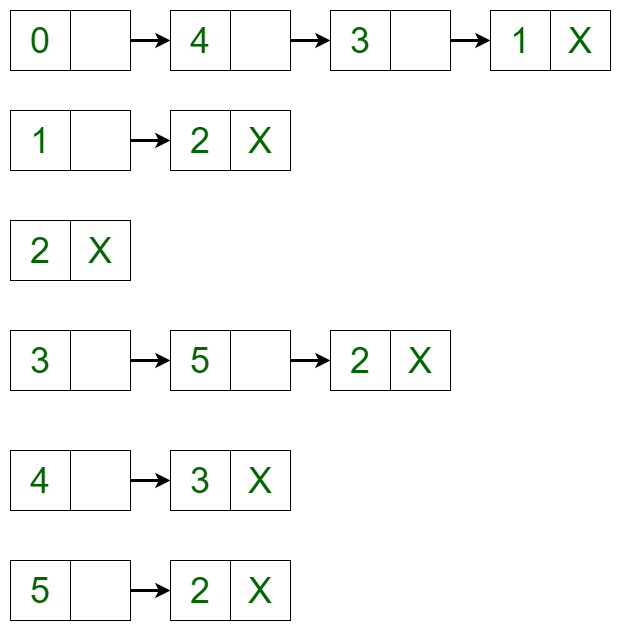Add and Remove vertex in Adjacency List representation of Graph (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 29 Jan, 2025
**Prerequisites: Linked List, Graph Data Structure
In this article, adding and removing a vertex is discussed in a given adjacency list representation. Let the Directed Graph be: 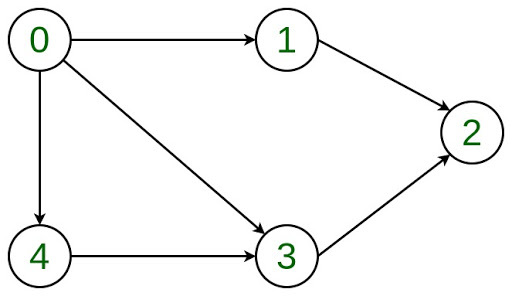 The graph can be represented in the Adjacency List representation as:
The graph can be represented in the Adjacency List representation as: 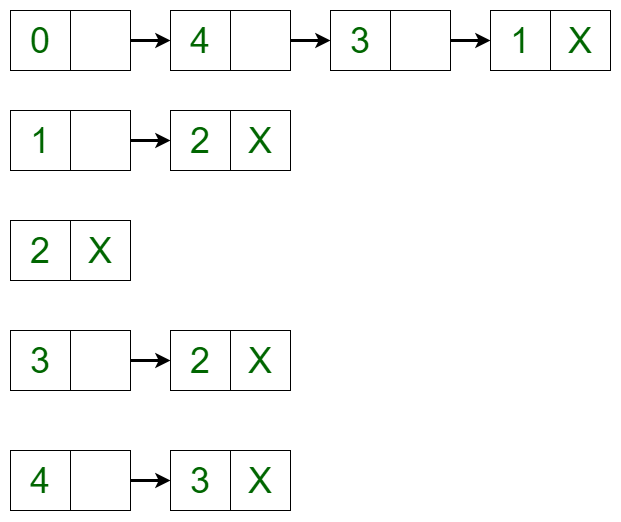 It is a Linked List representation where the head of the linked list is a vertex in the graph and all the connected nodes are the vertices to which the first vertex is connected. For example, from the graph, it is clear that vertex **0 is connected to vertex **4, **3 and **1. The same is represented in the adjacency list(or Linked List) representation.
It is a Linked List representation where the head of the linked list is a vertex in the graph and all the connected nodes are the vertices to which the first vertex is connected. For example, from the graph, it is clear that vertex **0 is connected to vertex **4, **3 and **1. The same is represented in the adjacency list(or Linked List) representation.
**Adding a Vertex in the Adjacency List:
To add a vertex in the graph, the adjacency list can be iterated to the place where the insertion is required and the new node can be created using linked list implementation. For example, if 5 needs to be added between vertex 2 and vertex 3 such that vertex 3 points to vertex 5 and vertex 5 points to vertex 2, then a new edge is created between vertex 5 and vertex 3 and a new edge is created from vertex 5 and vertex 2. After adding the vertex, the adjacency list changes to:
**Removing a Vertex in Adjacency List:
To delete a vertex in the graph, iterate through the list of each vertex if an edge is present or not. If the edge is present, then delete the vertex in the same way as delete is performed in a linked list. For example, the adjacency list translates to the below list if vertex 4 is deleted from the list: Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
#include
using namespace std;
// Node to store adjacency list class AdjNode { public: int vertex; AdjNode* next; AdjNode(int data) { vertex = data; next = NULL; } };
// Adjacency List representation class AdjList { private: int v; AdjNode** graph;
public: AdjList(int vertices) { v = vertices; graph = new AdjNode*[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) graph[i] = NULL; }
// Function to add an edge from a source vertex
// to a destination vertex
void addEdge(int source, int destination)
{
AdjNode* node = new AdjNode(destination);
node->next = graph[source];
graph[source] = node;
}
// Function to add a vertex between two vertices
void addVertex(int vk, int source, int destination)
{
addEdge(source, vk);
addEdge(vk, destination);
}
// Function to print the graph
void printGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
if (graph[i] == NULL)
continue;
cout << i << " ";
AdjNode* temp = graph[i];
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << "-> " << temp->vertex << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Function to delete a vertex
void delVertex(int k) {
// Iterate through all the vertices of the graph
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
AdjNode *curr = graph[i], *prev = nullptr;
if (i == k) {
graph[i] = nullptr;
while (curr != nullptr) {
AdjNode* next = curr->next;
delete (curr);
curr = next;
}
} else {
while (curr != nullptr) {
if (curr->vertex == k) {
if (prev == nullptr) {
// If k is at the start of the list, remove it
graph[i] = curr->next;
} else {
// If k is in the middle or end, remove it
prev->next = curr->next;
}
delete curr;
break;
}
prev = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
}
}
}};
int main() { int V = 6; AdjList graph(V); graph.addEdge(0, 1); graph.addEdge(0, 3); graph.addEdge(0, 4); graph.addEdge(1, 2); graph.addEdge(3, 2); graph.addEdge(4, 3);
cout << "Initial adjacency list" << endl;
graph.printGraph();
// Add vertex
graph.addVertex(5, 3, 2);
cout << "Adjacency list after adding vertex" << endl;
graph.printGraph();
// Delete vertex
graph.delVertex(4);
cout << "Adjacency list after deleting vertex" << endl;
graph.printGraph();
return 0;}
Java
// GFG // JAVA implementation of the above approach // Implementing Linked List representation
import java.util.*;
// Node to store adjacency list class AdjNode { int vertex; AdjNode next;
public AdjNode(int data)
{
vertex = data;
next = null;
}}
// Adjacency List representation class AdjList { private int v; private AdjNode[] graph;
public AdjList(int vertices)
{
v = vertices;
graph = new AdjNode[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
graph[i] = null;
}
}
// Function to add an edge from a source vertex
// to a destination vertex
public void addEdge(int source, int destination)
{
AdjNode node = new AdjNode(destination);
node.next = graph[source];
graph[source] = node;
}
// Function to add a vertex between two vertices
public void addVertex(int vk, int source,
int destination)
{
addEdge(source, vk);
addEdge(vk, destination);
}
// Function to print the graph
public void printGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
AdjNode temp = graph[i];
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print("-> " + temp.vertex + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Function to delete a vertex
public void delVertex(int k) {
// Iterate through all the vertices of the graph
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
AdjNode curr = graph[i], prev = null;
if (i == k) {
graph[i] = null;
} else {
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.vertex == k) {
if (prev == null) {
// If k is at the start of the list, remove it
graph[i] = curr.next;
} else {
// If k is in the middle or end, remove it
prev.next = curr.next;
}
break;
}
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
}
}
}}
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int V = 6; AdjList graph = new AdjList(V); graph.addEdge(0, 1); graph.addEdge(0, 3); graph.addEdge(0, 4); graph.addEdge(1, 2); graph.addEdge(3, 2); graph.addEdge(4, 3);
System.out.println("Initial adjacency list");
graph.printGraph();
// Add vertex
graph.addVertex(5, 3, 2);
System.out.println("Adjacency list after adding vertex");
graph.printGraph();
// Delete vertex
graph.delVertex(4);
System.out.println("Adjacency list after deleting vertex");
graph.printGraph();
}}
Python
Python implementation of the above approach
Implementing Linked List representation
class AdjNode(object): def init(self, data): self.vertex = data self.next = None
Adjacency List representation
class AdjList(object):
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.v = vertices
self.graph = [None] * self.v
# Function to add an edge from a source vertex
# to a destination vertex
def addedge(self, source, destination):
node = AdjNode(destination)
node.next = self.graph[source]
self.graph[source] = node
# Function to call the above function.
def addvertex(self, vk, source, destination):
self.addedge(source, vk)
self.addedge(vk, destination)
# Function to print the graph
def print_graph(self):
for i in range(self.v):
print(i, end=" ")
temp = self.graph[i]
while temp:
print("->", temp.vertex, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
print("\n")
# Function to delete a vertex
def delVertex(self, k):
for i in range(self.v):
curr = self.graph[i]
prev = None
if i == k:
self.graph[i] = None
else:
while curr is not None:
if curr.vertex == k:
if prev is None:
# If k is at the start of the list, remove it
self.graph[i] = curr.next
else:
# If k is in the middle or end, remove it
prev.next = curr.next
break
prev = curr
curr = curr.nextDriver code
if name == "main":
V = 6
graph = AdjList(V)
graph.addedge(0, 1)
graph.addedge(0, 3)
graph.addedge(0, 4)
graph.addedge(1, 2)
graph.addedge(3, 2)
graph.addedge(4, 3)
print("Initial adjacency list")
graph.print_graph()
# Add vertex
graph.addvertex(5, 3, 2)
print("Adjacency list after adding vertex")
graph.print_graph()
# Delete vertex
graph.delVertex(4)
print("Adjacency list after deleting vertex")
graph.print_graph()C#
// C# implementation of the above approach Implementing // Linked List representation
using System;
// Node to store adjacency list class AdjNode { public int vertex; public AdjNode next;
public AdjNode(int data)
{
vertex = data;
next = null;
}}
// Adjacency List representation class AdjList { private int v; private AdjNode[] graph;
public AdjList(int vertices)
{
v = vertices;
graph = new AdjNode[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
graph[i] = null;
}
}
// Function to add an edge from a source vertex
// to a destination vertex
public void addEdge(int source, int destination)
{
AdjNode node = new AdjNode(destination);
node.next = graph[source];
graph[source] = node;
}
// Function to add a vertex between two vertices
public void addVertex(int vk, int source,
int destination)
{
addEdge(source, vk);
addEdge(vk, destination);
}
// Function to print the graph
public void printGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) {
Console.Write(i + " ");
AdjNode temp = graph[i];
while (temp != null) {
Console.Write("-> " + temp.vertex + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Function to delete a vertex
public void delVertex(int k)
{
// Iterate through all the vertices of the graph
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
{
AdjNode curr = graph[i];
AdjNode prev = null;
if (i == k)
{
graph[i] = null;
}
else
{
while (curr != null)
{
if (curr.vertex == k)
{
if (prev == null)
{
// If k is at the start of the list, remove it
graph[i] = curr.next;
}
else
{
// If k is in the middle or end, remove it
prev.next = curr.next;
}
break;
}
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
}
}
}}
public class GFG {
static public void Main()
{
// Code
int V = 6;
AdjList graph = new AdjList(V);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0, 3);
graph.addEdge(0, 4);
graph.addEdge(1, 2);
graph.addEdge(3, 2);
graph.addEdge(4, 3);
Console.WriteLine("Initial adjacency list");
graph.printGraph();
// Add vertex
graph.addVertex(5, 3, 2);
Console.WriteLine( "Adjacency list after adding vertex");
graph.printGraph();
// Delete vertex
graph.delVertex(4);
Console.WriteLine("Adjacency list after deleting vertex");
graph.printGraph();
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript code implementation:
// Node to store adjacency list class AdjNode { constructor(data) { this.vertex = data; this.next = null; } }
// Adjacency List representation class AdjList { constructor(vertices) { this.v = vertices; this.graph = new Array(this.v).fill(null); }
// Function to add an edge from a source vertex to a destination vertex addEdge(source, destination) { const node = new AdjNode(destination); node.next = this.graph[source]; this.graph[source] = node; }
// Function to add a vertex between two vertices addVertex(vk, source, destination) { this.addEdge(source, vk); this.addEdge(vk, destination); }
// Function to print the graph printGraph() { for (let i = 0; i < this.v; ++i) { let str = i + " "; let temp = this.graph[i]; while (temp != null) { str += "-> " + temp.vertex + " "; temp = temp.next; } console.log(str); } }
// Function to delete a vertex delVertex(k) { // Iterate through all the vertices of the graph for (let i = 0; i < this.v; ++i) { let curr = this.graph[i]; let prev = null;
if (i === k) {
this.graph[i] = null;
} else {
while (curr !== null) {
if (curr.vertex === k) {
if (prev === null) {
// If k is at the start of the list, remove it
this.graph[i] = curr.next;
} else {
// If k is in the middle or end, remove it
prev.next = curr.next;
}
break;
}
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
}
}
}}
const V = 6; const graph = new AdjList(V); graph.addEdge(0, 1); graph.addEdge(0, 3); graph.addEdge(0, 4); graph.addEdge(1, 2); graph.addEdge(3, 2); graph.addEdge(4, 3);
console.log("Initial adjacency list"); graph.printGraph();
// Add vertex graph.addVertex(5, 3, 2); console.log("Adjacency list after adding vertex"); graph.printGraph();
// Delete vertex graph.delVertex(4); console.log("Adjacency list after deleting vertex"); graph.printGraph();
`
Output
Initial adjacency list 0 -> 4 -> 3 -> 1 1 -> 2 3 -> 2 4 -> 3 Adjacency list after adding vertex 0 -> 4 -> 3 -> 1 1 -> 2 3 -> 5 -> 2 4 -> 3 5 -> 2 Adjacency list after deleting vertex 0 -> 3 -...