Integrated Management Systems: Literature Review and Proposal of Instrument for Integration Assessment (original) (raw)

Global Journal on Humanites & Social Sciences
Issue 2 (2015) 27-34
Selected Paper of 3rd World Congress of Administrative and Political Sciences, (APDOL-2014) 28-29 November 2014, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain.
Integrated Management Systems: Literature Review and Proposal of Instrument for Integration Assessment
Camila Fabrício Poltronieri *, Sao Carlos School of Engineering (EESC), Avenida Trabalhador Sao Carlense, 400, Sao Carlos, 13566-560, Brazil.
Mateus Cecílio Gerolamo, Sao Carlos School of Engineering (EESC), Avenida Trabalhador Sao Carlense, 400, Sao Carlos, 13566-560, Brazil.
Luiz Cesar Ribeiro Carpinetti, Sao Carlos School of Engineering (EESC), Avenida Trabalhador Sao Carlense, 400, Sao Carlos, 13566-560, Brazil.
Suggested Citation:
Poltronieri, C., F., Gerolamo, M., C. & Carpinetti, L., C., R. (2015). Integrated Management Systems: Literature Review and Proposal of Instrument for Integration Assessment, Global Journal on Humanites & Social Sciences. [Online]. 02, pp 27-34. Available from:http://www.world-educationcenter.org/index.php/pntsbs
Received May 01, 2014;revised July 16, 2014; accepted September 07, 2014.
Selection and peer review under responsibility of Prof. Dr. Andreea Iluzia IACOB, Bucharest Academy of Economic Studies, Romania.
©2015 Academic World Education & Research Center. All rights reserved.
Abstract
Standards facilitate the access to new markets because they reduce the divergences in management. The number of companies that have adopted global standards, such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and OHSAS 18001 has increased in the last decade. The union of two or more standards is called Integrated Management System (IMS). The integration of standards is important because it improves communication, eliminates conflicts, reduces bureaucracy and costs, improves both decision-making process and resource utilization and promotes a better alignment with strategic planning. In this research, a Systematic Literature Review about Integrated Management System is firstly presented. It has the purpose of understanding what has being published in this area. After, a proposal of a tool is presented aiming at assessing the degree of integration of management systems based in the Maturity Model’s Theory. Based on the Systematic Literature Review, few publications have been found and Spain is the country that has conducted more studies on such an issue. Although this number has increased since 2010, more research into IMS is necessary in other countries, especially on topics, such as performance evaluation, integration strategies, auditing and maturity of integration. It is expected that the tool presented in this research can help organizations to evaluate the degree of mature.
- ADDRESS FOR CORRESPONDENCE: Camila Fabrício Poltronieri, Sao Carlos School of Engineering (EESC), Avenida Trabalhador Sao Carlense, 400, Sao Carlos, 13566-560, Brazil. E-mail address:camila_fabricio@sc.usp.br / Tel.: +55-016-3373-9428
↩︎
- ADDRESS FOR CORRESPONDENCE: Camila Fabrício Poltronieri, Sao Carlos School of Engineering (EESC), Avenida Trabalhador Sao Carlense, 400, Sao Carlos, 13566-560, Brazil. E-mail address:camila_fabricio@sc.usp.br / Tel.: +55-016-3373-9428
Keywords: integrated management systems, assessment, maturity model.
1. Introduction
The increase of standards such as ISO occurs due their universal nature and generality. Firstly, it was introduced in manufacture sector, but nowadays they are used in government agencies, hospitals, transport and many other sectors (Boiral, 2011).
The implementation of parallel systems requires duplicate efforts for the organization in terms of documentation, control forms, procedures beyond the difficulty of ensuring that the alignment of these different management systems are in accordance with the company’s strategy (Zeng, Shi & Lou, 2007). While there has been noted an increase in the numbers of organizations that adopt different management systems, several problems related to the use of standards separately are also observed such as difficult of forms control, duplicate documents and lack of alignment between different systems with company’s strategy. Therefore, it is important to investigate the integration of standards.
Once the standard utilization has increased, one can suppose that both the assessment of integration among management systems and the maturity level of the integration become even more relevant. For Fraser, Moultrie and Gregory (2002), maturity is linked to the idea of ripening, conveying the notion of transition from an early stage to another advanced, being necessary to evolve through several intermediate stages until the effective maturity is reached. The use of maturity models in different areas has grown over the years and Wendler (2012) reveals that between 2003 and 2009 the number of publications increased from 15 to 34.
In this paper, a Systematic Literature Review about Integrated Management System (IMS) is presented and a tool for assessment of the degree of integration based in Maturity Model’s Theory is proposed. The relevance of this research lies on the current context where organizations are adopting increasingly more than one management system and are suffering with integration problems.
2. Research development
Initially, an exploratory search was carried out in national and international databases about Integrated Management System and 21 articles were found. After, a Systematic Literature Review about Integrated Management System was conducted according the article of Conforto, Amaral and Silva (2011). They highlight that this kind of review helps in increasing the accuracy and trustworthiness of the literature review.
Through of articles searched in exploratory review, the research string was defined and used in the databases Web of Science and Scopus. The string is a compound of terms that are used to promote standardization in different databases searches. The search was done selecting title, abstract and keywords. The expressions used were the combination of “ISO”, “OHSAS”; “integrated management system”; “normalized management system” and “integrat*”.
The total of articles analyzed between exploratory and systematic literature review was 55 and, after, a further research was made based on articles read and alerts registered in the databases. In this last search, 19 articles were found. According to the literature review on IMS, it was observed that there is a gap related to the lack of maturity model for IMS. Then, a literature review about maturity model was carried out and a tool for assessment of the degree of integration based in maturity models was developed.
For developing this tool, widespread standards were used, such as ISO 9001-Quality Management System (ISO, 2008a), ISO 14001-Environmental Management System (ISO, 2004) and OHSAS 18001Occupational Health and Safety Management System (British Standards Institution, 2007). Moreover two maturity models were considered: the ISO 9004 - Managing for the sustained success of an
organization-A quality management approach (ISO, 2009) and the CMMI-Capability Maturity Model Integration (Chrissis, Konrad & Shrum, 2003).
While in development process, the tool was evaluated for academic specialists and professional of industries and modifications were suggested resulting in its final version. Figure 1 shows the resume of the research method.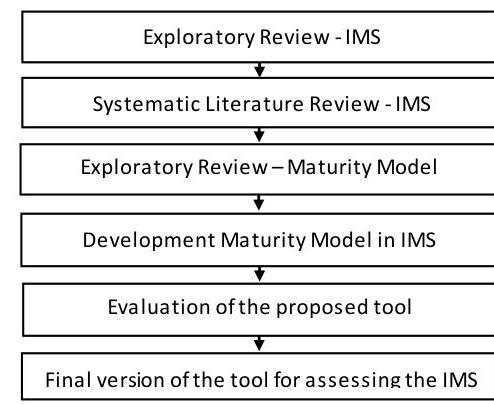
Figure 1. Summary of the research method
3. Theoretical background
3.1. Integrated Management System
According to ISO (ISO, 2008b), a management system aims to contribute to the management of risk relating to the delivery of products and services to customers and stakeholders. Moreover, these norms collaborate to promote continuous improvement in the organization. Among the major components of a management systems are: vision and strategy, goals and objectives, customers and other stakeholders, product and market, structure and resources, product and product realization process, and support processes.
The emergence of integrated systems occurs when two or more systems join resulting in the loss of independence of one or both systems, but without giving up their individual identities. This integration varies with the scope and control (Karapetrovic & Willborn, 1998).
3.2. Maturity Model
According Helgesson, Host & Weyns (2012), the formulation of maturity models is seen as a useful way to communicate best practices, by consolidating the knowledge in a way that promotes improvement initiatives.
The first maturity model was done by Crosby and became known as Crosby’s Quality Management Maturity Grid (Maier, Moultrie & Clarkson, 2012). The concept was published in the book “Quality is Free” in 1979. It was divided in 5 levels and it has 6 categories or points evaluated (Crosby, 1979).
One of the most popular models, the CMM - Capability Maturity Model, was inspired by the Crosby’s Quality Management Maturity Grid (Paulk, 2008). The CMM was developed by the Software Engineering Institute (SEI) - Carnegie Mellon, and the institute has produced several other models after the CMM, including CMMI - Capability Maturity Model Integration (Bruin, Rosemann, Freeze & Kulkarni, 2005). Other known maturity model is presented in ISO 9004 that is used to assess the maturity in quality management.
Poltronieri, C., F., Gerolamo, M., C. & Carpinetti, L., C., R. (2015). Integrated Management Systems: literature review and proposal of instrument for integration assessment, Global Journal on Humanites & Social Sciences. [Online]. 02, pp 27-34. Available from:http://www.world-education-center.org/index.php/pntsbs
4. Systematic literature review
According to the survey conducted in the literature, the number of publications on IMS from 1998 is continuously increasing, mainly during the last five years (see Figure 2).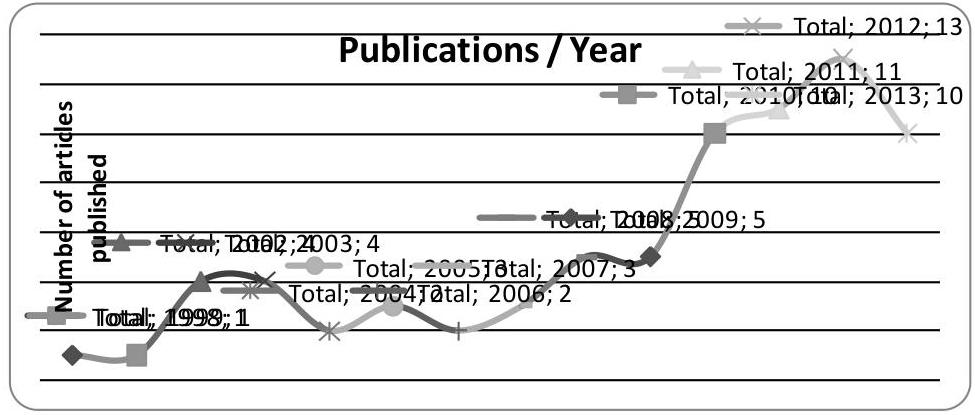
Figure 2. Number of publications per year
With regard to countries that have published and researched on the subject are Spain, followed by China, Portugal and Canada. Table 1 presents the authors who have published on the subject. The journals that published more articles about IMS were, “Journal of Cleaner Production” with 11 publications and “The TQM Journal” with 8 publications. Most of the research focuses on researching models for integration as well as the benefits, challenges and motivations for the integration of management systems.
Table 1. Authors who most frequently publish on IMS
| Authors | Number of articles |
|---|---|
| Karapetrovic, S. | 16 |
| Casadesus, M. | 11 |
| Bernardo, M. | 7 |
| Heras, I. | 6 |
| Simon, A. | 5 |
| Zeng, S.X. | 5 |
The majority of research used survey as research method in which a structured questionnaire was sent to companies that respond without being visited by a researcher. Other widely used methods are the theoretical research and case studies. A very small number of researches in this area have made use of methods known as action research and interviews with experts. The Figure 3 show this information.

Figure 3. Research method used in published articles
5. Assessment of the degree of integration
Based on the literature review on Maturity Model and on the structure of standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and OHSAS 18001, a tool for assessment of the degree of integration was developed. The main maturity models that influenced the development of this work were the CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) and the maturity model presented in ISO 9004 (Managing for the sustained success of an organization: A quality management approach).
As can be seen in Figure 4, the tool for assessing the IMS has in its first line the levels of maturity based on the levels presented in CMMI. In the first column is presented the activities and key elements that are important for the integration of management systems. These activities and key elements were gathered from common elements found in ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and OHSAS 18001. The intercessions of these elements result in the level of integration from 1 (low maturity level) to 5 (high maturity level). Figure 1 shows part of the tool.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POLICY | |||||
| Existence of integrated policy | Each standard has its own policy | Each standard has its own policy and there is an alignment between them in order to avoid contradictions | There is a single policy considering all standards | There is a single policy that integrates all standards. Items of politics are aligned with the strategic plan and are broken down into quantitative indicators | There is a single policy that integrates all standards. Items of politics are aligned with the strategic plan and are broken down into quantitative indicators constantly revised |
Figure 4. Part of the tool for assessing the IMS (continuation)
Poltronieri, C., F., Gerolamo, M., C. & Carpinetti, L., C., R. (2015). Integrated Management Systems: literature review and proposal of instrument for integration assessment, Global Journal on Humanites & Social Sciences. [Online]. 02, pp 27-34. Available from:http://www.world-education-center.org/index.php/pntsbs
PLANNING
| Preparation of planning | The planning of standards is done independently | The planning of standards is done jointly and when you register on paper they are considered separateform | The planning is done jointly and as a result the company has a single plan | The planning is done jointly, the company has a single plan and quantitative / qualitative targets are established to monitor the implementation of the plan | The planning is done jointly, the company has a single plan and quantitative / qualitative targets are established to monitor the implementation of the plan. Periodic reviewsis made |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMPLEMENTATION / EXECUTION | |||||
| Operational control (operations and key activities) | The identification of key operations and activities for each of the management systems is done separately | The identification of key operations and activities for each of the management systems is made separately and aligned | The identification of key operations and activities for each of the management systems is made jointly and indicators are used to determine which operations and activities are important | The identification of key operations and activities for each of the management systems is made jointly and indicators are used to determine which operations and activities are important. Revisions are made aiming at a higher operational performance | |
| VERIFICATION / ACTION | |||||
| Internalaudit | Internalaudits are done by different teams at different times and generate separate reports | Internalaudits are conducted bya single team and at the same time, generating separate reports | Internalaudits are conducted bya single team and at the same time generating a single report. Indicators are established to evaluate the evolution of systems | Internalaudits are conducted bya single team and at the same time generating a single report. Indicators are established to evaluate the evolution of systems |
Figure 4. Part of the tool for assessing the IMS (final)
For each line, the respondent should mark only one of the alternatives. In the end, the more alternatives the one has noted on the extreme right, greater the organization’s level of integration. The points that should be firstly improved are precisely those which are marked in the left columns.
This tool in its full format is divided into four parts as shown in Figure 5. For example, there are 4 questions about Policy addressing existence of integrated policy, involvement of senior management in relationship of policy elaboration, updating and documentation of this policy and dissemination of policy. In total, there are 21 questions.
| #\# Questions | Area | Issues |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Policy | existence of integrated policy; involvement of senior management; updating and documentation; dissemination |
| 6 | Planning | Elaboration; team; goals and objectives; manual; procedures / instructions / registers; control procedures / instructions / records |
| 7 | Implementation / Execution | operational control; roles / responsibilities/ authorities; staff; resources; training; communication; monitoring |
| 4 | Verification / Action | internal audit; external audit; nonconformities / corrective and preventive actions; analysis of administration |
Figure 5. Number of questions divided by area and by points
The instrument aims to be easily self-applied by the specialists who work directly with management systems and is designed to be used by any type of organization. Moreover, the tool presented will help companies that have more than one management system. They will be able to make a self-analysis of how the integration is as well as can be the basis to make a plan of action to achieve a higher level of integration.
6. Conclusion
Through the systematicliterature review, an increase of publications about IMS could be noted. In 2002 there was 4 articles published and in 2012 this number passed to 13. At the same time, this research showed that there was not a tool for assessing the level of integration of management systems based on the maturity model’s theory.
The integration provides a decrease in the number of documents, reduced costs, improved communication, reduced number of audits, improved decision making and better use of resources. The organization that chooses to work with management systems separately will encounter difficulty to ensure alignment between different systems and probably will generate duplicate work. Other results found in the literature review show that the Spain is the country with the biggest number of publications about IMS and the journals “Journal of Cleaner Production” and “The TQM Journal” present most of the publications.
The tool presented here can contribute to reach a more level of integration in management systems. In this way, it is necessary that the professionals responsible for the integration of management systems fill the tool and then stimulate their organizations to improve the points that have the lowest levels of maturity.
A limitation of this study is that the proposed instrument was not applied in organizations in order to assess the level of integration, but only in order to evaluate the tool. One suggestion for future work is to apply it to companies for this purpose.
Poltronieri, C., F., Gerolamo, M., C. & Carpinetti, L., C., R. (2015). Integrated Management Systems: literature review and proposal of instrument for integration assessment, Global Journal on Humanites & Social Sciences. [Online]. 02, pp 27-34. Available from:http://www.world-education-center.org/index.php/pmtsbs
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the The National Council for Scientific and Technological Development ( CNPq ) for the financial support.
References
Boiral, O. (2011). Managing with ISO Systems: Lessons from Practice. Long Range Planning, 44(3), 197-220. doi:10.1016/j.lrp.2010.12.003
British Standards Institution. (2007). OHSAS 18001:2007. British Standards Institution (2nd ed., p. 22). London: OHSAS Project Group.
Bruin, T. de, Rosemann, M., Freeze, R., & Kulkarni, U. (2005). Understanding the Main Phases of Developing a Maturity Assessment Model. 16th Australasian Conference on Information Systems.
Chrissis, M., B., Konrad, M., & Shrum, S. (2003). CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration): Guidelines for Process Integration and Product Improvement (p. 663). Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Conforto, E., C., Amaral, D., C., & Silva, S., L. da. (2011). Roteiro para revisa o bibliográfica sistemática : aplicação no desenvolvimento de produtos e gerenciamento de projetos. 8∘8^{\circ} Congresso Brasileiro de Gestão de Desenvolvimento de Produto (pp. 1-12).
Crosby, P., B. (1979). Quality is free. (McGraw-Hill, Ed.) (p. 309). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Fraser, P., Moultrie, J., & Gregory, M. (2002). The use of maturity models / grids as a tool in assessing product development capability. IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (pp. 244-249). Retrieved from: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=1038431&isnumb er=22257&tag=1
Helgesson, Y., Y., L., Host, M., & Weyns, K. (2012). A review of methods for evaluation of maturity models for process improvement. Journal of Software Maintenance and Evolution: Research and Practice, 436-454. doi:10.1002/smr
ISO. (2004). ISO 14001:2004 - Environmental management systems: Requirements with guidance for use (p. 23). Geneve: International Organization for Standardization.
ISO. (2008a). ISO 9001:2008 - Quality management systems: Requirements (p. 27). Geneve: International Organization for Standardization.
ISO. (2008b). The Integrated Use of Management System Standards. (ISO, Ed.)ISO (1st ed., p. 145). Switzerland: ISO.
ISO. (2009). ISO 9004:2009 - Managing for the sustained success of an organization: A quality management approach (p. 46). Geneve: International Organization for Standardization.
Karapetrovic, S., & Willborn, W. (1998). Integration of quality and environmental management systems. The TQM Magazine, 10(3), 204-213.
Maier, A., M., Moultrie, J., & Clarkson, P. J. (2012). Assessing Organizational Capabilities: Reviewing and Guiding the Development of Maturity Grids. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 59(1), 138-159. doi:10.1109/TEM.2010.2077289
Paulk, M., C. (2008). A Taxonomy for Improvement Frameworks. World Congr. Softw. Qual (pp. 1-15). Bethesda, MD.
Wendler, R. (2012). The maturity of maturity model research: A systematic mapping study. Information and Software Technology, 54(12), 1317-1339. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2012.07.007
Zeng, S., X., Shi, J., J., & Lou, G., X. (2007). A synergetic model for implementing an integrated management system: an empirical study in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 15(18), 1760-1767. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2006.03.007