A Survey on Wireless Security (original) (raw)
Abstract
A Wireless Network is a wireless communication system that allows mobile computers and workstations to communicate and exchange data with each other using radio waves as the transmission medium. Nowadays wireless networks are used in many areas such as universities, healthcare-centers, hospitals, police department, military, airports, etc. WLAN (Wireless LAN) is commonly referred to as " Wi-Fi " (wireless fidelity) that gives freedom to move mobile nodes like laptops, PDA, etc. from one place to another within their offices and organizations without the need of wires and without losing network connectivity. Most of the businesses, research, day to day activity, etc. are shifting from wired to wireless. At present the wireless system is not very secured and needs various hardware and software techniques to protect the data/information from unauthorized access. Therefore, it is essential to enhance the network security in order to protect the information in the wireless network. This survey paper deals with various security protocol standards, attacks, threats, etc. in WPAN, WMAN and WWAN.
Figures (12)
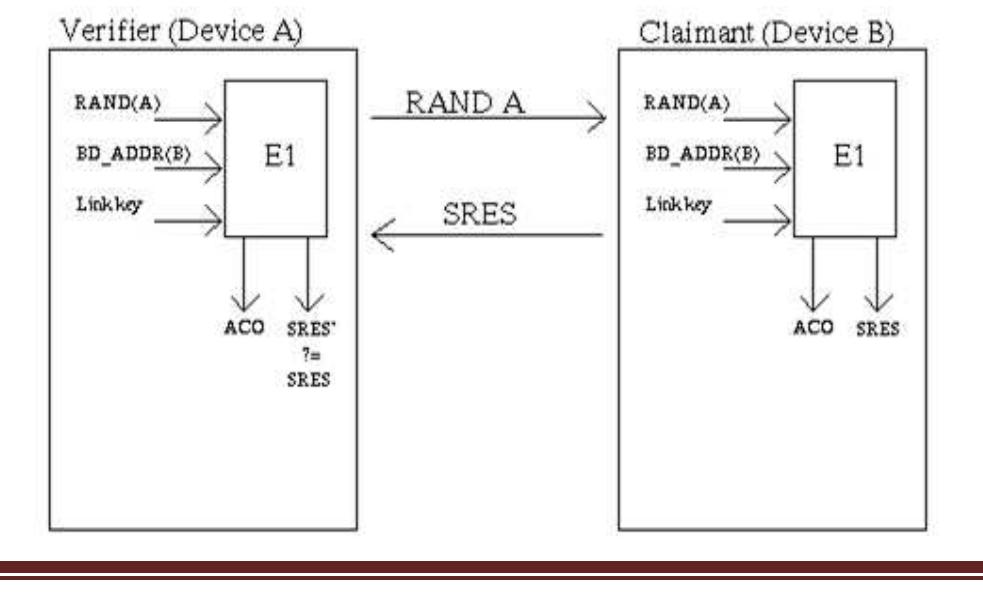
used to check whether the other party knows the secret key. Authentication: The Bluetooth authentication scheme uses encryption mode 3, all traffic is encrypted with the master key. As the encryption key size varies from 8 bits to 128 bits, the size of the encryption key used between two devices must be negotiated. In each device, there is a parameter defining the maximum allowed key length. In the key size negotiation, the master sends its suggestion for the encryption Key size to the slave. The slave can either accept and acknowledge it, or send another suggestion. This is continued, until a consensus is reached or one of the devices aborts the negotiation. The abortion of the negotiation is done by the used application. In every application, there is defined a minimum acceptable key size, and if the requirement is not met by either of the participants, the application aborts the negotiation and the encryption cannot be used. This is necessary to avoid the situation where a malicious device forces the encryption to be low in order to do some harm. The encryption algorithm uses four LFSRs of lengths 25, 31, 33 and 39, with the total length of 128. The initial 128-bit value of the four LFSRs is derived from the key stream generator itself using the encryption key, a 128-bit random number, the Bluetooth device address of the device and the 26-bit value of the master clock. The feedback polynomials used by the LFSRs are all primitive, with the Hamming weight of 5. The polynomials used are (25, 20, 12, 8, 0), (31, 24, 16, 12, 0), (33, 28, 24, 4, 0) and (39, 36, 28, 4, 0). Information on the fundamentals of LFSRs is found in.
Fig -3: Authentications and Authorization Privacy key management: In both IEEE 802.16-2004 and IEEE 802.16e-2005 standards, MAC layer contains a security sub-layer. To protect network services from attacks and to guarantee secure distribution of susceptible data from the base station to his subscriber station, WIMAX applies strong support for authentication, key management, encryption and decryption, control and management of plain text protection and security protocol optimization.
Fig - 4 Public Key Infrastructure validates the certificate, thus validating the user identity. Internet Connectivity Service Network (CSN) WiMAX Access Service Network (ASN) Gateway (GW) A Base Station (BS) Authentication Server Control (R6) Data (IP) Firewall Additional Operator Servers IP network Management System X.509 Digital Certificate Mobile Station (MS) Public- Key Exchange.
Fig -5: EAP-based authentications WiMAX uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to perform user authentication and access control are shown in fig-5. EAP is actually an authentication framework that requires the use of "EAP methods" to perform the actual work of authentication. The network operator may choose an EAP method such as EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security), or EAP-TTLS MS-CHAP v2 (Tunneled TLS with Microsoft Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol version 2). The messages defined sent from the mobile station to by the EAP method are an authenticator. The authenticator then forwards the messages to the authentication server using either the RADIUS or DIAMETER protocols [9]. that requires the use of "EAP methods" to perform the
Fig -7: GSM authentication architecture The Authentication Process [2]: - In GSM, the users are first identified and authenticated then the services are granted. The GSM authentication protocol consists of a challenge-response mechanism. The authentication is based on a secret key Ki which is shared between HLR and MS. After a visited MS gets a free channel by requesting BS, it makes a request for its location update to MSC through BSC. The MSC, in response, asks MS for its authentication. Thus in the authentication process, three major actors like MS, MSC/VLR and HLR/AuC are responsible.
Fig -13: Mobile WiMAX Network The ASN-GW provides security anchoring, traffic accounting and mobility support for the mobile station (MS). The mobile IP home agent (HA) in the CSN enables global mobility. There are a number of key elements in the operation of the WiMAX network architecture. First, the AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) server located in the CSN network processes control signals from the ASN-GW to authenticate the MS against the MS’s profile stored in the AAA server’s database. Once authenticated, the AAA server sends the MS’s profile including the QoS parameters to the ASN-GW. The Home Agent (HA) processes control signals from the ASN-GW and assigns a Mobile IP address to the MS and anchors the IP payload. The HA server provides connectivity to the Internet for data traffic. The HA server provides connectivity to the Internet for data
If the MS makes a VoIP call, control is passed to the CSN IM: (IP Multimedia System) servers which then process the call If the call is to a telephone number that is outside the WiMAX network, the IMS servers select the appropriat Media Gateway Controller (MGC) / Media Gateway (MGW to interface to the Public Switched Telephone Networl (PSTN). Alternatively, if the call is to an end unit in anothe 3GPP or 3GPP2 network, it is routed through the Interworking Gateway Unit within the CSN. Mobile Station: (MS) communicate with Base Stations (BS) using the 802.16e (802.16m in the future) air interface. Th communication between the MS and BS is via an all-II bearer and control. WiMAX does not have a TDM (Tim« Division Multiplexing) bearer. Like LTE, it is an all-IP fla network. WiMAX MS user traffic is tunneled as payloac between the BS and ASN-GW. In most service provide configurations, the CSN network elements are redundan and geographically separate. The ASN-GW _networl elements within the ASN are also configured in a redundan manner typically within the same premises. A Networl Access Provider (NAP) can have multiple ASNs. Mobilit within these ASNs does not have to be anchored at the CSN Roaming is supported when the MS roams out of its Home Network Service Provider (NSP) to a Visited NSP. In sucl cases, the AAA server in the Visited NSP uses contro signaling to obtain the credentials and profiles from th« Home NSP. Bearer traffic is not sent from the visited NSP t« the home NSP. Various mobility scenarios are supportec including intra-ASN-GW, inter-ASN-GW and anchored CS} mobility. When the MS moves from one BS to another B: served by the same ASN-GW, calls can be switcher seamlessly using signaling.
Key takeaways
AI
- Enhancing wireless network security is critical due to vulnerabilities in WPAN, WLAN, WMAN, and WWAN.
- The paper surveys various security protocols, threats, and attacks in wireless networks.
- Key management techniques include Initialization Key, Unit Key, and Master Key in WPAN.
- WiMAX employs mutual authentication via PKMv2 to prevent MITM attacks.
- GSM utilizes a challenge-response mechanism for user authentication and encryption key management.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (14)
- B. FLECK, J. DIMOV, Wireless access points and ARPpoisoning: wireless vulnerabilities that expose the wired network. White paper by Cigital Inc., (2001). http://www.cigitallabs.com/resources/ papers/download/arppoison.pdf
- I. MARTINOVIC, F. A. ZDARSKY, A. BACHOREK, C. JUNG, J. B. SCHMITT, Phishing in the Wireless: Implementationand Analysis. Kaiserslauterer Uniweiter Elektronischer Dokumentenserver, UniversitatsbibliothekKaiserslautern, (2006). http://kluedo.ub.uni- kl.de/volltexte/2006/2035/pdf/martinovic.pdf
- G. RUPINDE, S. JASON, C. ANDREW, SpecificationBasedIntrusionDetectioninWLANs.22ndAn nual ComputerSecurityApplicationsConference,Miami Beach, Florida,(2006). 39025942, 60152756p00.htm
- L. HAN, A Threat Analysis of The Extensible Authentication Protocol. Honours Project, School of ComputerScience, Carleton University,(2006).
- http://www.scs.carleton.ca/ barbeau/ Honours/Lei Han.pdf [5] NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND TECHNOLOGY, FIPS Pub197: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), (2001).
- D. WHITING, R. HOUSLEY, N. FERGUSON, Counter with CBC-MAC (CCM). RFC 3610,(2003).
- I. KUMAR, Cryptology. Laguna Hills, CA: Aegean Park Press, (1997).
- M. DWORKIN, Recommendation for Block Cipher Modes of Operation -Methods and Techniques. NIST,(2001).
- FIPSPUBLICATION197,AdvancedEncryptionStandard (AES). U.S. DoC /NIST, November 26, (2001).
- Chip Craig J. Mathias Principal, Farpoint Group COMNET 2003 -Wireless Security: Critical Issues and Solutions‖ 29 January 2003
- Sandra Kay Miller -Facing the Challenge of Wireless Security‖ July 2001
- T. Karygiannis and L. Owens. Wireless Network Security:802.11, Bluetooth and Handheld Devices. In NIST Special Publication 800-48, November 2002.
- Paulo Salvador, Ant´onio Nogueira, Rui Valadas -Predicting QoS Characteristics on Wireless Networks‖ 25 June 2007.
- Jim Kurose -Open issues and challenges in providing quality of service in high-speed networks‖ Computer Communication Review, 23(1):6-15, January 1993.



![Fig -5: EAP-based authentications WiMAX uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to perform user authentication and access control are shown in fig-5. EAP is actually an authentication framework that requires the use of "EAP methods" to perform the actual work of authentication. The network operator may choose an EAP method such as EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security), or EAP-TTLS MS-CHAP v2 (Tunneled TLS with Microsoft Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol version 2). The messages defined sent from the mobile station to by the EAP method are an authenticator. The authenticator then forwards the messages to the authentication server using either the RADIUS or DIAMETER protocols [9]. that requires the use of "EAP methods" to perform the](https://figures.academia-assets.com/54341327/figure_005.jpg) ](
](![Fig -7: GSM authentication architecture The Authentication Process [2]: - In GSM, the users are first identified and authenticated then the services are granted. The GSM authentication protocol consists of a challenge-response mechanism. The authentication is based on a secret key Ki which is shared between HLR and MS. After a visited MS gets a free channel by requesting BS, it makes a request for its location update to MSC through BSC. The MSC, in response, asks MS for its authentication. Thus in the authentication process, three major actors like MS, MSC/VLR and HLR/AuC are responsible.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/54341327/figure_006.jpg) ](
](




