Climate change and deforestation threaten world’s largest tropical peatland - Carbon Brief (original) (raw)
Just over a year ago, scientists announced the discovery of the world’s largest intact tropical peatland in a remote part of the Congo’s vast swampy basin.
The Cuvette Centrale peatlands stretch across an area of central Africa that is larger than the size of England and stores as much as 30bn tonnes of carbon.
Now, the same research team has published a new study finding that future climate change, along with deforestation, could threaten the peatlands’ ability to soak up and store large amounts of carbon.
If left unaddressed, these threats could cause the Congo peatlands to turn from a carbon sink to a carbon source, the study says. This means that the peatlands could contribute to climate change by releasing more carbon than they are able to absorb.
Protecting the peatlands from climate change will require “an international effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions”, the lead author tells Carbon Brief.
Peat power
The Cuvette Centrale, which spans both the Republic of the Congo and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) (see map below), is the second-largest tropical wetland in the world.
Location of the Cuvette Centrale wetlands in Africa (in green) Source: Dargie et al. (2017)
The peatlands within the Cuvette Centrale covers 145,500 sq km and contains 30% of the world’s tropical peatland carbon, according to the 2017 Nature paper. This is equivalent to about 20 years’ worth of US CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels.
Across the world, peat covers just 3% of the land’s surface, but stores one-third of the Earth’s soil carbon.
Peat is a wetland soil made of partially decomposed plant debris. It is usually found in cooler, waterlogged environments, explains Dr Greta Dargie, a research fellow from the University of Leeds and lead author of the study published in the journal Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change. She tells Carbon Brief:
“Under waterlogged conditions, the usual decomposition of dead trees and leaves is slowed, meaning there is a build-up of carbon-rich material which we call peat. A long slow build-up means that peatlands store enormous quantities of carbon.”
Heating up
![]()
Glossary
RCP2.6: The RCPs (Representative Concentration Pathways) are scenarios of future concentrations of greenhouse gases and other forcings. RCP2.6 (also sometimes referred to as “RCP3-PD”) is a “peak and decline” scenario where stringent mitigation and carbon dioxide removal technologies mean atmospheric CO2 concentration peaks and then falls during this century. By 2100, CO2 levels increase to around 420ppm – around 20ppm above current levels – equivalent to 475ppm once other forcings are included (in CO2e). By 2100, global temperatures are likely to rise by 1.3-1.9C above pre-industrial levels.
RCP2.6: The RCPs (Representative Concentration Pathways) are scenarios of future concentrations of greenhouse gases and other forcings. RCP2.6 (also sometimes referred to as “RCP3-PD”) is a “peak and decline” scenario where stringent mitigation… Read More
Future climate change presents one of the largest threats to the Congo peatlands, the new study finds.
The latest assessment report (pdf) from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) finds that the region could warm by around 0.5C from 2000 to the end of the century under a low-emissions scenario (RCP2.6) and by 4.5C under a high-emissions scenario (RCP8.5).
It is less clear how global warming could affect rainfall in the region, but research (pdf) suggests that the peatlands could experience an overall reduction in rainfall and an increase in the number of dry periods as the climate warms.
![]()
Glossary
RCP8.5: The RCPs (Representative Concentration Pathways) are scenarios of future concentrations of greenhouse gases and other forcings. RCP8.5 is a “very high baseline” emission scenario brought about by rapid population growth, high energy demand, fossil fuel dominance and an absence of climate change policies. This scenario is the highest of the RCPs and sees atmospheric CO2 rise to around 935ppm by 2100, equivalent to 1,370ppm once other forcings are included (in CO2e). The likely range of global temperatures by 2100 for RCP8.5 is 4.0-6.1C above pre-industrial levels. The release of the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) has introduced a number of additional “no-new-policy” scenarios, meaning RCP8.5 is no longer the sole option available to researchers as a high-end no-mitigation pathway.
RCP8.5: The RCPs (Representative Concentration Pathways) are scenarios of future concentrations of greenhouse gases and other forcings. RCP8.5 is a “very-high baseline” emission scenario brought about by rapid population growth, high energy… Read More
A combination of less rainfall and higher temperatures could cause parts of the peatlands to dry out, which could increase the rate of plant decomposition and, therefore, reduce the rate that the peatlands can absorb carbon from the atmosphere.
Drier conditions could also prompt the peatlands to start releasing larger amounts of carbon, says Prof Simon Lewis, a study author from the University of Leeds and University College London, and one of Carbon Brief’s contributing editors. He tells Carbon Brief:
“The critical insight here is that the central Congo peatlands are probably maintained by rainwater. So, even modest reductions in dry season water-logging, perhaps through rising temperatures and increasing evaporation rates, would mean the whole system moves from a carbon sink to a carbon source.”
In other words, climate change could cause the Congo peatlands to start releasing more carbon into the atmosphere than it is able to absorb.
Forest under threat
Another threat to Congo’s peatlands could come from a potential rise in deforestation for wood and palm oil production in the region, the study notes.
The removal of trees from above peatlands can leave large areas of ground exposed to the sun, which can cause the boggy ground to dry out. This can cause the peatlands to release carbon at a faster rate.
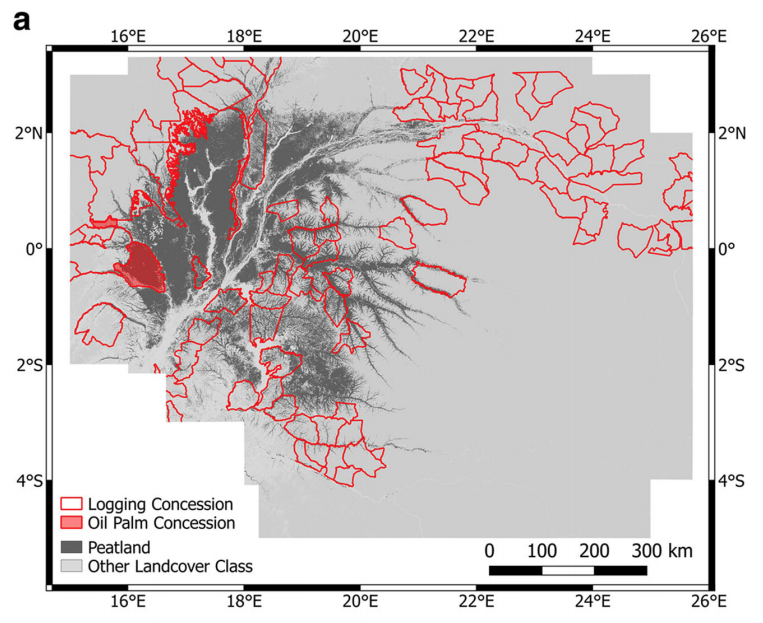
At present, government officials from the DRC have granted logging access to 20% of the forested peatlands. The extent of the logging concession agreements (red outlines) is shown on the chart below, where dark grey indicates peatland and light grey shows other types of land cover.
At least one concession agreement (shown in shaded red) has also been approved for the construction of an oil palm plantation in the Republic of the Congo part of the peatlands, which would take up 4,200km sq of forested peatlands.
Extent of logging concessions (red outlines) and oil palm concessions (shaded red) granted in the Cuvette Centrale. Dark grey shows the location of the Cuvette Centrale peatlands, while light grey shows other types of land cover. Source: Dargie et al. (2018)
Despite these agreements being reached, logging operations are yet to commence in the peatland forests. This is likely to be because the DRC introduced a national ban on logging in 2002, the study notes.
However, the country’s government is currently considering lifting this ban, which would mean logging could be permitted across large areas of the peatland region.
Plans to lift the ban are being driven forward by the French Development Agency (AFD) with financial support from the Norway-led Central African Forests Initiative (CAFI), Lewis says. These groups argue that lifting the ban could aid social development in the region and make it easier to curb illegal and unregulated deforestation.
On top of this, the peatlands could also be affected by plans to construct hydroelectric dams in region, including the Grand Inga hydropower project. Such projects could divert water away from the wetlands, the study notes.
Overall, the peatlands face an immediate risk from deforestation and land-use change and a more long-term threat from climate change, Lewis says:
“The competing threats of direct land-use change and climate change are difficult to compare. The speed with which land can be converted is fast and can quickly kill large areas of swamp forest. But other areas would probably remain unaffected. The speed of climate change is slower than the movement of bulldozers, but could affect the entire peatland.”
Protecting peat
To protect the peatlands in the short term, policymakers should consider introducing new environmental protections to the region, the authors write in their paper:
“Further research, therefore, needs to integrate knowledge from local communities, the natural sciences and social sciences, to develop a more holistic understanding of the Cuvette Centrale peatlands and facilitate local communities and their governments to manage and protect this globally significant region.”
However, protecting the peatlands from the threat of climate change will require a long-term “international effort”, Dargie says:
“With climate change, there is also the added complication that Republic of the Congo and DRC government policies and interventions alone will not be enough to avoid any negative impacts on the Congo Basin peatlands. That will require an international effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.”
Expert analysis direct to your inbox.
Get a round-up of all the important articles and papers selected by Carbon Brief by email. Find out more about our newsletters here.
Get a round-up of all the important articles and papers selected by Carbon Brief by email. Find out more about our newsletters here.