Enhancing satellite broadcasting services using multiresolution modulations (original) (raw)
Abstract
In this paper we propose to take advantage of the energy link margin that can exist of satellite connections to enrich the DVB-S services with WEBlike interactive services. The exploitation of such margin is obtained by using multiresolution modulation techniques. The system architecture analysed is asymmetrical, composed of a satellite forward link and a narrowband terrestrial reverse link. The A T M is adopted to support different &OS for different type of information to be delivered. The satellite propagation delay and the traffic and congestion control of the A T M suggest to modify the slow start and the congestion avoidance of the TCP. Our approach is based on the combination of a fixed window flow control a t transport layer with the A T M traffic and congestion control. Our analysis shows that the system performance is satisfactory if some bounds of the TCP buffer size are respected and the spacing of the R M cells is within a given range of values.
Figures (17)
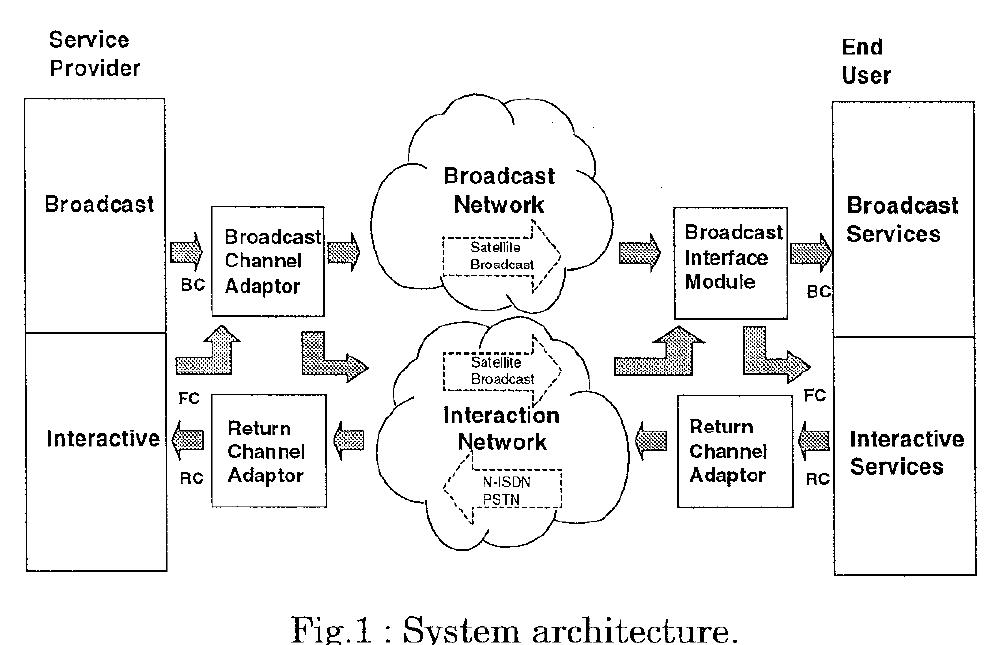
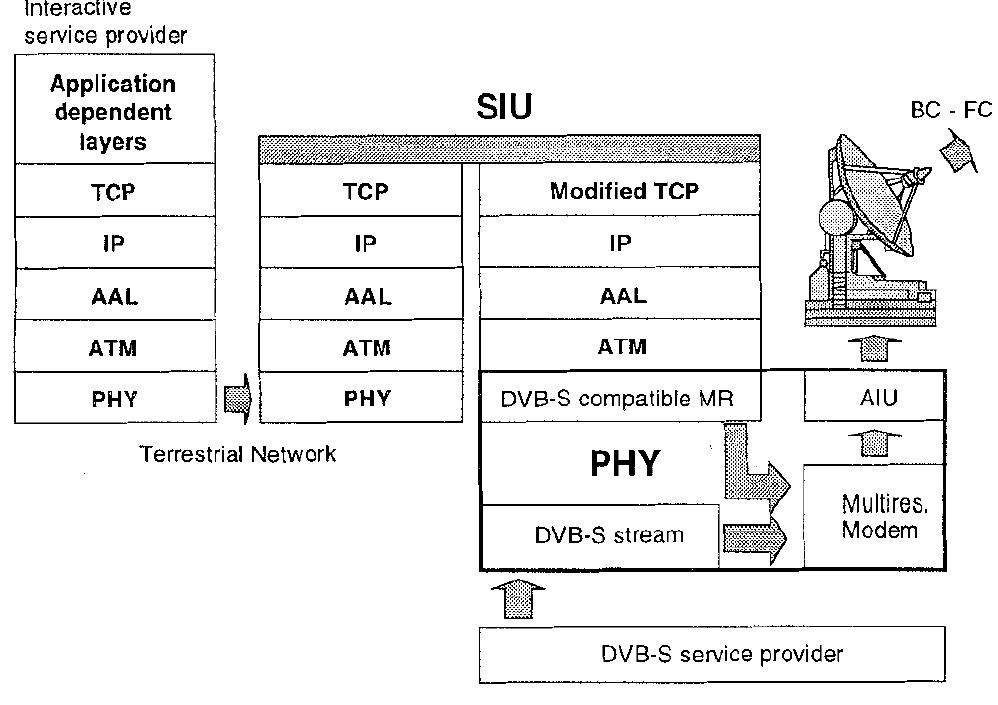
System configuration
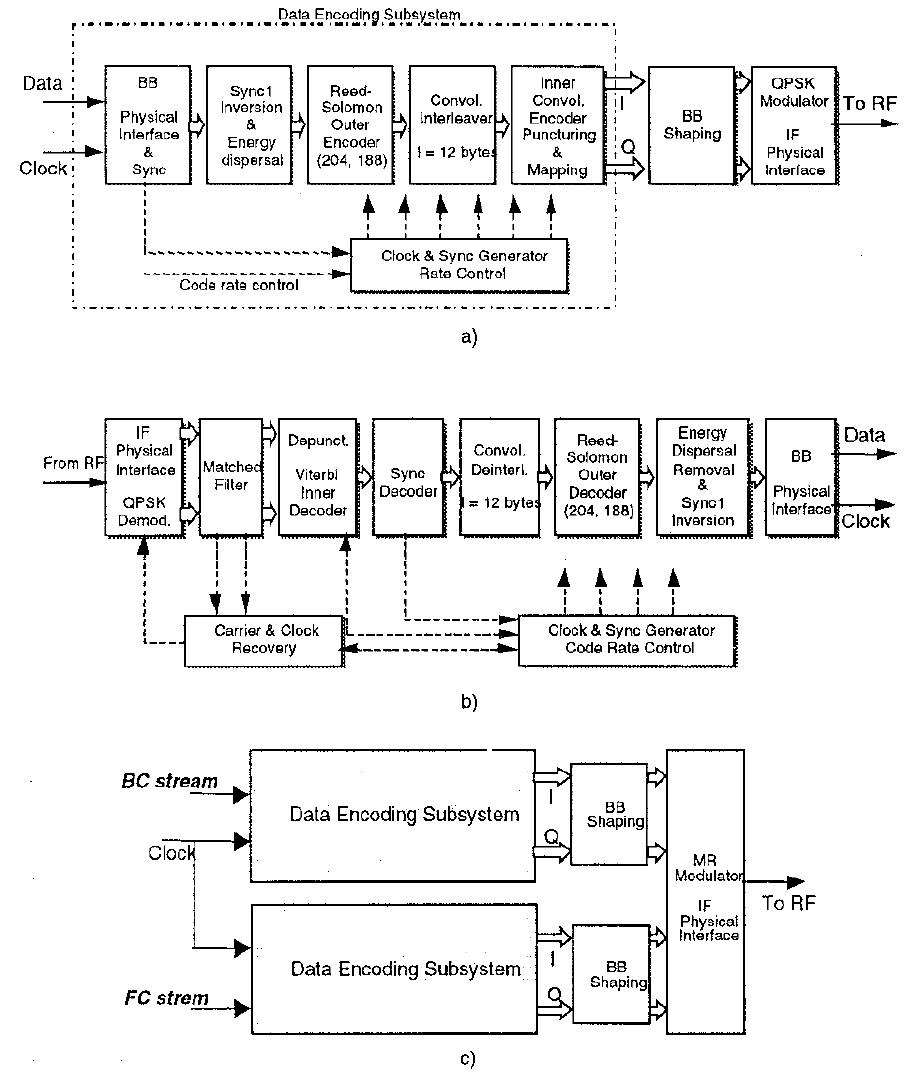
MEARS UAB AW SAARI ANS WA VE Ate Se MBCA he The demodulation of the HP stream ignores completely the presence of the LP data, since the sub- constellations produce noise-like symbol broadening. In this work, the BC data form the HP stream that, therefore, 1s simply decoded according to the DVB-S specifications. The procedure used to demodulate the low priority (LP) bits, that carry the FC data, is realised by an iteration, based on a preliminary hard decoding of the HP symbols and a soft decoding of the LP stream. For instance, we describe below in details the demodulation process for a 8-PSK MR constellation obtained by splitting in two points each QPSK symbol. Fig. 2: Functional blocks of the DVB-S transmitter (a), DVB- S receiver (b) and MR modem (c).
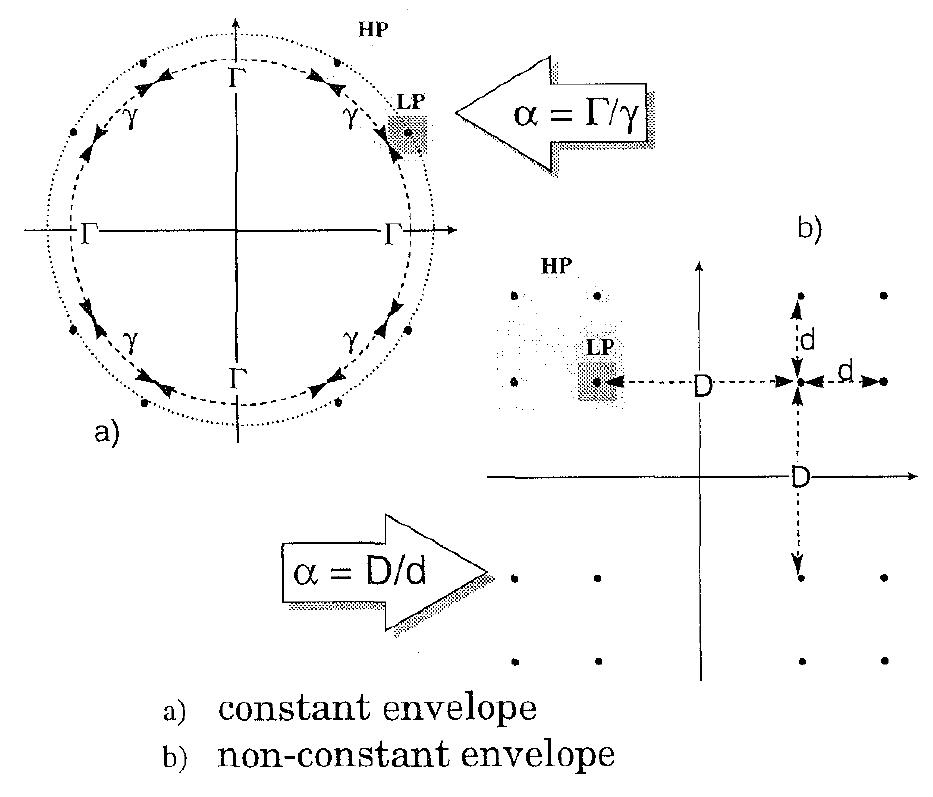
Fig. 3: Multiresolution constellations.
Fig.4: Protocol stack of FC delivery system. Since we are analysing the last-hop of a network delivering messages to users located within the satellite coverage arca, we must consider that the network portion upstream the satellite link delivers TCP/IP traffic over an ATM switched network to the SIU.
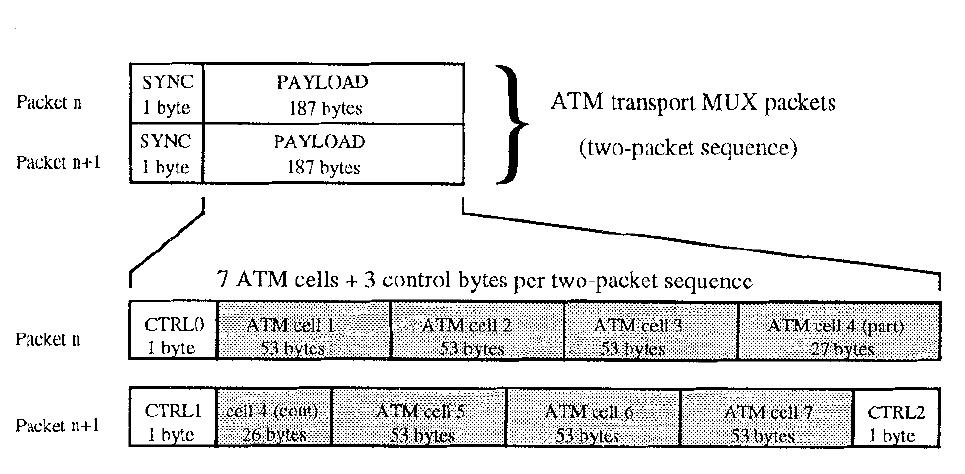
Fig.5: Encapsulation of the ATM cells into the MPEG2
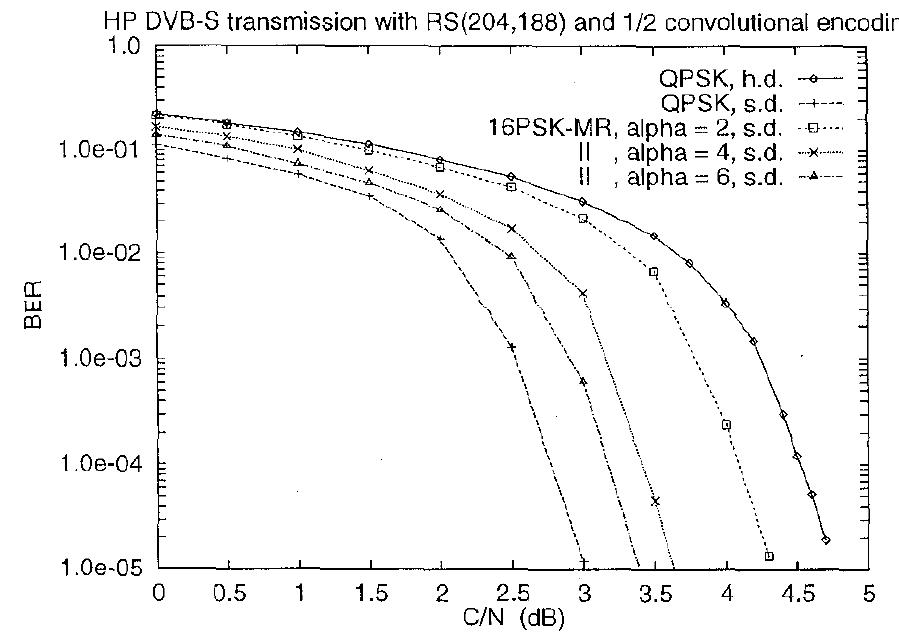
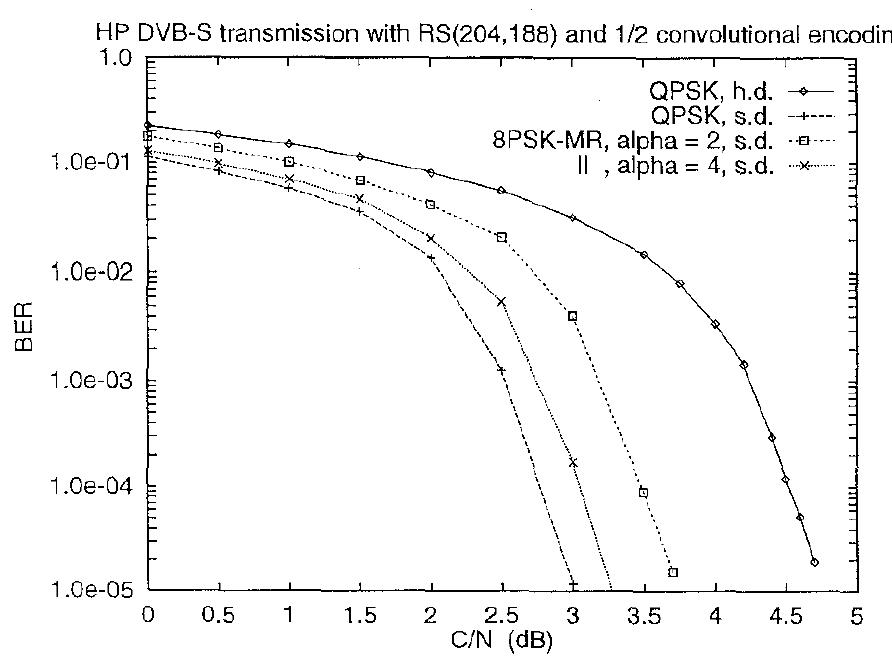
Fig. 7: BER of the QPSK and of the HP stream of the MR 16-PSK (h.d.: hard decoding; s.d.: soft decoding). Fig. 6: BER of the QPSK and of the HP stream of the MR 8-PSK (h.d.: hard decoding; s.d.: soft decoding).
Symbol and bit rates of HP and LP streams for different transponder bandwidths.
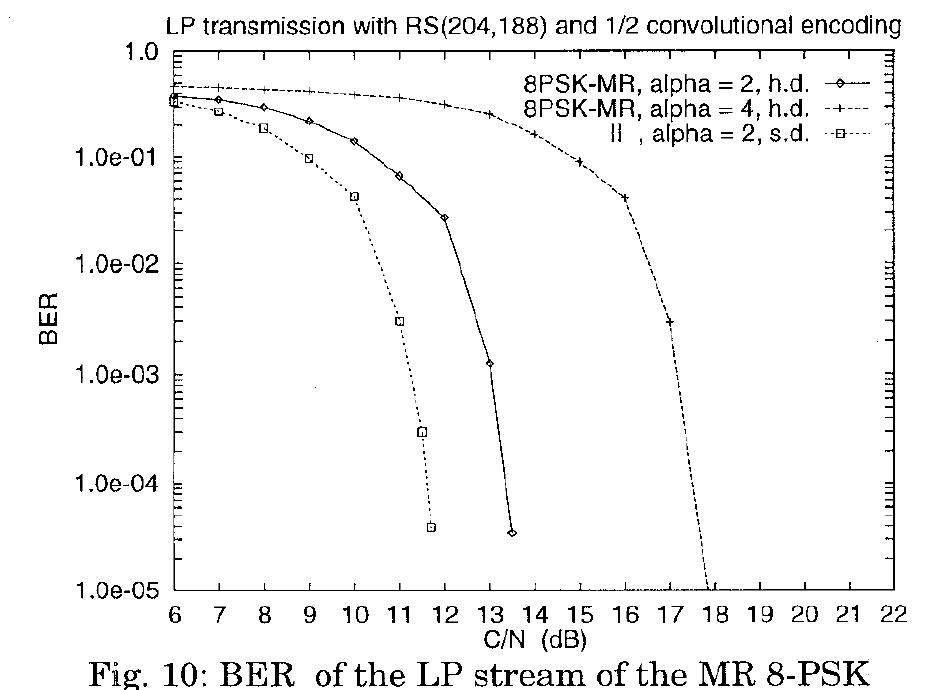
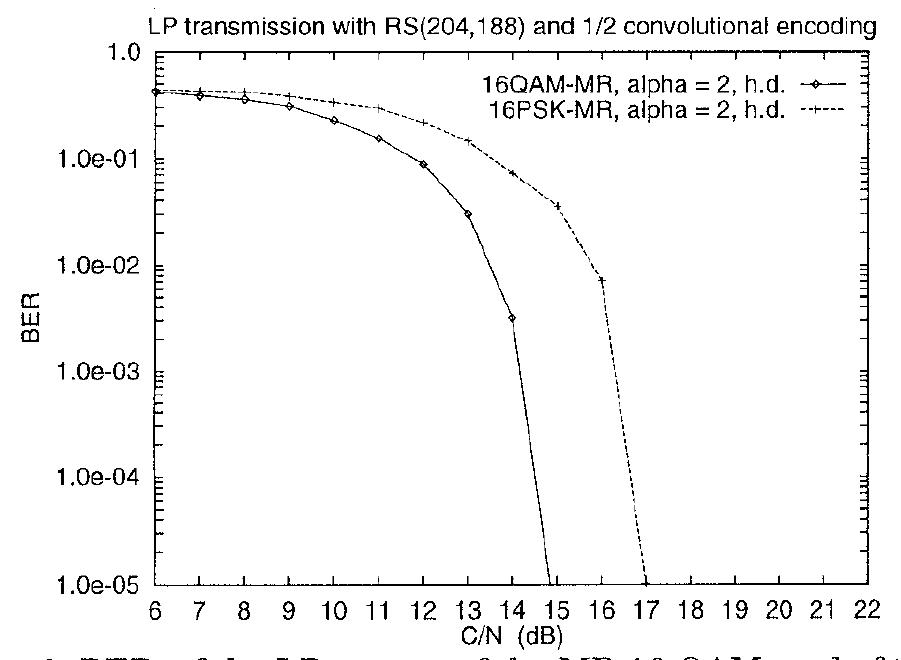
SS, of ooo Fig. 9: BER ofthe LP stream of the MR 16- QAM and of the MR 16-PSK (h.d.: hard decoding; s.d.: soft decoding).
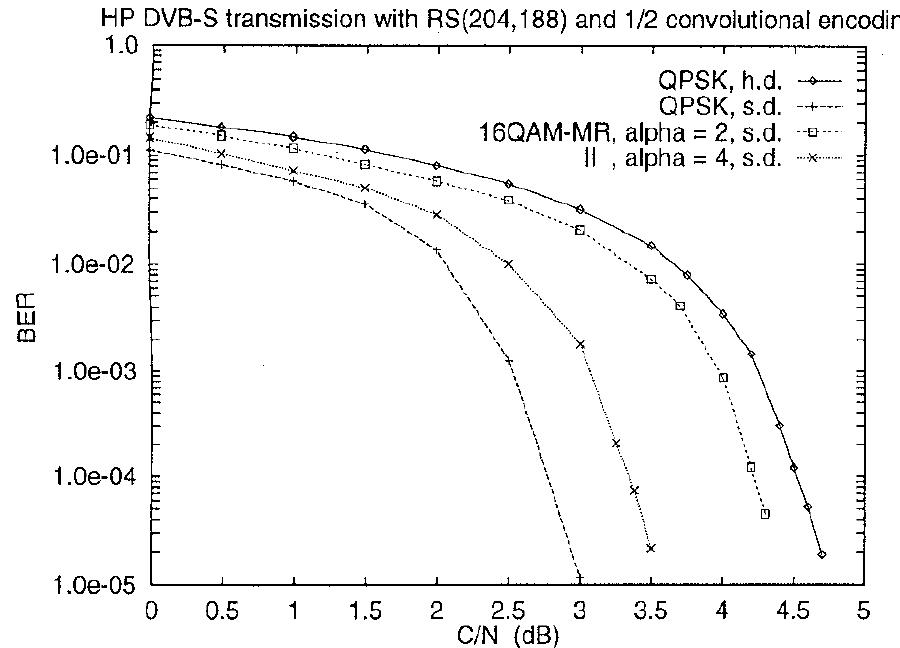
Fig. 8: BER of the QPSK and of the HP stream of the MR 16-QAM (h.d.: hard decoding; s.d.: soft decoding)
satellite link is a currently debated matter [8]. In any case, in our analysis sessions are treated separately, no matter about their establishment. IIL.3 Statistics of Packet Delivery
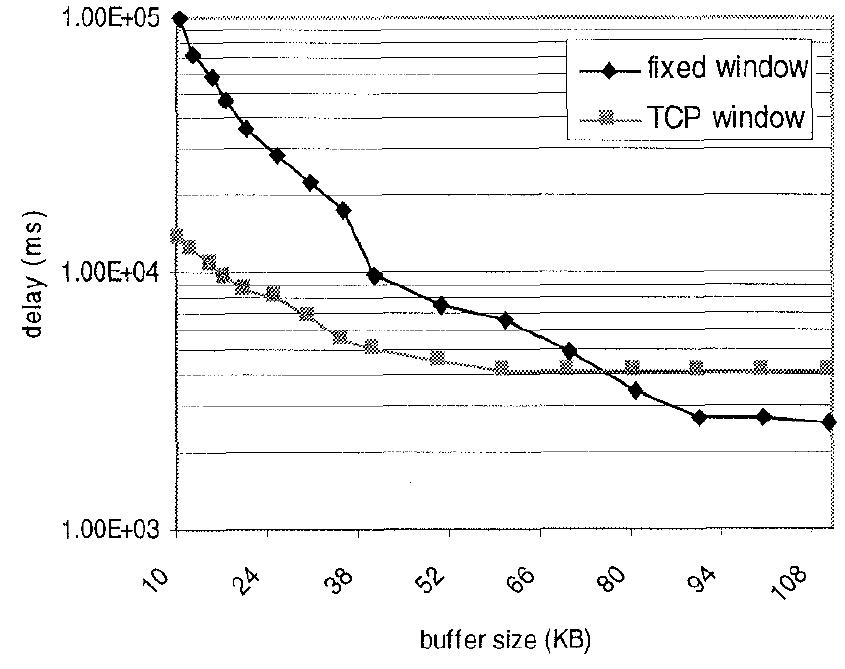
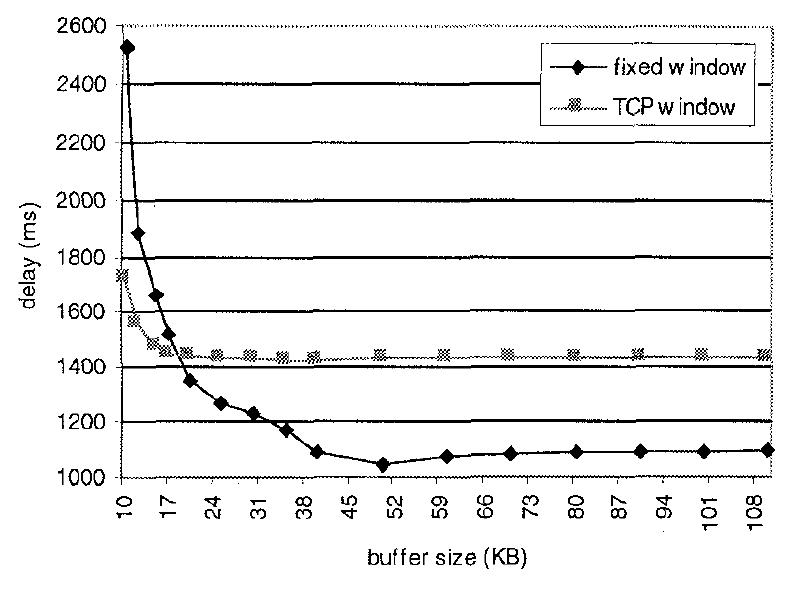
Fig. 13: Maximum delay of the WEB messages versus TCP buffer size. Fig. 12: Mean delay of the WEB messages versus TCP buffer size.
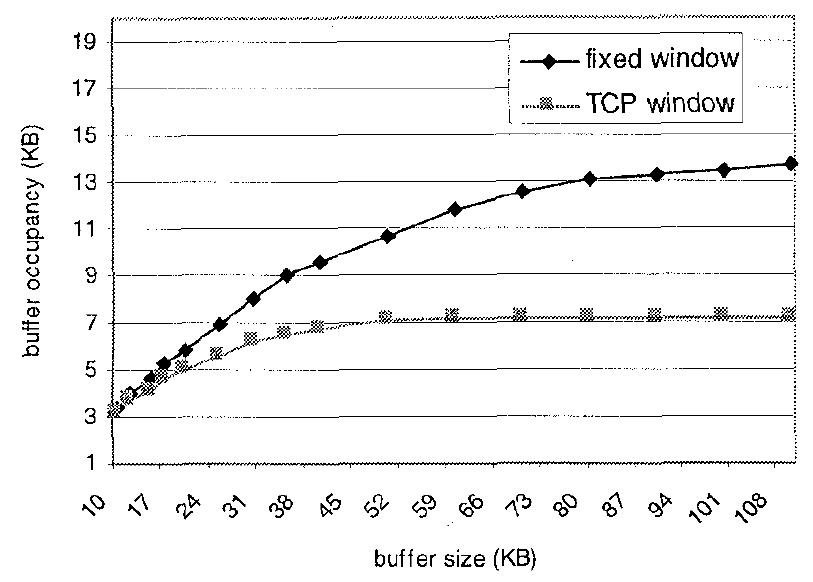
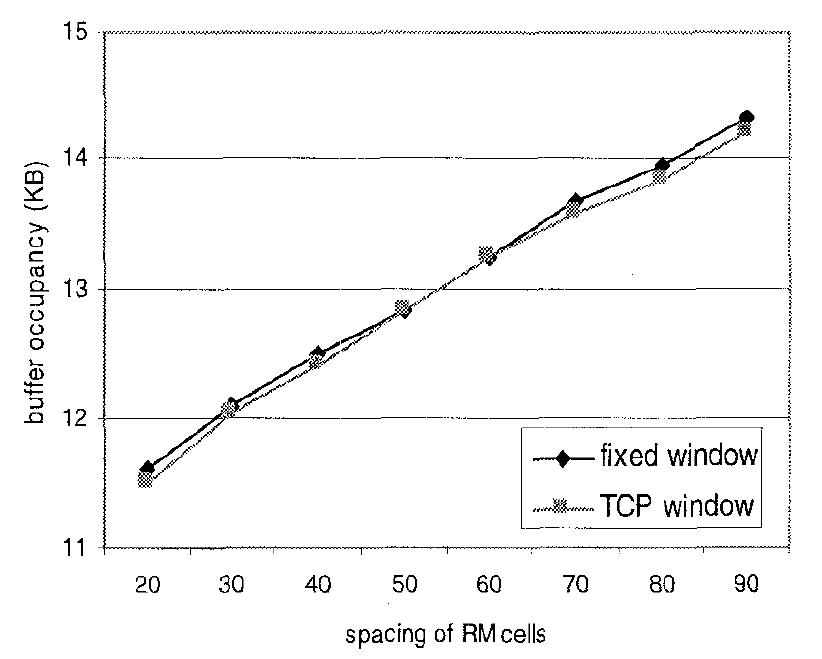
Fig. 14: Mean TCP buffer occupancy versus its size.
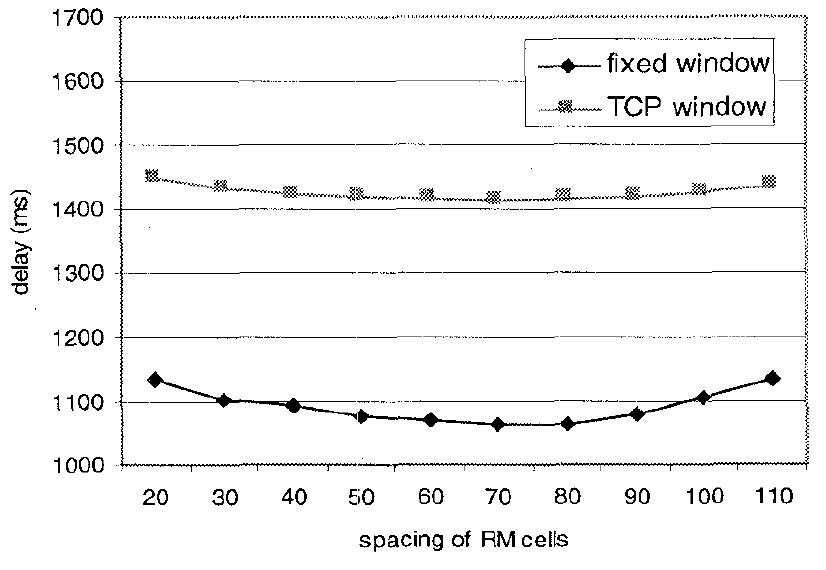
Fig. 17: Mean delay of the WEB messages versus the number of cells between two RM cells. Fig. 16: Maximum occupancy of the ATM buffer versus the number of cells between two RM cells.
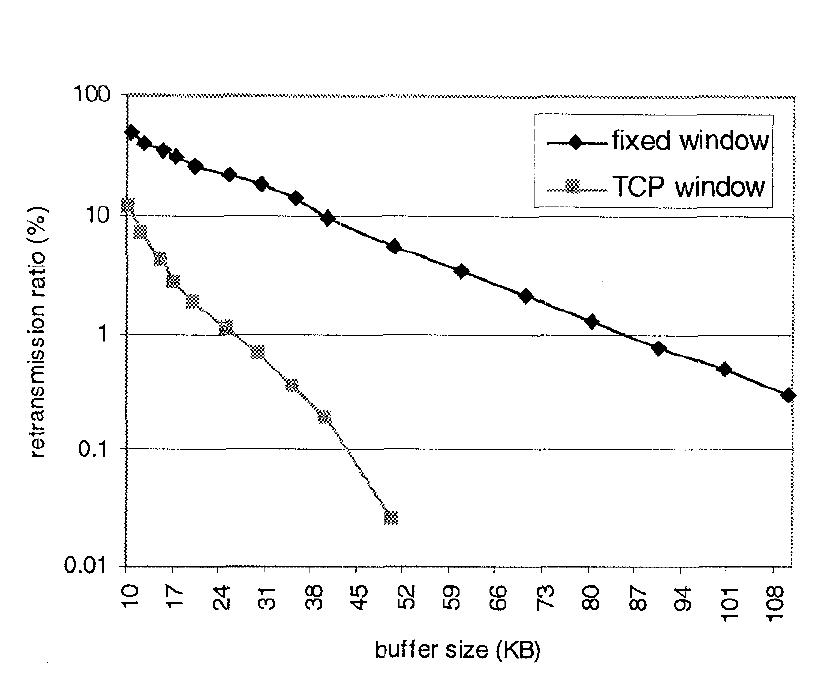
Fig. 15: Percentage of retransmitted TCP packets delivering WEB traffic.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
![satellite link is a currently debated matter [8]. In any case, in our analysis sessions are treated separately, no matter about their establishment. IIL.3 Statistics of Packet Delivery](https://figures.academia-assets.com/48064590/figure_011.jpg) ](
](