Mutate function in R (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 02 May, 2025
The mutate() function in R Programming Language is used to add new variables in a data frame which are formed by performing operations on existing variables. It can be used by loading the **dplyr library.
**Syntax:
mutate(x, expr)
**Parameters:
- **x: Data Frame
- **expr: operation on variables
Types of mutate() Function in R
In R there are five types of main function for mutate that are describe as below. We will use dplyr package in R for all mutate functions. The dplyr library can be installed using the install.packages() function.
R `
install.packages("dplyr") library(dplyr)
`
1. mutate() Function in R
The mutate() function in R is used to create new variables or modify existing variables in a data frame without removing any other variables. It allows you to apply transformations or calculations to columns and add the result as new columns or overwrite existing ones.
R `
library(dplyr)
d <- data.frame( name = c("Abhi", "Bhavesh", "Chaman", "Dimri"), age = c(7, 5, 9, 16), ht = c(46, NA, NA, 69), school = c("yes", "yes", "no", "no") )
mutate(d, x3 = ht + age)
`
**Output:
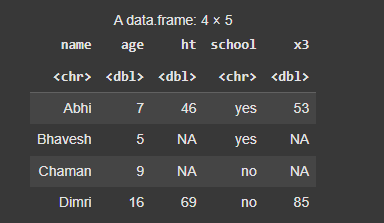
Mutate function in R
**2. transmute() Function in R
The transmute() function in R is used to create new variables or modify existing variables in a data frame, while simultaneously dropping the variables that are not part of the result.
R `
library(dplyr)
d <- data.frame( name = c("Abhi", "Bhavesh", "Chaman", "Dimri"), age = c(7, 5, 9, 16), ht = c(46, NA, NA, 69), school = c("yes", "yes", "no", "no") )
result <- transmute(d, name = name, age_in_months = age * 12, ht, school)
return(result)
`
**Output:
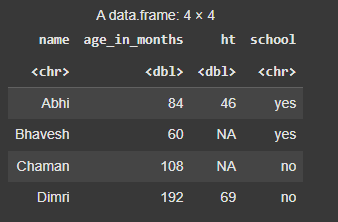
Mutate function in R
3. mutate_all() Function in R
The mutate_all() function is used to apply a transformation to all variables in a data frame simultaneously.
R `
library(dplyr)
d <- data.frame( name = c("Abhi", "Bhavesh", "Chaman", "Dimri"), age = c(7, 5, 9, 16), ht = c(46, NA, NA, 69), school = c("yes", "yes", "no", "no") )
d_mutate_all <- d %>% mutate_all(~ ifelse(is.numeric(.), . * 2, .))
return(d_mutate_all)
`
**Output:
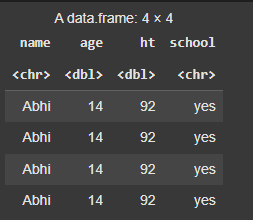
Mutate function in R
**4. mutate_at() Function in R
The mutate_at() function in R is used to apply transformations to specific columns in a data frame, based on a condition, such as column names or positions.
R `
library(dplyr)
d <- data.frame( name = c("Abhi", "Bhavesh", "Chaman", "Dimri"), age = c(7, 5, 9, 16), ht = c(46, NA, NA, 69), school = c("yes", "yes", "no", "no") )
d_mutate_at <- d %>% mutate_at(vars(age), ~ .^2)
print(d_mutate_at)
`
**Output:
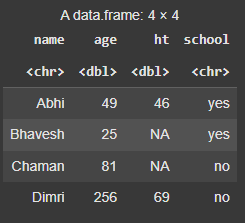
Mutate function in R
**5. mutate_if() Function in R
The mutate_if() function in R, part of the dplyr package, is used to apply a transformation to variables in a data frame based on a specific condition. It allows you to selectively apply a mutation only to the variables that satisfy the specified condition.
R `
library(dplyr)
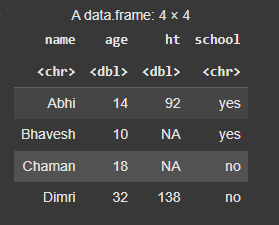
d <- data.frame( name = c("Abhi", "Bhavesh", "Chaman", "Dimri"), age = c(7, 5, 9, 16), ht = c(46, NA, NA, 69), school = c("yes", "yes", "no", "no") )
d_mutate_if <- d %>% mutate_if(is.numeric, ~ . * 2)
return(d_mutate_if)
`
**Output:
Mutate function in R
In this article, we explored how to add new variables to a data frame using existing variables in R Programming, with the help of the mutate() function.