Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Blended Films: Mechanical, Thermal and Surface Investigations (original) (raw)
Abstract
In this study, blends of chitosan (CS) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) (CS/PVA) having various proportions were prepared and characterized by universal mechanical tester, the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and contact angle measurements. Studying the mechanical properties of the films showed that blending improved the tensile strength, which increased with increasing PVA content up to 40% while the elongation% at break of the blends was decreased compared to that of the pure components. The obtained results of DSC suggested that some interaction between chitosan and PVA mostly took place. Static water contact angle measurements showed an improvement in the wettability of the obtained films.
Figures (6)
Table 1. Composition of the chitosan and PVA mixtures Preparation of blended films
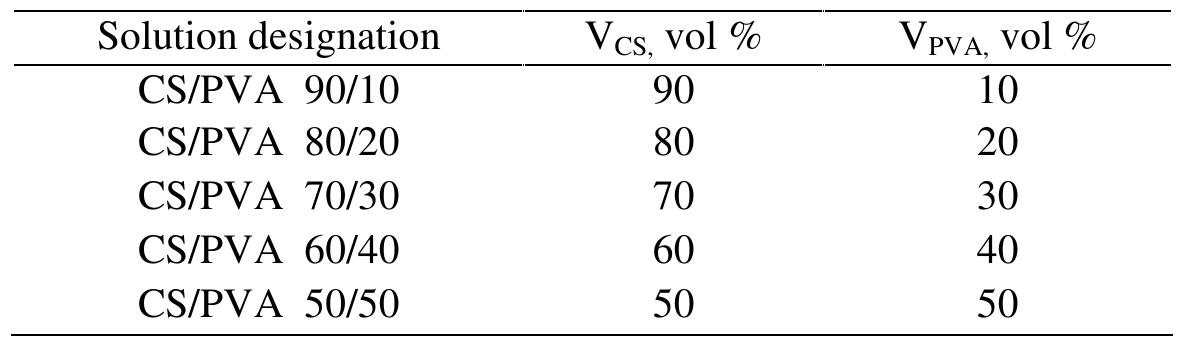
were more brittle and less flexible than the pure components. Similar behavior was reported in the literature for chitosan associated with PVA. For example, Park er al'’ reported that PVA/CS blended film cast from acetic acid recorded higher values of TS and lower E% than the pure polymers. Hyder and Chen" and Bahrami et al'° also reported similar behavior of PVA/CS blended films with respect to TS.
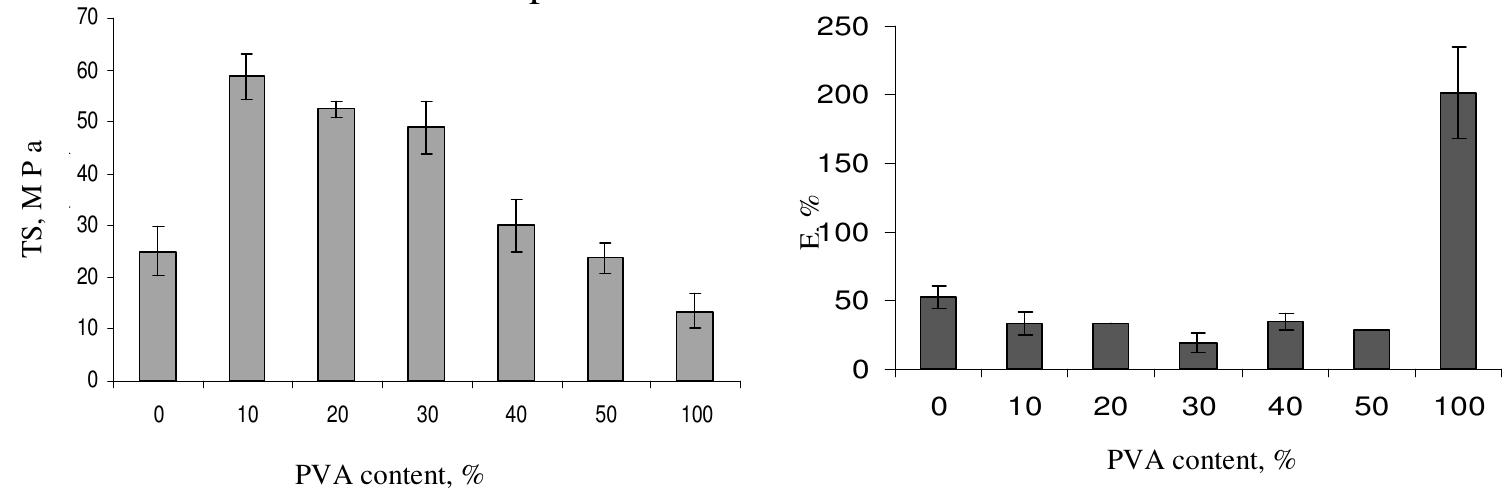
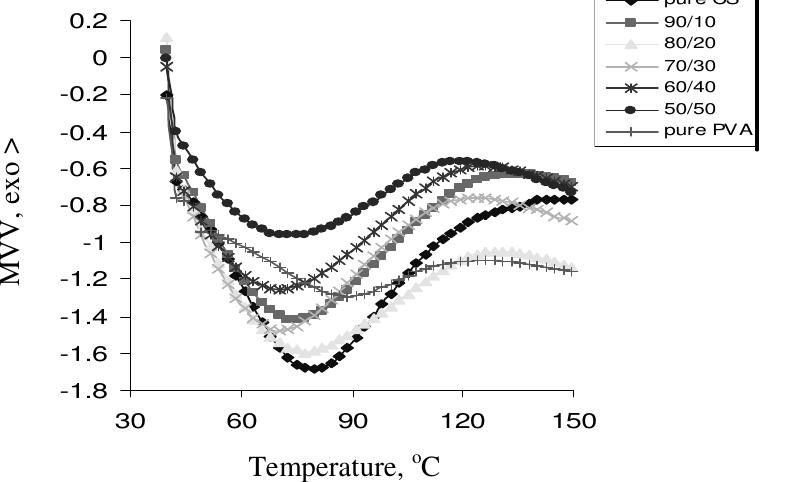
Figure 3. The DSC first run curves of CS/PVA blended films Figure 3 shows the DSC curves of the blended CS/PVA films together with their pure CS and PVA components. As can be seen, DSC curve of chitosan film shows a broad endothermic peak at about 79 °C while PVA film shows a smaller endothermic peak at ~ 89 °C. All compositions exhibited broad endothermic peaks at lower positions than the pure components in the range of 70.3 to 77.3 °C (Table 2). This endothermic peak, often termed as dehydration temperature (Tp), is due to the evaporation of water associated with the hydrophilic groups of the polymers” and responsible for the strength of water-polvmer interaction!’. The Tp of chitosan film obtained is in close agreement with previous studies'*'’. The presence of Tp suggests that some bound water was still not removed from the samples after drying. A closer look at Figure 3 reveals that there is a difference in the endothermic peak area of all films, i.e., they vary in their water-holding capacity in a way showing that pure chitosan film has the highest water content while pure PVA one has the lowest water content unlike the blend films which their Tp shows lower values and stands in between those of their pure components and is a function of the composition. The variation in Tp of blended film is believed to be due to the physical and molecular changes caused by the molecular chains interaction between chitosan and PVA, which suggests the formation of more stable films
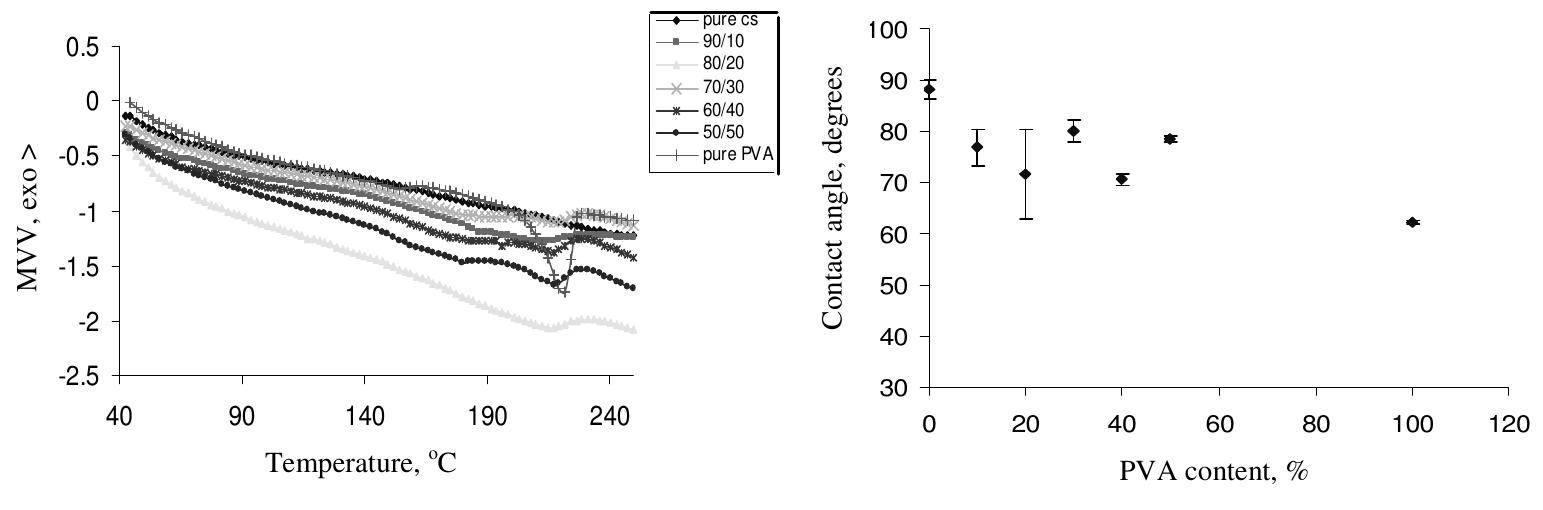
Table 2. The thermal properties of CS/PVA blended films with different PVA content The contact angle of pure CS was 88.12°+1.91, which agrees well with the literature~** while the contact angle of the blended films ranged from about 70.47°+ 0.96 to 80.02°+ 2.27. In general, the contact angles for all the blended films were less than 90°, indicating good hydrophilicity of the surfaces of the obtained films.
Figure 5 shows the static water contact angle versus the PVA content. A general decrease in the static water contact angle with increasing PVA content in the blend is observed i.e., there is an increase in the wettability with increasing the PVA concentration in the blend.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (24)
- Taravel M N and Domard A, Biomaterials, 1996, 17(4), 451-455.
- 2 Mucha M, React Funct Polym., 1998, 38, 19.
- Srinivasa P C, Ramesh M N, Kumar K R and Tharanathan R N, Carbohydr Polym., 2003, 53(4), 431-438.
- Shanmugasundaram N, Ravichandran P, Neelakanta P R, Nalini R, Subrata P and Rao K P, Biomaterials, 2001, 22, 1943.
- Chen X G, Wang Z, Liu W S and Park H J, Biomaterials, 2002, 23(23), 4609-4614.
- Sionkowska A, Wisniewski M, Skopinska J, Kennedy C J and Wess T J, Biomaterials, 2004, 25(5), 795-801.
- Engelberg I and Kohn J, Biomaterials, 1991, 12, 292-304.
- El-hefian E A, Nasef M M and Yahaya A,. E-J Chem., 2010, 7(4), 1212-1219.
- El-hefian E A, Nasef M M and Yahaya A H, E-J Chem., 2010, 7(S1), S349-S357.
- Muzzarelli R A A and Rochetti R, Carbohydr Polym., 1985, 5, 461-472.
- ASTM, Standard test methods for tensile properties of thin plastic sheeting (D 882- 91), In annual book of ASTM standards, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 1995.
- Kim J H, Kim J Y, Lee Y M and Kim K Y, J Appl Polym Sci., 1992, 45. 1711.
- Park S Y, Jun S T and Marsh K S, Food Hydrocol., 2001, 15, 499-502.
- Hyder M N and Chen P, J Membr Sci., 2009, 340(1-2), 171-80.
- Bahrami S B, Kordestani S S, Mirzadeh H and Mansoori P, Iran Polym J., 2003, 12, 139-146.
- Cheung M K, Wan K P Y and Yu P H, J Appl Polym Sci., 2002, 86, 1253-1258.
- Kittur F S, Prashanth K V H, Sankar K U and Tharanathan R N, Carbohydr Polym., 2002, 49, 185.
- Lima C G A, De Oliveira R S, Figueiro S D, Wehmann C F, Goes Sombra J C and Ombra A S B, Mater Chem Phys., 2006, 99, 284.
- Wang Y C, Lin M, Wang D and Hsieh H, Biomaterials, 2003, 24, 1047.
- Yang J M, Su W Y, Leu T L and Yang M C, J Membr Sci., 2004, 236, 39-51.
- Shi R, Bi J, Zhang Z, Zhu A, Chen D, Zhou X, Zhang L and Tian W, Carbohydr Polym., 2008, 74(4), 763-770.
- Yang X, Zhu Z, Liu Q, Chen X and Ma M, Radiat Phys Chem., 2008, 77, 954-960.
- Tangpasuthadol V, Pongchaisirikul N and Hoven V P, Carbohydr Res., 2003, 338(9), 937-942.
- De Britto D and Assis O B G, Carbohydr Polym., 2007, 69(2), 305-310.