Paragraph Writing Research Papers - Academia.edu (original) (raw)
2025, IJAZ ARABI: Journal of Arabic Learning
This paper examined an activity-based approach that fosters Arabic paragraph writing of AFL (Arabic as a Foreign Language) undergraduate learners at The New College, Chennai, India. A total of 25 learners were chosen for this study.... more
2025, Journal of new advances in English Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics (JELTAL)
This study examined the comparative effects of conceptual and strategic scaffolding on paragraph writing proficiency among Iranian EFL learners. A total of 40 intermediate-level female learners from a language institute in Hamedan, Iran... more
This study examined the comparative effects of conceptual and strategic scaffolding on paragraph writing proficiency among Iranian EFL learners. A total of 40 intermediate-level female learners from a language institute in Hamedan, Iran were selected via the Oxford Placement Test (OPT) and randomly assigned to two groups: one received conceptual scaffolding, and the other strategic scaffolding for paragraph writing. Over eight sessions, the conceptual scaffolding group focused on foundational writing principles such as topic sentences, coherence, and unity, while the strategic scaffolding group learned techniques like brainstorming, outlining, and revising. A pretest and posttest, scored using Jacob's (1981) rubric, assessed learners' writing proficiency. Both groups showed significant improvement, as indicated by the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test. However, the Mann-Whitney U test revealed that the strategic scaffolding group outperformed the conceptual scaffolding group in terms of writing gains. These findings suggest that while both scaffolding methods are effective, strategic scaffolding may lead to greater improvements in writing proficiency. The study has important implications for EFL instructors, learners, and curriculum developers.
2025, Arab World English Journal
English language proficiency exceptionally verbal communication is essential in achieving Sustainable Development Goal four, which is a good quality higher education. Nevertheless, past literature reported a lack of verbal communication... more
English language proficiency exceptionally verbal communication is essential in achieving Sustainable Development Goal four, which is a good quality higher education. Nevertheless, past literature reported a lack of verbal communication among the graduates of English as a second language. Due to the emphasis on technology integration in Malaysian Education Blueprint 2015-2025, blended learning has been widely implemented in most tertiary institutions. However, learners complain they face challenges during verbal communication learning, particularly in learner-to-instructor interaction in a blended environment. Therefore, this study explores the learners’ opinions regarding learner-to-instructor interaction for verbal communication learning in a blended environment. The result of this research is substantial to English language instructors, curriculum designers, and English language learners as the input provides the information to understand the phenomenon in-depth and suggestions t...
2025, International Journal of English Language and Literature Studies
Due to recent development of Malaysian education, the transformation of local classroom curriculum for English learning is gradually progressing towards global standard since the introduction of Common European Framework of Reference... more
Due to recent development of Malaysian education, the transformation of local classroom curriculum for English learning is gradually progressing towards global standard since the introduction of Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR) that aligned with the Standard Curriculum Primary School (KSSR). To attract and retain students' attention towards fun and interesting learning, grammar context is embedded indirectly in all types of language learning skills for younger primary students in a normal classroom. Hence, via 'inverted' learning, this study was aimed to look at English as a Second Language (ESL) primary 3 students' perception in tenses learning using flipped classroom approach involving 36 students from a rural school in Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. The perceptions of the students were measured through questionnaire comprising a survey and open ended questions. The finding of this study revealed that most students were positive to learn grammar through flipped classroom as opposed to traditional learning. Moreover, even for those who perceived negatively also agreed in the end that this approach would improve their understanding. Thus, it is hoped that this study gives educators better insights in using flipped classroom on students' preferences not just in tenses learning but others as well. Contribution/ Originality: This study contributes to the current existing approach of flipped classroom in tenses learning. Much has been said about its potential but limited studies have examined the perspective of younger students at the age of nine in a rural area. Therefore, this adds to the existing literature on this issue.
2025, Arab World English Journal (AWEJ)
In the era of globalization, language contact is inevitable, necessitating guidance on using a learner's native language to support second language acquisition effectively while minimizing drawbacks that could hinder progress. This study... more
In the era of globalization, language contact is inevitable, necessitating guidance on using a learner's native language to support second language acquisition effectively while minimizing drawbacks that could hinder progress. This study aims to investigate how Vietnamese university students perceive the use of their native language during the brainstorming phase of English essay writing classes. To do that, it is necessary to understand what makes second language learners employ their mother tongue in their study and their perception of doing so. The study participants included 42 university students in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam who learned English as their major. A survey and in-depth interviews were the research instruments used to analyze their attitudes toward using their first language for idea brainstorming during their writing lessons. The findings showed that English-major students had positive attitudes toward the roles of both Vietnamese and English brainstorming in improving writing performance. However, their Vietnamese use depended on the complexity and difficulties of the topics they had to deal with to support them with necessary ideas. Therefore, the first language could be a supporting method for developing second language essay writing.
2025
In the era of globalization, language contact is inevitable, necessitating guidance on using a learner's native language to support second language acquisition effectively while minimizing drawbacks that could hinder progress. This study... more
In the era of globalization, language contact is inevitable, necessitating guidance on using a learner's native language to support second language acquisition effectively while minimizing drawbacks that could hinder progress. This study aims to investigate how Vietnamese university students perceive the use of their native language during the brainstorming phase of English essay writing classes. To do that, it is necessary to understand what makes second language learners employ their mother tongue in their study and their perception of doing so. The study participants included 42 university students in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam who learned English as their major. A survey and in-depth interviews were the research instruments used to analyze their attitudes toward using their first language for idea brainstorming during their writing lessons. The findings showed that English-major students had positive attitudes toward the roles of both Vietnamese and English brainstorming in improving writing performance. However, their Vietnamese use depended on the complexity and difficulties of the topics they had to deal with to support them with necessary ideas. Therefore, the first language could be a supporting method for developing second language essay writing.
2025, Arab World English Journal (AWEJ)
This research adopts a quantitative-qualitative mixed-methods approach to examine the role of flipped classroom pedagogy in fostering critical thinking skills in English argumentative essays among Chinese EFL undergraduates. Specifically,... more
This research adopts a quantitative-qualitative mixed-methods approach to examine the role of flipped classroom pedagogy in fostering critical thinking skills in English argumentative essays among Chinese EFL undergraduates. Specifically, the pilot study compares the mean scores of the pretest and posttest, focusing on the performance in English argumentative essays between the experimental group (N=32) and the control group (N=28). It investigates the impact of the flipped classroom on developing critical thinking skills in argumentative essays. It explores the experiences and perceptions of Chinese EFL learners regarding how the flipped classroom enhances their critical thinking skills in such essays. The ultimate goal is to assist these students in improving their writing quality, achieving better academic outcomes, and enhancing their competitiveness in future job markets. The significance of this research lies in its potential to promote the adoption of the flipped classroom as an effective pedagogical tool for supporting Chinese EFL undergraduates. The findings indicate that the experimental group's mean scores steadily increased throughout the intervention, providing robust evidence of the effectiveness of the flipped classroom approach in fostering critical thinking skills in Chinese EFL undergraduates' argumentative essays writing. We hope this study will inspire more researchers to propose meaningful pedagogical implications and recommendations to improve teaching and learning processes within EFL contexts.
2025, International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE)
The intention of this study was to examine how a flipped classroom with a collaborative learning approach improved the writing skills of Indonesian higher education students. To achieve the study’s aim of 48 Indonesian higher education... more
The intention of this study was to examine how a flipped classroom with a collaborative learning approach improved the writing skills of Indonesian higher education students. To achieve the study’s aim of 48 Indonesian higher education participants, the Oxford Quick Placement Test (OQPT) was employed. They were divided into two groups: experiment and control. Following that, as a pre-test, both groups were given a written exam. The experimental class (EC) was then positioned in a flipped classroom. Students were permitted to bring smartphones to class and utilize them while learning, and the flipped classroom was equipped with an internet connection, a laptop, and a projector. The control class (CC) got standard classroom instruction. This strategy was employed until the very last session. The experimental group outperformed the control group on the post-test, according to the results of the independent samples t-test and one-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA). Furthermore, the results revealed a significant difference in post test performance between the EC and CC.
2025, Teaching english with technology
Flipped classroom innovation has attracted the attention of English Language Teaching (ELT) researchers to examine its effectiveness. This inquiry, therefore, elaborates on the effect of flipping (i.e. reversing) individual and... more
Flipped classroom innovation has attracted the attention of English Language Teaching (ELT) researchers to examine its effectiveness. This inquiry, therefore, elaborates on the effect of flipping (i.e. reversing) individual and collaborative instruction using a WhatsApp application on the cohesive ability of English as a Foreign Language (EFL) learners as one of the essential elements of writing skills. A quasi-experimental study with a non-equivalent control group and a pre-test/post-test design was implemented to find any significant difference between the two combinations. The first group (N=25) was treated using 5 to 10 minutes of cohesion-based video materials and tasks from the WhatsApp group activities of the group members. Meanwhile, the second group (N=25) was treated similarly using individual WhatsApp activities. The findings reveal that the mean score from the collaborative group at 66.17 is higher than the mean score of individual ones at 50.19 with a level of significa...
2025
This research concerned on writing skill, especially about coherence and cohesion as the important elements in writing. The aim of this research was to find out the students" difficulties in maintaining their coherence and cohesion... more
This research concerned on writing skill, especially about coherence and cohesion as the important elements in writing. The aim of this research was to find out the students" difficulties in maintaining their coherence and cohesion in writing process. This research employed descriptive qualitative study. It was conducted in English Education Department of Tarbiyah and Teaching Science Faculty of UIN Alauddin Makassar. The subject of this research was the students of the Department of Tarbiyah of English group 1 and 2 in academic year 2016/2017. The total numbers of students were 36 students. Written test and interview was the instrument used to collect the data in this research. The findings of this research showed that there were some difficulties faced by the students in maintaining their coherence and cohesion in writing process, specifically in determining and stating their ideas, fulfilling the supporting details, and using the proper signals and spelling as well as punctu...
2025
Many research studies have investigated the effects of peer feedback in writing classrooms because it can be applied in L2 writing teaching to great advantage. However, not many studies have conducted in-depth investigations of the... more
Many research studies have investigated the effects of peer feedback in writing classrooms because it can be applied in L2 writing teaching to great advantage. However, not many studies have conducted in-depth investigations of the incorporation of peer feedback into revision. This study is an attempt to fill this gap. This 11-week case study reports the experiences of written peer feedback of 92 English-major students. The study examines the quality of trained written peer feedback and the effects of trained written peer feedback on students’ revisions. Based on the analyses of the written feedback participants received and comparisons of their initial and revised drafts, the study shows that most of the peer comments were revision-oriented and the quantity of accurate comments was remarkably higher than the quantity of miscorrections. In addition, most of the revisions in the second drafts were triggered by peer comments, and the writing quality was significantly improved among bo...
2024
Peer feedback is one of the commonly practised pedagogical approaches in writing classes. It can be seen as a powerful tool to provide students with an authentic audience who give different views on their writings and, thus, able to... more
Peer feedback is one of the commonly practised pedagogical approaches in writing classes. It can be seen as a powerful tool to provide students with an authentic audience who give different views on their writings and, thus, able to increase the student writers’ confidence and motivation. The aim of this exploratory classroom study was to investigate how peer feedback was valued in a writing course. It also explored the potential benefits of peer feedback application in the writing class. The findings reveal that peer feedback was well-received by the students as it gave them the benefits of additional point of views from a wider audience. However, the findings also show that peers’ linguistic competence, attitude and cultural values could affect the value and validity of the feedback which, in turn, could affect the effectiveness of this approach.
2024, BASE FOR ELECTRONIC EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES
The aim of this research is to develop a course model in the field of academic writing that international students studying at undergraduate/graduate level need to prepare qualified research papers, reports, scientific writings by... more
The aim of this research is to develop a course model in the field of academic writing that international students studying at undergraduate/graduate level need to prepare qualified research papers, reports, scientific writings by determining the structural organization and metadiscoursal features appropriate to the subject and to transfer this writing culture to more comprehensive texts such as articles, papers and theses. This course model is limited to introductory writing and introductory models in academic texts. The grammatical structures, vocabulary, basic phrases, connectors, paragraph structure and planning stages of thoughts specific to introductory section models constitute the content of the course model. In this study, content analysis was used to determine the introductory paragraph models; in order to reveal the success level of the course model, the course model was developed and implemented and the academic writing achievement test was applied as pre-test and post-test. With this approach, some templates regarding the text structure of the introductory paragraph(s) were revealed thanks to the data obtained as a result of the analyses of hundreds of academic texts. Text analyses were carried out based on text structure criteria. In the first stage, small structure analysis and paragraph description were performed. Here, a grammatical analysis was made based on cohesion criteria and the focus was on the words and phrases on the surface of the text. In the second stage, large structure analysis and paragraph analysis were carried out. At this stage, the meaning level of the text was analyzed under the subheadings of coherence, meaning of the text, structural elements that make up the meaning, acceptability, informativeness and key concepts. As a result of the analyses made within the scope of small-scale and large-scale textuality criteria, it was possible to interpret the paragraphs and the types of introductory paragraphs were determined at the superstructure stage. A course model was prepared to transfer the data obtained as a result of the analysis of academic texts to the text production process. In the prepared lesson model, the elements that make up the determined introductory paragraph types and structural organization were emphasized. The funnel model, chronological model, model starting with an interesting or remarkable event and model starting with a question are presented together with text analyses showing how they are formed.
2024, Academy of Education and Social Sciences Review
Writing something worthy of reading in a foreign language is a challenging task. Students learning English as a foreign or a second language suffer most in writing especially in paragraph writing. Although studies have been conducted to... more
Writing something worthy of reading in a foreign language is a challenging task. Students learning English as a foreign or a second language suffer most in writing especially in paragraph writing. Although studies have been conducted to explore language errors in English composition of Pakistani students, paragraph organization errors have received little attention. Therefore, this study investigated errors in the unity, development, and coherence in the paragraphs written by Pakistani college students. Besides, the study also explored the factors that cause errors in the paragraphs. In this regard, writing samples of purposively selected 20 college participants were analyzed using error analysis classification by Liu and Wang (2011). Thereafter, five participants were interviewed individually through semi-structured interviews to explore factors that cause errors in the paragraphs of college students. The findings revealed that the students made most errors in paragraph unity, followed by paragraph development, and then paragraph coherence. Besides, the thematic analysis of the interviews revealed that cramming culture, excessive attention given to grammar and lack of quality feedback were the key factors that had affected the paragraph organization skills of these students. The study discusses implications for students and teachers.
2024, University of Chitral Journal of Linguistics & Literature
Writing in English is extremely important language skill especially when it comes to academic and professional success. As a result, writing in English has received attention around the world including Pakistan. Like all other nonnative... more
Writing in English is extremely important language skill especially when it comes to academic and professional success. As a result, writing in English has received attention around the world including Pakistan. Like all other nonnative English language learners across the world, Pakistani students struggle to write well-organized paragraphs which are a key component of secondary and higher secondary exams. Under qualitative research paradigm, the current study was, therefore, conducted to explore the challenges for college students in paragraph writing at a public sector college in Pakistan. The data was collected through semi-structured interviews from four purposively sampled female participants. Thematic analysis of the interview transcripts revealed that students faced problems related to pedagogy, assessment, feedback and revision. More specifically, majority of the participants shared that they reproduced paragraphs rather than writing on their own; the assessment was grammar-focused; there was a lack of constructive feedback on paragraphs; also, there were very limited opportunities for revision. Although the study is an addition to the literature on writing skills in Pakistani context, its significance lies in highlighting females' voices in the literature. The study will have implications for teachers teaching English in public sector colleges.
2024, Persuasive Essay Outline
This document is uploaded to assist students with understanding how to construct a persuasive essay.
2024, International Journal for Quality Research
analysing the effect of peer feedback in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teaching and learning. The authors hypothesized that peer feedback was not percieved as a genuine strategy for learning languages, while it could be put forth as... more
analysing the effect of peer feedback in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teaching and learning. The authors hypothesized that peer feedback was not percieved as a genuine strategy for learning languages, while it could be put forth as a useful strategy for improving not only language skills but also critical thinking, as well as empathy. Based on the participants' responses, the students' perceptions were anlyzed with an aim of encouraging them to become more confident learners, to improve their English language proficiency and to gain feedback skills. The study was conducted throughout the second semester of the academic year 2018-2019. Acknowledging convenience sampling, the 21 (n=21) subjects who participated in this study included 14 (n=14) students from the seventh semester of the UT, English Language and Literature Department and 12 (n=12) students from USAMVB "King Michael I of Romania" from Timisoara, Romania. The effects and perceptions of peer feedback were discussed from the students' perspective and from our corroborated points of view. Data were collected using student questionnaires in which participants were asked to reflect back on their experience on peer feedback throughout their studies. Student responses were subjected to a modified content analysis to identify the main themes and topics. Semi-structured interviews with 12 students were undertaken to substantiate the essential findings of content analysis.
2024, Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Global Education and Society Science, ICOGESS 2019,14 March, Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
This research used a descriptive qualitative method and in a single case study aimed at analyzing students used the four square writing method in developing narrative writing. It also sought to identify the writing aspects that can be... more
This research used a descriptive qualitative method and in a single case study aimed at analyzing students used the four square writing method in developing narrative writing. It also sought to identify the writing aspects that can be improved by using this method. For the sample of this research, thirty nine grade five students were chosen because they had learned quite a lot of English vocabulary which would enable them to write in paragraphs. The instruments for data gathering were the students' writing, observation and questionnaire. The intervention was limited to three sessions of the four square writing. The analysis of the students' writing showed quite good results. The four square writing method was well-received by the students who could follow its structured approach. The study helped identify prewriting strategies that the students need to develop. This research showed the types of writing skills that if present could be more likely to lead to writing success.
2024, El-Yazji Bookshop
This book is designed to provide a practical guide to the process of writing research papers in the field of language and literature. It leads English department students through the step-by-step process of writing research papers, from... more
This book is designed to provide a practical guide to the process of writing research papers in the field of language and literature. It leads English department students through the step-by-step process of writing research papers, from the initial research skills of choosing a topic searching sources and taking notes to the skills of drafting, citing, revising and editing.
The main purpose of the book is to improve the skills of small-scale academic research leading to a longer-term paper required by many English language departments.
Having the following features make the book highly suitable to courses taught in the English departments such as Research Writing, Advanced Writing and Research Skills:
• Involving students in a step-by-step approach to research and writing
• Exposing students to extensive authentic examples and samples of language and literary writings.
• Involving students in a variety of practical tasks relevant to the students’ knowledge and study experience.
• Providing students with ample sample student's written excerpts that reflect weak and effective writing skills
• Assisting students to make use of a wealth of classified web-based sources that enable them to respond to language and literature research assignments.
• Exposing students to easy and exemplified documentation styles.
• Involving students in critical reading and critical observation of model authentic written texts
2024
Research on multiword clusters (chunks) is based on the assumption that native speakers use plenty of chunks in their everyday language and they are considered as fluent speakers of language. Therefore the present study was an attempt to... more
Research on multiword clusters (chunks) is based on the assumption that native speakers use plenty of chunks in their everyday language and they are considered as fluent speakers of language. Therefore the present study was an attempt to investigate the impact of using chunks on speaking fluency of Iranian EFL learners. In the first phase of the study, the students of two intermediate classes sat for a general proficiency test and then were interviewed for their speaking ability. Next, the two groups were statistically compared in terms of their general proficiency and speaking fluency which indicated that they belonged to the same population. The 18-session instruction of the control and experimental groups included the same content and skills, but the experimental group received training on how to use chunks. At the end of the instruction period, the participants were interviewed once again in a posttest to track possible differences in their speaking improvement with respect to t...
2024
This study aims at investigating the effects of training for written peer feedback on students’ revising their first drafts and providing written comments on each other's writings. For this purpose, an empirical study was conducted... more
This study aims at investigating the effects of training for written peer feedback on students’ revising their first drafts and providing written comments on each other's writings. For this purpose, an empirical study was conducted with 36 firstyear intermediate level students who were enrolled in the ELT Department of Faculty of Education at Anadolu University. The effects of written peer feedback were investigated through a comparison of the subjects divided into two groups. One group was trained in how to provide written peer feedback to the various types of essays and the others were not trained. The statistical analysis of the data revealed that the students in the experimental group produced better writing quality than the ones in the control group.
2024
langue turque, ou Tables analytiques de la langue turque usuelle, avec leur développement, dédiés au Roi sous les auspices de M. le comte de Choiseul-Gouffier, Constantinople, Imprimerie du Palais de France, 1790 ; Laurent Jean-François... more
langue turque, ou Tables analytiques de la langue turque usuelle, avec leur développement, dédiés au Roi sous les auspices de M. le comte de Choiseul-Gouffier, Constantinople, Imprimerie du Palais de France, 1790 ; Laurent Jean-François TRUGUET, Uṣūl ül-maʿārif fī vech-i taṣfīf-i sefāyin-i donanma ve fenn-i tedbīr-i ḥarekātihā. Traité de manoeuvre pratique, Constantinople,
2024, Journal of English for Academic Purposes
Halliday's work on the texture of texts and thematic structure is fundamental in enabling EAP students to follow the advice often given by lecturers to 'write clearly and logically'. An understanding of thematic structure can equip... more
Halliday's work on the texture of texts and thematic structure is fundamental in enabling EAP students to follow the advice often given by lecturers to 'write clearly and logically'. An understanding of thematic structure can equip students with the tools to construct paragraphs that communicate their own ideas in ways that are easy to read. This approach takes students beyond topic sentences and discourse markers to a more nuanced presentation of their arguments. In this researching EAP practice paper, I will trace the coverage of Theme and thematic structure in the research literature, in handbooks for teachers and in coursebooks for students, which influenced my own use of these concepts. I will show how these concepts were incorporated into teaching materials to help EAP students write effective paragraphs.
2024, JOURNAL OF DIGITAL EDUCATION, COMMUNICATION, AND ARTS (DECA)
This article reports on a case study designed to examine the implementation of flipped classroom in the EFL classroom in Taiwan. In addition, students’ perception of flipped classroom was also investigated. Sixty-one senior high school... more
This article reports on a case study designed to examine the implementation of flipped classroom in the EFL classroom in Taiwan. In addition, students’ perception of flipped classroom was also investigated. Sixty-one senior high school students participated in this study; data were gathered from students’ English midterm exam score and questionnaire. The data then were quantitatively analyzed by using T-test and descriptive statistics. The results show that students’ English proficiency in flipped classroom was not significantly different with students in traditional classroom. However, the results reveal that students’ perception of flipped classroom were generally favorable. Students’ contended that flipped classroom enhanced their motivation in learning English, as they liked the self-pace through the course and they stated that flipped classroom gave them more class time to practice English. The results presented here may facilitate improvements in the implementation of flipped...
2024
TESOL. Firstly, thank you Dr. Garcia for advising my fellow candidates and me in the field project writing process. Secondly, I want to thank all my fellow classmates in the MA program, especially Deborah, Dorothy, Elizabeth, and Laura.... more
TESOL. Firstly, thank you Dr. Garcia for advising my fellow candidates and me in the field project writing process. Secondly, I want to thank all my fellow classmates in the MA program, especially Deborah, Dorothy, Elizabeth, and Laura. Their high standards, insights, dedication, and sense of humor kept me going when I felt discouraged and overwhelmed. Thirdly, I would like to thank my family and friends who supported me and listened to me talk about my various readings and assignments-even when they did not understand what I was talking about or why it took me so long to write this paper. Lastly, I would like to offer special thanks to Dr. Popal. I would not be completing the MA in TESOL were it not for his example of professionalism and dedication to the field of TESOL. He has inspired me to aim high and view TESOL as a profession from the very first class I had with him. My sincerest thanks to all of you.
2024, Arab World English Journal
Present study examines pedagogically the effect of blended learning activities to augment listening and speaking at tertiary level. Teachers provided content online that allowed measuring the students' engagement, satisfaction, teacher's... more
Present study examines pedagogically the effect of blended learning activities to augment listening and speaking at tertiary level. Teachers provided content online that allowed measuring the students' engagement, satisfaction, teacher's role, and content and examination. Using the tools online on Blackboard®, discussion on forums and listening activities, the teacher provided the blended learning activities. The three-step strategy (3SS) framework was adopted for language learning.It provided students strategies that generated, supported and manipulated the blended learning activities for learning in the face to face sessions. The study investigates how blended learning activities motivate the engagement of students, their satisfaction, the role of the teacher, content and assessment from the students' point of view. The study uses a population of 38 students from two sections of a listening and speaking class (control G1 n = 20 and blended G2 n = 18), a placement test, examination results and responses from a questionnaire as instruments for examining the effect of blended learning activities on the students' engagement, satisfaction, teacher's role, content and examination. The results using descriptive statistics demonstrate positive effects of using blended learning activities in supporting the improvement of students' learning on listening and speaking at elementary level.e. In brief, using the evidence from the study reveals that exposing foundation year students to blended learning activities have positive effects on students' engagement, satisfaction, teacher's role, content and examination when learning English. The paper situated itself in the discussion of providing enriched language learning content online for supporting and measuring learning through the objective measurement of the content from the opinion of the students.
2023
The purpose of this research was to describe the third year students' problems in writing compound sentences expressing contrast, reason, and additional idea at English Department of Bung Hatta University. Descriptive method was used as... more
The purpose of this research was to describe the third year students' problems in writing compound sentences expressing contrast, reason, and additional idea at English Department of Bung Hatta University. Descriptive method was used as the design of this research. The number of population members was 53 students. The writer used total sampling technique to select the sample. Writing test was the instrument to get the data. The students were asked to write 21 compound sentences : 7 sentences expressing contrast, 7 sentences expressing reason, and 7 sentences expressing additional idea. The test was reliable because the reliability of the test was high (0.98).The result of this research showed that generally the third year students at English Department of Bung Hatta University had problems in writing compound sentences. They had problems in writing compound sentences expressing contrast, reason, and additional idea. Among those problems, the most problem the students face was writing compound sentences expressing reason (39.49%). In writing compound sentences expressing reason, the most problem the students face was in mechanics (41.06%), especially in punctuation (25.13%).Dealing with the conclusion, the writer suggested to the lecturers to use matching picture as the media to teach compound sentence to the students. The students are suggested to do more exercises in writing compound sentences expressing reason by using matching pictures. The next writers are expected to find out students' problems in writing compound sentences in other conjunction such as compound sentences with semicolon, correlative conjunction, and conjunctive adverbs.
2023, Arab World English Journal
This study aimed to explore the impact of ChatGPT on English language teaching, learning, and assessment. Specifically, it aimed to answer the following questions: 1) How can ChatGPT enhance English language learning, teaching, and... more
This study aimed to explore the impact of ChatGPT on English language teaching, learning, and assessment. Specifically, it aimed to answer the following questions: 1) How can ChatGPT enhance English language learning, teaching, and assessment? and 2) What are the issues associated with ChatGPT in terms of language teaching, learning, and assessment? Utilizing Rapid Literature Review as a methodology guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) framework, this study found that ChatGPT can support and enhance English language learning by providing meaning-focused inputs, offering scaffoldings during the production of meaning-focused outputs, giving feedback on the accuracy of learners’ language outputs, and facilitating fluency development through extensive language practice. Moreover, this study also found that ChatGPT can enhance English language teaching by assisting teachers in designing bespoke lesson plans, facilitating language learning inside and outside language classrooms, developing customized instructional materials, assessing L2 learning, and giving immediate, individualized feedback. However, despite the benefits it can provide to English language teachers and learners, its use in the classroom is faced with many issues such as inaccurate responses, academic dishonesty and plagiarism, skills deterioration, generic responses, inherent biases, privacy breaches, non-emotionality, technical limitations, educational inequity, and teacher job security threat. Detailed results and implications for policymaking and language teacher development are discussed.
2023, Iranian Journal of Applied Language Studies
The use of educational technology (Ed-Tech) and the Internet in acquiring foreign language skills has led to an increased interest in alternative teaching strategies such as flipped and blended learning. This study investigates the... more
The use of educational technology (Ed-Tech) and the Internet in acquiring foreign language skills has led to an increased interest in alternative teaching strategies such as flipped and blended learning. This study investigates the effects of flipped, blended, and traditional face-to-face teaching methods on the utilization of cohesive devices in paragraph writing among EFL learners. From a pool of 110 junior EFL students, 90 participants were selected. Afterwards, they were randomly divided into three groups: flipped, blended, or face-to-face. To evaluate their paragraph writing abilities, a pretest was conducted prior to the treatment. The first comparative group received instruction using the flipped teaching method, while the second group experienced a blended learning environment (combining face-to-face and online classes). The control group received traditional face-to-face instruction. Following the treatment sessions, all groups completed a posttest on paragraph writing. The findings indicated that both the flipped and blended groups demonstrated significantly better performance compared to the control group. These results provide valuable insights for EFL teachers, curriculum designers, and learners.
2023, Arab World English Journal
This study aimed to explore the impact of ChatGPT on English language teaching, learning, and assessment. Specifically, it aimed to answer the following questions: 1) How can ChatGPT enhance English language learning, teaching, and... more
This study aimed to explore the impact of ChatGPT on English language teaching, learning, and assessment. Specifically, it aimed to answer the following questions: 1) How can ChatGPT enhance English language learning, teaching, and assessment? and 2) What are the issues associated with ChatGPT in terms of language teaching, learning, and assessment? Utilizing Rapid Literature Review as a methodology guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) framework, this study found that ChatGPT can support and enhance English language learning by providing meaning-focused inputs, offering scaffoldings during the production of meaning-focused outputs, giving feedback on the accuracy of learners’ language outputs, and facilitating fluency development through extensive language practice. Moreover, this study also found that ChatGPT can enhance English language teaching by assisting teachers in designing bespoke lesson plans, facilitating language learning inside and outside language classrooms, developing customized instructional materials, assessing L2 learning, and giving immediate, individualized feedback. However, despite the benefits it can provide to English language teachers and learners, its use in the classroom is faced with many issues such as inaccurate responses, academic dishonesty and plagiarism, skills deterioration, generic responses, inherent biases, privacy breaches, non-emotionality, technical limitations, educational inequity, and teacher job security threat. Detailed results and implications for policymaking and language teacher development are discussed.
2023
The main focus of the research is to find out whether there is significant difference between students’ reading comprehension taught by using SCROL (Survey, Connection, Read, Outline, Look Back) strategy and students’ reading... more
The main focus of the research is to find out whether there is significant difference between students’ reading comprehension taught by using SCROL (Survey, Connection, Read, Outline, Look Back) strategy and students’ reading comprehension taught by using conventional strategy. In the research, the type of the research was quasi-experimental research. The writer used nonrandomized control group pretest-posttest design. The writer used two classes as sample consist of 60 students. The first class was as experimental and the second was as control. Experimental class taught by using SCROL (Survey, Connection, Read, Outline, Look Back) strategy and control class taught by using conventional strategy. The technique of data collecting was observation and test. Observation was used in order to collect the data of using SCROL (Survey, Connection, Read, Outline, Look Back) strategy and test was used in order to collect the data of students’ reading comprehension at the second year of MTs Dar...
2023
The purpose of this paper is to put together a tool for Freshman University Students with an ESL level, which will assist them to avoid errors in syntax precision and sentence generation. Both these aspects are problematic for students... more
The purpose of this paper is to put together a tool for Freshman University Students with an ESL level, which will assist them to avoid errors in syntax precision and sentence generation. Both these aspects are problematic for students with a SOV language as mother-tongue who then have to produce with a SVO challenge. When their own language is a post-positional language as opposed to English as a prepositional language, that situation may complicate matters for these students even more. The grid is designed in such a way to allow the student to start from the left and work his way to the right selecting one item from the list constructing a meaningful communication as he/she goes along. The overall intention is towards greater precision and correctness, raising the level of accuracy in syntax and other grammatical aspects. The grammar selected for this purpose is the traditional grammar chosen for its simplicity, stability, and continuity functional in millennia of grammar didactic...
2023
Siti Wahyuni. 14111320129. A Comparative Analysis on Coherence Used in the Two EFL Undergraduate Papers: A Discourse Analysis Perspective. This study aims to compare coherence in the two undergraduate papers as noted by Eggins,... more
Siti Wahyuni. 14111320129. A Comparative Analysis on Coherence Used in the Two EFL Undergraduate Papers: A Discourse Analysis Perspective. This study aims to compare coherence in the two undergraduate papers as noted by Eggins, Schleppegrell that coherence constructed by registerial coherence and as Halliday and Hasan stated that cohesion is a semantic ties that link sentences to another sentence. This study adopts three metafunction analysis to explore coherence of the paper is realized by situational context. This study is qualitative study which is content analysis. The technique of collecting data is documentation from two undergraduate papers in chapter 3. The result of analysis shows that registerial coherence in paper A on field is dominated by relational with 494 clauses or 43.7%. The tenor of the paper A in interpersonal mood structure is impersonality third person declarative mood with 100%. The mode in the paper A is dominated by marked theme with 60.6% and indicates that...
2023, Arab World English Journal
The COVID-19 pandemic has shifted English teaching to online platforms, such as Blackboard Collaborate, but whether online platforms affect the acquisition of core English language skills like speaking has yet to be studied extensively in... more
The COVID-19 pandemic has shifted English teaching to online platforms, such as Blackboard Collaborate, but whether online platforms affect the acquisition of core English language skills like speaking has yet to be studied extensively in the Saudi context. This study addressed and analyzed the perceptions of English as a foreign language instructors and students at the University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia concerning the use of Blackboard Collaborate to develop speaking skills through an explanatory sequential mixed-method design. In the first phase, participants completed an online cross-sectional questionnaire for the quantitative approach. Data analysis revealed positive perceptions of speaking skill development through Blackboard Collaborate among both students and instructors. Female students and less experienced instructors reported more satisfaction with learning English through Blackboard Collaborate than male students and experienced instructors, respectively. In Phase 2, the researcher conducted in-person interviews with 10 instructors and 10 students, focusing on three areas: the Blackboard Collaborate user experience, instructors' and students' beliefs, and the challenges of and suggested improvements for Blackboard Collaborate. Instructors and students were fully aware of how to use the platform, and their motivation to use it was very high. This study further uncovered how Saudi students have shifted their learning style from passive to active learning following the student-centered approach. It also highlights the benefits Saudi women gained, as they were more comfortable practicing conversation through Blackboard Collaborate and the avoidance of cultural barriers. Studying the effects of culture on language learning through technology is a necessary direction for future research.
2023, Acuity : journal of English language pedagogy, literature and culture
English Department students are expected to be able to write an academic essay as they learn the theories of writing an academic essay in Writing courses. Yet, their academic essays still contain structure errors. This study aims to... more
English Department students are expected to be able to write an academic essay as they learn the theories of writing an academic essay in Writing courses. Yet, their academic essays still contain structure errors. This study aims to analyze the structure errors in the fields of unity and coherence. The methods of this study are first identifying the structure errors on the data and second classifying the errors on whether the error is about the unity or coherence. The finding shows a significant number of errors on unity and coherence in most paragraphs of the essays.
2023
The study focused on feedback-based writing conferences (FBWCs) that involve feedback sessions with the teacher in a more dialogic and collaborative atmosphere to respond to students' writing. The rationale behind eliciting students'... more
The study focused on feedback-based writing conferences (FBWCs) that involve feedback sessions with the teacher in a more dialogic and collaborative atmosphere to respond to students' writing. The rationale behind eliciting students' views and preferences regarding one-on-one and group FBWCs stemmed from the importance of fostering effective collaboration between students and their teachers using the learners' preferred approaches of critical and constructive discussions. Three research questions were developed to guide the mixed methods study, which focused on students' perceptions, their preferences concerning individual or group FBWCs, and their suggestions for better implementation of FBWCs in foundational academic writing courses. The study's participants were 77 first-year female university students majoring in English. All the students responded to an online survey, and nine of them voluntarily participated in semi-structured interviews. Statistical analyses of quantitative data were performed by SPSS, using a descriptive analysis approach in addition to using paired t tests. A thematic analysis approach was used to analyse qualitative data. Findings revealed students' satisfactions with, and their positive views about, the usefulness of FBWCs for their academic writing development. The students' responses indicated no significant differences between their preferences for individual or group FBWCs; however, students emphasized their needs for adequate and meaningful feedback in collaborative and motivating environments. The results identified implications for EFL teaching, namely, that teachers should play facilitating and guiding roles during individual and group FBWCs, given that students expressed preferences for the teacher's feedback over peer-and self-evaluation.
2023, American journal of social sciences and humanities
The study focused on feedback-based writing conferences (FBWCs) that involve feedback sessions with the teacher in a more dialogic and collaborative atmosphere to respond to students' writing. The rationale behind eliciting students'... more
The study focused on feedback-based writing conferences (FBWCs) that involve feedback sessions with the teacher in a more dialogic and collaborative atmosphere to respond to students' writing. The rationale behind eliciting students' views and preferences regarding one-on-one and group FBWCs stemmed from the importance of fostering effective collaboration between students and their teachers using the learners' preferred approaches of critical and constructive discussions. Three research questions were developed to guide the mixed methods study, which focused on students' perceptions, their preferences concerning individual or group FBWCs, and their suggestions for better implementation of FBWCs in foundational academic writing courses. The study's participants were 77 first-year female university students majoring in English. All the students responded to an online survey, and nine of them voluntarily participated in semi-structured interviews. Statistical analyses of quantitative data were performed by SPSS, using a descriptive analysis approach in addition to using paired t tests. A thematic analysis approach was used to analyse qualitative data. Findings revealed students' satisfactions with, and their positive views about, the usefulness of FBWCs for their academic writing development. The students' responses indicated no significant differences between their preferences for individual or group FBWCs; however, students emphasized their needs for adequate and meaningful feedback in collaborative and motivating environments. The results identified implications for EFL teaching, namely, that teachers should play facilitating and guiding roles during individual and group FBWCs, given that students expressed preferences for the teacher's feedback over peer-and self-evaluation.
2023, International Journal for Quality Research
analysing the effect of peer feedback in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teaching and learning. The authors hypothesized that peer feedback was not percieved as a genuine strategy for learning languages, while it could be put forth as... more
analysing the effect of peer feedback in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teaching and learning. The authors hypothesized that peer feedback was not percieved as a genuine strategy for learning languages, while it could be put forth as a useful strategy for improving not only language skills but also critical thinking, as well as empathy. Based on the participants' responses, the students' perceptions were anlyzed with an aim of encouraging them to become more confident learners, to improve their English language proficiency and to gain feedback skills. The study was conducted throughout the second semester of the academic year 2018-2019. Acknowledging convenience sampling, the 21 (n=21) subjects who participated in this study included 14 (n=14) students from the seventh semester of the UT, English Language and Literature Department and 12 (n=12) students from USAMVB "King Michael I of Romania" from Timisoara, Romania. The effects and perceptions of peer feedback were discussed from the students' perspective and from our corroborated points of view. Data were collected using student questionnaires in which participants were asked to reflect back on their experience on peer feedback throughout their studies. Student responses were subjected to a modified content analysis to identify the main themes and topics. Semi-structured interviews with 12 students were undertaken to substantiate the essential findings of content analysis.
2023, Linguistica Antverpiensia, New Series – Themes in Translation Studies
China's rise to global prominence has been coupled with a development aid approach and narrative that contradicts long-standing Western-oriented models and discourses. Despite the existence of tangible development projects that bear... more
China's rise to global prominence has been coupled with a development aid approach and narrative that contradicts long-standing Western-oriented models and discourses. Despite the existence of tangible development projects that bear testimony to Chinese aid to developing countries and which clearly espouse the principles upon which the aid is founded, critics continue to allege that the aid is a façade that enables China to advance its political ideology and vision. Using a corpus-based approach, we investigated the extent to which China's political discourse finds its way into the development aid discourse either by senior party officials or through a government-managed collaborative translation mechanism. To do so, we designed a monolingual corpus of the speeches of top-ranking CPC party officials presented at party-organized events and bilingual (Chinese-English) corpora of the discourse used by Chinese government officials during development aid exchanges. We extracted political terms, based mostly on their frequency of use, from the monolingual corpus and verified the extent of their presence in the bilingual corpora of the development aid discourse. Furthermore, we studied the terms and their contexts of use in the bilingual corpora to determine whether translation served as a medium through which China's political discourse was possibly being introduced into its development aid discourse. Our investigation led us to conclude that China's development aid discourse contains an insignificant amount of political terminology mirroring China's own development path. We also concluded that translation did not constitute, in any tangible way, a means by which the presence of China's political discourse in its development aid discourse could be enhanced. However, we uncovered issues related to terminology management, literal translation, and machine translation which suggest that China was struggling to cope with preserving source text and, presumably, target text linguistic and cultural elements, while taking advantage of current Tekwa, K. & Li, M. (2022). Translation, politics, and development: A corpus-based approach to evaluating China's development aid discourse. Linguistica Antverpiensia, New Series: Themes in Translation Studies, 21, 107-131. DOI available online. 108 advances in translation technology. We propose both structural and translational modifications that could help China curb anti-development aid criticism while enhancing its development aid discourse.
2023, Anki Endiar Manika
Writing skill is one of the language skills that students need to master in learning English. However, through the observation of students' writing abilities, it was found that they have not been using proper grammar in their texts, face... more
Writing skill is one of the language skills that students need to master in learning English. However, through the observation of students' writing abilities, it was found that they have not been using proper grammar in their texts, face difficulties in organizing their ideas into structured and coherent texts, have not organized their writings in the format of a recount text, and lack the ability to present additional information in their texts. This study is an action research that utilizes the hamburger paragraph strategy to assist students in writing recount paragraphs. The study was conducted with 10th-grade vocational school students in Surakarta. The results of the study indicate that there is an improvement in students' writing skills when using the hamburger paragraph strategy. The average writing scores of students increased by 20.85% from the pretest scores. Additionally, there were improvements in the comparison between pre-test and post-test results, including an increase in the highest score from 77 to 90, a decrease in the percentage of students below the minimum passing grade, and an increase in the percentage of students exceeding the minimum passing grade. Therefore, it can be concluded that the implementation of the hamburger paragraph strategy can enhance students' writing skills. dan organisasi. Sehingga dapat diambil kesimpulan bahwa penggunaan strategi paragraph hamburger dapat digunakan untuk meningkatkan keterampilan menulis peserta didik.
2023, Social Science Research Network
The study aims to find out the perceptions of university faculty who taught the courses online during the Covid-19 pandemic in March 2020. The purpose is to highlight the issues of students and faculty involved in the new context of... more
The study aims to find out the perceptions of university faculty who taught the courses online during the Covid-19 pandemic in March 2020. The purpose is to highlight the issues of students and faculty involved in the new context of teaching and learning and prepare them to face the technical and academic challenges. A questionnaire is circulated among the faculty of universities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The majority of the university faculty who taught the courses online from the middle of the semester are satisfied with their teaching. However, they prefer face-to-face instruction to online instruction. A few of them are in favor of blended learning. The faculty accepts technical and academic issues and issues related to the trust and the value of online instruction. The study is helpful for all the educational institutions, teachers, and students across the world to understand how to conduct online education during crises and calamities to eradicate the technical and academic problems present in the online mode of teaching, and to update and accept the changing trends and developments in the field of education. The article is original because it studies the perceptions of the regular university faculty who taught half of the course face-to-face and the other half online. The novelty lies in finding out how they participated in online teaching during the lockdown period of the Covid-19 pandemic.
2023, OAlib
The study is an attempt to assess the methods of development in the compositions of students who are reading various business-oriented courses in private universities in Ghana. This area has received little attention from researchers in... more
The study is an attempt to assess the methods of development in the compositions of students who are reading various business-oriented courses in private universities in Ghana. This area has received little attention from researchers in Ghana. Two private universities-Christian Service and Ghana Baptist University College-were the two selected cases. Prior investigations exposed students' writing flaws in the form of wrong usage of the features of a particular method of development when writing essays. Therefore, the literature reviewed was mostly based on these gaps indicated. The primary data collected from the field were from texts (classroom-based and take-home-based texts). Basically, probability sampling techniques were employed to sample the population of the cases selected. All the data gathered were descriptively analysed. The findings showed that students have problems composing descriptive and comparison and contrast paragraphs or essays. But, the study brought to light that students handled narrative, argumentative, and cause and effect essays knowledgeably. It was recommended that enough attention should be given to the teaching and learning of descriptive and comparison and contrast essays. It is our expectation that the findings and recommendations of the work would influence the decisions of policy makers in the field of English language.
2023
National Council of Teachers of English, 1111 W. Kenyon Road, Urbana, IL 61801-1096 (Stock No. 56711-3050: 28.95members,28.95 members, 28.95members,34.95 nonmembers). Tel: 800-369-6283; Web site: http://www.ncte.org. ... National Council of Teachers of English,... more
National Council of Teachers of English, 1111 W. Kenyon Road, Urbana, IL 61801-1096 (Stock No. 56711-3050: 28.95members,28.95 members, 28.95members,34.95 nonmembers). Tel: 800-369-6283; Web site: http://www.ncte.org. ... National Council of Teachers of English, Urbana, IL.
2023
DEDICATION To my parents The dearest persons to my heart. Thank you for all your encouragement, and above all your love. I dedicate my work to my family Thank you for your patience and support. 2 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I wish to express my... more
DEDICATION To my parents The dearest persons to my heart. Thank you for all your encouragement, and above all your love. I dedicate my work to my family Thank you for your patience and support. 2 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I wish to express my gratitude to my supervisor Dr. Ahmed Moumene for his constant help. I thank all my friends who help me. Acknowledgements and thanks go also to all my teachers. Abstract The purpose of this research work is to check whether students are familiar with the use of grammatical cohesive devices in writing essays. It also aims at finding the importance of using cohesive devices to create cohesive discourse. Thus, it hypothesizes that the use of grammatical cohesive devices would strength students' writing. The hypothesis is evaluated by a descriptive study inferred from the results of the students' test. They show that the use of grammatical cohesive devices by Second-Year Students of enough. However, some inappropriate uses of grammatical cohesive devi...
2023, English Language Teaching
This paper aims to review the theoretical concept of interlingual interference of the mother tongue, Thai to the target language, English and intralingual interference found in EFL student writing in Thai context with the attempt to... more
This paper aims to review the theoretical concept of interlingual interference of the mother tongue, Thai to the target language, English and intralingual interference found in EFL student writing in Thai context with the attempt to define the existence of errors according to their sources. This review article also exemplifies some frequent errors normally found in Thai student writing based on three perspectives of interlingual interference; lexical, syntactic and discourse interference and seven aspects of intralingual interference; false analogy, misanalysis, incomplete rule application, exploiting redundancy, overlooking cooccurrence restrictions, hypercorrection and overgeneralization. The pedagogical implication for EFL context is also discussed.
2023
Paragraph writing is a subject which is taught in most of the research classes for research student, where the medium of instruction is in English. A paragraph is a group of sentences that develops a single topic or idea. The purpose of... more
Paragraph writing is a subject which is taught in most of the research classes for research student, where the medium of instruction is in English. A paragraph is a group of sentences that develops a single topic or idea. The purpose of this research is to recognize and analyze the paragraph writing that will be expected in academic writing. This research paper uses the descriptive research with the aim of exposing research scholar of academic writing in various faculty of Research University. The objects of this research are the parts of paragraph and unity and coherence of paragraph.
2023, Arab World English Journal
English language proficiency exceptionally verbal communication is essential in achieving Sustainable Development Goal four, which is a good quality higher education. Nevertheless, past literature reported a lack of verbal communication... more
English language proficiency exceptionally verbal communication is essential in achieving Sustainable Development Goal four, which is a good quality higher education. Nevertheless, past literature reported a lack of verbal communication among the graduates of English as a second language. Due to the emphasis on technology integration in Malaysian Education Blueprint 2015-2025, blended learning has been widely implemented in most tertiary institutions. However, learners complain they face challenges during verbal communication learning, particularly in learner-to-instructor interaction in a blended environment. Therefore, this study explores the learners' opinions regarding learner-to-instructor interaction for verbal communication learning in a blended environment. The result of this research is substantial to English language instructors, curriculum designers, and English language learners as the input provides the information to understand the phenomenon in-depth and suggestions to improve verbal communication problems in learner-to-instructor interaction in the blended learning environment. The research question this study intends to answer is "What are the informants' opinions on learner-toinstructor interaction for verbal communication learning in a blended environment?".This study employed qualitative research inquiry, particularly phenomenological design, and the data was collected through semi-structured interviews, written accounts, and a focus group discussion. The data was then analyzed using thematic analysis. The findings revealed two significant themes related to the phenomenon: the roles of the instructor and the issues in the learner-to-instructor interaction as well as six sub-themes. Future studies might consider including English language instructors to obtain different perspectives.
2023, NOBEL: Journal of Literature and Language Teaching
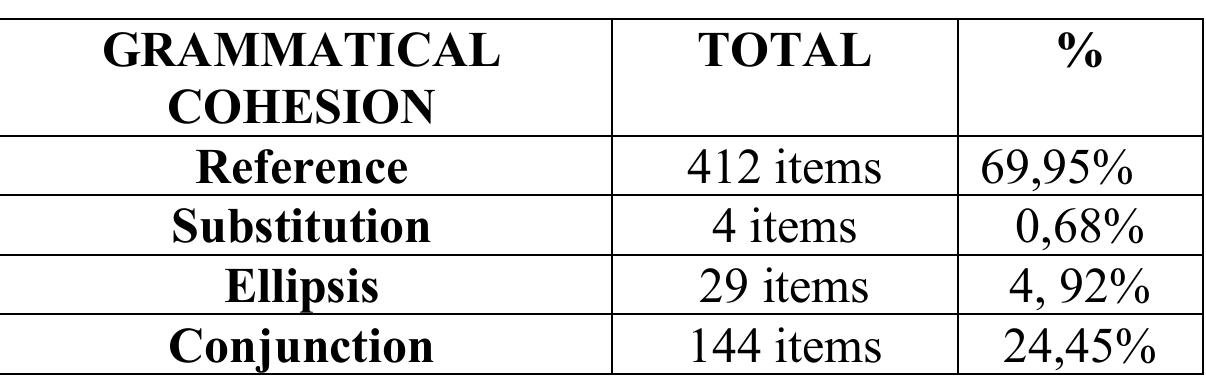
This study investigatesthe types of grammatical cohesion and the frequency of grammatical cohesionin the short story "Tanya's Reunion" By Valarie Flournoy. The study investigation is based onHasan and Halliday theory of Grammatical... more
This study investigatesthe types of grammatical cohesion and the frequency of grammatical cohesionin the short story "Tanya's Reunion" By Valarie Flournoy. The study investigation is based onHasan and Halliday theory of Grammatical Cohesion. This study employs a descriptive qualitative method.The data of this study were taken from the short story entitled "Tanya's Reunion" in the forms ofwords, phrases, clauses, and sentences.In this study, the researcher is the key instrument who interprets the data. The result of the analysis shows that grammatical cohesion found in the short story "