The exploration of classroom strategies for facilitating communication with learners with autism : a case of two schools at Umlazi District (original) (raw)
Abstract
I would like to dedicate this study to the Lord Almighty and giver of life, who gave me the strength, and commitment to succeed in the completion of my study.
Figures (8)
4UIVY). IM addagiuon, Understandings VYPOUNSKY S UICOTIeS OF OULIGINE a Classroom where mMteracuon Is prominent helps develop effective teaching and learning therefore, classrooms need to promote good Sollaborating and communication. Good and functional communication will result in good social interaction (Powell & Kalina, 2009), as illustrated in the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) diagram in Figure 1. Figure 2.1: Diagram illustrating the different zones of the ZPD as they relate to classroom interaction interaction Engelbrecht (2013, p. 40) contests that “ZPD, according to Vygotsky’s ZPD theory, productive
The teachers were assembled for this study by purposeful sampling. The profile of the interviewees is 3.6.4. Brief Description of Siphosethu Special School Participants
3.7 Data Generation process 3.6.5 Brief Description of Sibongile Special School Participants In a case study more than one method of data generation can be employed in order to allow the
main broad themes, sub-themes and categories are shown in 4.1 below. learners with autism at Umlazi special schools in this study
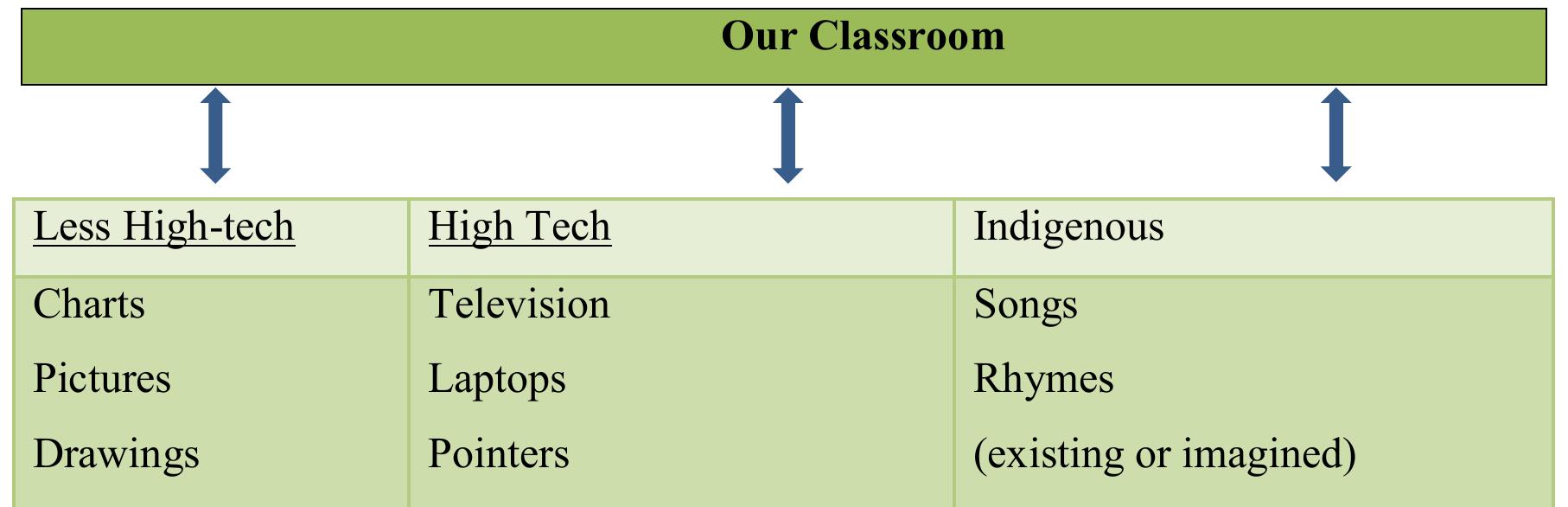
classroom As indicated in Figure 4.2, participants draw from multi-media resources within their school which As indicated in Figure 4.2, participants draw from multi-media resources within their school which they regard as important in facilitating effective communication with learners with autism in their classrooms. Most participants indicated the use of what the researchers has classified as ‘high tech’ as ee * 44 #«x£x£f? 4a,

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (221)
- Abrahams, B. S., & Geschwind, D. H. (2008). Advances in autism genetics: on the threshold of a new neurobiology. Nature Review Genetics, 9(5), 341-355.
- Achmadi, D., Kagohara, D. M., van der Meer, L., O'Reilly, M. F., Lancioni, G. E., Sutherland, D., ...
- & Sigafoos, J. (2012). Teaching advanced operation of an iPod-based speech-generating device to two students with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(4), 1258-1264.
- American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Treatment Works: Major Depressive Disorder: a Patient and Family Guide. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Pub.
- American Psychiatric Association, (2013). Diagnostic and Statically manual of mental Disorder (DSM-5). (5 th ed.). Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing.
- Ametepee, L. K., & Chitiyo, M. (2009). What we know about autism in Africa: A brief research synthesis. The Journal of the International Association of Special Education, 10(1), 11-13.
- Anthony, M., & Bartlett, P. L. (2009). Neural network learning: Theoretical foundations. Cambridge university press.
- Arthur-Kelly, M., Sigafoos, J., Green, V., Mathisen, B., & Arthur-Kelly, R. (2009). Issues in the use of visual supports to promote communication in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Disability and rehabilitation, 31(18), 1474-1486.
- Ashcroft, W., Argio, S., Koehane, J. (2010). Success Strategies for Teaching Kids with Autism. Waco, Texas: Prufrock Press Inc.
- Autism & Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network Surveillance Year Principal Investigators. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders-Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network (2009).MMWR Surveillance Summary , 58(10),1-20.
- Ayres, K. M., & Langone, J. (2007). A comparison of video modelling perspectives for students with autism. Journal of Special Education Technology, 22(2), 15.
- Babbie, E. (2013). The practice of social research (12ed.). California: Cengage Learning.
- Bailey, E., Montgomery, R. (2012). The Essential Guide to Asperger's syndrome. London: Penguin.
- Baird, G., Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., Meldrum, D., & Charman, T. (2006). Prevalence of disorders of the autism spectrum in a population cohort of children in South Thames: The Special Needs and Autism Project (SNAP), The Lancet, 368(9531), 210-215.
- Bakare, M. O., & Munir, K. M. (2011). Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in Africa: a perspective. African journal of psychiatry, 14(3), 208-210.
- Banda, D. R., Copple, K. S., Koul, R. K., Sancibrian, S. L., & Bogschutz, R. J. (2010). Video modelling interventions to teach spontaneous requesting using AAC devices to individuals with autism: a preliminary investigation. Disability and rehabilitation, 32 (16), 1364- 1372.
- Banister, P., Dunn, G., Burman, E., Daniels, J., Duckett, P., Goodley, D., Lawthom, R., Parker, I., Runswick-Cole, K., Sixsmith, J., Smailes, S., Tindall, C., & Whelan, P. (2011). Qualitative methods in psychology: A research guide (2 nd ed). Maidenhead: Open University Press/ McGraw Hill. B.
- Barker, C. (2003). Cultural studies: Theory and practice (2 nd Ed.). London: Sage Publications.
- Barnea-Goraly, N., Lotspeich, L. J., & Reiss, A. L. (2010). Similar white matter aberrations in children with autism and their unaffected siblings: a diffusion tensor imaging study using tract-based spatial statistics. Archives of general psychiatry, 67(10), 1052-1060.
- Barton, E. E., Harn, B. (2012a). Educating Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: London: Sage Publications Ltd.
- Barton, E. E., Harn, B. (2012b). Educating Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. In M Tincan and Zawacki (Ed.), Evidence-Based Practises for Communication Skills Acquisition (p.172). Thousand Oaks: Sage Publication.
- Baxter, S., Enderby, P., Evans, P., & Judge, S. (2012). Barriers and facilitators to the use of high- technology augmentative and alternative communication devices: a systematic review and qualitative synthesis. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 47(2), 115-129.
- Bellin, S., & Akullian, J. (2007). A meta-analysis of video self-modeling interventions for children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Exceptional Children, 73(3), 264-287.
- Berk, L. E., & Winsler, A. (2002). Scaffolding Children's Learning: Vygotsky and Early Childhood Education. Washington D C: National Association for the Education of Young Children.
- Bertram, C., & Christiansen, I. (2014). Understanding research: An introduction to reading research. Hatfield Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers.
- Beukelman, D., & Mirenda, P. (2005). Augmentative and alternative communication: Supporting children and adults with complex communication needs. Baltimore MD: Paul H Brookers.
- Blumberg, B., Cooper, D, & Scindler, P. (2008). Quantitative and qualitative research. Business Research Methods, 200-375.
- Bogdan, R. C., & Biklen, S. K. (2007). Research for education: An introduction to theories and methods. Boston: Pearson.
- Bondy, A., & Frost, L. (2001). The picture exchange communication system. Behavior modification, 25(5), 725-744.
- Boyd, B. A., & Shaw, E. (2010). Autism in the classroom: A group of students changing in population and presentation. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 54(4), 211-219.
- Braun, V. & Clarke V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3(2), 77-101.
- Brueningsen, C., & Watchorn, V. (2011). Virtual learning: An evidence-based overview of cleaning programmes and trends. Ubiquitous Learning: An International Journal, 3(2), 97-104.
- Bunn-Bannister Carbone, V. J., Sweeney-Kerwin, E. J., Attanasio, V., & Kasper, T. (2010). Increasing the vocal responses of children with autism and developmental disabilities using manual sign mand training and prompt delay. Journal of Applied Behaviour Analysis, 43(4), 705-709.
- Case-Smith, J., & Arbesman, M. (2008). Evidence-based review of interventions for autism used in or of relevance to occupational therapy. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 62(4), 416-429.
- Casely-Hayford, L., Lynch, P., & Initiative, A. I. K. (2003). A review of good practice in ICT and special educational needs for Africa. Imfundo.
- Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. (2009). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders- Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, six sites. . Surveillance Summaries. MMWR : 58(10): 1-24.
- Centre for Disease Control and Preventive, (2012). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders-autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network. MMRW Surveillance Summary, 61, 1- 19.
- Cerit, Y., & Yüksel, S. (2015). Teachers perception of management orientation in Turkish and Latvia contexts: A comparative study. Journal of Educational & Instructional Studies in the World, 5(3), 1-10.
- Charlop-Christy, M., Malmberg, D. B., Rocha, M., & Schreibman, L. (2007). Treating autistic spectrum disorder. In R. J. Morris & T.R. Kratochwill (Eds.), The practice of Child Therapy (pp. 299-335, 4 th ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
- Charlop-Christy, M.H., Le, L., & Freeman, K.A. (2000). A comparison of video modelling with in vivo modeling for teaching children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(6), 537-552.
- Charlop, M. H., Malmberg, D. B., & Berquist, K. L. (2008). An application of the Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS) with children with autism and a visually impaired therapist. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 20(6), 509-525.
- Charman, T., & Baird, G. (2002). Practitioner review: Diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in 2- and 3-year-old children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43(3), 289-305.
- Christie, P. (2008). Opening the doors of learning: Changing schools in South Africa. Johannesburg: Heinemann.
- Clapper, T.C. (2015). Cooperative-based learning and the zone of proximal development. Simulation & Gaming, 46(2), 148-158.
- Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6(4), 331-339.
- Cohen, L., Manion, L., Morrison K. (2011a). Research Methods in Education. (7 th ed.). New York: Routledge.
- Cohen M.J., & Sloan, D.L. (2007). Visual supports for people with autism: a guide for parents and professionals. Woodbine House.
- Cooper, D. R., Schindler, P. S., & Sun, J. (2006). Business research methods (Vol. 9). New York: McGraw-hill.
- Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2007). Applied behaviour analysis (2 nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Crain, W. (1992). Theories of development concepts and application. Egelwoods Cliffs NJ: Prentice Hall Creswell, J. W. (2012a). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
- Cresswell, J. W. (2012b). Educational Research Planning, conducting and evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research. (4 th ed.). Boston: Pearson Publishers.
- Cumine, V., Dunlop, J., & Stevenson, G. (2010). Autism in the early years: A practical guide. London: Routledge.
- Davydov, V. V., & Kerr, S. T. (1995). The influence of LS Vygotsky on education theory, research, and practice. Educational Researcher, 24 (3) 12-21.
- Dawson, G., & Osterling, J. (1997). Early intervention in autism: Effectiveness and common elements of current approaches. In M.J. Guralnick (Eds.), The effectiveness of early intervention (pp. 307-326). Baltimore, MD: Brookers.
- Day Ashely, L., (2012). Case Study research. In J. Arthur, M. Waring, R. Coe, & L.V. Hedges (Eds.). Research methods and methodologies in Education (pp.102-107). London: SAGE Publications.
- Dell, A. G., Nexton, D., & Petroff, J.G., (2011). Assistive technology in the classroom: Enhancing the school experiences of students with disabilities: Pearson Higher Ed. Department of Education 1996. South African Schools Act, Act no 84 of 1996. Pretoria: Government Printer.
- Department of Education. (1996). South African Schools Act. Government Gazette, Notice, (84) of 1996. Department of Education (DoE) (2001). Inclusive Education. White Paper 6. Pretoria: Department of Education. Department of Basic Education. (2014). Policy on Screening, Identification Assessment and Support. Pretoria: Republic of South Africa.
- DePoy, E., & Gilson, S. F. (2008). Evaluation practice: how to do good evaluation research in work settings. Psychology Press.
- Denzin, N., and Lincoln, Y.S., (Eds.). (2005). Qualitative Research. The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research, (3 rd ed.).Thousand Oaks: Sage Publishers.
- Deris, A. R. (2012). Investigation of social support for parents of children with autism. International Journal of Early Childhood Special Education, 4(1), 17-31.
- Durrheim, K. (2006). Research Design. In M.T. Blanche, & Durrheim, & D. Painter (Eds.), Research in Practice: Applied methods for social science (pp. 34-59). South Africa, Cape Town: University of Cape Town Press.
- Dettmer, S., Simpson R. L., Myles, B. S., & Ganz, J. B. (2000). The use of visual supports to facilitate transitions of students with autism. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 15(3), 163-169.
- DiCicco-Bloom, B., & Crabtree, B. F. (2006). The Qualitative research interview. Medical Education, 40, 314-321.
- Donald, D., Lazarus, S., & Lolwana, P. (2010). Educational psychology in social context. Economic applications in southern Africa. Cape Town: Oxford University Press.
- Elsabbagh, M., Divan, G., Koh, Y.J., Kim, Y.S., Kauchali, S., Marcin, C., Montiel-Nava, C., Patel, V., Paula, C.S., Wang, C., Yasmy, M. T., & Fombonne, E. (2012). Global prevalence of autism and other pervasive developmental disorders. Autism Research, 5, 160-179.
- Engelbrecht, A. (2013). Managing classroom environments in large multi-level classes. In M. Nel, & A. Hugo (Eds.). Embracing diversity: through multi-level teaching for foundation intermediate and senior phase (pp.131-136, Cape Town: Juta and Company Ltd.
- Fish, W. W. (2008). The IEP meeting: Perception of parents of students who receive special education services. Preventing School Failure: Alternative Education for Children and Youth, 53(1), 8-14.
- Flippin, M., Reszka, S., & Watson, L.R. (2010). Effectiveness of the picture exchange communication system (PECS) on communication and speech for children with autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis. American Journal Speech-language Pathology, 19(2), 178-195.
- Flores, M., Musgrove, K., Renner, S., Hinton, V., Strozier, S., Franklin, S., & Hil, D. (2012). A comparison of communication using the Apple iPad and picture -based system. Augmentative and Alternative Communications, 28(2), 74-84.
- Forbes, J., & Weiner, G. (2013). Gendering/ed research spaces: insight from a study of independent schooling. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, 26(4), 455-469.
- Friend, M., & Cook, L. (2009). Interactions: collaboration skills for school professionals. (6 th ed.). Boston: Pearson Education.
- Friedlander, R., & Moss, S. (2008). Mental health assessment of children and adolescents with learning disability. Advances in Mental Health and Learning Disabilities, 2(4), 29-36.
- Frith, U. (1991). Autism and Asperger syndrome. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Furneaux, B., & Roberts, B. (1977). Autistic Children: Teaching, community and research approaches. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul Ltd.
- Gallagher, P. A, Rhodes, C. A., & Darling, S. M. (2004). Parents as professionals in early intervention: A parent educator model. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 24(1), 5-13.
- Golan, O., and Baron-Cohen, S. (2006). Systematic empathy: Teaching adults with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism through an interactive multimedia. Developmental and Psychopathology, 18, 591-617.
- Ganz, J. B., Earles-Vollrath, T. L., & Cook, K. E. (2011). Video modelling: A visually based intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder. Teaching Exceptional Children, 43(6), 8-19.
- Ganz, J. B., Earles-Vollrath, T. L., Mason, R. A., Rispoli, M. J., Heath, A. K., Parker, I. (2011). An aggregate study of single case research involving aided AAC: Participant characteristics of individuals with autism spectrum disorders: Research In Autism Spectrum Disorder,5 (4),1500-1509.
- Ganz, J. B., & Flores, M. M. (2010). Implementing visual cues for young children with autism spectrum disorders and their classmates. YC Young Children, 65 (3), 78.
- Ganz, J. B., Simpson, R. L., & Corbin-Newsome, J. (2008). The impact of the Picture Exchange Communication System on requesting and speech development in pre-schoolers with autism spectrum disorders and similar characteristics. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2, 157-169.
- Ganz, J. B., Simpson, R. L., & Lund, E. (2012). The picture exchange communication system (PECS): A promising method for improving communication skills of learners with autism spectrum disorders. Education and Training in Autism and Developmental Disabilities, 176-186.
- Greeff, M. (2011). Information Collection: Interviewing. In, A.S. de Vos. H. Srtydom., C,B Fouche, & CSL Delport. Research at Grassroots: For the Social Sciences and human service professions, (pp. 341-374). Pretoria: Van Schaik.
- Gillberg, C. (1998). Asperger syndrome and high-functioning autism. The British journal of psychiatry, 172(3), 200-209.
- Grinnell Jr, R. M., & Unrau, Y. A. (2010). Social work research and evaluation: Foundations of evidence-based practice. New York: Oxford University Press, USA.
- Greenberg, A. L. Tomaino, M. A. E., & Charlop, M. H. (2012). Assessing generalization of the picture exchange communication system in children with autism. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 24(6), 539-558.
- Greenspan, S. I. (2006). Understanding autism: Working with the challenges autism brings. Early Childhood Today, 20(4), 22.
- Grinker, R. R., Chambers, N., Njongwe, N., Langman, A. E., Guthrie, W., Stronach, S., Richard, B. O., Kauchali, S. Killian, B. Chhagan, M., & Yucel, F. (2012). "Communities" in community engagement: Lessons learned from autism research in South Korea and South Africa. Autism Research, 5(3), 201-210.
- Hall, H. R. (2012). Families of children with autism: Behaviors of children, community support and coping. Issues in comprehensive pediatric nursing, 35(2), 111-132.
- Hannah L. (2004) Teaching young children with autistic spectrum disorders to learn. Norwich, England. Crows.
- Harniss, M.K., Epstein, M.H., Bursuck, W.D., Nelson, J., Jayanthi, M. (2001). Resolving homework related communication problems: Recommendations of parents of children with and without problems: Recommendations of parents of children with and without disabilities. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 17, 205-225.
- Hart, S. L., & Banda, D. R. (2010). Picture Exchange Communication System with individuals with developmental disabilities: A meta-analysis of single subject studies. Remedial and Special Education, 31(6), 476-488.
- Hayes, D. B. (2014). Inclusion and Autism: General Education Teachers Perceptions. Electronic Theses and Dissertations, Paper 2323.
- Heflin, J., & Alaimo, D. F. (2007). Student with autism spectrum disorders: Effective Instructional Practices. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson.
- Henning, E., Gravett, S., & Van Rensburg, W. (2002). Finding your way in academic writing (2 nd ed.) Pretoria: Van Schaik.
- Henning, E., Van Rensburg, W., Smit, B. (2009). Finding your way in qualitative research (3 rd ed.). Pretoria: Van Schaik.
- Henninnk, M., Huttler, I. A. (2011). Qualitative research methods. London: Sage Publications.
- Henry, K. A. (2010). How do I teach this kid to read?: Teaching literacy skills to young children with autism, form phonics to fluency. Texas: Future Horizons.
- Hesse-Biber, S. & Leavy, P. (2006). The Practice of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks CA: Sage Publications.
- Hess, K. L Morrier, M. J, Heflin, J. L., Ivey, M. L. (2008). Autism treatment survey: Services received by children with autism spectrum disorders in public school classrooms. Journal of autism and development disorders, 38(5), 961-971.
- Heward, W. L .(2006). Teaching exceptional children. An introduction to special education. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
- Holloway, I., & Todres, L. (2003). The status of methods: flexibility, consistency and coherence. Qualitative research, 3(3), 345-357.
- Isaias, P., Spector, I.P., Ifenthaler, D., Simpson, D.G. (2015). E-learning systems, environments and approaches: Theory and implementation. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing.
- Johnson, B., & Lazarus, S. (2008). The role of schools in building the resilience of youth faced with adversity. Journal of psychology in Africa, 18(1), 19-30.
- Jordan, R., & Jones, G. (2012). Meeting the needs of children with autistic spectrum disorders. Routledge.
- Kadesjö, B., Gillberg, C., & Hagberg, B. (1999). Brief report: autism and Asperger syndrome in seven-year-old children: a total population study. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 29 (4), 327-331.
- Kagohara, D. M., van der Meer, L., Achmadi, D., Green, V. A., O'Reilly, M. F., Mulloy, A., ... & Sigafoos, J. (2010). Behavioral intervention promotes successful use of an iPod-based communication device by an adolescent with autism. Clinical Case Studies, 9(5), 328-338.
- Kaiser, A. P., Hancock, T. B., & Nietfeld, J. P. (2000). The effects of parent-implemented enhanced milieu teaching on the social communication of children who have autism. Early Education and Development, 11(4), 423-446.
- Kamer, L. (1943). Autistic disturbance of Affective contact Nervous Child: 1943 2, 217-250
- Ker, P. & Wakeford, L. (2007). Improving the performance of a young child with autism during self- care task using embedded song interventions: A case study. Music Therapy Perspectives, 25(1): 43-51
- Kim, J., Wigram, T., & Gold, C. (2008). The effects of improvisational music therapy on joint attention behaviours in autistic children: a randomized controlled study. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 38(9), 1758-1766.
- Kim, Y. S., Leventhal, B. L., Koh, Y. J., Fombonne, E., Laska, E., Lim, E. C., ... & Grinker, R. R. (2011). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders in a total population sample. American Journal of Psychiatry, 168(9), 904-912.
- Koegel, R. L., & Kern Koegel, L. (2006). Pivotal Response Treatments for Autism: Communication, Social, and Academic Development. Baltimore: Brookes Publishing Company.
- Kogan, M. D., Blumberg, S. J., Schieve, L. A., Boyle, C. A., Perrin, J. M., Ghandour, R. M., ... & van Dyck, P. C. (2009). Prevalence of parent-reported diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder among children in the US, 2007. Pediatrics, 124(5), 1395-1403.
- Kravits, T. R., Kamps, D. M., Kemmerer, K., & Potucek, J. (2002). Brief report: Increasing communication skills for an elementary-aged student with autism using the picture exchange communication system. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 32(3), 225-230.
- Kumar, R. (2011). Research Methodology. A step-by-step guide for beginners. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publication.
- Kvale, S., & Brinkmann, S. (2009). Interviews: Learning the craft of Qualitative research interviewing. London: Sage.
- Kvale, S., & Brinkmann, S. (2009). Interviews: Learning the craft of qualitative research interviewing. London: Sage.
- Lancioni, G. E., O'Reilly, M. F., Cuvo, A. J., Singh, N. N., Sigafoos, J., & Didden, R. (2007). PECS and VOCAs to enable students with developmental disabilities to make requests: An overview of the literature. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 28(5), 468-488.
- Landsberg, E. (2011). Learning Support. In Landsberg, D. Kruger & E. Swart (Eds.). Addressing barriers to learning. Pretoria; Van Schaik.
- Lang, R., Machalicek, W., Rispoli, M., & Regester, A. (2009). Training parents to implement communication interventions for children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD): A systematic review. Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention, 3(3), 174-190.
- Leach, D., & Duffy, M. L., (2009). Supporting students with autism spectrum disorder in inclusive settings. Intervention in School and Clinic, 43(1), 31-37.
- Lemmer, E., & Van Wyk, N. (2010). Themes in South African Education. Cape Town: Heinemann.
- Le Couter, A., Baird G. (2003). National initiative for autism: Screening and assessment (NIASA). National Autism Plan for children (NAPC): Plan for the identification, assessment, diagnosis and access to early interventions for pre-school and primary school aged children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). London: National Autistic Society.
- Lewis, L. L., Kim, Y. A., & Bey, J. A. (2011). Teaching practices and strategies to involve inner- city parents at home and in school. Teaching and Teacher Education, 27, 221-234.
- Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba , E. G. (1985). Naturalistic Inquiry. Beverly Hills: Sage.
- Liu, C.H., Matthews, R. (2005). Vygotsky's Philosophy: Constructivism and its criticism examined. International Education Journal, 6(3), 386-399.
- Lord, C., Risi, S., DiLavore, P. S., Shulman, C., Thurm, A., and Pickles, A. (2006). Autism from 2 to 9 years of age. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63(6), 694-701.
- Lovanne, R., Dunlap, G.H., Kincaid, D. (2003). Effective educational practices for students with autism spectrum disorders. A Journal of the Hammill Institute on Disabilities, 18(3), 150-165.
- Lubas, M., Mittchell, J., De Leo, G. (2014). User-centered design and augmentative and alternative communication apps for children with autism spectrum disorders, 4(2), 1- 10.
- Lund, S. K., & Troha, J. M. (2008). Teaching young people who are blind and have autism to make requests using a variation on the Picture Exchange Communication System with Tactical symbols: A preliminary investigation. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(4), 719-730.
- MacDonald, V., & Speece, D.L. (2001). Making a time a Teachers Report on her first Year of Teaching children with emotional Disabilities. The journal of special Education, 35(2), 84-91 Sage Publications, Boston
- MacKenzie, H. (2008). Reaching and teaching the child with autism spectrum disorder using learning preferences and strengths. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers.
- Mash, E., J. & Wolfe, D. A. (2012). Abnormal child Psychology (4 th ed.).Wadsworth: Cengage Learning.
- Massaro, D. W., & Bosseler, A. (2006). Read my lips: The Importance of the Face in the computer-animated tutor for vocabulary learning by children with autism. Autism, 10(5), 495-510.
- Maree, K., & Pietersen, J. (2012). Sampling. In K. Maree. First steps in Research. (pp. 171- 181).Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers.
- McLeod, S.A. (2010). Zone of Proximal Development. SymplyPsychology. Retrieved from July, 28, 2013.
- Mirenda, P. (2009). Introduction to AAC for individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Autism spectrum, disorders and AAC, 3-22.
- Mitchel, D. (2014). What really works in special and inclusive education: Using evidence based teaching strategies. (2 nd ed.), 2 Park Square, Milton Park , Abingdon: Routledge
- Mitter, P. (2008). Planning for the future: Planning for the 2040s: everybody's business. British Journal of Special Education, 35(1), 3-10.
- Moh, T. A., & Magiati, I. (2012). Factors associated with parental stress and satisfaction during the process of diagnosis of children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(1), 293-303.
- Moore, D., & Taylor, J. (2000). Interactive multimedia systems for students with autism. Journal of Educational Media, 25(3), 169-177.
- Moore, M., & Calvert, S. (2000). Brief report: Vocabulary acquisition for children with autism: Teacher or computer instruction. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(4), 359-362.
- Moreti, P., Zoghbi, H.Y., (2006). MeCP2 dysfunction in rett syndrome and related disorders. Current Opinion and Genetic Developmental Disorders: 16(3), 276-281.
- Mubaiwa, L. (2008). Autism: understanding basic concepts: hot topics. South African Journal of Child Health (SAJCH), 2(1) 6-7.
- Mazurik-Charles, R., & Stefanou, C. (2010). Using paraprofessionals to teach social skills to children with autism spectrum disorders in the general education classroom. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 37(2), 161.
- Nash, J. M. (2002). The secrets of autism. Time, 159(18), 46-56. National Institutes of Health. (2009). Autism Fact Sheet.
- Nel, N., Nel, M., & Hugo, A. (2012). Inclusive education: the necessity to provide support to all learners. Learner support in a diverse classroom. A guide for foundation, intermediate and senior phase teachers of language and mathematics. Pretoria: Van Schaik, 3-24.
- Neuman, W. L., (2006). Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative approaches (6 th ed.).Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
- Neuman, W. L. & Kreuger, L. (2003). Social work research methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
- Neuman, W. L. (2011). Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches (7 th ed.) Boston: Pearson.
- Niewenhuis J. (2012). Qualitative research design and data gathering teaching techniques. In K. Maree. (Eds.). First Steps in Research. (pp.75). Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers.
- & Bellamy, C. (2012). Principles of Methodology: Research Design in Social science. London: Sage Publication.
- Petscher, E. S., Rey, C., and Bailey, J.S. (2009). A review of empirical support and differential reinforcement of alternate behaviour. Research in Developmental Disorders, 32, 249- 261.
- Pinborough-Zimmerman, J., Bakian, A., Fombonne, E., Bilder, D., Taylor, J., & McMahon, W. M. (2011). Changes in the administrative prevalence of autism spectrum disorders: Contribution of special education and health from 2002-2008. Journal of Autism and Development Disorder, 42(4), 521-530.
- Powel, K. C., & Kalina, C. J. (2009). Cognitive and social constructivism: Developing tools for an effective classroom: Education, 130(2), 241-250.
- Pratt, D., Collins, J., & Selinger, S. (2001). Development and Use of the Teaching Perspectives Inventory (TPI).In unpublished paper presented at the AERA annual conference, Seattle Washington.
- Preston, D., & Carter, M. (2009). A review of the efficacy of the picture exchange communication system intervention. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(10), 1471-1486.
- Prizant, B. M., Wetherby, A. M. (2005). Critical issues in enhancing communication abilities for persons with autism spectrum disorders. In F. R Volkmar, R. Paul, A. Klin, & D. Cohen, (Eds.). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders, (3 rd ed.) (2), (pp.925-945). Hoboken: John Wiley & Son, Inc.
- Ramdoss, S., Lang, R., Mulloy, A., Franco, J., O'Reilly, M., Didden, R., & Lancioni, G. (2011). Use of computer-based interventions to tach communication skills to children with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Journal of Behavioral Education, 20(1), 55-76.
- Rao, S. M., & Gagie, B. (2006). Learning through seeing and doing: Visual supports for children with autism. Teaching Exceptional Children, 38(6), 26. Republic of South Africa (RSA), 1996b South African Schools Act. Act No.84 of 1996 Government Gazette 377-17579, Cape Town: Office of the President (1867). Republic of South Africa. RSA (2000a). Norms and Standards for educators. Government Gazzette 415, no 2000 Pretoria: Government Printer: Republic of South Africa.
- Republic OF South Africa (RSA) (1996b). Constitution of the Republic of Republic of South Africa, Act 108 of 19996. Government Gazette378, 17678, Pretoria: Presidents Office.
- Rispoli, M.J., O'Reilly, M.F., Singfoos, J., Lang, R., Kang, S., Lancoini, G., & Parker, R. (2011). Effects of precession situation on challenging behaviour and academic engagement for children with autism during classroom instruction. Education and Training in Autism and Development Disabilities, 607-618.
- Rule, P. & John, V. (2011).Your guide to case study research. Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers.
- Sableski, M.K. (2010). Scaffolding as impetus for change when working with struggling Readers Journal of Reading Education, 34(3), 30-37.
- Sansosti, F. J., & Powell-Smith, K. A. (2008). Using computer-presented social stories and video models to increase the social communication skills of children with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Positive Behaviour Interventions, 10(3), 162-178.
- Santrock, J. W. (2009). Educational Psychology. (4 th ed.). New York McGraw-Hill Companies.
- Sapon-Shevin, M. (2010). Because we can change the world. Thousand Oaks, California: Corwin.
- Sayed, Y., Subrahmanian, R., & Carrim, N. (2007). Education exclusion and inclusion: Policy and implementation in South Africa and India. London: Fuller-Davies, for Department for International Development.
- Schlosser, R. W., Singafoos, J., & Koul, R. (2009). Speech output and speech-generating devices in autism spectrum disorders. Autism spectrum disorders and AAC, 141-170.
- Schlosser, R. W., & Wendt, O. (2008). Effects of augmentative and alternate communication intervention on speech production in children with autism: American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 17, 212-239.
- Scholper, E., Van Bourgodien, M. E., Wellman, G.T., & Love, S. R. (2010). The Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS2). Los Angeles: Writer, Presentation and Spreadsheets.
- Scholper, E., & Mesibov, G. B., (Eds). (2013). High -functioning individuals with autism. New York: Springer Science & Business Media.
- Schwartz, J. B., and Nye, C., (2006). A systematic review, synthesis, and evaluation of the evidence for teaching sign language to children with autism. EBP Briefs 1, 1-17.
- Sennott, S., & Bowker, A. (2009). Autism, AAC, and proloquo2go. SIG 12 Perspectives on Augmentative and Communication, 18(4), 137-145.
- Shane, H. C., Laubscher, E. H., Schlosser, R. W., Flynn, S., Sorce, J. F., & Abramson, J. (2012). Applying technology to visually support language and communication in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(6), 1228- 1235.
- Shane, H. C., and Albert, P. D., (2008). Electronic screens media for person with autism disorders: Results of a survey. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorder, 38, 1499-1508.
- Sharma, U., Forlin, C., & Loreman, T. (2008). Impact of training on pre-service teacher's attitudes and concerns about inclusive education and sentiments about persons with disabilities, Disability & Society, 23(7), 773-785.
- Sicile-kira, C. (2014).Autismthe complete guide to understanding Autism (Eds.). New York City: Perigree book.
- Sigafoos, J., O'Reilly, M., Ganz, J. Lancloni, G.E. and Schlosser, R.W. (2007). Assessing corresponding following acquisition of an exchange-based communication system. Research in Development Disabilities, 28, 71-83.
- Simpson, R. L. (2005) Evidence-Based Practises and Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 20(3), 140-149.
- Simpson R. L., Myles, B. S., & Ganz, J. B. (2008). Efficacious interventions and treatment for learners with autism spectrum disorder: Educating children and youth with autism. Strategies for Effective Practice, 2, 477-512.
- Snell, M. E., Brandy, N., Mclean. L., Ogletree, B. T., Siegel, E., Sylvester, L., … & Sevcik, R. (2010). Twenty years of communication intervention research with individuals who have severe intellectual and developmental disabilities. American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, 115(5), 364-380.
- Snowman, J., & Biehler, R. (2006). Psychology applied to teaching (11 th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
- Stahmer, A. C., Colling, S. N. M., & Palinkas, L. A. (2005). Early intervention practices for children with autism: Description from community providers. Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 20(2), 66-79.
- Stewart, V. (2012). A world class education learning from international models of excellence and innovation. New York: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
- Stoner, J. B., Beck, A. R., Dennis, M., & Parette Jr, H. P. (2011). The use of instructional technology in direct vocabulary instruction. Journal of Special Education Technology, 26(3), 35.
- Struwig, F. W., & Stead, G. B. (2004). Planning, designing, and reporting research. Cape Town: Pearson.
- Stead, G. B. (2001). Planning, designing and reporting research. Cape Town: Pearson.
- Sulaiman, T., Baki., & Rahman, P. Z. M A. (2011). The level of cognitive ability among learning disabilities. Children in Malacca Malaysia. International Journal of Psychological Studies, 3(1), 69.
- Sulzer-Azaroff, B., Hoffman, A. O., Horton, C.B., Bond, A., & Frost, L. (2009). The Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS): what do the data say?. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 24, 89-103.
- Swart, E. Pettipher, R. (2006). A Framework for Understanding Inclusion. In E Landsberg, Addressing Barriers to Learning, a South African Perspective. (pp.3-23) . Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers.
- Tchaconas, A., and Adesman, A. (2013). Autism spectrum disorder: A pediatric overview and update. Current of Autism Opinion in Pediatrics, 25,130-143.
- Theo Peeters, & Chris Gillberg. (1999). Autism: Medical and educational aspects. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
- Tien, K. (2008). Effectiveness of the picture exchange communication system as a functional communication intervention for individuals with autism spectrum disorders: A practice- based research synthesis. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 43(1), 61-76.
- Tincani, M., Crozier, S., & Alazetta, L. (2006).The Picture exchange communication system: Effects on mending and speech development for school-aged children with autism. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 177-184.
- Tincani, M., Devis, K. (2010). Qualitative synthesis and component analysis of single participant studies on the Picture Exchange Communication System. Remedial and Special Education, 32(6)458-470.
- Tincani, M., & Zawacki, J. (2012). Evidence-based practices for communication skill acquisition. In Educating Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. (pp. 171-191). Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
- Trochim, W. M., & Donnelly, J. P. (2007). The research methods knowledge based. (3 rd ed.). Mason, OH.Tampa: Thomson.
- Vaiouli, P., Grimmet, K., & Ruich, L. J. (2013). "Bill is now singing": Joint engagement and the emergence of social communication of the three young children with autism. Autism, 19 (1), 76-83.
- Van der Meer, L., Kagohara, D., Achmadi, D., Green, V.A., Herrington, C., Sigafoos, J., … & Rispoli, M. (2011). Teaching functional use of an iPod based speech-generating device to individuals with developmental disabilities. Journal of Special Education Technology, 26 (3), 1-11.
- Van der Meer, L. A., & Rispoli, M. (2010). Communication interventions involving speech- generating devices for children with autism: A review of the literature. Developmental Neurorehabilitation, 13 (4), 294-306.
- Van Wyk, N., & Emeritus, (2010). Theories Policies and Practises of Parent Involvement in Education. In E. Lemmer & N Van Wyk. Themes in South African Education (pp. 199- 221), Cape Town: Pearson Education.
- Visagie, A. (2010). Research Methodology. Midrand : Graduate Institute.
- Volkmar, F. R., Klin, A., & Cohen, D. J. (Eds.). (2005). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders, Diagnosis, Development, Neurobiology, and Behavior (Vol. 1). Haboken New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
- Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological process. Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
- Wainer, A. L., & Ingersoll, B. R. (2010). The use of innovative computer technology for teaching social communication to individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 5(1), 96-107.
- Wall, K. (2010). Autism and Early years Practice: (2 nd ed.). University of Chichester: Sage Publications.
- Walworth, D. D. (2009). Effects of developmental music groups for parents and premature or typical infants under two years on parental responsiveness and infant social development. Journal of Music Therapy, 46(1), 32-52.
- Warnock, T. (2012).Vocal connections: how voice work in music therapy helped a young girl with severe learning disabilities and autism to engage in her learning. Approaches: Music Therapy & Special Music Education, 4(2), 85-92.
- Webbe, E., Morey, J., Thompsen, W., Butler, C., Barber, M., & Fraser W.I. (2003). The prevalence of autistic spectrum disorder in children attending mainstream schools in a Welsh education authority. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 45(06), 337-384.
- Welman, C. Kruger, F., & Mitchel, B. (2010). Research Methodology. (3 rd ed.). Cape Town: Oxford University Press.
- White, S. W. Scahill, L., Klin, A., Koenig., & Volkmar, F. R. (2007). Educational placements and service use patterns of individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(8), 1403-1412.
- Will S. C. (2009. Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Strategies that work. YC Young Children, 64(1), 81-82, 84-89.
- Willis, C. (2009). Young children with autism spectrum disorder: Strategies that work. YC Young Children, 64(1), 81.
- Williams, C., Wright. B., Callaghan, G., & Coughlan, B. (2002). Do children with autism learn to read more readily by computer assisted instruction or traditional book methods? A pilot study. Autism, 6(1), 71-91.
- Wing, L. (1980). Autistic children: A guide for parents: Constable and Company Limite d.
- Wood, D., Bruner, J., Ross, G. (1976). The role of tutoring in problem solving. Journal of Child Psychology and Child Psychiatry, (17) 89-100.
- World Health Organisation (2015). mhGAP guide for mental neurological and substance use disorders in non-specialised settings. The Lancent.
- Worth S, (2005). Autistic Spectrum Disorder. MPG Books, Ltd, Bodmin Cornwall.
- Yin, R. K. (2003). Case study research: Designs and Methods (3 th ed.). Thosand Oaks, California: Sage Publication
- Yin, R. K., (2009). Case study Research: Design and Methods (4 th ed.). Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publication.