Real-time illumination and shadowing by virtual lights in a mixed real-ity setting (original) (raw)
Abstract
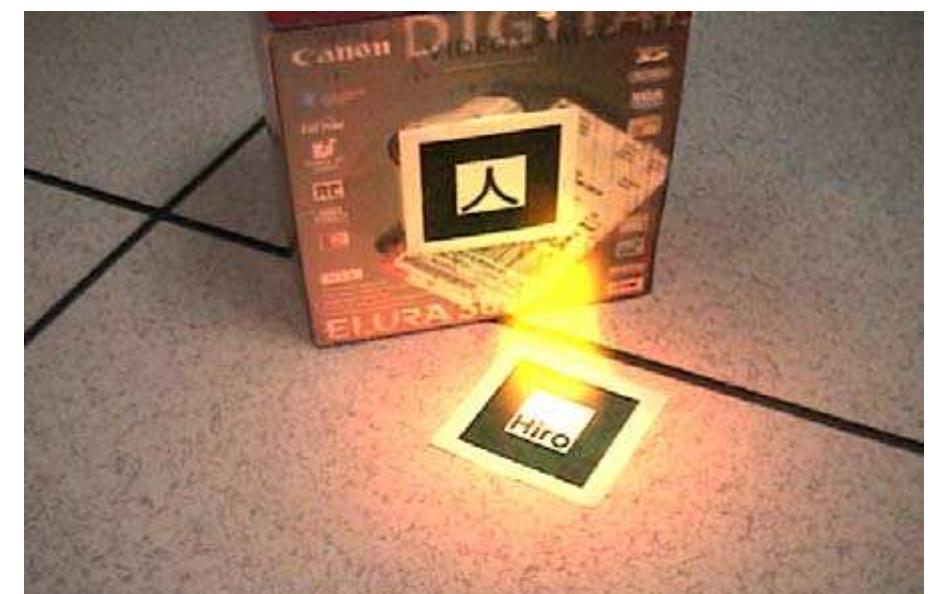
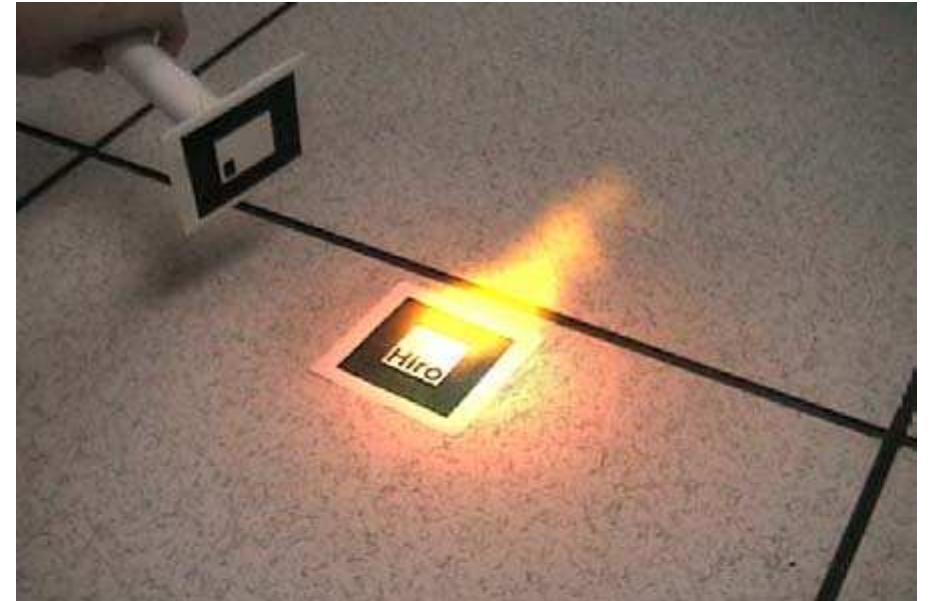
Figure 1: Virtual fire illuminating a real Figure 2: Virtual flashlight (top edge) scene (video attached).
Figures (9)
Figure 1: Virtual fire illuminating a real scene (video attached).
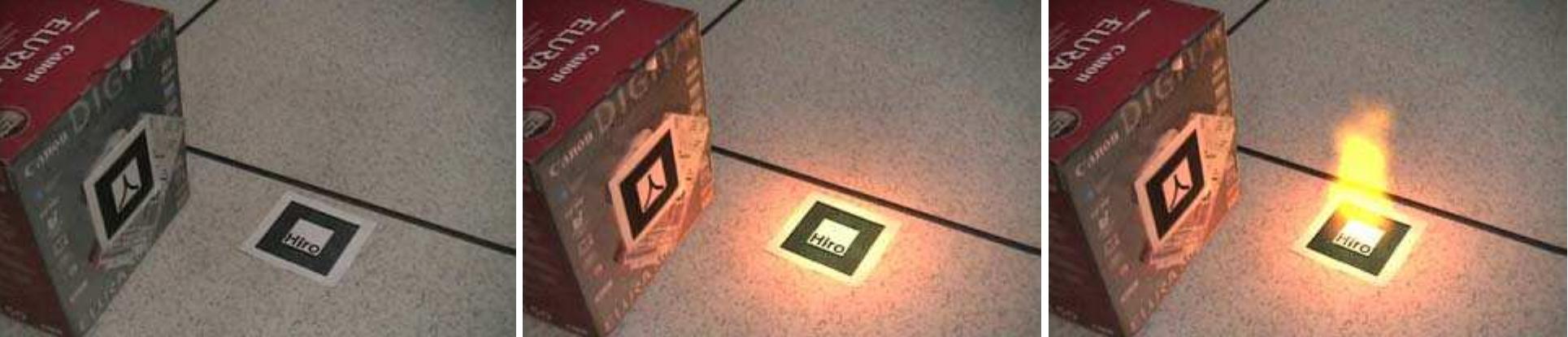
Figure 4: Illumination is consistent from different view point. Figure 3: Sequence of virtual fire brightening a real scene, from left to right: (a) Original intensity, (b) Illumination of real scene without virtual flames, (c) final scene with composited virtual flames.
Figure 5: Wind effect applied from “fan” (top left corner) on the fire
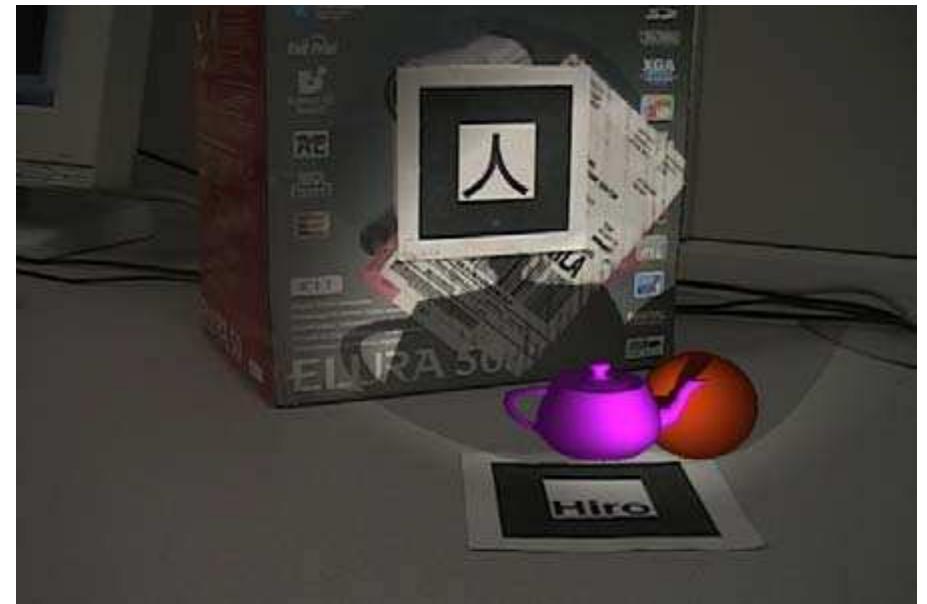
Figure 7: Virtual flashlight with multiple real objects (light direction fixed). Figure 6: Sequence of virtual flashlight illuminating a real scene, clockwise from top-left corner: (a) Original intensity, (b) partially darkened image for pixels with no depth information, (c) virtual-to-real shadowing, (d) virtual-to- real lighting, (e) unlit virtual objects, (f) lit objects with real-to-virtual shadows.
For the lighting calculation, we chose a point light- based approximation of the light contributed by all particles. We sorted each particle into separate groups based on the particle’s remaining life, and used the average positions and intensities in each group to calculate a point light for that group. The total light contribution would then be the sum of light contribution from each point light. We used the method from Section 3.4.1 to brighten surrounding pixels based on these point lights. A more physically accurate lighting model would certainly give much better results and could be implemented without having to change the underlying shading method.
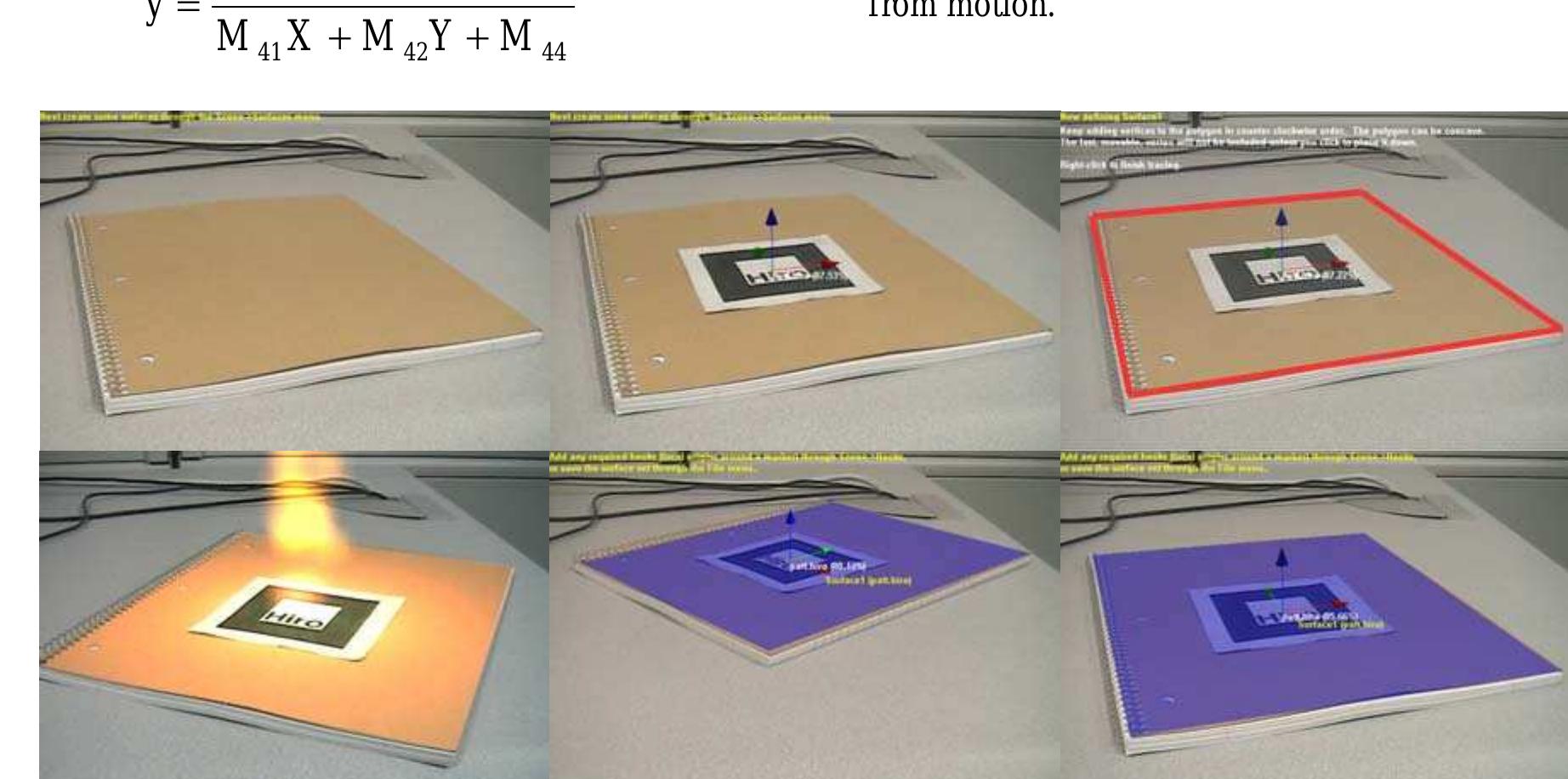
Figure 9: Sequence of interactive phantom generation for a notebook, clockwise from top- left: (a) notebook added to scene, (b) marker placed on notebook, (c) surface polygon being traced, (d) 3D phantom surface, (e) phantom from a different angle, (f) notebook lit by virtual fire.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (8)
- REFERENCES
- F. C. Crow, Shadow algorithms for computer graphics. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 77, pages 242-248, 1977.
- M. Haller, S. Drab and W. Hartmann. A real- time shadow approach for an Augmented Reality application using shadow volumes. In Proceedings of ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology (VRST), pages 56-65, October 2003.
- R. Surdulescu. Cg Shadow Volumes, URL: http://www.gamedev.net/reference/articles/articl e1990.asp, September 2003.
- T. Naemura, T. Nitta, A. Mimura, and H. Harashima. Virtual Shadows in Mixed Reality Environment Using Flashlight-like Devices. In Trans. Virtual Reality Society of Japan, pages 227-237, 2002.
- R. Ng, R. Ramamoorthi, and P. Hanrahan. All- frequency Shadows Using Non-linear Wavelet Lighting Approximation. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 03, pages 376-381, 2003.
- M. McGuire, J. F. Hughes, K. T. Evan, M. J. Kilgard, and C. Everitt. Fast, Practical and Robust Shadows. Brown University and nVIDIA Corporation, November 2003.
- ARToolKit, URL: http:// www.hitl.washington.edu/artoolkit