Medicinal plants: Treasure trove for green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications (original) (raw)
Abstract
The cornerstone of nanoscience and nanotechnology are nanoparticles which have immense power and functional ability in diverse fields. Nanoparticles are synthesized by physical, chemical methos but limitations are due to its toxicity. We have discussed few green synthesis routes which are eco friendly and less toxic methods, including alage, microorganisms, plants etc.. Expoiting the potential of medicinal plants, is one of the green synthesis routes and is significant because the current therapeutic approaches have toxicity problems and microbial multidrug resistance issues. As the metal nanoparticles have received great attention across the globe, so in this study we have discussed and focused many different metallic nanoparticles obtained by green synthesis using medicinal plants. We have also discussed the types, size and medicinal properties like antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, antiviral activities of nanoparticles. The biomolecules, secondary metabolites and coenzymes present in the plants help in easy reduction of metal ions to nanoparticles. Such nanoparticles are considered as potential antioxidants and promising candidates in cancer treatment. The simplified model summarises the green synthesis, its characterization using physicochemical means and their biomedical applications. Succinctly, we have discussed the recent advances in green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles, milestones, therapeutic applications and future perspectives of biosynthesized nanoparticles from some important medicinal plants.
Figures (10)
Fig. 1. (Upper) Number of papers reporting the keyword search “green AND synthesis AND nanoparticles AND plant” from SCOPUS (data were analysed form 1996 to 2018) (Lower) Geographical map depicting India, with more than 1400 published papers rom 1996 to 2018 followed by Iran that published about 260 papers, as the most active region working in this field of research. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
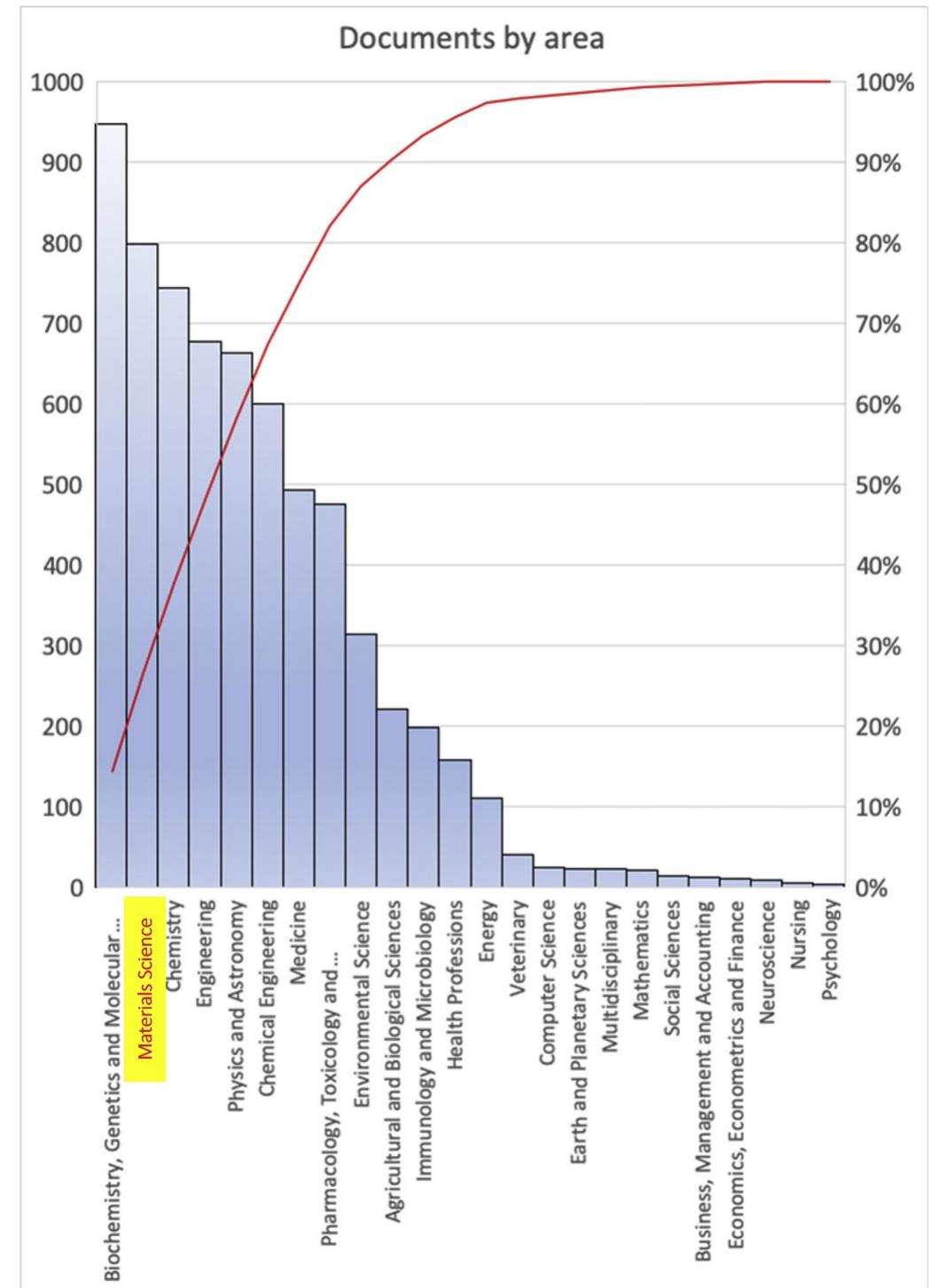
Fig. 2. The field of materials science is second one after the Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology area containing the largest amount of publications.
Another group of organisms like fungi have enzymes and proteins which can reduce metal ions into nanoparticles and also stabilize the resulting nanoparticles (Khandel and Shahi, 2018). Plethora of different proteins in fungi convert the metallic salts into corresponding Fig. 3. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles, their physico-chemical characterization and biomedical applications. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
Metallic nanoparticles synthesized from different medicinal plants, plant part used, size in nm, and their medicinal properties.
The authors are thankful to Dr. Hemant Ritturaj Kushwaha, Jawa- harlal Nehru University, New Delhi, India for critically reading the manuscript.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (166)
- Abdel-Fattah, W.I., Ali, G.W., 2018. On the anti-cancer activities of silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 5 (1), 43-46. https://doi.org/10.15406/ jabb.2018.05.00116.
- Abdullah, A.A., Al-Moslih, M.I., 2005. Prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. East. Mediterr. Health. J. 11, 1045-1052.
- Ahmad, A., Senapati, S., Khan, M.I., Kumar, R., Sastry, M., 2005. Extra-/intracellular, biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by an alkalotolerant fungus, Trichothecium sp. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 1, 47-53.
- Ahmad, N., Sharma, S., 2012. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extracts of Ananas comosus. Green Sustain. Chem. 2 (4) https://doi.org/10.4236/ gsc.2012.24020. Article ID: 24781.
- Akhtar, M.S., Panwar, J., Yun, Y.S., 2013. Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by plant extracts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1 (6), 591-602.
- Albers, H.F., 2002. Resin in Tooth Coloured Restoratives. Principle and Technique, ninth ed., pp. 82-273
- Al-Sheddi, E.S., Farshori, N.N., Al-Oqail, M.M., Al-Massarani, S.M., Saquib, Q., Wahab, R., Musarrat, J., Al-Khedhairy, A.A., Siddiqui, M.A., 2018. Anticancer potential of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using extract of Nepeta deflersiana against human cervical cancer cells (HeLA). Bioinorgan. Chem. Appl. https://doi. org/10.1155/2018/9390784. Article ID 9390784.
- Ankanna, S., Prasad, T.N.V.K.V., Elumalai, E.K., Savithramma, N., 2010. Production of Biogenic silver nano particles using Boswellia ovalifoliolata stem bark. Dig. J. Nano. Mat. Biostruct. 5, 369-372.
- Arunachalam, K.D., Annamalai, S.K., Hari, S., 2013. One-step green synthesis and characterization of leaf extract-mediated biocompatible silver and gold nanoparticles from Memecylo numbellatum. Int. J. Nanomed. 8, 1307-1315.
- Baker, S., Harini, B.P., Rakshith, D., Satish, S., 2013. Marine microbes: Invisible nanofactories.J. Pharm. Res. 6, 383-388.
- Bala, N., Srimoyee, S., Chakraborty, M., Moumita, M., Das, S., Basu, R., Nandy, P., 2015. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and anti-diabetic activity. RSC Adv. 5, 4993-5003.
- Banerjee, J., Narendhirakannan, R.T., 2011. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Syzygium cumini (L.) seed extract and evaluation of their in Vitro antioxidant activities. Dig. J. Nano. Biostruct. 6 (3), 961-968.
- Bar, H., Bhui, D.K., Sahoo, G.P., Sarkar, P., de Sankar, P., Misra, A., 2009. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of Jatropha curcas. Colloids Surf., A 339, 134-139.
- Baram-Pinto, D., Shukla, S., Perkas, N., Gedanken, A., Sarid, R., 2009. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by silver nanoparticles capped with mercaptoethane sulfonate. Bioconjugate Chem. 20, 1497-1502.
- Bartkowiak, A., Suchanek, K., Menaszek, E., Szaraniec, B., Lekki, J., Perzanowski, M., Marszalek, M., 2018. Biological effect of hydrothermally synthesized silica nanoparticles within crystalline hydroxyapatite coatings for titanium implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 92, 88-95.
- Bell, I.R., Koithan, M., 2012. A model for homeopathic remedy effects: low dose nanoparticles, allostatic cross-adaptation, and time-dependent sensitization in a complex adaptive system. BMC Compl. Alternative Med. 12, 191. https://doi.org/ 10.1186/1472-6882-12-191.
- Benelli, G., 2016. Plant-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles as an emerging tool against mosquitoes of medical and veterinary importance: a Review. Parasitol. Res. 115, 23-34.
- Chandra, H., Patel, D., Kumari, P., Jangwan, J.S., Yadav, S., 2019. Phytomediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle of Berberis aristata: characterisation, antioxidant activity and antibacterial activity with special reference to urinary tract infection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 102, 212-220.
- Chandra, H., Bishnoi, P., Yadav, A., Patni, B., Mishra, A.P., Nautiyal, A.R., 2017. Antimicrobial resistance and the alternative resources with special emphasis on plant-based antimicrobials-A Review. Plants 6, 16.
- Chandran, S.P., Chaudhary, M., Pasricha, R., Ahmad, A., Sastry, M., 2006. Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 22, 577-583.
- Chaudhary, A., 2011. Ayurvedic Bhasma: nanomedicine of ancient India-Its global contemporary perspective. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 7 (1), 68-69.
- Cheng, L., Weir, M.D., Xu, H.H., Antonucci, J.M., Kraigsley, A.M., Lin, N.J., Lin- Gibson, S., Zhou, X., 2012a. Antibacterial amorphous calcium phosphate nanocomposites with a quaternary ammonium dimethacrylate and silver nanoparticles. Dent. Mater. 28 (5), 561-572.
- Cheng, L., Weir, M.D., Xu, H.H.K., et al., 2012b. Effect of amorphous calcium phosphate and silver nanocomposites on dental plaque microcosm biofilms. J. Biomed. Mat. Res. B. Appl. Biomater. 100 (5), 1378-1386.
- Correa, J.M., Mori, M., Sanches, H.L., da Cruz, A.D., Poiate Jr., E., Poiate, I.A., 2015. Silver nanoparticles in dental biomaterials. Int. J. Biomater. 485275.
- Darr, J.A., Poliakoff, M., 1999. New directions in inorganic and metal organic coordination chemistry in Supercritical Fluids. Chem. Rev. 99, 495-541.
- Daszak, P., Zambrana-Torrelio, C., Bogich, T.L., Fernandez, M., Epstein, J.H., Murray, K. A., Hamilton, H., 2013. Interdisciplinary approaches to understanding disease emergence: the past, present, and future drivers of Nipah virus emergence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 3681-3688.
- De Stefano, D., Carnuccio, R., Maiuri, M.C., 2012. Nanomaterials toxicity and cell death modalities. J. Drug Deliv. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/167896.
- Deepika, S., Selvaraj, C.I., Roopan, S.M., 2020. Screening bioactivities of Caesalpinia pulcherrima L. swartz and cytotoxicity of extract synthesized silver nanoparticles on HCT116 cell line. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. msec.2019.110279. Article 110279.
- Devipriya, D., Roopan, S.M., 2017. Cissus quadrangularis mediated ecofriendly synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its antifungal studies against Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 80, 38-44.
- Dhand, C., Dwivedi, N., Loh, X.J., Ying, A.N.J., Verma, N.K., Beuerman, R.W., Lakshminarayanan, R., Ramakrishna, S., 2015. Methods and strategies for the synthesis of diverse nanoparticles and their applications: a comprehensive overview. RSC Adv. 5, 105003-105037.
- Dipankar, C., Murugan, S., 2012. The green synthesis, characterization and evaluation of the biological activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Iresine herbstii leaf aqueous extracts. Colloids Surf., B 98, 112-119.
- Divyapriya, S.1., Sowmia, C., Sasikala, S., 2014. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle and antimicrobial activity of Murraya koeiniggi. World J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci. 3 (12), 1635-1645.
- Dobrucka, R., Długaszewska, J., 2016. Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower extract. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 23 (4), 517-523.
- Durner, J., Stojanovic, M., Urcan, E., Hickel, R., Reichl, F.X., 2011. Influence of silver nano-particles on monomer elution from light-cured composites. Dent. Mater. 27 (7), 631-636.
- Elemike, E.E., Uzoh, I.M., Onwudiwe, D.C., Babalola, O.O., 2019. The role of nanotechnology in the fortification of plant nutrients and improvement of crop production. Appl. Sci. 9 (3), 499.
- El-Rafie, H.M., El-Rafie, M.H., Zahran, M.K., 2013. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using polysaccharides extracted from marine macro algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 96, 403-410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.071.
- Elumalai, K., Velmurugan, S., 2015. Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (L.). Appl. Surf. Sci. 345, 329-336.
- Etheridge, M.L., Campbell, S.A., Erdman, A.G., Haynes, C.L., Wolf, S.M., McCullough, J., 2013. The big picture on nanomedicine: the state of investigational and approved nanomedicine products. Nanomedicine 9, 1-14.
- Fair, R.J., Tor, Y., 2014.Antibiotics. and bacterial resistance in the 21st century. Perspect. Med. Chem. 6, 25-64.
- Farshchi, H.K., Azizi, M., Jaafari, M.R., Nemati, S.H., Fotovat, A., 2018. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles by rosemary extract and cytotoxicity effect evaluation on cancer cell lines. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 16, 54-62.
- Flores, C.Y., Diaz, C., Rubert, A., Benítez, G.A., Moreno, M.S., Fern� andez Lorenzo de Mele, M.A., Salvarezza, R.C., Schilardi, P.L., Vericat, C., 2010. Spontaneous adsorption of silver nanoparticles on Ti/TiO2 surfaces. Antibacterial effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 350 (2), 402-408.
- Foxman, B., 2010. The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nat. Rev. Urol. 27, 653-660.
- Francis, S., Joseph, S., Koshy, E.P., Mathew, B., 2017. Green synthesis and characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles using Mussaendo glabrata leaf extract and their environmental applications to dye degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 24, 17347-17357.
- Galdiero, S., Falanga, A., Vitiello, M., Cantisani, M., Marra, V., Galdiero, M., 2011. Silver nanoparticles as potential antiviral agents. Molecules 16 (10), 8894-8918. https:// doi.org/10.3390/molecules16108894.
- Gavhane, A.J., Padmanabhan, P., Kamble, S.P., Jangle, S.N., 2012. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extract of Neem leaf and Triphala and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 3, 88-100.
- Golinska, P., Wypij, M., Ingle, A.P., Gupta, I., Dahm, H., Rai, M., 2014. Biogenic synthesis of metal nanoparticles from actinomycetes: biomedical applications and cytotoxicity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98, 8083-8097.
- Gopinath, V., MubarakAli, D., Priyadarshini, S., Priyadharsshini, N.M., Thajuddin, N., Velusamya, P., 2012. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tribulus terrestris and its antimicrobial activity: a novel biological approach. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 96, 69-74.
- Gopinath, V., Priyadarshini, S., Venkatkumar, G., Saravanan, M., MubarakAli, D., 2015. Tribulus terrestris leaf mediated biosynthesis of stable Antibacterial silver nanoparticles. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 3, 26-34.
- Gowramma, B., Keerthi, U., Mokula, R., Rao, D.M., 2015. Biogenic silver nanoparticles production and characterization from native stain of Corynebacterium species and its antimicrobial activity. 3 Biotech 5, 195-201.
- Hanafy, N.A., Leporatti, S., El-Kemary, M.A., 2019. Mucoadhesive hydrogel nanoparticles as smart biomedical drug delivery system. Appl. Sci. 9, 825.
- Hemanth Kumar, N.K., Andia, J.D., Manjunatha, S., Murali, M., Amruthesh, K.N., Jagannath, S., 2019. Antimitotic and DNA-binding potential of biosynthesized ZnO- NPs from leaf extract of Justicia wynaadensis (Nees) Heyne -a medicinal herb. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 18, 101024.
- Husseiny, M.I., El-Aziz, M.A., Badr, Y., Mahmoud, M.A., 2007. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Spectrochim. Acta A. 67, 1003-1006.
- Ik€ aheimo, R., Siitonen, A., Heiskanen, T., K€ arkk€ ainen, U., Kuosmanen, P., Lipponen, P., M€ akel€ a, P.H., 1996. Recurrence of urinary tract infection in a primary care setting: analysis of a 1-year follow-up of 179 women. Clin. Infect. Dis. 22, 91-99.
- Iravani, S., 2011. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 13, 2638-2650.
- Jacob, S., Finub, J., Narayanan, A., 2011. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Piper longum leaf extracts and its cytotoxic activity against Hep-2 cell line. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 91, 212-214.
- Jaggessar, A., Yarlagadda, P.K.D.V., 2020. Modelling the growth of hydrothermally synthesised bactericidal nanostructures, as a function of processing conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110434\. Article 110434.
- Jagtap, U., Bapat, V.A., 2013. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Ind. Crop. Prod. 46, 132-137.
- Jamdagni, P., Khatri, P., Rana, J.S., 2018. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 30 (2), 168-175.
- Jayaseelan, C., Rahuman, A.A., Rajakumar, G., Vishnu Kirthi, A., Santhoshkumar, T., Marimuthu, S., Bagavan, A., Kamaraj, C., Zahir, A.A., Abdul, A., Elango, G., 2011. Synthesis of pediculocidal and larvicidal silver nanoparticles by leaf extract from heartleaf moonseed plant, Tinospora cordifolia Miers. Parasitol. Res. 109 (1), 185-194.
- Jeyabalan, A., Lain, K.Y., 2007. Anatomic and functional changes of the upper urinary tract during pregnancy. Urol. Clin. 34, 1-6.
- Jeyaraj, M., Rajesh, M., Arun, R., MubarakAli, D., Sathishkumar, G., Sivanandhan, G., Dev, G.K., Manickavasagam, M., Premkumar, K., Thajuddin, N., Ganapathi, A., 2013. An investigation on the cytotoxicity and caspase-mediated apoptotic effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Podophyllum hexandrum on human cervical carcinoma cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 102, 708-717.
- Jha, A.K., Prasad, K., 2010. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cycas Leaf. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. 1, 110-117.
- Jha, A.K., Prasad, K., Kulkarni, A.R., 2009. Plant system: nature's nanofactory. Colloids Surf., B 73, 219-223.
- Kang, C., Kim, J., Park, D.W., et al., 2018. Clinical practice guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of community-acquired urinary tract infections. Infect. Chemother. 50 (1), 67-100.
- Kannan, R.R.R., Arumugam, R., Ramya, D., Manivannan, K., Anantharaman, P., 2013. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine macroalga Chaetomorpha linum. Appl. Nanosci. 3, 229-233.
- Karthikeyan, A.P., Kadarkarai, M., Chellasamy, P., Sekar, P., Jiang-Shiou, H., Marcello, N., 2012. Biolarvicidal and pupicidal potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Euphorbia hirta against Anopheles stephensi Liston (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 111, 997-1006.
- Kassaee, M.Z., Akhavan, A., Sheikh, N., Sodagar, A., 2008. Antibacterial effects of a new dental acrylic resin containing silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 110, 1699-1703.
- Kathiresan, K., Manivannan, S., Nabeel, M.A., Dhivya, B., 2009. Studies on silver nanoparticles synthesized by a marine fungus, Penicillium fellutanum isolated from coastal mangrove sediment. Colloids Surf., B 71, 133-137.
- Khalil, M.M.H., Ismail, E.H., El-Baghdady, K.Z., Mohamed, D., 2014. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using olive leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 7, 1131-1139.
- Khandel, P., Shahi, S.K., 2018. Mycogenic nanoparticles and their bio-prospective applications: current status and future challenges. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 8, 369-391.
- Khatami, M., Alijani, H.Q., Nejad, M.S., Varma, R.S., 2018. Core@shell nanoparticles: greener synthesis using natural plant products. Appl. Sci. 8 (3), 411.
- Kim, D., Jeong, S., Moon, J., 2006. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the polyol process and the influence of precursor injection. Nanotechnology 17, 4019-4024.
- Korbekandi, H., Mohseni, S., Mardani, J.R., Pourhossein, M., Iravani, S., 2016. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 44, 235-239.
- Kowshik, M., Arhtaputre, S., Kharrazi, S., Vogel, W., Urban, J., Kulkarni, S.K., Paknikar, K.M., 2003. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by a silver- tolerant yeast strain MKY3. Nanotechnology 14, 95-100.
- Krishnamoorthy, P., Jayalakshmi, T., 2012. Preparation, characterization and synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using Phyllanthus niruri for the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxic effects. J. Chem. Pharmaceut. Res. 4 (11), 4783-4794.
- Krishnaraj, C., Jagan, E.G., Rajasekar, S., Selvakumar, P., Kalaichelvan, P.T., Mohan, N., 2010. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 76 (1), 50-56.
- Lara, H.H., Ayala-Nuñez, N.V., Ixtepan-Turrent, L., Rodriguez-Padilla, C., 2010. Mode of antiviral action of silver nanoparticles against HIV-1. J. Nanobiotechnol. 8, 1-10.
- Lee, D.S., Lee, S.J., Choe, H.S., 2018. Community-acquired urinary tract infection by Escherichia coli in the era of antibiotic resistance. BioMed Res. Int. 7656752 https:// doi.org/10.1155/2018/7656752.
- Lok, C.N., Ho, C.M., Chen, R., et al., 2006. Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles. J. Proteome Res. 5 (4), 916-924.
- Lotfi, M., Vosoughhosseini, S., Ranjkesh, B., Khani, S., Saghiri, M., Zand, V., 2011. Antimicrobial efficacy of nanosilver, sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine gluconate against Enterococcus faecalis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10 (35), 6799-6803.
- Lu, L., Sun, R.W., Chen, R., Hui, C.K., Ho, C.M., Luk, J.M., Lau, G.K., Che, C.M., 2008. Silver nanoparticles inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. Antivir. Ther. 13, 253-262.
- Mahendran, V., Gurusamy, A., 2013. Coleus aromaticus leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its bactericidal activity. Appl. Nanosci. 3, 217-223.
- Malik, M.A., Wani, M.Y., Hashim, M.A., 2012. Microemulsion method: a novel route to synthesize organic and inorganic nanomaterials. Arab. J. Chem. 5, 397-417.
- Mallikarjuna, K., Narasimha, G., Dillip, G.R., Praveen, B., Shreedhar, B., Sree Lakshmi, C., Reddy, B.V.S., Raju, B.D.P., 2011. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum leaf extract and their characterization. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 6 (1), 181-186.
- Manikandan, V., Velmurugan, P., Park, J.H., Chang, W.S., Park, Y.J., Jayanthi, P., Cho, M., Oh, B.T., 2017. Green synthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against dental pathogens. 3 Biotech 7 (1), 72. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s13205-017-0670-4.
- Menon, S., Shrudhi Devi, K.S., Santhiya, R., Rajeshkumar, S., Kumar, V., 2018. Selenium nanoparticles: a potent chemotherapeutic agent and an elucidation of its mechanism. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 170, 280-292.
- Mittal, A.K., Chisti, Y., Banerjee, U.C., 2013. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plants. Biotechnol. Adv. 31, 346-356.
- Moghaddam, A.B., Namvar, F., Moniri, M., Tahir, P.M., Azizi, S., Mohamad, R., 2015. Nanoparticles biosynthesized by fungi and yeast: a review of their preparation, properties, and medical applications. Molecules 20, 16540-16565.
- Mousavi, B., Tafvizi, F., Bostanabad, S.Z., 2018. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia turcomanica leaf extract and the study of anti-cancer effect and apoptosis induction on gastric cancer cell line (AGS), Artificial Cells. Nanomed. Biotech. 46 (1), 499-510. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1430697.
- MubarakAli, D., Thajuddin, N., Jeganathan, K., Gunasekaran, M., 2011. Plant extract mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 85, 360-365.
- Muhammad Mailafiya, M., Abubakar, K., Danmaigoro, A., Musa Chiroma, S., Bin Abdul Rahim, E., Aris Mohd Moklas, M., Abu Bakar Zakaria, Z., 2019. Cockle shell-derived calcium carbonate (aragonite) nanoparticles: a dynamite to nanomedicine. Appl. Sci. 9, 2897.
- Murugan, K., Benelli, G., Panneerselvam, C., Subramaniam, J., Jeyalalitha, T., Dinesh, D., Nicoletti, M., Hwang, J.S., Suresh, U., Madhiyazhagan, P., 2015. Cymbopogon citratus synthesized gold nanoparticles boost the predation efficiency of copepod Mesocyclops aspericornis against malaria and dengue mosquitoes. Exp. Parasitol. 1053, 129-138.
- Muthu, K., Rangasamy, R., 2013. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ixora coccinea leaves extract. Mater. Lett. 97, 141-143.
- Nagajyothi, P.C., Muthuraman, P., Sreekanth, T.V.M., Kim, D.H., Shim, J., 2017. Green synthesis: in-vitro anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles against human cervical carcinoma cells. Arab. J. Chem. 10, 215-225.
- Nam, K.Y., 2011. In vitro antimicrobial effect of the tissue conditioner containing silver nanoparticles. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 3 (1), 20-24.
- Narayanan, K.B., Sakthivel, N., 2010. Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 156, 1-13.
- National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme, 2012. Strategic Plan for Malaria Control in India 2012-2017: A Five-Year Strategic Plan. Available at: http://nvbdcp. gov.in/Doc/Strategic-Action-Plan-Malaria-2012-17-Co.pdf.
- Nayak, B.K., Nanda, A., Prabhakar, V., 2018. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticle from wasp nest soil fungus, Penicillium italicum and its analysis against multi drug resistance pathogens. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 16, 412-418. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.bcab.2018.09.014.
- Nikalje, A.P., 2015. Nanotechnology and its applications in medicine. Med. Chem. 5, 81-89.
- Owens, G.J., Singh, R.K., Foroutan, F., Alqaysi, M., Han, C.M., Mahapatra, C., Kim, H.W., Knowles, J.C., 2016. Sol-gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 77, 1-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.12.001.
- Pal, D., Sahu, C.K., Haldar, A., 2014. Bhasma : the ancient Indian nanomedicine. "J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Research"" (JAPTR)" 5 (1), 4-12.
- Panneerselvam, C., Murugan, K., Amerasan, D., 2015. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extract and its anti-plasmodial property. Adv. Mater. Res. 1086, 11-30.
- Panneerselvam, C., Ponarulselvam, S., Murugan, K., 2011. Potential anti-plasmodial activity of synthesized silver nanoparticle using Andrographis paniculata nees (Acanthaceae). Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 3 (6), 208-217.
- Parida, U.K., Bindhani, B.K., Nayak, P., 2011. Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using onion (Allium cepa) extract. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 1, 93-98.
- Patil, S.V., Borase, H.P., Patil, C.D., Salunke, B.K., 2012. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex from few Euphorbian plants and their antimicrobial potential. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 167 (4), 776-790.
- Pazhayattil, G.S., Shirali, A.C., 2014. Drug-induced impairment of renal function. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovascular Dis. 7, 457-468.
- Philip, D., 2009. Biosynthesis of Au, Ag and Au-Ag nanoparticles using edible mushroom extract. Spectrochim. Acta A. 73, 374-381.
- Philip, D., 2010. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Hibiscus rosa sinensis. Phys. E 42, 1417-1424.
- Ponarulselvam, S., Panneerselvam, C., Murugan, K., Aarthi, N., Kalimuthu, K., Thangamani, S., 2012. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves of Catharanthus roseus Linn. G. Don and their antiplasmodial activities. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2 (7), 574-580.
- Prabhu, K., Murugan, K., Nareshkumar, A., Ramasubramanian, N., Bragadeeswaran, S., 2011. Larvicidal and repellent potential of Moringa oleifera against malarial vector, Anopheles stephensi Liston (Insecta: Diptera: Culicidae). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 1 (2), 124-129.
- Premkumar, J., Sudhakar, T., Dhakal, A., Shrestha, J.B., Krishnakumar, S., Balashanmugam, P., 2018. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from cinnamon against bacterial pathogens. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 15, 311-316.
- Priyadarshini, S., Mainal, A., Sonsudin, F., Yahya, R., Abdullah, Alyousef, A.A., Mohammed, A., 2019. Biosynthesis of TiO 2 nanoparticles and their superior antibacterial effect against human nosocomial bacterial pathogens. Res. Chem. Intermed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03857-6.
- Priyadarsini, S., Mukherjee, S., Mishra, M., 2018. Nanoparticles used in dentistry: a review. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofac. Res. 8, 58-67.
- Radovic-Moreno, A.F., Lu, T.K., Puscasu, V.A., Yoon, C.J., Langer, R., Farokhzad, O.C., 2012. Surface charge-switching polymeric nanoparticles for bacterial cell wall- targeted delivery of antibiotics. ACS Nano 6, 4279-4287.
- Rai, M., Yadav, A., Gade, A., 2009. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 27 (1), 76-83.
- Rajakumar, G., Rahuman, A., 2011. Larvicidal activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles using Eclipta prostrata leaf extract against filariasis and malaria vectors. Acta Trop. 118, 196-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2011.03.003.
- Rajeshkumar, S., Bharath, L.V., 2017. Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles -a review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem. Biol. Interact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cbi.2017.06.019.
- Ramesh, M., Anbuvannan, M., Viruthagiri, G., 2015. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 136, 864-870.
- Rane, A., Kanny, K., Abitha, V.K., Thomas, Sabu, 2018. Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. In: Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticle. Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam, pp. 121-139. https://doi.org/10.1016/ B978-0-08-101975-7.00005-1.
- Ravikumar, S., Gokulakrishnan, R., Boomi, P., 2012. In vitro antibacterial activity of the metal oxide nanoparticles against urinary tract infections bacterial pathogens. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2, 85-89.
- Rogers, J.V., Parkinson, C.V., Choi, Y.W., Speshock, J.L., Hussain, S.M., 2008. A preliminary assessment of silver nanoparticles inhibition of monkeypox virus plaque formation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3, 129-133.
- Roh, Y., Lauf, R.J., McMillan, A.D., Zhang, C., Rawn, C.J., Bai, J., Phelps, T.J., 2001. Microbial synthesis and the characterization of metal-substituted magnetites. Solid State Commun. 118, 529-534.
- Roser, M., 2016. Life expectancy. OurWorldInData.org. Available at. ourworldindata.org /data/population-growth-vital-statistics/life-expectancy/.
- Roy, A., Bulut, O., Some, S., Mandal, A.K., Yilmaz, M.D., 2019. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 9, 2673-2702.
- Samiei, M., Aghazadeh, M., Lotfi, M., Shakoei, S., Aghazadeh, Z., Pakdel, S.M.V., 2013. Antimicrobial efficacy of mineral trioxide aggregate with and without silver nanoparticles. Iran. Endodont. J. 8 (4), 166-170.
- Sangeetha, G., Rajeshwari, S., Rajendran, V., 2011. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2560-2566.
- Santhoshkumar, J., Kumar, S.V., Rajeshkumar, S., 2017. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Res. Efficient Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2017.05.001.
- Santhoshkumar, T., Rahuman, A.A., Rajakumar, G., Marimuthu, S., Bagavan, A., Jayaseelan, C., Zahir, A.A., Gandhi, E., Kamaraj, C., 2011. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Nelumbo nucifera leaf extract and its larvicidal activity against malaria and filariasis vectors. Parasitol. Res. 108 (3), 693-702.
- Sarkar, S., Kotteeswaran, V., 2018. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from aqueous leaf extract of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) and their anticancer activity on human cervical cancer cells. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9 (2), 25014, 9025014.
- Scherrer, P., 2018. Bestimmung der Groβe und der inneren struktur von kolloidteilichen mittels Rontgenstrahlen, nachrichten von der von der Gesellschaft der Wissenchaften zu Gottingen. Math. Phys. Klasse 98-100.
- Schmalz, G., Arenholt-Bindslev, D., 2009. Biocompatibility of Dental Materials. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 71-72.
- Sewify, M., Nair, S., Warsame, S., Murad, M., Alhubail, A., Behbehani, K., Al-Refaei, F., Tiss, A., 2016. Prevalence of urinary tract infection and antimicrobial susceptibility among diabetic patients with controlled and uncontrolled glycemia in Kuwait. J. Diabetes. Res. 6573215.
- Shah, M., Fawcett, D., Sharma, S., Tripathy, S.K., Poinern, G.E.J., 2015. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Materials 8, 7278-7308.
- Sharma, R., Prajapati, P.K., 2016. Nanotechnology in medicine: leads from Ayurveda. J. Pharm. BioAllied Sci. 8, 80-81.
- Sharma, V., Kaushik, S., Pandit, P., Dhull, D., Yadav, J.P., Kaushik, S., 2019. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from medicinal plants and evaluation of their antiviral potential against chikungunya virus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 103, 881-891.
- Shi, J., Xiao, Z., Kamaly, N., Farokhzad, O.C., 2011. Self-assembled targeted nanoparticles: evolution of technologies and bench to bedside translation. Acc. Chem. Res. 44, 1123-1134.
- Singh, A., Jain, D., Upadhyay, M.K., Khandelwal, N., Verma, H.N., 2010. Green synthesis of silver Nanoparticles Using Argemone mexicana leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostr. 5 (2), 483-489.
- Sivaraj, R., Rahman, P.K., Rajiv, P., Salam, H.A., Venckatesh, R., 2014. Biogenic copper oxide nanoparticles synthesis using Tabernaemontana divaricate leaf extract and its antibacterial activity against urinary tract pathogen. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 133, 178-181.
- Soni, N., Prakash, S., 2012. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the fungus Aspergillus niger and its efficacy against mosquito larvae. Rep. Parasitol. 2, 1-7.
- Soni, N., Prakash, S., 2014. Green nanoparticles for mosquito control. Sci. World J. 6 https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/496362.
- Srinivas, M.A., Chandrashekar, U.K., Shivashankara, K.N., Pruthvi, B.C., 2014. Clinical profile of urinary tract infections in diabetics and non-diabetic. Australas. Med. J. 7 (1), 29-34.
- Srivastava, J., Chandra, H., Nautiyal, A.R., Kalra, S.S., 2014. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and plant-derived antimicrobials (PDAms) as an alternative drug line to control infections. 3 Biotech 4, 451-460.
- Suganya, K.S., Govindaraju, K., Kumar, V.G., Dhas, T.S., Karthick, V., Singaravelu, G., Elanchezhiyan, M., 2015. Blue green alga mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles and its antibacterial efficacy against gram positive organisms. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 47, 351-356.
- Suk, J.S., Xu, Q., Kim, N., Hanes, J., Ensign, L.M., 2016. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 99, 28-51.
- Sukanya, M.K., Saju, K.A., Praseetha, P.K., Sakthivel, G., 2013. Therapeutic potential of biologically reduced silver nanoparticles from Actinomycete cultures. J. Nanosci. 1-8.
- Sukirtha, R., Priyanka, K.M., Antony, J.J., Kamalakkannan, S., Ramar, T., Palani, G., 2011. Cytotoxic effect of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Melia azedarach against in vitro HeLa cell lines and lymphoma mice model. Process Biochem. 47, 273-279.
- Sun, R.W., Chen, R., Chung, N.P., Ho, C.M., Lin, C.L., Che, C.M., 2005. Silver nanoparticles fabricated in Hepes buffer exhibit cytoprotective activities toward HIV-1 infected cells. Chem. Commun. 40, 5059-5061.
- Sundararajan, B., Kumari, B.R., 2017. Novel synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Artemisia vulgaris L. leaf extract and their efficacy of larvicidal activity against dengue fever vector Aedes aegypti L. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 43, 187-196.
- Sunkar, S., Nachiyar, C.V., 2012. Biogenesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles using the endophytic bacterium Bacillus cereus isolated from Garcinia xanthochymu. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 12, 953-959.
- Suriyaraj, S.P., Ramadoss, G., Chandraraj, K., Selvakumar, R., 2019. One pot facile green synthesis of crystalline bio-ZrO2 nanoparticles using Acinetobacter sp. KCSI1 under room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 105, 110021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. msec.2019.110021.
- Tan, S.Y., Tatsumura, Y., 2015. Alexander Fleming (1881-1955): discoverer of penicillin. Singapore Med. J. 56, 366-367. https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2015105.
- Taylor, P., 2013. Alternative natural sources for a new generation of antibacterial agents. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 42 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.05.004.
- Thiagarajan, S., Sanmugam, A., Vikraman, D., 2017. Facile methodology of sol-gel synthesis for metal oxide nanostructures. Recent Appl. Sol Gel Synth. 1-16.
- Veerakumar, K., Govindarajan, M., Rajeswary, M., Muthukumaran, U., 2014. Low-cost and eco-friendly green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Feronia elephantum (Rutaceae) against Culex quinquefasciatus, Anopheles stephensi, and Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 113, 2363-2373.
- Veerasamy, R., Xin, T.Z., Gunasagaran, S., Wei Xiang, T.F., Chou Yang, E.F., Jeyakumar, N., Dhanaraj, S.A., 2011. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using mangosteen leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 15, 113-120.
- Ventola, C.L., 2015. The antibiotic resistance crisis. Pharm. Ther. 40 (4), 277-283.
- Vigneshwaran, N., Ashtaputre, N.M., Varadarajan, P.V., Nachane, R.P., Paralikar, K.M., Balasubramanya, R.H., 2007. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus flavus. Mater. Lett. 61, 1413-1418.
- Vinayak, S., Biswas, S., Dev, V., Kumar, A., Ansari, M.A., Sharma, Y.D., 2003. Prevalence of the K76T mutation in the pfcrt gene of Plasmodium falciparum among chloroquine responders in India. Acta Trop. 87, 287-293.
- von Overbeck, J., 2003. Insurance and epidemics: SARS, West Nile virus and Nipah virus. J. Insur. Med. 35, 165-173.
- Wagner, V., Dullaart, A., Bock, A.K., Zweck, A., 2006. The emerging nanomedicine landscape. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 1211-1217.
- Wang, Z., Colombi Ciacchi, L., Wei, G., 2017. Recent advances in the synthesis of graphene-based nanomaterials for controlled drug delivery. Appl. Sci. 7, 1175.
- Yamamoto, K., Ohashi, S., Aono, M., Kokubo, T., Yamada, I., Yamauchi, J., 1996. Antibacterial activity of silver ions implanted in SiO 2 filler on oral streptococci. Dent. Mater. 12, 227.
- Yong, P., Rowsen, N.A., Farr, J.P.G., Harris, I.R., Macaskie, L.E., 2002. Bioreduction and biocrystallization of palladium by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans NCIMB 8307. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 80, 369-379.
- Zargar, M., Hamid, A.A., Bakar, F.A., Shamsudin, M.N., Shameli, K., Jahanshiri, F., Farahani, F., 2011. Green synthesis and antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles using Vitex negundo. L. Mol. 16 (8), 6667-6676.
- Zayed, M.F., Eisa, W.H., Shabaka, A.A., 2012. Malva parviflora extract assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 98, 423-428.
- Zhao, L., Wang, H., Huo, K., Cui, L., Zhang, W., Ni, H., Zhang, Y., Wu, Z., Chu, P.K., 2011. Antibacterial nano-structured titania coating incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 32 (24), 5706-5716.