Advice About Eating Fish (original) (raw)
![]()
Fish provide key nutrients that support a child’s brain development.
Fish are part of a healthy eating pattern and provide key nutrients during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and/or early childhood to support a child’s brain development:
- Omega-3 (called DHA and EPA) and omega-6 fats
- Iron
- Iodine (during pregnancy)
- Choline
Choline also supports development of the baby’s spinal cord. Fish provide iron and zinc to support children’s immune systems. Fish are a source of other nutrients like protein, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and selenium too.

![]()
Eating fish can provide other health benefits too.
Fish intake during pregnancy is recommended because moderate scientific evidence shows it can help your baby’s cognitive development.
Strong evidence shows that eating fish, as part of a healthy eating pattern, may have heart health benefits.
A healthy eating pattern consists of choices across all food groups (vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy, and protein foods, which includes fish), eaten in recommended amounts, and within calorie needs. Healthy eating patterns include foods that provide vitamins, minerals, and other health-promoting components and have no or little added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium.
Healthy eating patterns that include fish may have other benefits too. Moderate scientific evidence shows that eating patterns relatively higher in fish but also in other foods, including vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, low- or non-fat dairy, lean meats and poultry, nuts, and unsaturated vegetable oils, and lower in red and processed meats, sugar-sweetened foods and beverages, and refined grains are associated with:
- Promotion of bone health – decreases the risk for hip fractures*
- Decreases in the risk of becoming overweight or obese*
- Decreases in the risk for colon and rectal cancers*

![]()
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends eating fish as part of a healthy eating pattern.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends:
- At least 8 ounces of seafood (less for children§) per week based on a 2,000 calorie diet.
- Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding consume between 8 and 12 ounces per week of a variety of seafood from choices that are lower in mercury.

![]()
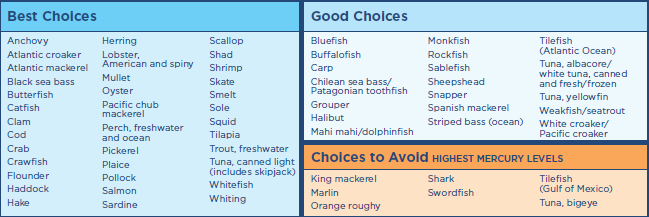
Choose a variety of fish that are lower in mercury.
While it is important to limit mercury in the diets of those who are pregnant or breastfeeding and children, many types of fish are both nutritious and lower in mercury.
This chart can help you choose which fish to eat, and how often to eat them, based on their mercury levels.
What is a serving? As a guide, use the palm of your hand.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
1 serving is 4 ounces
Eat 2 to 3 servings a week from the "Best Choices" list
(OR 1 serving from the "Good Choices" list).

Childhood:
On average, a serving is about:
1 ounce at age 1 to 3
2 ounces at age 4 to 7
3 ounces at age 8 to 10
4 ounces at age 11
Eat 2 servings a week from the “Best Choices” list.

Enlarge in PDF | View Text Version | En español
What about fish caught by family or friends? Check for fish and shellfish advisories to tell you how often you can safely eat those fish. If there is no advisory, eat only one serving and no other fish that week. Some fish caught by family and friends, such as larger carp, catfish, trout and perch, are more likely to have fish advisories due to mercury or other contaminants.
This advice supports the recommendations of the _Dietary Guidelines for American_s, which reflects current science on nutrition to improve public health. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans focuses on dietary patterns and the effects of food and nutrient characteristics on health.
* There is moderate scientific evidence of a relationship between the eating pattern as a whole and the potential health benefit.
§For some children, the amounts of fish in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans are higher than in this FDA/EPA advice. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans states that to consume those higher amounts, children should only be fed fish from the “Best Choices” list that are even lower in mercury – these fish are anchovies, Atlantic mackerel, catfish, clams, crab, crawfish, flounder, haddock, mullet, oysters, plaice, pollock, salmon, sardines, scallops, shad, shrimp, sole, squid, tilapia, trout, and whiting.
Advice revised October 2021