
Fellow AES state Burkina Faso is far from stable, even with Russian support. Captain Ibrahim Traoré’s military regime has survived four coup attempts since it took power in September 2022 and began to evict French and American forces in favor of Russian mercenaries. In the worst terrorist attack in Burkina Faso’s history, JNIM militants killed as many as 400 people at Barsalogho on August 24, including government troops, militia members and civilians (Bamada.net [Bamako], September 17).
A week later, 100 Russian troops of the “Bear Brigade” were withdrawn from Burkina Faso to fight on the Kursk front in Russia after a short three-month deployment. The unit (officially the 81st Bear Special Forces Volunteer Brigade) is a Russian PMC composed of special forces veterans supplied with arms and equipment by the Russian Defense Ministry (L’Indépendent/AFP, August 31). Its members have signed contracts with the GRU (AFP, August 30).
 Captain Ibrahim Traoré with Bear Brigade Commander Viktor Yermolaev (Le Monde)
Captain Ibrahim Traoré with Bear Brigade Commander Viktor Yermolaev (Le Monde)
Led by commander Viktor Yermolaev (a.k.a. “Jedi”), one hundred members of the brigade arrived in Burkina Faso in late May to provide security for junta leader Captain Ibrahim Traoré; they were later joined by up to 200 more members. In what might be interpreted as unsettling news for AES junta leaders dependent on Russian military support, Yermolaev announced that “When the enemy arrives on our territory, all Russian soldiers forget about internal problems and unite against a common enemy” (Le Monde, August 29). However, he did promise that his Russian troops would return once their mission in Russia was complete (RFI, August 29).
Niger, the third AES member, is also facing an upsurge in attacks by religious extremists since replacing French and American forces with GRU “mercenaries.” Two days before the strike on Bamako, JNIM’s Katiba Hanifa raided a military post in Niakatire, Niger, killing at least 27 members of a special forces battalion (Chirpwire, September 20, via BBCM; Wamaps, September 15). Katiba Hanifa is a branch of the JNIM/al-Qaeda network led by Abu Hanifa, (A.K.A. Oumarou), a Malian Fulani.
Russia’s strong-handed tactics have not restored order to the post-coup Sahel nations; on the contrary, civilian and military deaths have sky-rocketed. Civilian fatalities are reported to have risen by 65% over the previous year, with both sides bearing responsibility (Reuters, September 11). Nearly half the territory of Sahel Alliance nations is now under rebel or separatist control. Rebel anger and desire for revenge is fuelled by Russian massacres large and small. The Sahelian coup leaders cannot acknowledge the reality of a Russian failure; having seized power unlawfully on the pretext of needing to evict the Western military presence, their credibility rests on Russian-backed military success against the jihadists and separatists who challenge them.
Andrew McGregor
Eurasia Daily Monitor 21(130)
Washington DC, September 11, 2024
Executive Summary:
- The July attack by Tuareg rebels in Mali that killed Malian government troops and Wagner Group mercenaries has been connected to Ukraine, causing substantial international backlash for Kyiv.
- The death of multiple members of Mali’s army in the attack would mean Ukraine was involved in the killing of regular army members of a sovereign state unengaged in any hostilities with Ukraine, past or present.
- If Ukraine were involved in the clash at Tinzawatène, it would find little in international law to support its intervention, which could risk international support for Kyiv.
During fighting that took place on July 25, 26 and 27 around the north Malian border town of Tinzawatène, Tuareg rebels launched a devastating ambush that killed scores of Malian government troops and their Russian Africa Corps allies. Reports later emerged that the Tuareg fighters had received substantial aid and training from Ukraine, quickly sparking an international backlash.
The Tuareg forces involved in the battle hailed from a coalition of armed separatist groups, the Cadre Stratégique pour la Défense du Peuple de l’Azawad (CSP-DPA), and the al-Qaeda affiliated Jama’at Nusrat al-Islam wa’l-Muslimin (JNIM). It is Ukraine’s alleged involvement with the latter that has contributed most to creating an international incident.
After the ambush, a photo was posted in Kyiv Post showing victorious Tuareg fighters holding a Ukrainian flag. Sources in Ukraine’s defence and security forces confirmed the photo’s authenticity, asserting that Ukraine fully supports any forces in the various parts of Africa that are fighting against Wagner terrorists. (Kyiv Post, July 29; Ukrainska Pravda, July 29).
Russia’s foreign ministry seized the opportunity to declare that Kiev’s support for al-Qaeda-affiliated terrorist groups was “not surprising at all,” citing Ukraine’s alleged “terrorist methods on the territory of the Russian Federation, committing sabotage, political assassinations and regularly bombing civilian targets” (Agence de Presse Africaine [Dakar], August 7).
Malian media described the ambush as a “secret project” of the Ukrainian GUR (Main Directorate of Intelligence of the Ministry of Defence of Ukraine), including the training of “terrorists in combat techniques and supplying equipment, drones and weapons” for destabilization operations (Maliweb, August 17). The alleged director of this project is GUR Lieutenant Colonel Andrii Romanenko, though the source of this information appears to be Anatoly Chari, a controversial Ukrainian journalist and politician (Maliweb, August 16). Chari is generally viewed as pro-Russian (though he denies this), and was charged with High Treason by the Ukrainian Security Service (SBU) in 2021.
The first cohort of Tuareg fighters is reported to have started combat training under Ukrainian direction in early 2024 (LeFaso.net [Bamako], August 15). An investigation by Malian authorities is reported to have established the training was carried out in Mauritania, where local authorities have launched their own investigation at Bamako’s request (LeFaso.net [Bamako], August 5). It has also been reported that some members of the Tuareg alliance were sent to Ukraine for intensive training (Le Monde, August 7).
Andrii Yusov, spokesman for Ukraine’s Defence Intelligence (GUR), told Ukrainian public broadcaster Suspilne TV that the rebel fighters had received from Ukraine “useful information, and not just that, which allowed them to carry out a successful military operation against Russian war criminals” (Kyiv Independent, August 5). Despite this, a CSP-DPA spokesman downplayed any special ties to Ukraine’s intelligence services: “We have links with the Ukrainians, but just as we have with everyone else, the French, Americans and others” (Le Monde, August 2).
Mali’s transitional government announced it had learned “with deep shock” of Yusov’s admission that Ukraine was involved “in a cowardly, treacherous and barbaric attack by armed terrorist groups.” These actions had not only violated Mali’s sovereignty, but constituted “a clear aggression against Mali and support for international terrorism, in flagrant violation of international law, including the Charter of the United Nations” (Maliweb [Bamako], August 4). Yusov later issued a retraction of his remarks, claiming he was not speaking of the involvement of Ukrainian intelligence services (Maliweb, August 17).
Matters were worsened when Yurii Pyvovarov, Ukraine’s Dakar-based ambassador to Senegal, published a Facebook video which Senegalese authorities described as providing “unequivocal and unqualified support for the terrorist attack” in Mali.(al-Jazeera, August 7). While the post was deleted within 24 hours, Pyvovarov was summoned by Senegalese authorities to account for it, while the pro-Russian Alliance des États du Sahel (AES – Mali, Niger and Burkina Faso) encouraged Senegal to break diplomatic relations with Ukraine (Sputnik, August 5; Maliweb, August 10). Mali severed diplomatic relations with Ukraine on August 4, referring to the “neo-Nazi and villainous nature” of Ukrainian authorities (Maliweb [Bamako], August 4). Niger followed suit on August 6 (Le Monde/AFP, August 6).
Ukraine’s foreign ministry described Mali’s break as “unfriendly… short-sighted and hasty,” adding that Bamako had failed to provide “any evidence of Ukraine’s involvement” in the ambush. The ministry further denied Ukrainian support for terrorism and reiterated its commitment to international law and “the inviolability of the sovereignty and territorial integrity of other countries” (Kyiv Independent, August 5).
On August 19, the foreign ministers of the AES states sent a joint letter to the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) denouncing Ukraine’s alleged support for international terrorism and calling upon the Council to take appropriate measures against Ukraine (L’Essor [Bamako], August 22; Asharq al-Awsat, August 22). As the UNSC does not have a mandate to address conflicts between member states, the letter could be a preliminary step to bringing the matter before international courts (RFI, August 22).
Accusations of Ukrainian support for terrorism will be welcomed by Putin-admiring Western politicians seeking to defund Western support for Ukraine’s defense. The death of multiple members of Mali’s army in the attack would mean Ukraine was involved in the killing of regular army members of a sovereign nation (albeit a military dictatorship), unengaged in any hostilities with Ukraine, past or present.
Mali has the right to partner with another country (e.g. Russia) for defensive purposes, but this does not give the right to a nation belligerent with that partner to combat its enemy on Mali’s sovereign territory. In May 2023, GUR director General Kyrylo Budanov famously declared “we’ve been killing Russians and we will keep killing Russians anywhere on the face of this world until the complete victory of Ukraine” (Yahoo!News, May 5, 2023). However, if Ukraine was involved in any way in the clash at Tinzawatène, it will find little in international law to support its intervention. Kiev’s decision to expand its war against Russia may prove to have been a serious misstep.