Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir extracts, fractions and isolated compounds (original) (raw)
Abstract
Pterocarpus erinaceus has been chosen based on ethnobotanical surveys carried out in the Tchamba district of the Republic of Togo. Investigation of the antibacterial as well as cytotoxic activities of whole extracts, fractions and compounds isolated from the leaves, trunk bark and roots of Pterocarpus erinaceus. Bio-guided fractionation of the raw extracts of plant parts and subsequent isolation of compounds from active fractions using normal phase open column chromatography. The broth microdilution method was used to evaluate the antibacterial activity, based on the determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) against several bacterial species representative of the most commonly encountered infectious diseases worldwide. The cytotoxicity of the raw extract and the most active fractions on a human non-cancerous cell (namely MRC-5) was estimated with a MTT assay. The chemical structure of the compounds isolated was elucidated using a combination of advanced Nuclear Magne...
Figures (8)
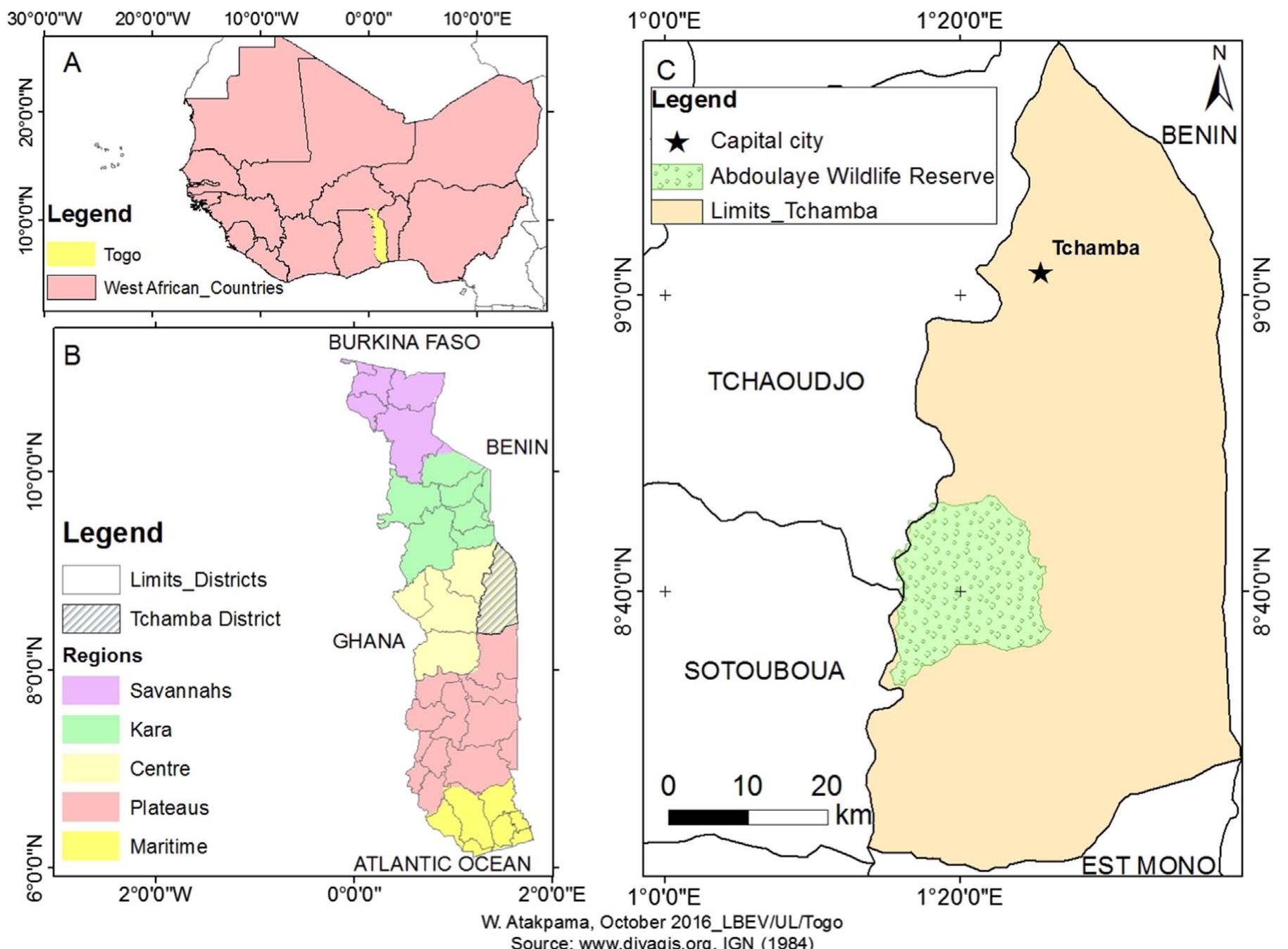
Fig. 1. Map of Republic of Togo and the geographical area relevant to the research described. A: Location of the Republic of Togo in West Africa; B: Togo and its different regions an Districts; C: Tchamba district. “ Indeed, in Togo, economic hardship and an uneven access to healthcare facilities and modern medication promote the spread of in- fectious diseases, which in this country rank among the top ten priority diseases (Tittikpina, 2012; Ministére de la santé et de la protection sociale du Togo, 2015). Natural remedies based on locally grown plants and traditional knowledge related to them often represent the only source and resource to treat such infectious diseases. It is therefore advisable to conduct studies on the different plants used to treat those diseases, firstly because they are used on humans already - and in some cases, have been for centuries — and secondly because they may indeed contain substances with interesting therapeutic activities (Tittikpina et al., 2016a). Therefore, we conducted a study based on semi-struc- tured individual interviews with 53 traditional healers (TH) from the Tchamba district of Togo (Fig. 1) to identify the plants they used to treat infectious diseases. We recorded and identified 43 different plant species (Tittikpina et al., 2017). Among those 43 plants, P. erinaceus has been identified by us as being among the most interesting plants (Tittikpina, 2012; Tittikpina et al., 2013). Some studies have already explored the biological activities of this plant, which is found in several Western African countries; but, to the best of our knowledge, no in depth studies have been conducted so far on the antibacterial activities of the extracts, fractions and compounds derived from this plant. Based
Plant materials used in the study and extraction yields for each extracts. Raw extracts and fractions of the different parts of Pterocarpus erinaceus. Table 1
Antibacterial activities of the raw extracts (MeOH-DCM, 1:1) of P. erinaceus parts. Raw extract: methanolic-dichloromethane (MeOH-DCM) extract. Antibacterial activity is based on the determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC, ie. concentration that inhibits 100% of bacterial growth) valu MICs are marked in bold. > 256: no MIC observed at the highest concentration (256 g/mL) tested. X%: PI (percentage of inhibition of bacterial growth) observed at 256 ,1g/mL, the highest concentration under investigation. Each experiment has been repeated in three different occasions (n = 3). Table 2
Antibacterial activities of the most effective fractions against MRSA and S. epidermidis. MRSA: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus; S. epidermidis: Staphylococcus epi- dermidis. MICs are marked in bold. PIso: concentration at which a 50% of bacterial growth is inhibited at a concentration lower than 256 g/mL. ND: not determined. Tests have repeated in 3 different occasions (n = 3).
Antibacterial activities of the fractions derived from the raw extracts of P. erinaceus. MUGS are Marked in DOId. > 256: no MIC (concentration that inhibits 100% of bacterial growth) observed at the highest concentration (256 g/mL) tested X%: PI (percentage of inhibition of bacterial growth) observed at 256 1.g/mL, the highest concentration under investigation. Each experiment has been repeated in three different occasions (n = 3).
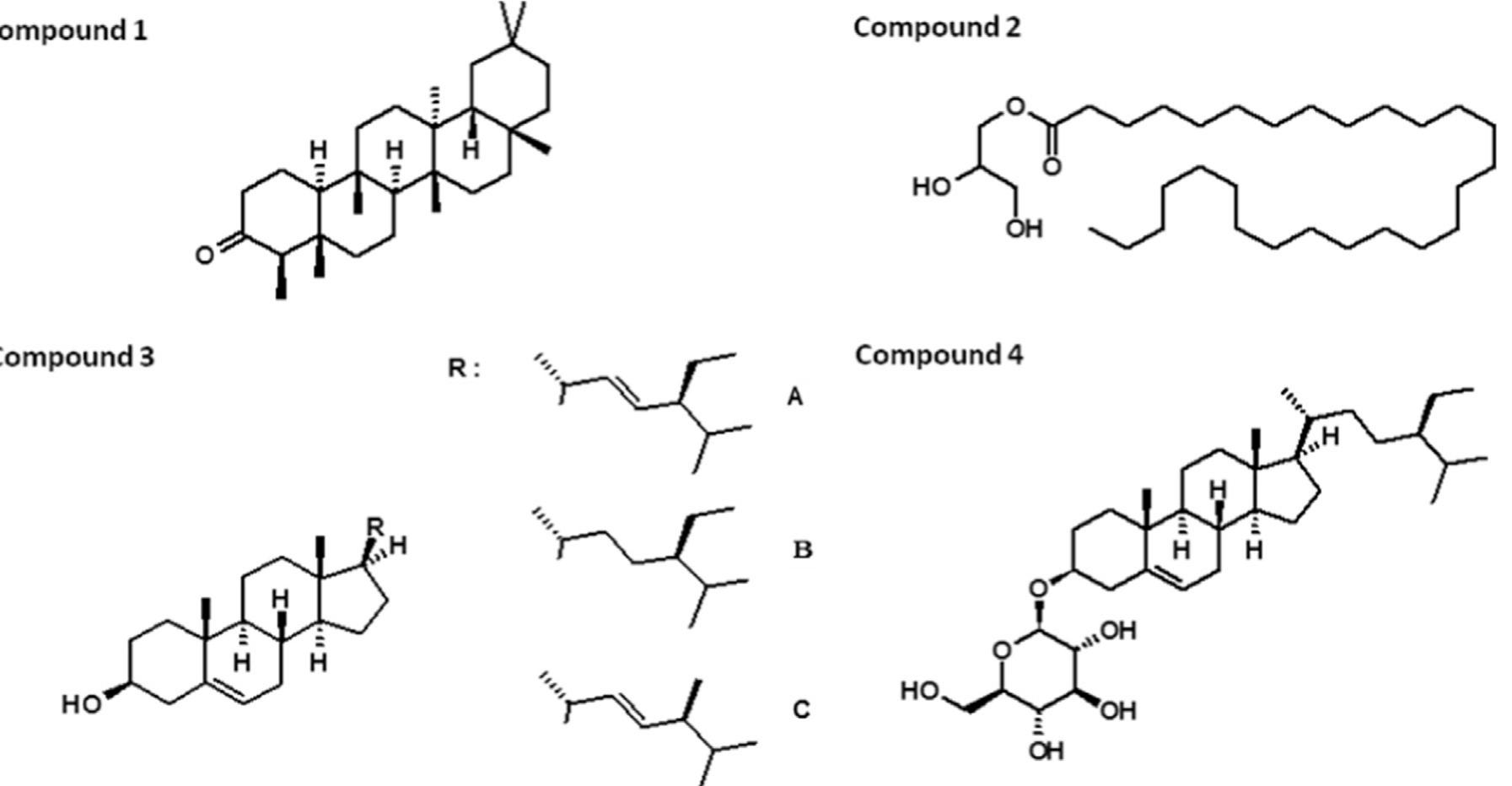
Fig. 3. Chemical structures of compounds isolated from the trunk bark. Compound 1: Friedeline. Compound 2: 2,3 dihydroxypropyloctacosanoate. Compound 3: mixture of phytosterols: 39.6% of stigmasterol (A), 40.4% of B-sitosterol (B) and 20% of campesterol (C). Compound 4: f-sitosteryl-8-D-glucopyranoside.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (26)
- Arora, M., Kalia, A.N., 2013. Isolation and characterization of stigmasterol and β-sitos- terol-D-glycoside from ethanolic axtract of the stems of Salvadora persica Linn. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 5, 245-249 (ISSN-0975-1491).
- Camporese, A., Balick, M.J., Arvigo, R., Esposito, R.G., Morsellino, N., De Simone, F., Tubaro, A., 2003. Screening of anti-bacterial activity of medicinal plants from Belize (Central America). J. Ethnopharmacol. 87, 103-107. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/ S0378-8741(03)00115-6.
- CLSI, 2009. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard M07-A8, 8th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
- Fontanay, S., Grare, M., Mayer, J., Finance, C., Duval, R.E., 2008. Ursolic, oleanolic and betulinic acids: antibacterial spectra and selectivity indexes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 120, 272-276. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2008.09.001.
- Hage, S., Stanga, S., Marinangeli, C., Octave, J.N., Dewachter, I., Quetin-Leclercq, J., Kienlen-Campard, P., 2015. Characterization of Pterocarpus erinaceus kino extract and its gamma-secretase inhibitory properties. J. Ethnopharmacol. 163, 192-202. http:// dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.028.
- Karou, D., Dicko, M.H., Simpore, J., Traore, A.S., 2005. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of polyphenols from ethnomedicinal plants of Burkina Faso. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 4, 823-828.
- Kombate, K., Dagnra, A.Y., Saka, B., Mouhari-Toure, A., Akakpo, S., Tchangaï-Walla, K., Pitche, P., 2011. Prévalence de Staphylococcus aureus résistant à la méticilline (SARM) au cours des infections cutanées communautaires à Lomé (Togo). Med. Trop. 71, 68-70 (ISSN 0025-682X).
- Kuete, V., Nana, F., Ngameni, B., Mbaveng, A.T., Keumedjio, F., Ngadjui, B.T., 2009. Antimicrobial activity of the crude extract, fractions and compounds from stem bark of Ficus ovata (Moraceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 124, 556-561. http://dx.doi.org/10\. 1016/j.jep.2009.05.003.
- Luhata Lokadi, P., Munkombwe Namboole, M., 2015. Isolation and characterisation of Stigmasterol and Β -Sitosterol from Odontonema Strictum (Acanthaceae). J. Innov. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2, 88-95.
- Ministère de la santé et de la protection sociale du Togo, 2015. -Principaux indicateurs de santé. p. 66. Retrieved from 〈http://www.sante.gouv.tg/fr/content/principaux- indicateurs-de-sante-2015-0〉.
- Mosmann, T., 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 65, 55-63.
- O'Neill, J., 2016. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Retrieved from 〈https:// amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf〉.
- Ouédraogo, N., Sawadogo, R.W., Tibiri, A., Bayet, C., Lompo, M., Hay, A.E., Koudou, J., Dijoux, M.G., Guissou, I.P., 2012. Pharmacological properties and related con- stituents of stem bark of Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir. (Fabaceae). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 5, 46-51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(11)60244-7.
- Queiroga, C.L., Silva, G.F., Dias, P.C., Possenti, A., Carvalho, J.E., 2000. Evaluation of the antiulcerogenic activity of friedelan-3-ol and friedelin isolated from Maytenus ilicifolia (Celastraceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 72, 465-468. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0378- 8741(00)00237-3.
- Salawu, O.A., Aliyu, M., Tijani, A.Y., 2008. Haematological studies on the ethanolic stem bark extract of Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir (Fabaceae). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 7, 1212-1215.
- Tittikpina, N.K., 2012. Contribution à l'évaluation des propriétés anti-microbiennes de: Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir (Faboïdeae), Daniellia oliveri (Rolfe) Hutch. et Dalz (Caesalpinoïdeae) et Anchomanes difformis (Blume) Engler (Araceae), utilisées en médecine traditionnelle dans la Préfecture de Tchamba (TOGO) (Th. D. Pharm). University of Lomé, pp. 89.
- Tittikpina, N.K., Agban, A., Gbogbo, K.A., Hoekou, Y.P., Pereki, H., Batawila, K., Akpagana, K., 2013. Évaluation des propriétés antimicrobiennes de Pterocarpus eri- naceus Poir (Faboïdeae) et Daniellia oliveri (Rolfe) Hutch. et Dalz (Caesalpinoïdeae), utilisées en médecine traditionnelle au Togo. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 7, 1586-1594. http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/ijbcs.v7i4.15.
- Tittikpina, N.K., Ejike, E.C.C.C., Estevam, E.C., Nasim, M.J., Griffin, S., Chaimbault, P., Kirsch, G., Atakpama, W., Batawila, K., Jacob, C., 2016a. Togo to go: products and compounds derived from local plants for the treatment of diseases endemic in sub- saharan Africa. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 13, 85-94. http://dx.doi. org/10.4314/ajtcam.v13i1.3664.
- Tittikpina, N.K., Nana, F., Fontanay, S., Batawila, K., Akpagana, K., Kirsch, G., Duval, R.E., Chaimbault, P., Jacob, C., 2016b. Study of Pterocarpus erinaceus, a promising plant from Togo to treat infectious diseases. Planta Med. 81, S1-S381. http://dx.doi. org/10.1055/s-0036-1596502.
- Tittikpina, N.K., Atakpama, W., Pereki, H., Nasim, M.J., Wesam, A., Fontanay, S., Nana, F., Ejike, C.E.C.C., Kirsch, G., Duval, R.E., Chaimbault, P., Karou, S.D., Batawila, K., Akpagana, K., Jacob, C., 2017. "Capiture" plants with interesting biological activities: a case to go. Open Chem. 15, 208-218. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/chem-2017-0024.
- Tu, Y., 2011. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 17, 1217-1220. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm.2471.
- Van Vuuren, S.F., 2008. Antimicrobial activity of South African medicinal plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 124, 462-472. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2008.05.038.
- Viswanathan, M.B., Jeya Ananthi, J.D., Sathish Kumar, P., 2012. Antimicrobial activity of bioactive compounds and leaf extracts in Jatropha tanjorensis. Fitoterapia 83, 1153-1159. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.07.007.
- World Health Organization (WHO), 2010. The African Health Monitor -Special Issue: African Traditional Medicine Day, p. 104. Retrieved from 〈http://apps.who.int/ medicinedocs/documents/s21374en/s21374en.pdf〉.
- World Health Organization (WHO), 2012. Global Report for Research on Infectious Diseases of Poverty, p. 168. Retrieved from 〈http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/ 10665/44850/1/9789241564489_eng.pdf〉.
- World Health Organization (WHO), 2017. Fact Sheet: The Top 10 Causes of Death. Retrieved from 〈http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/〉.