Survey of loss minimization methods in tram systems (original) (raw)
Abstract
This paper analyzes energy flows, conversions and losses in tram systems. Proposals for improvement of the efficiency of tram systems by the help of energy storage modules are described. In addition, such advanced methods of energy efficiency improvement as load sharing, real-time traffic management and Ecodriving are discussed.
FAQs
AI
What energy savings are possible with modernized tram systems?add
The modernization of trams, such as the ÝKD Tatra KT4, has led to a 48% reduction in energy consumption from the catenary after implementing IGBT-based choppers and energy storage systems since 2006.
How do supercapacitors enhance tram energy efficiency?add
Supercapacitors can reduce peak current by 75%, leading to approximately 44% lower line losses, and when fully utilized, can improve energy efficiency by up to 65% compared to traditional trams.
What are the impacts of voltage drops in tram systems?add
Voltage drops become critical due to the lower 600 VDC operating levels, causing inefficiencies during regenerative braking and requiring resistive dissipaters, which can be mitigated through proper energy storage integration.
How do energy storage strategies differ for trams?add
Different strategies include reducing current peaks to 75% for energy savings and maximizing the elimination of current peaks, which can decrease overhead line losses by up to 300 times but requires more storage capacity.
What role does real-time traffic management play in energy optimization?add
Real-time traffic management enables demand-side strategies to minimize substation overloads by limiting simultaneous vehicle acceleration and optimizing traffic light sequences for smoother operations.
Figures (7)
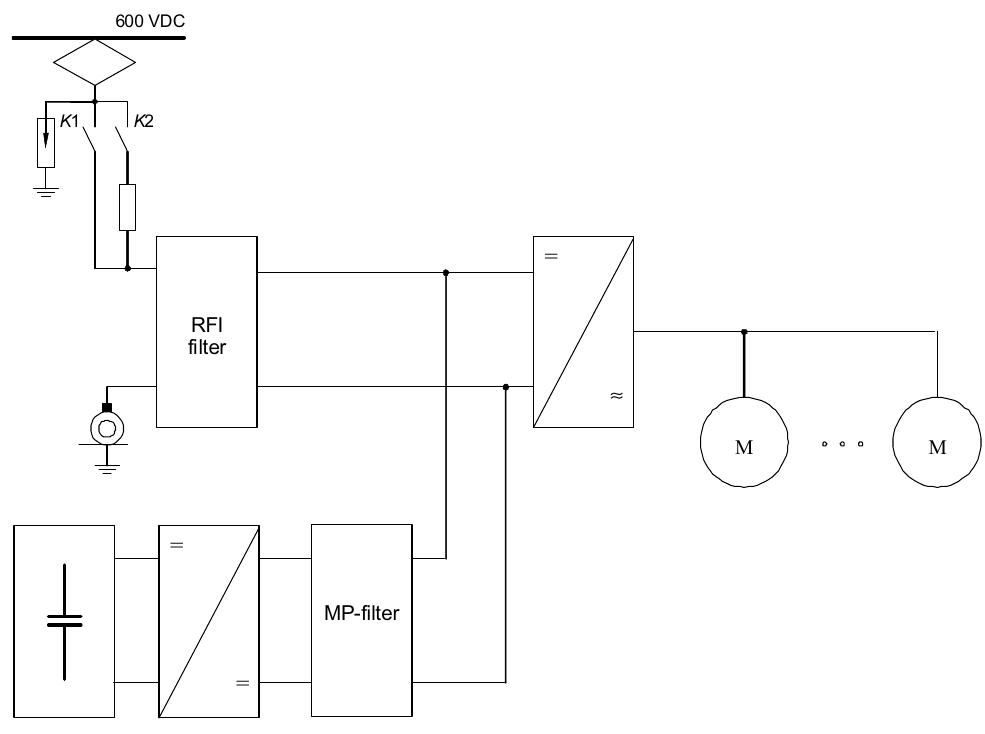
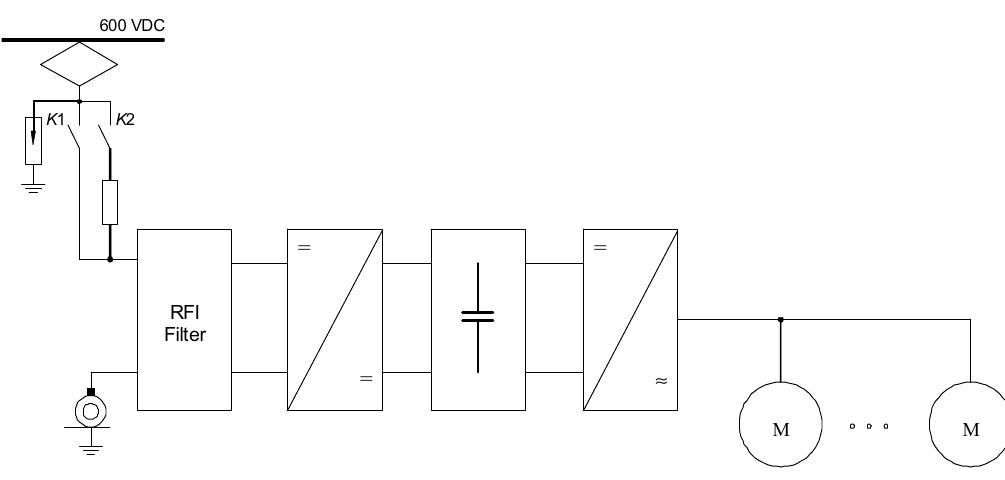
There are two general possibilities of the supercapacitor stack integration into the traction drive of a tram: parallel (Fig. 2) or series combination.
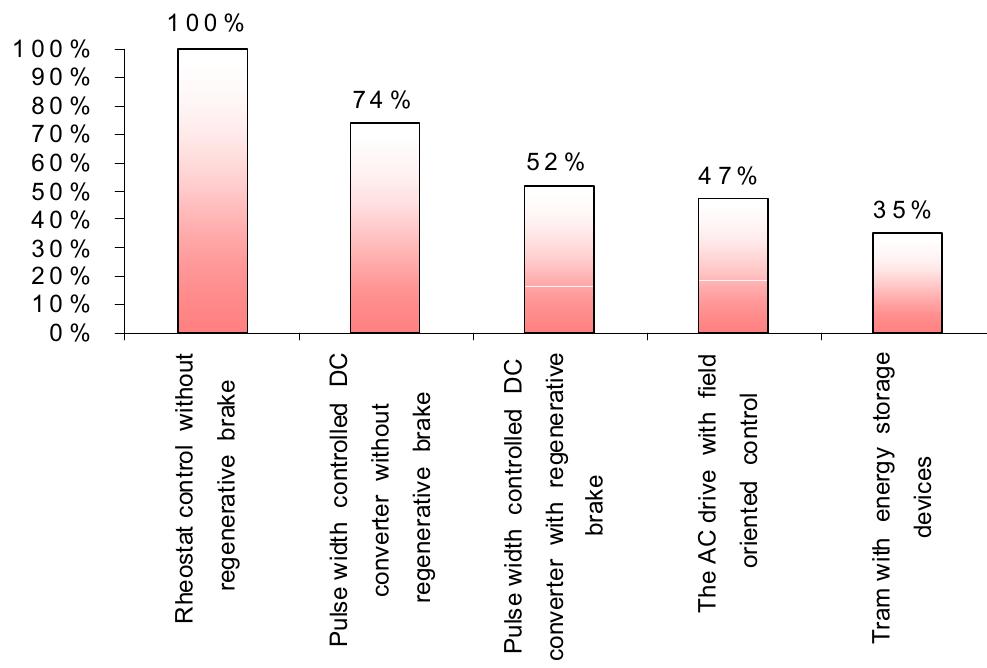
Fig. 5. Relative energy consumption of different tram traction drives To demonstrate the resulting advantages of the energy storage modules in traction drives of trams, the energy consumption of different kinds of tram traction drives is compared in Fig. 5. It is seen that by the help of the implementation of traction drives with regenerative braking and load levelling with supercapacitors, the energy efficiency of trams could be improved by 65 % in comparison to conventional trams with rheostat control.
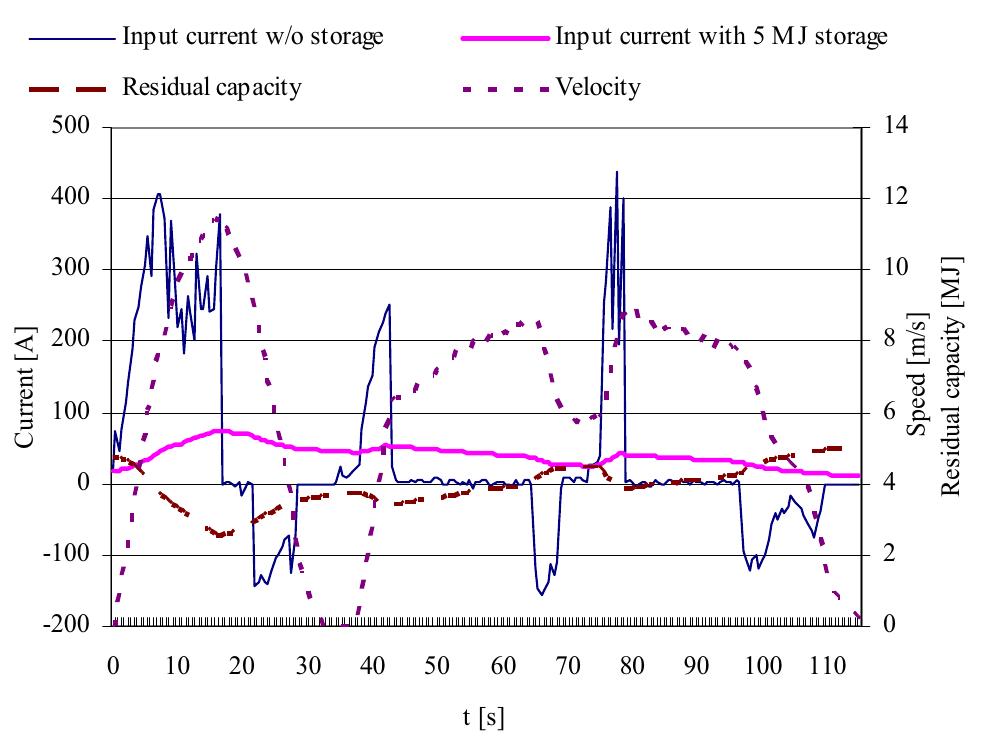
If correctly dimensioned and installed, energy storages could provide the remarkable efficiency rise for the traction drive. An example of the consumption current of a tram with and without a supercapacitor is provided in Fig. 4. It is shown that by the implementation of the discussed energy storage in the traction drive the peak currents during the tram acceleration could be effectively dampened. Moreover, the power available from the regenerative braking is fully utilized by the supercapacitor and re-used during next acceleration, thus increasing the energy efficiency of the tram. Fig. 4. Modelled consumption current of a tram traction drive with and without an onboard energy storage unit
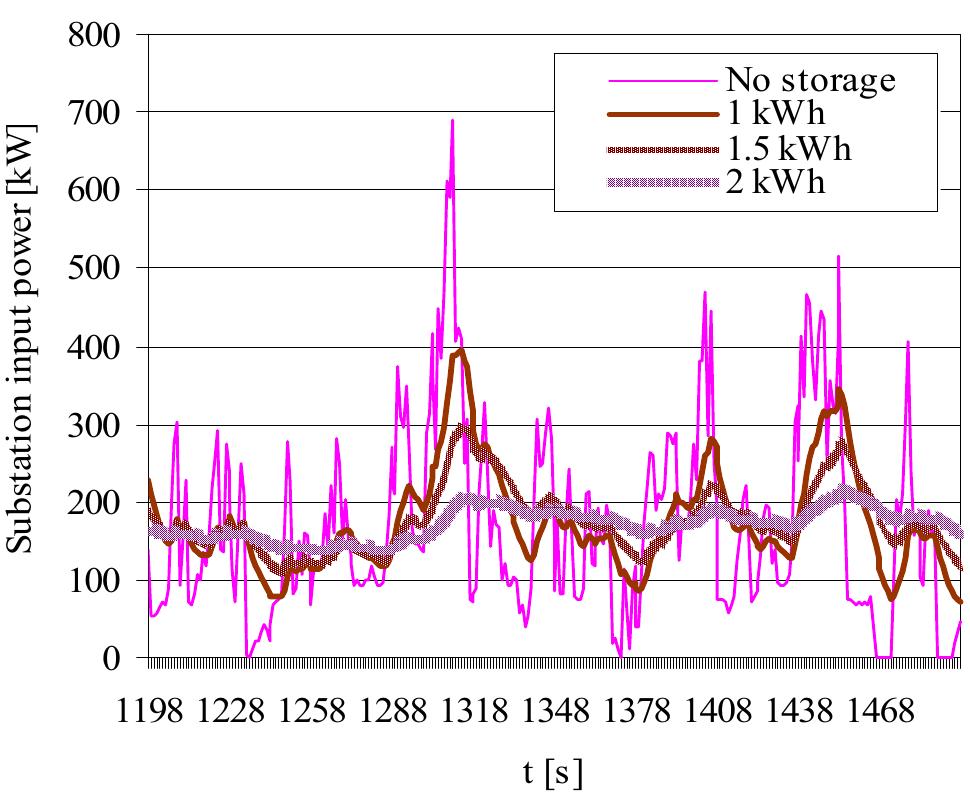
The energy storage units in traction substations level its load imposed by the tram system and facilitate the recycling of braking energy. With the storage unit acting as a low-pass filter, the fluctuations will be suppressed, thus minimizing the peak values in the primary medium- voltage grid. By minimizing the peaks, the transformer and rectifier ratings of the substations can be reduced. It is a benefit that the storage units can be stationary and high powered, the dimensions are less limited and the number of storage units is small. The disadvantage of such a centralized approach is that line losses do not decrease significantly. Integrated energy storage units help to level the substation input power, as depicted in Fig. 6. Fig. 6. Modelled load levelling of tram traction substation by help of energy storage units
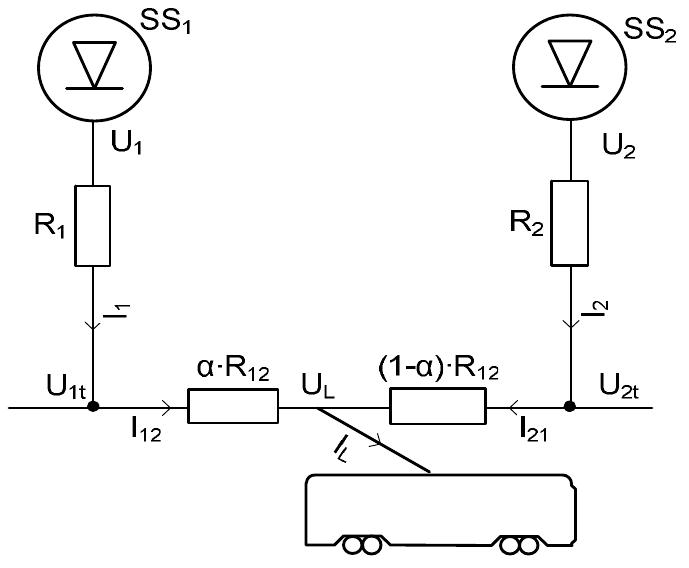
Fig. 7. An example of load sharing between two adjacent substations Load sharing between two adjacent substations SS, and SS, can be illustrated by Fig. 7. Termination voltages U,, and U>, differ from busbar voltages U; and U> due to voltage drops in the cables, represented by series resistances R, and R>. The contact wires and rails between the feeding points build up an equivalent resistance R,>. In practice, cable resistances can often be considered negligible compared to those of contact wires. Currents J; and J, drawn from adjacent substations are
The demand-side load management can as well be implemented on a single vehicle, basically it means controlling the power demand by the acceleration limitation. Peak loads are frequently determined by the human factor, i.e. the driving style of an individual driver. Fig. 8 represents the speed and power demand of tram coaching between two stops. Fig. 8. Recorded speed and power profiles of a tram’s operating cycle Optimal motion planning is often discussed in robotics, where trajectories with certain constraints must be programmed; fewer papers are dedicated to public vehicles [15], [16]. In real city traffic conditions where it is not possible to foresee all circumstances, like other vehicles blocking the track, these planning algorithms may not be fully implemented. Finally, ecodriving can be shortly characterized as reducing the human participation in driving and allowing the onboard computer to calculate the smoothest and optimal trajectory [10].

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (16)
- Meinert, M., Rechenberg, K., Hein, G. Energy efficient solutions for the complete railway system. 2007
- Laugis, J., Lehtla, T., Joller, J., Rosin, A., Vinnikov, D., Lehtla, M. Traction and Control of Light Rail Vehicles. Tallinn University of Technology Press, 2008, 220 pp.
- Joller, J. Research and Development of Energy Saving Traction Drives for Trams, PhD. thesis, Dept. El. Drives Pow. Elec., Tallinn Univ. Tech., Estonia, 2001.
- Joller, J., Lehtla, M. Power Analysis of a Tram System with Energy Storage Devices. In Proc. of 8th Biennial Baltic Electronics Conference BEC2002, October 6-9, 2002, Tallinn.
- Joller, J., Lehtla, M. Power Analysis and New Loss Minimisation Possibilities of a Tram System. In Proc. of 10-th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference EPE-PEMC 2002, Cavtat & Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2002.
- Vinnikov, D. Research, Design and Implementation of Auxiliary Power Supplies for the Light Rail Vehicles, PhD. thesis, Dept. El. Drives Pow. Elec., Tallinn Univ. Tech., Estonia, 2005.
- Steiner, M., Klohr, M. Energy storage system with ultracaps on board of railway vehicles. 2007 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Sept 2-5, 2007, pp. 10.
- Richardson, M.B. Flywheel Energy Storage System for Traction Applications. International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, July 4-7, 2002, pp. 275-279.
- Hõimoja, H. Energy Efficiency Estimation and Energy Storage Calculation Methods for Urban Electric Transportation. PhD thesis, 2009, Tallinn, 173 p.
- Destraz, B., Barrade, P., Rufer, A., Klohr, M. Study and Simulation of the Energy Balance of an Urban Transportation Network. 2007 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Sept 2-5, 2007, pp. 10.
- Rufer, A., Hotellier, D., Barrade, P. A Supercapacitor- Based Energy Storage Substation for Voltage Compensation in Weak Transportation Networks. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, June 23-26, Vol. 19, No. 2, April 2004, pp. 629-636.
- Mägi, M. Analysis of Modelling Electric Transportation Networks. 4th International Symposium "Topical Problems in the Field of Electrical and Power Engineering" and "Doctoral School of Energy and Geotechnology". Kuressaare, Estonia, Jan. 15-20, 2007, pp. 73-77.
- Xu, Z., Zhang, B. et al. The Emitter Turn-Off Thyristor- Based DC Circuit Breaker. IEEE Power Engineering Society winter Meeting, Jan 27-31, 2002, Vol. 1, pp 288- 293.
- Flowers, J.B. Load Sharing with Thyristor Controlled Rectifier Substations. 1995 IEEE/ACME Joint Railroad Conference, Apr 4-6, 1995, pp 69-73.
- Bocharnikov, Y.V.; Tobias, A.M. et al. Optimal Driving Strategy for Traction Energy Saving on DC Suburban Railways. Electric Power Applications IET. Vol. 1, Issue 5, Sept. 2007, pp.: 675 -682.
- Miyatake, M., Matsuda, K. Optimal Speed and Charge/Discharge Control with Onboard Energy Storage with Minimum Energy Operation. SPEEDAM 2008, Ischia, June 10-13, 2008, pp. 1211-1216.
![The demand-side load management can as well be implemented on a single vehicle, basically it means controlling the power demand by the acceleration limitation. Peak loads are frequently determined by the human factor, i.e. the driving style of an individual driver. Fig. 8 represents the speed and power demand of tram coaching between two stops. Fig. 8. Recorded speed and power profiles of a tram’s operating cycle Optimal motion planning is often discussed in robotics, where trajectories with certain constraints must be programmed; fewer papers are dedicated to public vehicles [15], [16]. In real city traffic conditions where it is not possible to foresee all circumstances, like other vehicles blocking the track, these planning algorithms may not be fully implemented. Finally, ecodriving can be shortly characterized as reducing the human participation in driving and allowing the onboard computer to calculate the smoothest and optimal trajectory [10].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31829064/figure_007.jpg) ](
](