What is the Senate filibuster, and what would it take to eliminate it? (original) (raw)
A version of this Voter Vital was first published on October 15, 2019. It was updated on January 29, 2021.
Brookings hosted a debate on the merits of filibuster reform measures on January 20, 2021. Click here to watch a recording of the event where Richard Arenberg, director of the Taubman Center for American Politics and Policy at Brown University, argued to keep the filibuster and University of Texas, El Paso Assistant Professor Carlos Algara argued to eliminate it.
The Vitals
The Senate cloture rule—which requires 60 members to end debate on most topics and move to a vote—could pose a steep barrier to any incoming president’s policy agenda. Voices on both sides have called for reform in the face of partisan gridlock, and while change may be possible now that Democrats control Congress and the White House, complicated dynamics in the Senate would make it an uphill battle.
- The Senate has a number of options for curtailing the use of the filibuster, including by setting a new precedent, changing the rule itself, or placing restrictions on its use.
- President Joe Biden has expressed some openness to the idea, depending on how obstructive congressional Republicans become, but it’s ultimately up to the Senate to set the process in motion.
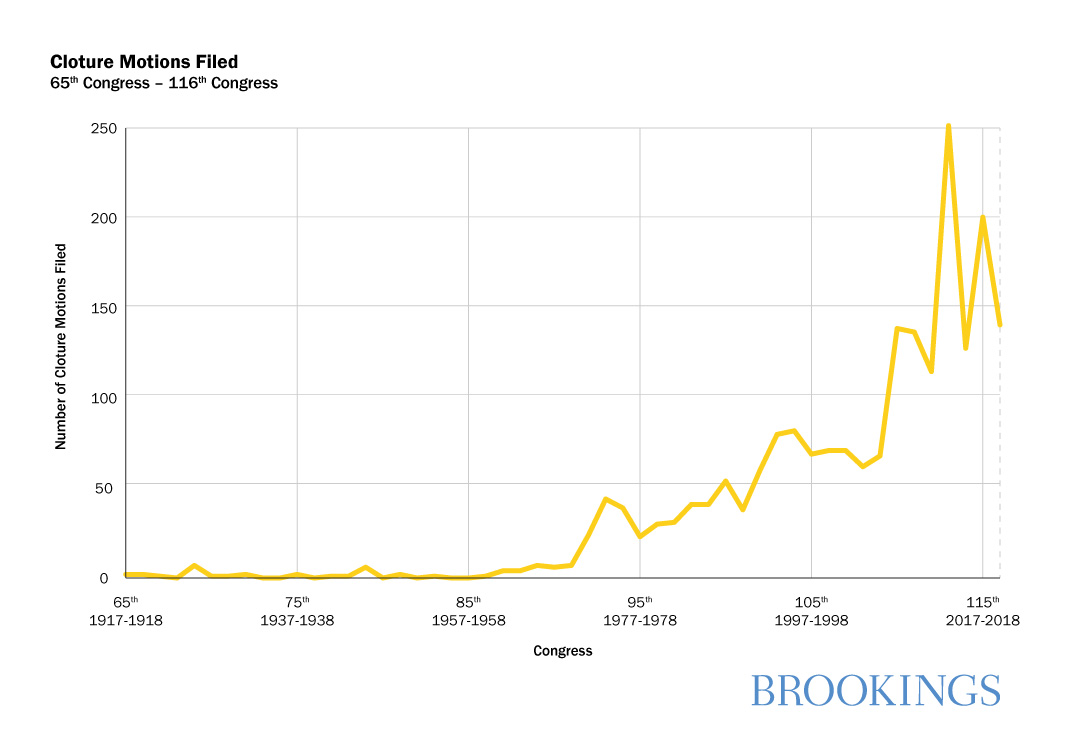
- Use of the Senate cloture rule has become far more common in the 21st century. More cloture motions have been filed in the last two decades than in the 80 years prior.
A Closer Look
Just weeks into Joe Biden’s presidency, it is clear that he faces considerable obstacles in pursuing his agenda in Congress. The Senate cloture rule—which requires 60 votes to cut off debate on most measures—is probably the highest hurdle. Democrats’ Senate majority rests on the tie-breaking vote of Vice President Kamala Harris, and even the process of organizing the Senate’s committees got bogged down by a debate over whether Democrats would attempt to eliminate the legislative filibuster in the opening weeks of the 117th Congress. While Democrats have some procedural options for circumventing the filibuster—discussed in greater detail below—the debate over whether to retain the procedure is likely to remain center stage as legislators work to address the range of challenges facing the country.
Where did the filibuster come from?
While our understanding of the Senate as a slower-moving, more deliberative body than the House of Representatives dates to the Constitutional Convention, the filibuster was not part of the founders’ original vision of the Senate. Rather, its emergence was made possible in 1806 when the Senate—at the advice of Vice President Aaron Burr—removed from its rules a provision (formally known as the previous question motion) allowing a simple majority to force a vote on the underlying question being debated. This decision was not a strategic or political one—it was a simple housekeeping matter, as the Senate was using the motion infrequently and had other motions available to it that did the same thing.
Filibusters then became a regular feature of Senate activity, both in the run-up to and aftermath of the Civil War. Senate leaders from both parties sought, but failed, to ban the filibuster throughout the 19th century. Opponents would simply filibuster the motion to ban the filibuster. In 1917, as part of a debate over a proposal to arm American merchant ships as the U.S. prepared to enter World War I, the chamber adopted the first version of its cloture rule: It allowed two-thirds of all senators present and voting to end debate on “any pending measure.” Several changes to the rule followed in the coming decades. More recently, in 1975, the number of votes needed to invoke cloture on legislative matters was reduced to three-fifths (or 60, if the Senate is at full strength). In 1979 and 1986, the Senate further limited debate once the Senate had imposed cloture on the pending business.
Consequently, for many matters in the Senate, debate can only be cut off if at least 60 senators support doing so. (This is not universally true, however, and we will see several consequential counterexamples below.) While Senate rules still require just a simple majority to actually pass a bill, several procedural steps along the way require a supermajority of 60 votes to end debate on bills.
How has the use of the filibuster changed over time?
There’s no perfect way to measure the frequency with which the filibuster has been used over time. Senators are not required to formally register their objection to ending debate until a cloture motion actually comes up for a vote. If Senate leaders know that at least 41 senators plan to oppose a cloture motion on a given measure or motion, they often choose not to schedule it for floor consideration. But the number of cloture motions filed is a useful proxy for measuring filibusters, and as we see below, the number of such motions has increased significantly during the 20th and 21st centuries.
How does the Senate get around the filibuster now?
Senators have two options when they seek to vote on a measure or motion. Most often, the majority leader (or another senator) seeks “unanimous consent,” asking if any of the 100 senators objects to ending debate and moving to a vote. If no objection is heard, the Senate proceeds to a vote. If the majority leader can’t secure the consent of all 100 senators, the leader (or another senator) typically files a cloture motion, which then requires 60 votes to adopt. If fewer than 60 senators—a supermajority of the chamber—support cloture, that’s when we often say that a measure has been filibustered.
While much of the Senate’s business now requires the filing of cloture motions, there are some important exceptions. One involves nominations to executive branch positions and federal judgeships on which, thanks to two procedural changes adopted in 2013 and 2017, only a simple majority is required to end debate. A second includes certain types of legislation for which Congress has previously written into law special procedures that limit the amount time for debate. Because there is a specified amount of time for debate in these cases, there is no need to use cloture to cut off debate. Perhaps the best known and most consequential example of these are special budget rules, known as the budget reconciliation process, that allow a simple majority to adopt certain bills addressing entitlement spending and revenue provisions, thereby prohibiting a filibuster.
How would eliminating the filibuster actually work?
The most straightforward way to eliminate the filibuster would be to formally change the text of Senate Rule 22, the cloture rule that requires 60 votes to end debate on legislation. Here’s the catch: Ending debate on a resolution to change the Senate’s standing rules requires the support of two-thirds of the members present and voting. Absent a large, bipartisan Senate majority that favors curtailing the right to debate, a formal change in Rule 22 is extremely unlikely.
A more complicated, but more likely, way to ban the filibuster would be to create a new Senate precedent. The chamber’s precedents exist alongside its formal rules to provide additional insight into how and when its rules have been applied in particular ways. Importantly, this approach to curtailing the filibuster—colloquially known as the “nuclear option” and more formally as “reform by ruling”—can, in certain circumstances, be employed with support from only a simple majority of senators.
The nuclear option leverages the fact that a new precedent can be created by a senator raising a point of order, or claiming that a Senate rule is being violated. If the presiding officer (typically a member of the Senate) agrees, that ruling establishes a new precedent. If the presiding officer disagrees, another senator can appeal the ruling of the chair. If a majority of the Senate votes to reverse the decision of the chair, then the opposite of the chair’s ruling becomes the new precedent.
In both 2013 and 2017, the Senate used this approach to reduce the number of votes needed to end debate on nominations. The majority leader used two non-debatable motions to bring up the relevant nominations, and then raised a point of order that the vote on cloture is by majority vote. The presiding officer ruled against the point of order, but his ruling was overturned on appeal—which, again, required only a majority in support. In sum, by following the right steps in a particular parliamentary circumstance, a simple majority of senators can establish a new interpretation of a Senate rule.
What are some ways to modify the filibuster without eliminating it entirely?
The Senate could also move to weaken the filibuster without eliminating it entirely. A Senate majority could detonate a “mini-nuke” that bans filibusters on particular motions but otherwise leaves the 60-vote rule intact. For example, a Senate majority could prevent senators from filibustering the motion used to call up a bill to start (known as the motion to proceed). This would preserve senators’ rights to obstruct the bill or amendment at hand, but would eliminate the supermajority hurdle for starting debate on a legislative measure.
A second option targets the so-called Byrd Rule, a feature of the budget reconciliation process. These bills have been critical to the enactment of major policy changes including, recently, the Affordable Care Act in 2010 and the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act in 2017. To guard against a majority stuffing a reconciliation measure with non-budgetary provisions, the Byrd Rule limits the contents of the bill and requires 60 votes to set aside. Because the Senate’s non-partisan parliamentarian plays a significant role in advising whether provisions comply with the Byrd Rule, some senators have proposed diluting the power of the Byrd Rule by targeting the parliamentarian. This approach would weaken the filibuster by making it easier for a majority party to squeeze more of its priorities into a reconciliation bill (which then only requires a simple majority to pass). For instance, the majority party could select a parliamentarian who is more willing to advise weaker enforcement of the Byrd Rule, and, indeed, there is some history of the parliamentarian’s application of the Byrd Rule affecting his or her appointment. Alternatively, the senator presiding over the chamber (or the vice president, if he or she is performing that function) could disregard the advice provided to him or her by the parliamentarian, undercutting the efficacy of the Byrd Rule.
In addition, discussions among Democratic senators, led by Senator Jeff Merkley (D-Ore.), have surfaced other ideas that aim to reduce the frequency of filibusters by making it more difficult for senators to use the tactic, including requiring senators who oppose a measure to be physically present in the chamber to prevent an end to debate.
How likely are we to see a change to the filibuster in 2021?
By winning majorities in both houses of Congress and the White House, Democrats have achieved one necessary condition for filibuster reform: unified party control of Washington. Under divided party government, a Senate majority gains little from banning the filibuster if the House or president of the other party will just block a bill’s progress.
But the filibuster could still survive unified party control. Senators often speak about their principled support for the filibuster. But senators’ views about the rules are more often shaped by their views about policy. There would likely need to be a specific measure that majority party senators both agreed upon and cared enough about to make banning the filibuster worth it. As Republicans’ experience in the first two years of the Trump administration suggest, such proposals may be easier imagined than achieved.
In addition, individual senators may find the filibuster useful to their own personal power and policy goals, as it allows them to take measures hostage with the hopes of securing concessions. For majority party leaders, meanwhile, the need to secure 60 votes to end debate helps them to shift blame to the minority party for inaction on issues that are popular with some, but not all, elements of their own party. Finally, senators may be concerned about the future; in an era of frequent shifts in control of the chamber, legislators may worry that a rule change now will put them at a disadvantage in the near future.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of the license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact. We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).