Bootstrapped Iterative Decoding Algorithms for Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) Codes (original) (raw)
Abstract
Reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping algorithm is one of the best hard decision decoding algorithms in performance. Recently several modifications are done to this technique either to improve performance or to lower the complexity. The implementation efficient reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping is developed targeting decreasing processing time of the decoding process. In this paper we are targeting improving performance of recent developed algorithm named low complex implementation efficient reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping by adding a bootstrap step to the decoding technique which leads to increase in reliability of received bits then number of decoded bits will be increased leading to improve in performance. Also a modification done to bootstrap step for further increase the performance.
Figures (7)
A. Implementation Efficient Reliability Ratio Based Weighted Bit-Flipping Reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping algorithm is an efficient hard decision decoding algorithm but it has a main drawback which is the long decoding time taken by the algorithm. Implementation efficient reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping was proposed in [5] to solve this problem by optimizing the algorithm to reduce the decoding time to be suitable for simulation and hardware implementation especially when the maximum number of iterations assigned for the algorithm is small.
We define the received value y, and its corresponding bit Figure 1. Bootstrap decoding procedure over tanner graph. The idea of the algorithm comes from the work done in [7]. In [7] a modification to the weighted bit-flipping algorithm is done by adding a bootstrap step to the decoding algorithm which leads to significant contribution in performance. The insertion of bootstrap step increases the received code words reliability which leads to improve the performance of weighted bit-flipping by decoding more code words than the algorithm can do without it. Bootstrap step is a combination between horizontal step and vertical step of min-sum algorithm which is a soft decision algorithm with superior performance over any hard decision algorithm. As a result for insertion of bootstrap step as it being part of soft decision decoding technique, it massively increased the performance of weighted bit-flipping algorithm. Bootstrap step will firstly be discussed for further explanation of the idea of using bootstrap step to improve the performance of the weighted bit flipping.
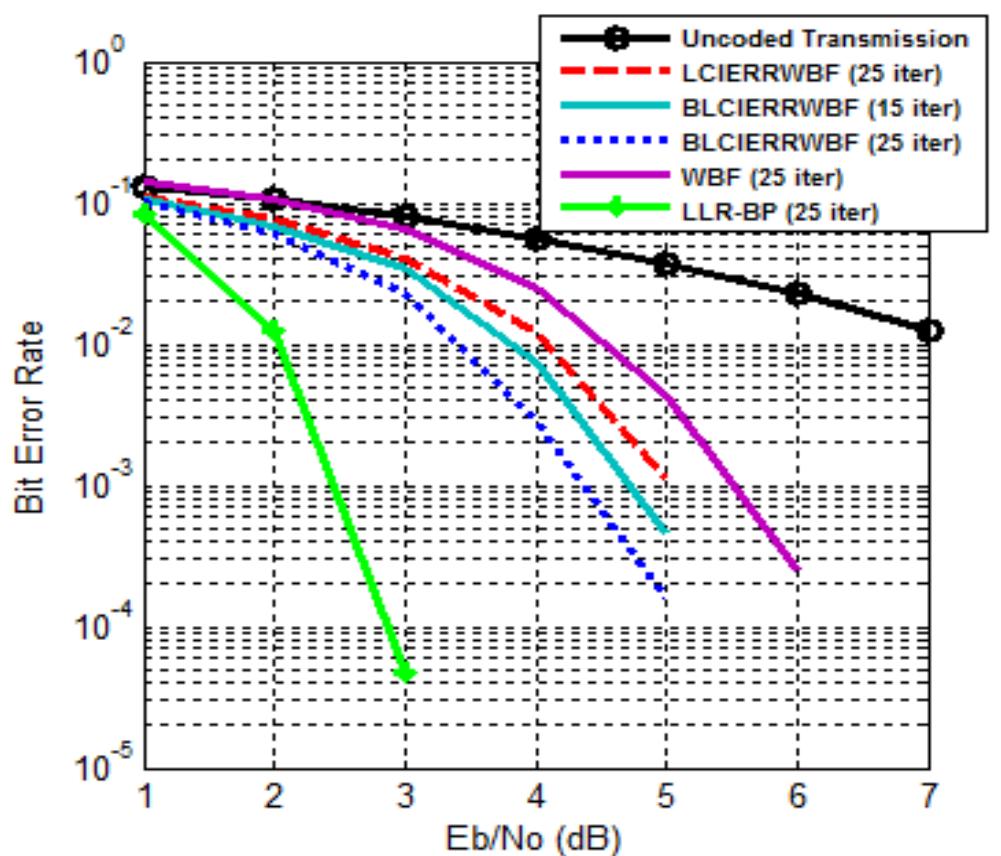
Figure 2. BER for (504,252,3) PEG-LDPC code decoded by WBF, LCIERRWBF, BLCIERRWBE, and LLR-BP. from 1 dB to 6 dB. The contribution in the performance increases as the maximum number of iterations increases or as the code length increases. The value of a for all codes is computed using simulation by observing bit error rate versus a to get the lowest bit error rate.
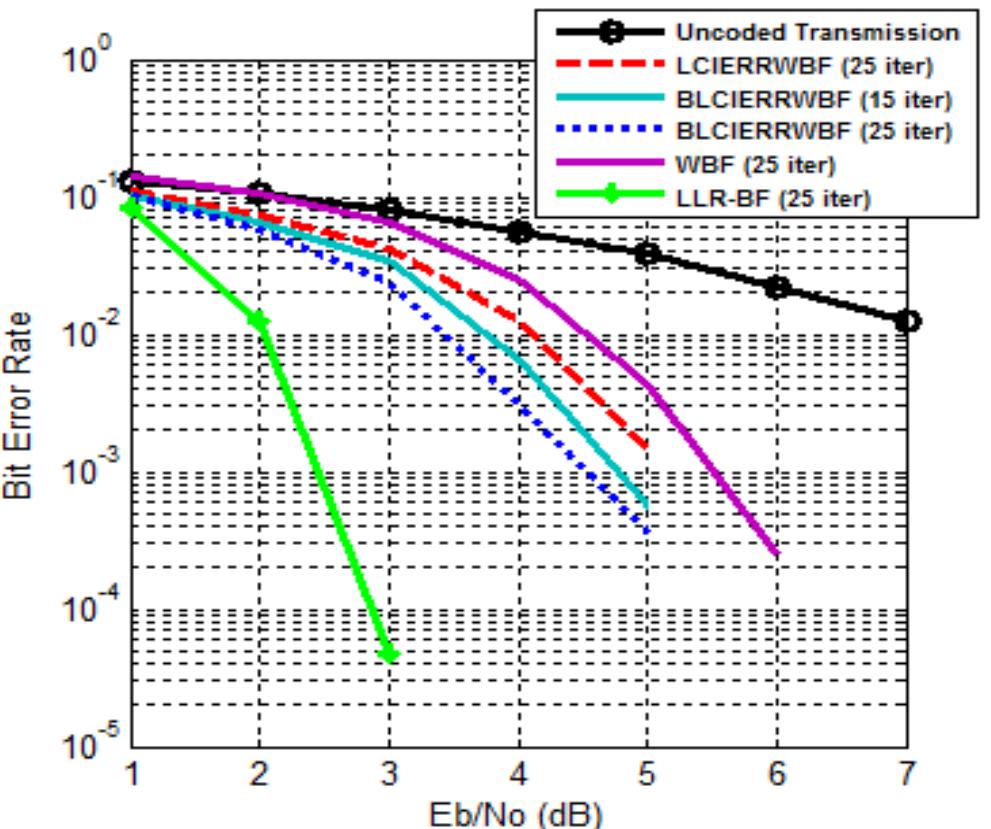
Figure 3. BER for (504,252,3) regular LDPC code decoded by WBF, LCIERRWBF, BLCIERRWBF, and LLR-BP.
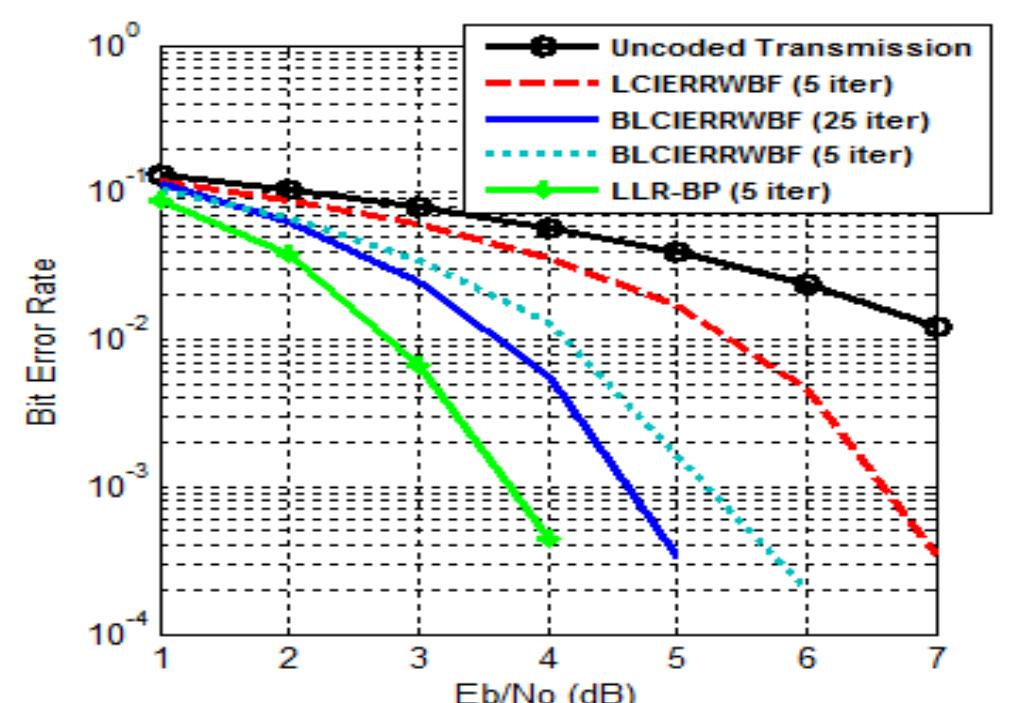
Figure 4. BER for (204,102,3) regular LDPC code decoded by LCIERRWBF, BLCIERRWBF and LLR-BP.
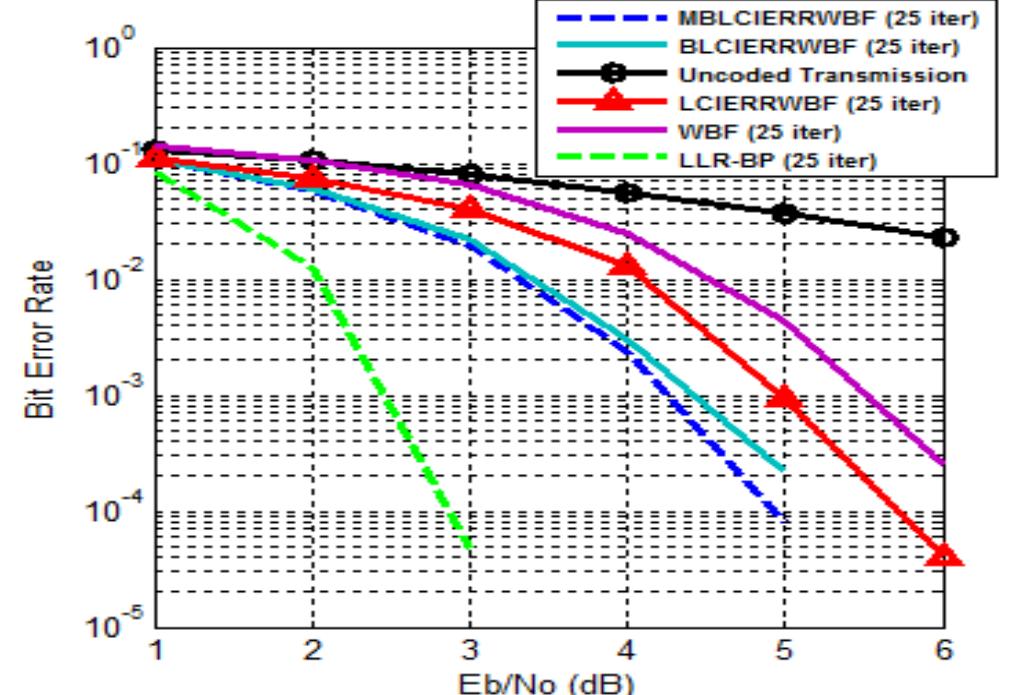
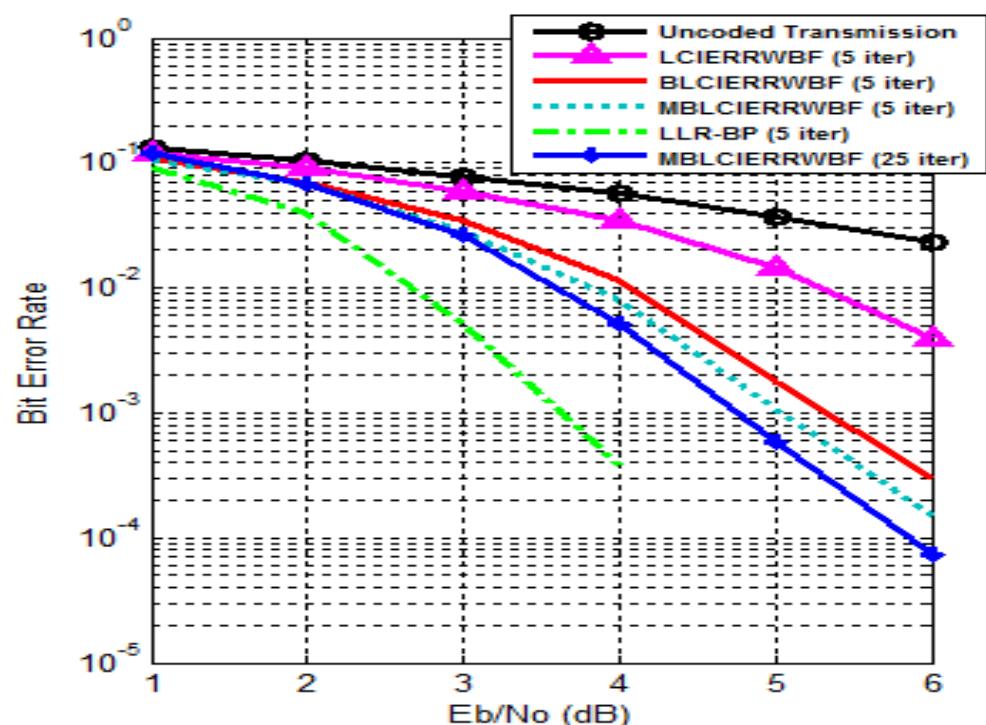
Figure 5. BER for (504,252,3) PEG-LDPC code decoded by WBF, LCIERRWBF, BLCIERRWBF, MBLCIERRWBEF and LLR-BP.
Figure 6. BER for (204,102,3) regular “LDPC code decoded by LCIERRWBF. BLCIERRWBF. MBLCIERRWBEF and LLR-BP.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (14)
- R. G. Gallager, "Low-Density Parity-Check Codes". Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1963.
- Y. Kou, S. Lin, and M. Fossorier, "Low density parity check codes based on finite geometries: A rediscovery and more", IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 47, issue 7, pp. 2711-2736, Aug. 2002.
- J. Z. Fossorier, "A modified weighted bit-flipping decoding of low- density parity-check codes", IEEE Communication. Letters, vol. 8, issue 3, pp. 165-167, Mar. 2004.
- F., Guo, and L., Hanzo, "Reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping decoding for low-density parity-check codes", Electronics Letters, vol. 40, issue 21, pp. 1356-1358, Oct. 2004.
- C.-H. Lee and W. Wolf, "Implementation-efficient reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping decoding for LDPC codes", Electronics Letters, vol. 41, issue 13, pp. 755-757, July 2005.
- H. R. Zeidan and M. M. Elsabrouty, "Low Complexity Iterative Decoding Algorithm for Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) codes", Wireless Days. WD '08. 1st IFIP, PP 1 -5, Apr. 2009.
- A. Nouh and A. H. Banihashemi. "Bootstrap decoding of low-density parity-check codes", Communications Letters, IEEE, vol. 6, issue 9, pp. 391-393, Nov. 2002.
- Y. Kou, S. Lin, and M. P. C. Fossorier, "Low-density parity-check codes based on finite geometries: A rediscovery and new results," IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 47, issue 7, pp. 2711-2736, Aug. 2002.
- D.J.MacKay Encyclopedia of Sparse Graph Codes. [Online]. Available:http://www.inference.phy.cam.ac.uk/mackay/codes/data.htm.
- Y. Inaba and T. Ohtsuki, "Performance of Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) Bootstrap Decoding Algorithm on a Fast Fading Channel", Vehicular Technology Conference, 2004. VTC 2004-Spring. 2004 IEEE 59th , vol. 1, PP. 333-337, Feb. 2005.
- "Digital video broadcasting (DVB); User guidelines for the second generation system for broadcasting, interactive services, news gathering and other broad-band satellite applications (DVB-S2)," European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), TR 102 376.
- J. Z. Fossorier and M. Zhang, "Improved Min-Sum Decoding of LDPC Codes Using 2-Dimensional Normalization", Global Telecommunications Conference, 2005. GLOBECOM '05. IEEE , vol. 3, 6 pp., Jan. 2006.
- M. Shan, C.M. Zhao, and M. Jiang," Improved weighted bit-flipping algorithm for decoding LDPC codes", Communications, IEE Proceedings, vol. 152, issue 6, pp. 919-922, Dec. 2005.
- D. J. C. MacKay and R. M. Neal, "Near Shannon limit performance of low density parity check codes," Electronics Lett., vol.32, issue 6, pp. 457-458, Aug. 2002.
![A. Implementation Efficient Reliability Ratio Based Weighted Bit-Flipping Reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping algorithm is an efficient hard decision decoding algorithm but it has a main drawback which is the long decoding time taken by the algorithm. Implementation efficient reliability ratio based weighted bit-flipping was proposed in [5] to solve this problem by optimizing the algorithm to reduce the decoding time to be suitable for simulation and hardware implementation especially when the maximum number of iterations assigned for the algorithm is small.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/48060528/figure_001.jpg) ](
](![We define the received value y, and its corresponding bit Figure 1. Bootstrap decoding procedure over tanner graph. The idea of the algorithm comes from the work done in [7]. In [7] a modification to the weighted bit-flipping algorithm is done by adding a bootstrap step to the decoding algorithm which leads to significant contribution in performance. The insertion of bootstrap step increases the received code words reliability which leads to improve the performance of weighted bit-flipping by decoding more code words than the algorithm can do without it. Bootstrap step is a combination between horizontal step and vertical step of min-sum algorithm which is a soft decision algorithm with superior performance over any hard decision algorithm. As a result for insertion of bootstrap step as it being part of soft decision decoding technique, it massively increased the performance of weighted bit-flipping algorithm. Bootstrap step will firstly be discussed for further explanation of the idea of using bootstrap step to improve the performance of the weighted bit flipping.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/48060528/figure_002.jpg) ](
](