Analysis of Pile Group under Vertical Loading in Clay and Sand using FEM (original) (raw)
Abstract
Pile foundations are the preferred choice for supporting heavy structures when hard bedrock is situated at considerable depths beneath weak soil conditions. The ultimate load-carrying capacity of these piles hinges on several factors, including material composition, soil properties, geometric attributes, and the mechanism of load transfer (end bearing or friction). This research focuses on investigating the load-bearing capacity and settlement characteristics of end-bearing piles in both soft clay and medium sand. The study explores these parameters by varying pile diameter, length, and spacing within a pile group. Utilizing ANSYS for analysis, the study draws comparisons between clay and sand. The study's findings reveal that clay exhibits a higher load-carrying capacity compared to sand. Additionally, it highlights that sand experiences significantly greater settlement compared to clay when an optimal pile diameter of 0.4 meters and a length of 4 meters are employed.
Key takeaways
AI
- Clay exhibits a higher load-carrying capacity than sand under vertical loading conditions.
- An optimal pile diameter of 0.4 meters yields 400 kN capacity with 39.23 mm settlement.
- Increasing pile length from 3m to 5m raises load capacity by 52.9%, with a 16% increase in settlement.
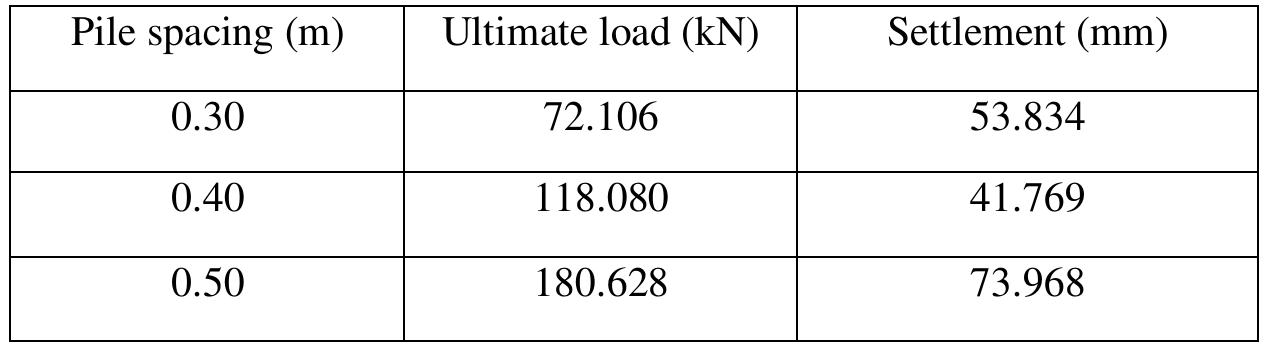
- Pile spacing of 2d is optimal for maximum load capacity and minimum settlement in a pile group.
- The study aims to analyze load-bearing capacity and settlement characteristics of pile foundations in clay and sand.
Figures (1)
TABLE VI

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (10)
- A. George and K. M. Lovely, "Analysis of Pile subjected to Lateral Loading in Clay modeled using ANSYS", International Journal of Engineering Development and Research, vol. 3, pp. 414-417, 2015.
- R. R. Chaudhari and K. N. Kadam, "Effect of Piled Raft Design on High-Rise Building Considering Soil Structure Interaction", International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, vol. 2, pp. 72-79, Jun. 2013.
- T. Kanimozhi and K. Ilamparuthi, "Performance of Pile under Lateral Load", in Proc. Indian Geotechnical Conference, pp 102-105, Dec. 2004.
- D. Naveen Kumar, "Numerical Analysis of Piled Raft Foundation using FEM with Interaction Effects", International Journal of TechnoChem Research, vol. 1, pp. 126-134, 2015.
- R. Z. Moayed and M. Safavian, "Pile raft foundation behavior with different Pile diameters", in Proc. International Conference on Earthquake Engineering - ICEE'07, 2007, p. 25.
- G. Srilakshmi, R. K. C. Gowda, "Analysis of Piled Raft Foundation by Finite Element Method", in Proc. International Conference on Engineering, 2012.
- G. Srilakshmi and D. Moudgalya, "Analysis of Piled Raft Foundation using FEM", International Journal of Engineering Research Science and Technology, vol. 2, pp. 89-96, Aug. 2013.
- G. Srilakshmi and M. P. Yashwanth, "Analysis of Pile Group using Finite Element Method", International Journal of Engineering Research Science and Technology, vol. 2, pp. 110-118, Aug. 2013.
- B. K. Huchegowda, M. Teja and G. K. Kumar, "Evaluation of Lateral Capacity of Pile Foundation Using Finite Element Method in Layered Soil", in Proc. Advances in Geotechnical and Transportation Engineering, Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol. 71, 2020.
- M. R. Al-Qaissy, S. F. A. Al-Wakel and A. S. Abdulrasool, "Three-Dimensional Dynamic Analysis of Pile Foundations by Using Finite Element Method", Eng. & Tech Journal, vol. 33, pp. 1-11, 2015.
FAQs
AI
How does pile diameter influence load capacity and settlement in clay foundations?add
The research shows increasing pile diameter from 0.30m to 0.50m raises load capacity by 35% and reduces settlement by 40.7%.
What impact does pile length have on the load capacity under vertical loading?add
Increasing pile length from 3m to 5m leads to a 52.9% rise in ultimate load capacity, while settlement increases by 16%.
How does spacing between piles affect the load capacity of a pile group?add
The study finds that increasing spacing from 2d to 3.5d decreases the ultimate load capacity by 46%, while reducing settlement by 28%.
What are the differences in behavior of pile groups in clay versus sand?add
The analysis reveals that pile groups in stiff clay exhibit higher load capacities than those in medium sand, with increased settlement in sand.
What FEM software was used in analyzing the behavior of pile groups?add
ANSYS Workbench 14.5 was utilized for finite element modeling of pile foundations to assess various parameters.